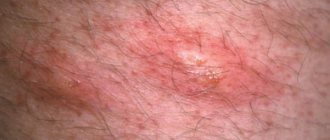
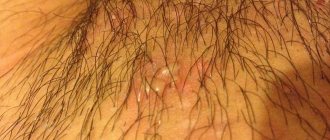
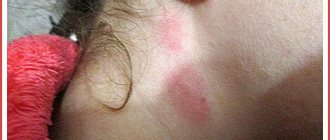
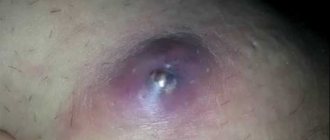
Redness in the groin is a sign of many diseases.
It usually indicates an inflammatory process.
It is caused by bacteria, fungi, sexually transmitted infections, allergic reactions or skin diseases.
Let's look at the main reasons.
Redness in the groin due to an STD
The corresponding symptoms may be caused by infectious diseases with sexual transmission.
They mainly affect the urethra or vagina.
But some can penetrate the skin.
In addition, vaginal discharge can cause redness and itching in the groin in women.
This usually occurs with trichomoniasis.
These bacteria secrete proteases.
Therefore, they damage skin cells if discharge gets on it.
This symptom is possible only with heavy discharge.
They are usually yellow, foamy, and have an unpleasant odor.
Less commonly, the cause is gonococcal infection.
This pathology more often causes redness in the groin in men.
With gonorrhea, they experience profuse discharge from the urethra.
When they get on the skin of the groin area, they cause the formation of erythema.
Subjective sensations are also possible.
Usually it is itching.
Slight redness may be associated with papillomavirus.
It appears only a few months after infection.
Redness of the skin may indicate the beginning of the growth of anogenital warts.
Usually the spots are small and hardly noticeable.
Therefore, human papillomavirus infection is often detected only after the appearance of condylomas.
Other sexually transmitted infections that can cause redness in the groin:
- herpetic;
- candida;
- syphilitic.
There are also sexually transmitted diseases that are not infections.
These are parasitic pathologies.
Scabies is a disease caused by the scabies mite.
After several mites hit the skin, they gnaw passages inside the skin and lay eggs.
The insects themselves cause the appearance of papules and red spots in the groin.
Due to the itching sensation, a man scratches the skin of the groin area, which is another factor contributing to the appearance of beauty.
Other pathogenetic mechanisms of rash formation are allergic reactions to mite metabolic products and secondary bacterial infection.
Phthiriasis is a disease caused by pubic lice.
With this pathology, red and blue spots may appear on the skin of the groin area.
Insects are transmitted through close household contact or during sexual intercourse.
Lice can be detected by inspection.
They are located near the hair, the oral apparatus is immersed in the skin.
Itching is felt, usually mild.
Prevention of itching in the groin area
To exclude secondary infection, drug therapy is combined with preventive measures:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- The patient’s bedding and underwear are washed at high temperatures or treated with specialized preparations. For example, A-Par spray;
- All household items are disinfected.
Itching, rash, redness in the groin area indicate various urological and parasitic diseases. The discomfort will not go away on its own. On the contrary, it will intensify every day. Only eradicating the root cause will improve your well-being.
Redness in the groin due to candidiasis
Fungal inflammatory processes usually occur in the area of the inguinal folds.
Candidiasis can be sexually transmitted or develop as an endogenous infection.
But with sexual transmission, signs of balanoposthitis or vulvovaginitis more often occur.
If redness appeared in the groin, then candidiasis manifested itself as an endogenous infectious disease.
This fungus is part of the opportunistic flora.
In some situations it provokes inflammation.
Most often, the culprit is constantly damp skin in the groin area.
In turn, its maceration occurs for the following reasons:
- hot weather;
- insufficient hygiene of the groin area;
- insufficient ventilation;
- obesity;
- sweating (for example, due to fever or hyperthyroidism).
Redness appears in the groin and papules appear.
Sometimes erosions appear.
They may be covered with a white coating.
With further progression of the disease, painful cracks and pustules appear.
They open with the formation of ulcers.
A fungal infection is often accompanied by a bacterial one.
In this case, the symptoms worsen.
