Inguinal dermatitis is an inflammatory disease that develops as a result of exposure to an external or internal irritant on the skin of the pubis, perineum and genital organs. Can occur at any age. Men, women, and small children get sick with equal frequency. In most cases, the cause of the development of pathology is a fungal infection, but there are other provoking factors.
Causes of genital dermatitis
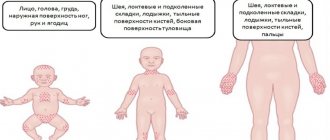
Inguinal dermatitis is a group of dermatological diseases characterized by damage to the skin in the groin. Inflammatory processes arise as a result of exposure to damaging factors of biological, chemical or physical origin on the epidermis. When the disease develops in men, the penis and skin folds in the groin are most often affected, and in women, the pubic area and genitals are most often affected.
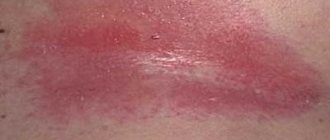
The nature of the rash in the groin area depends on the cause of the disease. In allergic reactions to irritating substances, vesicles (bubbles) with liquid contents often appear on the skin. In the case of a fungal groin infection, peeling, red spots, and pustules (ulcers) appear in the lesions. Dermatologists identify several factors that provoke the appearance of characteristic rashes in the perineal area in women and men:
- excessive sweating;
- non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules;
- hormonal disorders;
- antibiotic abuse;
- wearing synthetic clothing;
- diabetes;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- helminthic infestations;
- diabetes;
- autoimmune disorders;
- overweight.
Dermatitis in the groin in women often occurs as a result of an allergic reaction to poor-quality hygiene cosmetics. Visiting public baths and swimming pools can also cause bacterial or fungal infections. Genital dermatitis in men in 83% of cases occurs when wearing synthetic underwear and insufficient hygiene of the groin area.
Preventive measures
As part of prevention, it is necessary to protect from infection those people who live or are near sick patients. For this purpose, clothing and personal belongings are processed. Throughout the course of therapy, the patient and all his close people must observe the rules of personal hygiene.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to use exclusively your own personal hygiene items, observe the rules of hygiene in the bath or shower, and also regularly perform bath procedures.
General symptoms of the disease
Infectious dermatitis in the groin area indicates disturbances in the functioning of the immune system or a decrease in local immunity. Inflammation of an allergic nature is associated with constant contact with irritating substances - synthetic fabrics, low-quality cosmetics, etc. Regardless of the cause, the symptoms of dermatitis in women and men are not particularly different.
The occurrence of skin inflammation is indicated by:
- burning;
- itching;
- swelling;
- redness;
- peeling;
- red spots;
- bubbles;
- nodular formations;
- pustular rash;
- sores.
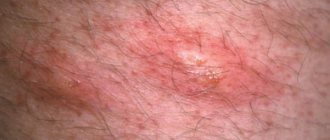
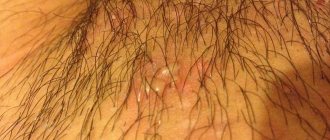
At the initial stage, dermatitis manifests itself in the form of severe itching and burning. During the day, the soft tissues swell and take on a red tint. Spots or vesicles form on the genitals, skin folds and pubis. They are separated from healthy areas by a red, rough border.
Inflammatory processes in the groin area often occur due to skin contact with irritating substances. Vulvar dermatitis is characterized by redness, itching, and peeling. After some time, a rash appears in the groin area in the form of small vesicles.
Dermatologists warn that the disease does not have specific symptoms, so it can easily be confused with manifestations of sexually transmitted infections and other pathologies. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis based on data from dermatoscopy, bacterial culture, microscopy and a general blood test.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor should diagnose the disease. If signs of damage to the groin area appear, you should immediately contact a dermatologist for an initial examination and laboratory tests.
First of all, a study of the skin scales should be carried out in order to identify the fungal nature of the disease.
Skin examination is a mandatory step in diagnosing a groin rash.
