Unpleasant itching and flaking in the groin area in women is a delicate problem that requires special attention. Such skin reactions can occur as a consequence of dermatological diseases, and if pathological symptoms occur on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, we can already talk about the development of gynecological diseases.
Typically, the appearance of peeling of the skin, accompanied by a feeling of itching and discomfort, is caused by the influence of external mechanical damage, skin or fungal infections, and internal inflammatory processes. It is very rare that accompanying symptoms do not appear - rashes in the groin, scales, flaking on the pubis, white plaque and spots on the inner thighs. Most often found in women who are obese and lead a sedentary lifestyle.
A symptom of what processes in the body is itching in the intimate area?
Severe itching and burning in the intimate area in women are symptoms that most often accompany the inflammatory process on the vaginal mucosa, often combined with damage to the external genitalia. It manifests itself as a feeling of irritation and redness (hyperemia) in the area of the external genitalia; in more advanced cases, dysuria (urinary problems associated with painful discharge) and dyspareunia (unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse) are noted.
The symptom in question is one of the most common complaints of gynecological patients. Despite the similarity of symptoms, it can have a very different origin (in other words, a variety of factors contribute to its occurrence, often not related to each other in any way). Understanding the root cause is very important - it is knowledge of the etiology of the process that allows you to determine the most appropriate treatment, which will bring maximum effect, since it will be directed not only against a specific symptom, but against the disease that causes the manifestations in question. So, why does itching and irritation appear in the genitals in women?
Prevention
Prevention of the occurrence and recurrence (re-occurrence) of itching after sex:
- A balanced diet enriched with fermented milk products and pectins (plant fiber). Maintaining rhythmic bowel function.
- Refrain from self-prescribing antibiotics and antibacterial agents. When prescribing antibiotics, always discuss with your doctor the possibility of solving the current situation using alternative methods: homeopathic remedies, herbal medicine, physiotherapy.
- Hygienic care should be carried out only for the external genitalia with water and baby soap without the use of antibacterial intimate hygiene products.
- Do not use vaginal tampons and sanitary pads if you experience at least one allergic reaction to them.
- Limit wearing synthetic underwear. Preference should be given to underwear made of cotton and linen fabrics.
- In hot weather, avoid wearing clothes that are tight and tight around the buttocks and thighs (trousers, leggings, etc.).
- When intimate with a partner who has not been tested for sexually transmitted infections, barrier contraception (condom) is preferable. The condom must be worn before intromission (insertion) of the penis.
- Contraception with a condom is also desirable for oral and anal-genital sex. A man’s intelligence and social status (education, profession, income level, etc.) do not guarantee a healthy oral cavity and genital area.
- Mandatory full examination of the permanent sexual partner and the intended (future) spouse by a urologist before marriage and first sexual intercourse without a condom.
- If sexual intercourse is unprotected with a condom, vaginal suppository (suppository), or cream, it is necessary to conduct a test for sexually transmitted infections.
Smears are collected for testing for chlamydia, ureaplasma, and mycoplasma using the PCR method 28 days after sexual intercourse. Blood tests for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV; AIDS) and syphilis are carried out after 3 and 6 months.
Collecting smears from the cervical canal and cervix for testing for human papillomavirus using PCR is carried out after 6-9 months.
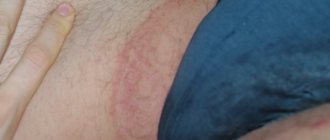
External causes of burning and itching
Often, the occurrence of these symptoms is associated with an allergic reaction to any chemical irritant or mechanical impact.
New cosmetic product
These symptoms can occur when a woman begins to use it for personal (intimate) hygiene or washes her underwear with a new detergent. Most likely, there is exclusively individual intolerance. In other words, it did not suit only one woman, causing her to have this kind of reaction (meaning itching and burning in the vagina).