Main reasons
First of all, you need to think about whether there have been injuries to the intimate area in the near future? After all, the delicate perineal area can easily be rubbed by underwear or squeezed by too-tight trousers. This happens especially often in hot weather, when the temperature and sweating in the intimate area increase, and the fabric interferes with the evaporation of moisture. Often blisters appear in horseback riding and cyclists from excessive rubbing of the skin. Even prolonged sex can be the cause, especially in the absence of sufficient hydration of the mucous membranes.
Allergy
Red, watery blisters in the groin area are a sign of allergic dermatitis. Hygiene products, napkins, washing powder, synthetic underwear, condoms, intimate lubricants with a large number of flavors and fragrances can act as irritants.
Pemphigus
Pemphigus, which looks like a small blistering rash, is considered a dangerous disease. Over time, the blisters burst on their own, leaving painful ulcers in their place. A person experiences fever and dehydration. The exact causes of autoimmune pathology are not fully understood, nor is an effective treatment plan determined. With properly selected timely therapy, in the best case scenario, it is possible to slow down the progression of the disease.
Impetigo
A staphylococcal or streptococcal infection can trigger the development of impetigo, a bacterial infection of the groin area. The causes of the pathology are trauma and damage to the skin, into which microorganisms penetrate, causing the appearance of blisters. In addition to a groin rash, impetigo can cause severe itching and burning. In place of the bursting rashes, erosions remain, which are covered with yellow crusts.
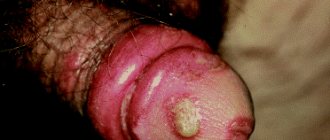
HPV
The human papillomavirus lives in the blood of 90% of the world's population. Some of its strains provoke the appearance of genital warts in the groin, similar to blisters. These are flesh-colored or pink small growths that resemble cauliflower. The pathogen is located in the tissues of the formations and is transmitted through sexual contact. This is why condylomas must be removed.
Redness in the groin with syphilis
Syphilitic infection can manifest itself as redness in the groin in the primary and secondary periods.
In the primary, circular erosion occurs.
More often it appears on the genitals.
But sometimes it occurs in the groin.
The erosion is painless and has a diameter of about 1 cm.
It is red.
Primary syphiloma disappears approximately a month after its appearance.
Soon after this, the second stage of the disease begins.
It is characterized by the appearance of a rash on the body.
Rashes are also possible in the groin area.
Papular syphilide often appears in the folds of the body.
It can take various forms.
Nummular syphilide - large papules appear in the groin, more than 2 cm in diameter.
When they resolve, atrophic scars or pigmentation remain.
Plaque syphilide is the result of the fusion of several papules.
The formation of extensive plaques is possible.
Weeping syphilide - the skin over the papular elements becomes loose.
Exudate leaks through it.
It contains many pale spirochetes.
Erosive syphilide - develops against the background of weeping.
On the surface of the papules, a regular erosion appears, raised above the skin level.
It is separated from the rest of the skin by a white rim.
The surface is wet.
There are practically no subjective sensations.
Ulcerative papular syphilide is a complication of erosive syphilide.
Develops when bacterial microflora joins.
Red erosion in the groin turns into an ulcer - a deep skin defect.
It is covered with a gray coating.
Often takes the form of a crack.
This type of syphilide is called ragadiform.
Redness in the groin with herpes type 2
Herpetic infection is transmitted sexually.
Its classic manifestation is bubbles.
They form not only in the groin, but also on the skin of the genitals.
However, vesicles do not appear immediately.
This process is preceded by pronounced hyperemia of the skin of the groin area.
Blisters appear on reddened skin.
They are surrounded by a bright red corolla.
After the rash resolves, the redness gradually disappears.
The disease has a relapsing course.
If the symptoms go away, this does not mean that the person is cured of herpes forever.
This is impossible - the virus persists in the nerve ganglia.
From time to time it becomes active and causes redness in the groin in women, a rash and pain.
The frequency and severity of relapses depend on the state of the immune system.
Redness in the groin with diabetes
In diabetes, carbohydrate metabolism is impaired.
This leads to many disorders if the process is not compensated by taking glucose-lowering drugs or insulin.
The mechanisms for the occurrence of red spots in the groin can be different.
For diabetes they are as follows:
- dermatoses associated with diabetes;
- the result of angiopathy (vascular damage);
- bacterial or fungal infections of the skin (they develop much more often and are more severe against the background of impaired carbohydrate metabolism).