An additional diagnostic method is a blood biochemistry test. Subspecialists may prescribe other tests.
Types and degrees of dermatitis on the genitals
Genital dermatitis is classified according to the causes and nature of the inflammatory processes. This makes it easier to make a diagnosis and select the optimal drugs for treatment. In dermatological practice, the following types of dermatitis are distinguished:
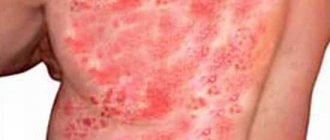
- Seborrheic. It occurs as a result of damage to the skin by pathogenic fungi of the genus Malassezia. A fungal infection appears as scaly red patches and severe itching in the groin area. The lesions are localized in the area of the anus, pubis and genitals. The disease is characterized by a chronic course with periods of exacerbation and remission. Relapses occur in the spring and autumn against the background of decreased immunity.
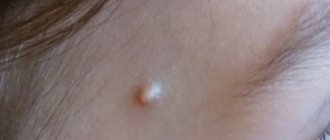
- Candida. An infectious disease caused by opportunistic fungi of the genus Candida. Dermatitis is indicated by nodular formations and scaly spots that appear on the pubis, inside the skin folds. If left untreated, lesions form on the genitals and anus.
- Allergic. Dermatosis that occurs upon contact with irritating substances. Allergens interact only with a small area of the skin, but increased sensitivity to it occurs throughout the entire body. Allergic dermatitis on the penis appears due to the use of low-quality underwear made of synthetic materials. It could also be a reaction to hygiene products - shower gels, shampoos, soaps, etc.
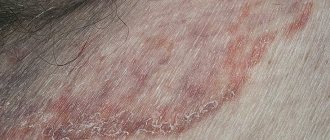
- Psoriasis (psoriatic). Psoriasis is a non-infectious skin disease caused by autoimmune disorders. It manifests itself in the formation of dry spots raised above the surface of the skin. They can merge, forming extensive pale red plaques.
- Erythrasma. Bacterial inflammation caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum. The infection affects only the outer layers of the skin and does not affect the hair follicles. The development of bacteria is facilitated by secondary immunodeficiencies, excessive sweating, hypovitaminosis, and poor hygiene. Dermatitis in the groin area is indicated by pinpoint scaly red spots. Merging, they form large lesions with uneven edges.
- Dermatophytosis is a contagious disease caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum, Trichophyton or Epidermophyton. Dermatophytosis is promoted by obesity, in which skin folds form in the groin area, decreased immunity, and insufficient hygiene of intimate areas. The infection is transmitted through household contact and spreads quickly. It often affects not only the skin, but also its appendages - sebaceous glands, nails, hair.
With mild inguinal dermatitis, the integrity of the skin is not compromised. If erosions form in the affected areas, a moderate degree of the disease is diagnosed.
Making an independent diagnosis and prescribing treatment is strictly prohibited, since such actions can provoke complications!
The most severe case is dermatitis, in which erosions merge with each other, causing extensive ulcers to form.
Hebra Eczema Detection
It is very important not to allow the process to go from acute to chronic, since otherwise it will be very difficult to get rid of the disease. Timely consultation with a doctor and implementation of all his recommendations is the basis for successful treatment. Diagnosis of pathology is based on:
- interviewing a doctor, during which he ascertains complaints of itching, burning and pain;
- examining affected areas of the skin;
- laboratory research methods: - detection of fungal mycelium during microscopic examination of scrapings from the surface of lesions; — isolation of a specific pathogen.