In this situation, you must do the following:
- Identify the product that causes redness in the intimate area after use. It is enough to simply remember what was used last. But there is an important point here, since an accumulation effect cannot be ruled out, when itching did not appear after the first use, but if the product was used for a certain time. This phenomenon complicates the task somewhat.
- Avoid using the drug (cosmetology or detergent in general).
- Take complex action antiallergic drugs (antihistamines). The most commonly used is Loratadine. It is enough to take one tablet before bed, while observing the course duration of three to four days, so that the effect can be clearly assessed. If Loratadine is ineffective or if there is liver pathology, attention should be paid to a drug called Aleron. A very good imported drug that can be safely used by both young girls and older women. The regimen and dosage are similar to Loratadine.
If none of these drugs helps, it is advisable to use Tavegil or Suprastin intramuscularly in a dose of 1 ml once.
You should not hope that the body, after an allergic reaction, will behave differently when using this product again. If there is individual intolerance, then it will not go away.
Uncomfortable underwear
Another, no less common factor leading to itching in the intimate area in women is mechanical irritation from uncomfortable underwear that restricts movement. In this case, you should simply refuse to use this underwear, buy the appropriate size and wear only underwear that is made from hypoallergenic natural fabrics (the ideal option is cotton, linen or natural silk).
Improper shaving in the intimate area
If this hygienic procedure is performed incorrectly (namely, shaving against the hair growth or on dry skin, using a dull blade or applying excessive pressure), microscopic damage can be caused through which pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate and lead to an inflammatory reaction. The situation will worsen significantly after scratching. Moreover, even without inflammation, severe irritation (itching and redness of the genital organs) can begin, which will also lead to undesirable consequences.
In order to eliminate all these phenomena, it is enough to use anti-allergenic ointment (Fenistil or Hydrocortisone) in combination with any alcohol-based lotion. Three to four days of use - and you can forget about itching.
Contraceptive vaginal pills
When using this method of contraception, some women experience itching in their intimate areas. The phenomenon is caused solely by individual intolerance to the components of the drug (most often, such a reaction is observed with the use of vaginal tablets Veropharm “Ginecotex” or “Pharmatex”). In this case, it is necessary to change the method of contraception, since by definition you cannot change the characteristics of your body.
Intolerance to condom lubricant, allergy to sperm
Another clear example of individual intolerance to certain chemical components. It should be noted that an allergic reaction to condom lubricant is much more common than an allergy to a partner’s sperm. And even then, in the latter case, this still needs to be proven by establishing a relationship between the appearance of irritation and contact with the skin of the intimate area of seminal fluid. In the first case, to solve the problem of redness and itching of the vagina, it is worth changing the method of contraception or using a different brand of condoms.
Gynecological pathologies
Candidiasis
Most often, itching in women occurs precisely because of this disease. Candidiasis is a fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the reproductive system, which is usually caused by microscopic fungi of the genus Candida, which have a whitish color. The cause of its occurrence is usually the irrational use of antibacterial drugs, the lack of adequate administration of probiotics, or a disorder of the immune system.
How to treat this disease? Therapy of the pathology in question is possible through the use of pharmacological agents, which include spores of beneficial microorganisms. Special vaginal suppositories are also used against thrush. The most commonly used suppositories are Livarol, Gino-pevaril, and Pimafucin. It is enough to take a course of treatment, 1 suppository once a day for 3 days, and everything will pass.
Lichen sclerosus of the vulva
This is a rare pathology that leads to severe itching. It consists of thickening the skin of the intimate area. Relief of manifestations is possible only with the help of corticosteroids. And then, the itching and burning of the labia will not be completely eliminated.
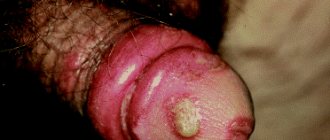
Erythroplasia Keira
The disease is one of the types of non-invasive squamous cell skin cancer. Caused by human papillomaviruses. The manifestations can be stopped by using 5% 5-fluorouracil ointment and X-rays, which have shallow penetration.