Diabetic scleredema is a frequently developing pathology.
Occurs in patients with insulin resistance and obesity.
There is thickening and redness of the skin.
Eruptive xanthomas - look like red papules 2-3 mm in diameter.
They can merge into plaques.
Lichen planus occurs much more often against the background of diabetes mellitus.
The pathology manifests itself as flat red papules in various areas of the body.
Including the groin area.
Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism are detected in approximately 20% of patients with lichen planus.
So diabetes is one of the main risk factors for this pathology.
Redness in the groin due to athlete's foot
With inguinal dermatophytosis, the process is of fungal origin.
It is caused by the same pathogens as mycoses of the feet.
Often combined with them.
Patients themselves introduce a fungal infection into their groin with their hands.
More often, dermatophytosis is the cause of redness and itching in the groin in men.
Risk factors:
- humid climate;
- tight trousers;
- obesity;
- local use of glucocorticoids (for example, to treat allergies).
Upon examination, red, scaly plaques are revealed in the groin.
Along their edges there are pustules and papules.
What to do if your scrotum itches?
If you have purchased new intimate hygiene products and refuse to use them, but the problem remains, you need to go to a dermatologist. Self-medication is extremely dangerous. This can cause serious problems and even impotence.
Therapy for scrotal redness and itching with accompanying symptoms in men depends on the diagnosis:
- allergic manifestations are treated with antihistamines;
- fungal diseases require the prescription of antifungal agents for systemic and local use;
- for pubic lice, the patient is prescribed special sprays, shampoos, ointments;
- psoriasis is treated comprehensively, and a man must constantly adhere to certain rules;
- for scabies, scabicides are applied to the skin, but not locally, but practically on the entire body, since the mite can lay larvae in almost all integuments.
You should not make any attempts to get rid of the problem yourself, since it is impossible to correctly diagnose the disease on your own.
Why does a child's scrotum itch?
Konstantin Pronin
Pediatrist
Ask a Question
In teenagers and children, itching is usually accompanied by redness. It can also be of infectious or non-infectious origin. A common cause is improper hygiene, untimely changing of diapers, use of low-quality powder, and bathing children. What to do if a child has itching in the scrotum area? You need to contact a specialist. In this case, visit the pediatrician first. Don't delay your visit to the doctor. Untimely treatment or normalization of care can lead to serious abnormalities in the development of the genital organs.
Dermatological diseases and redness in the groin
Some dermatological diseases lead to the appearance of this symptom.
It could be:
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- allergy;
- contact dermatitis;
- mechanical dermatitis;
- folliculitis;
- neurodermatitis.
It is often impossible to visually determine the cause of redness.
Because the symptoms of many diseases are similar.
The doctor must conduct various tests and take tests to determine the diagnosis.
Often it is necessary to resort to a skin biopsy with its pathomorphological examination.
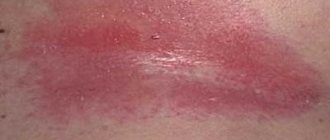
Redness in the groin due to rubbing
Sometimes redness in the groin is caused by constant and prolonged mechanical impact on it.
On the one hand, pathology is provoked by a traumatic factor.
On the other hand, the skin’s protection is weakened.
It becomes unstable to damage.
As a rule, this occurs as a result of its softening due to high humidity.
Thinning of the skin is also possible due to various diseases, including diabetes.
You can rub your skin with trousers, underwear, and hair.
Initially, a person does not feel anything, and only after the formation of erosions in the groin area begins to feel pain under any mechanical influence.
Over time it intensifies.
The inflammatory process of the skin occurs.
On examination, redness in the groin, swelling, and maceration of the skin are observed.
If left untreated, a bacterial or fungal infection may develop.
Symptoms of genital scabies
Scabies is characterized by a symptom that cannot be ignored - unbearable itching, worse in the evening and at night. If you can control yourself during the day and manage not to scratch the affected area, then at night it is impossible to do this.
Additional signs of scabies in the groin (manifested in 50% of clinical pictures):
Instructions for use of Uniderm cream and ointment
- Severe skin irritation;
- Spread of redness in the groin area;
- Small rash near the reproductive organ.