Treatment
If you notice characteristic rashes and spots in the intimate area, you should contact a dermatologist. Features of treatment in men and women are determined by the etiology of inguinal dermatitis. For fungal infections, antimycotics (antifungal agents) are prescribed, and for bacterial infections, antibiotics and local antimicrobial drugs are prescribed. Symptoms of allergic dermatosis are eliminated with antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Drugs
Inguinal dermatitis in women and men is treated with local and systemic agents. To eliminate a mild form of the disease, ointments, liniments, sprays or creams are prescribed. For moderate and severe dermatitis of infectious origin, tablet medications are used. Typically, the treatment regimen includes the following pharmaceuticals:
- antibiotics (Erythromycin, Sumamed) - destroy the cellular structure of bacteria, which helps eliminate bacterial inflammation;
- antiallergic drugs (Loratadine, Claritin) – eliminate itching, swelling, burning and redness in the lesions;
- antifungal ointments (Terbinafine, Miconazole) - destroy pathogenic flora in the perineum, represented by dermatophytes and pathogenic fungi;
- immunostimulants (Vetoron, Immunal) – have an antioxidant and immunostimulating effect, strengthen the immune system and prevent relapses of infectious diseases.
Vaginal dermatitis is treated with antiseptic drugs, wound healing creams or ointments. To eliminate itching, blistering rashes and erosions, Eplan, Chlorhexidine, D-Panthenol, Baneocin, Nitacid are used. To relieve pain, the lesions are treated with Methyluracil or Trimecaine.
Traditional methods
Herbal remedies help eliminate dermatitis between the legs and speed up tissue healing. In the acute course of the disease the following are indicated:
- Baths with herbal decoctions relieve inflammation, disinfect the skin and accelerate the restoration of its integrity. To cure dermatitis of the labia, use decoctions of medicinal chamomile flowers, celandine, sage or oak bark.
- Herbal infusions - increase the body's resistance to infections, relieve inflammation and itching. To improve well-being with inguinal dermatitis, it is recommended to take 100 ml of infusion of yarrow, St. John's wort or lingonberry per day.
- Birch tincture – eliminates redness, disinfects the skin and accelerates the healing of blisters. The affected area is treated with an alcohol solution at least 2-3 times a day. The product is used only if there are no open wounds in the groin area.
During therapy, dermatologists advise treating the external genitalia with chamomile decoction. Zinc-based ointments are used to dry and soften damaged tissues. For fungal infections, it is advisable to wash the genitals with warm water and tar soap. This will prevent the proliferation of pathogens and the spread of infection to healthy areas of the skin.
Folk remedies
Several recipes:
- Tincture of oak bark has antiseptic properties. For 100–150 g of wood chips, add a liter of water and cook over low heat until a dark liquid is obtained. Then leave for 3 hours and cool. You can wipe the areas with cotton wool or a bandage.
- You can brew chamomile in a similar way. You can buy a sachet or loose herb at the pharmacy.
- You can moisturize the affected area using vegetable oil heated in a water bath. Be sure to cool it before using.
Prevention of dermatitis in the intimate area
Preventive measures are aimed at prolonging the period of remission and reducing the risk of recurrent infection in the groin area.
Personal hygiene plays an important role not only in the process of treatment and getting rid of the disease, but also in its prevention.
It is very important to maintain hygiene and reduce exposure to factors that provoke the disease. To prevent genital dermatitis, you must:
- wear underwear only made from natural fabrics;
- immediately treat injuries on the body with antiseptics;
- use hypoallergenic hygiene products;
- include foods with vitamins E, C and B in your diet;
- promptly treat skin pathologies;
- treat the skin in the intimate area with special creams;
- for excessive sweating, use antifungal powders or talc;
- refuse to use other people's hygiene products.
Wearing clean and dry clothes made from natural materials prevents excessive sweating and the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms in the groin area. To prevent the re-development of dermatitis, it is advisable to use multivitamin complexes in the autumn-spring period, as well as promptly treat ENT infections and exacerbations of chronic diseases.
What is not recommended to do?
When treating inguinal dermatitis, hormonal ointments should not be used. In most cases, this can lead to the disease becoming chronic and latent. This means that dermatitis in the intimate area can occur without visible symptoms.
Avoid self-medication, because even if you notice positive results, it may ultimately harm you. Such treatment is rarely completely effective.
Ignoring the symptoms of inguinal dermatitis will not lead to anything good. As a rule, without seeking help from a doctor, the disease develops into a more acute form, the treatment of which is much more difficult.