How is the diagnosis done?
When visiting a medical institution, patients who complain of intimate itching are sent to undergo the following tests:
- First of all, the patient is sent to a gynecologist for a conversation and clarification of additional signs. After this, a detailed inspection with mirrors takes place.
- To exclude diabetes mellitus and cystitis, a urine test and a blood test will be necessary.
- A vaginal smear is mandatory.
- The complex of studies is completed by a rar test.
What is rar test
When the cause is established, the gynecologist determines the necessary course of treatment or gives recommendations for eliminating non-serious itching (arising from insufficient hygiene, allergies and other reasons).
Sexual infections that cause this symptom
Trichomoniasis
This is the most common sexually transmitted disease. In addition to severe itching, trichomoniasis causes discharge that has a yellow-green tint and an unpleasant odor. In addition, pain and tenesmus will be characteristic (false urge to defecate in the absence of feces, accompanied by severe discomfort).
The key approach to treatment will be the use of imidazole-based drugs in combination with Chlorhexidine. Both sexual partners should undergo therapy, even if only one of them has symptoms.
Gonorrhea and gardenellosis
Such STDs have similar manifestations. The difference will be the nature of the discharge, although culturing the discharge on biological media with further determination of the sensitivity of microorganisms to specific antibiotic therapy will have greater diagnostic value. This study is necessary in order to carry out etiotropic treatment, during which the pathogenic microorganism is destroyed.
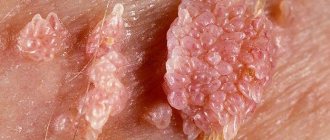
Genital herpes, chlamydia, ureoplasmosis, mycoplasmosis
They belong to the group of sexually transmitted diseases. With these pathologies, itching and burning in the intimate area in women is observed. We'll look at how to treat them below.
Often, specific antibacterial drugs of a narrow spectrum of action are used (a group of tetracyclines and macrolides) and drugs that have an antiprotozoal effect (the statement is true for all infections except herpes - they need specific antiviral drugs like Gerpevir or Acyclovir, both for oral and topical use).
The mechanism of itching is the development of an inflammatory reaction. And with a herpes infection, there is damage to the nerve endings at the local level, which also leads to a feeling of discomfort.
Diseases of older women
Krauroz
This disease is expressed in dystrophic, atrophic and sclerotic changes in tissues. Due to changes occurring in the structure of the organ, patients begin to feel discomfort, expressed in itching and a burning sensation.
If adequate measures are not taken to eliminate this pathology in a timely manner, it has every chance of developing into cancer.
Atrophic vulvovaginitis
This disease often affects women before and after menopause. The pathology is caused by a lack of female sex steroid hormones. Due to the fact that the level of estrogen in a woman’s body decreases, the epithelium thins and the mucus that covers the labia disappears. As a result, vaginal dryness, itching in the genitals, and bleeding on contact occur.
The disease has an irreversible course, which can only be stopped by complex hormonal therapy. In addition, women suffering from this pathology need to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene as strictly as possible, since they are at risk for the occurrence of petechiae and epithelial erosions, so itching and burning in an intimate place are far from the most dangerous symptoms of the condition in question.
Vulvar cancer
The disease is typical for women over 60 years of age. Features of the pathology: latent course, pain in the clitoris, itching in the intimate area in women and the appearance of copious foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
The scope of therapeutic interventions is determined by the stage at which the pathology is diagnosed.
Other diseases of the reproductive system
The most common among them are tumors of the uterus, vagina, and cervix, and the labia are itchy, both in benign and malignant tumors.
The causes of this symptom are the same in all situations - due to uncontrolled cell division, the histological structure of the organ is disrupted, which in turn leads to compression of the nerve endings. As a result, a feeling of itching, burning and other manifestations of discomfort occurs.
Again, the only way to combat these ailments is surgery.
It is necessary to promptly consult your doctor if itching occurs in the perineal area, since this symptom can accompany very serious pathologies.