When scratching, the skin is injured, small cracks and wounds are formed. A clear exudate is released from them, sometimes mixed with blood. When an additional infection occurs, pain develops and the rash becomes purulent.
Ignoring symptoms makes the situation worse. Numerous blisters with watery contents form on the genitals and groin. When they are damaged, an unpleasant odor is observed. Over time, the affected areas become crusted and spread throughout the entire groin.
Note: self-treatment rarely gives positive results. The therapy is complex, combining antiparasitic drugs and measures to prevent secondary infection.
Redness in the groin due to allergies
Allergic reactions are accompanied by the appearance of itching, red spots, blisters, and erosions.
It all depends on the type of allergy.
It can occur as toxicerma, urticaria, allergic dermatitis.
Sometimes it appears immediately after contact with the allergen, in some cases - only after a few hours or days.
Redness in the groin can be caused by various allergens:
- synthetic underwear;
- lubricants for sex;
- cosmetic creams;
- medical preparations.
For the symptoms to disappear, it is enough to protect the skin from contact with allergens.
Acute allergic inflammation often has to be treated with medications.
How to treat
In medicine, to make an accurate diagnosis, they take blood from a finger, blood from a vein, or scraping from the affected area.
Diaper rash is treated with a variety of liquids, creams, and ointments. First, they are treated with an antiseptic drug, then with drying ointments, healing and anti-inflammatory or complex ointments, which have all these properties. That is, they use zinc ointments, Boro Plus, Zhivitsa and many others. In advanced stages, when an infection occurs, more serious treatment must be used. We'll look at this later in the article.
To treat allergies, ointments Advantan, Sinaflan, Gistan, Elokom and others are used. In severe cases, I prescribe tablets such as Suprastin, Loratadine, Erius, vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
For the treatment of diseases such as seborrhea, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, vitamin complexes are prescribed; vitamins may differ in composition. Vitrum and Complivit are often prescribed; they are developed taking into account the complex of minerals and vitamins necessary to improve hair, skin, and nails. Also prescribed are tablets, capsules, and syrups to enhance immunity: “Imupred”, “Imunoris”, “Echinacea”.
And of course there are ointments, there are a lot of ointments for treatment, be careful, do not switch to hormonal ointments yourself, such as “Belosalik”, “Dermosalik”, these ointments are addictive, destroy bones, are prescribed in extreme conditions, although they temporarily help relieve inflammation. That is why, before you try anything, you need to go to an appointment with a doctor and agree with him.
As for infectious diseases, treatment in the form of vitamins, ointments, immunomodulators, long-term use of antibiotics, and various types of suppositories is used.
What medications to use, it all depends on what type of bacteria or fungi is causing the inflammation. In no case should you use medications without a doctor’s prescription, without knowing the diagnosis, since many medications that treat one inflammation can intensify another.
Conclusion
Having examined the causes and some diseases, you understand that it is very difficult to distinguish one from the other by appearance. Therefore, to establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to visit a doctor.
Redness in the groin: diagnosis
To know how to remove redness in the groin in men, you need to find out why this symptom appeared.
To do this, the doctor examines and interviews the patient.
It evaluates objective symptoms.
Then he takes tests to confirm the primary diagnosis in a laboratory.
The doctor may take a scraping from the surface of the skin in the area of redness.
He prepares a preparation from it and studies it under a microscope.
Gram stain may show some bacteria.
They are detected in the case of bacterial inflammation of the skin.
Staining with potassium hydroxide reveals fungi.
This could be dermatophytes or candida.
If syphilis is suspected, dark-field microscopy is performed.
Treponema pallidum can be identified in a dark field microscope - it looks like a spiral-shaped white motile bacterium.
Screening for other sexually transmitted infections is necessary.
Skin scrapings and smears from the urogenital tract are taken for examination for:
- herpes;
- trichomoniasis;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia.
Not all causes of redness in the groin are infectious.
Therefore, other laboratory tests are also carried out.
Blood is taken for sugar - this test allows you to identify disorders of carbohydrate metabolism.
A blood test is performed for immunoglobulins E.
When this indicator increases, the allergic nature of the redness in the groin is confirmed.
To diagnose dermatological diseases, the doctor examines the skin under a Wood's lamp.
He may take a skin biopsy for histological examination.