Traditional methods of treatment
Like other diseases, cracks are treated with folk remedies. It is important to know and understand that without consulting a doctor and taking medications, it will be quite difficult to get rid of this problem, or this process may take quite a long time. But before visiting a medical facility, you can try to relieve the pain yourself and soften the crust that has formed on the skin. Ointments or any other topical agents that have a softening antiseptic effect will help with this. Baths with various herbs have a wonderful effect.
Treatment is aimed at:
- strengthening the immune system so that it is easier for the body to fight pathogenic organisms;
- getting rid of the unpleasant odor that appears as a result of heavy vaginal discharge
Boron-based ointments are used to lubricate small cracks. They make lotions and compresses based on novocaine. Decoctions of chamomile and calendula help well. Women often use calendula tincture to treat genital microtraumas.
Preparing the tincture is not difficult. It is enough to have dried calendula flowers or a pharmacy tincture. You need to mix a spoonful of dried flowers with boiled water (70 ml), and the plant extract is mixed in the same proportions. Next, the mixture is poured with boiling water and simmered over low heat until half of the liquid has evaporated. The finished solution must be filtered and cooled. Lotions are applied once a day.
The tincture of dandelion and yarrow roots received quite good reviews. To prepare such a remedy, you need to combine dried and crushed dandelion root with a decoction of yarrow, which was prepared previously (1 tsp per 1 tbsp of boiling water). This mixture is drunk half an hour before meals, twice a day. If you are allergic to plants, you should not take this decoction.
Preserve the beauty of your intimate area!
Health and comfort are important components of a happy and carefree life for every woman. If a woman experiences discomfort associated with peeling of the outer labia, it is time to consult a doctor. Otherwise, the skin condition will worsen, which will affect your mood and intimate life.
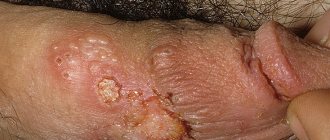
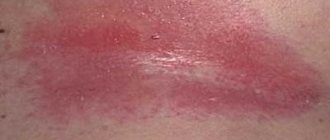
Cracks on the labia are a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane. This disorder can be caused by various factors and is accompanied by various unpleasant sensations, especially when urinating or during contact. The main symptoms of cracks in the labia: itching, burning sensation and hyperemia. Other symptoms may also occur.
Cracks in the labia minora and majora are not a separate disease. They occur as a result of a malfunction of the body or as a result of other infections. If they appear, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible to determine the cause and choose the right treatment. With timely treatment, all unpleasant symptoms disappear very quickly. If treatment is delayed, the cracks may become calloused. In this case, it will be much more difficult to cure them.
Diseases not related to gynecology, but accompanied by itching in the intimate area
Diabetes mellitus type 2
Due to the fact that blood flow in the vessels is disrupted, trophic changes occur in the epithelial cells, and they begin to peel off intensively. The result is severe itching in the vulva area. It will be possible to get rid of this symptom only by selecting the correct treatment for diabetes.
Psoriasis
The disease is accompanied by similar symptoms, manifested by severe itching of the skin, including in the intimate area.
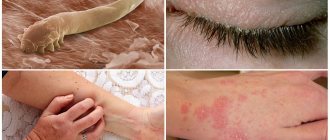
Helminthiasis and pubic lice
Parasitic infections, the appearance of which is directly related to violation of personal hygiene rules. The occurrence of itching and burning of the skin in the intimate area is explained by mechanical irritation of the tactile receptors of the skin by parasites and their waste products. The best way to get rid of this problem and relieve itching is to remove hair and treat the intimate area with the antiparasitic agent PARANIT Sensitive.
Severe fatigue and stress
“All problems come from nerves” - this statement, as old as time, is relevant in this case. Problems affecting the higher nervous activity of a person indirectly affect both the autonomic nervous system and the peripheral sensory organs, including tactile receptors, as a result of which the symptoms in question arise.
The only way to eliminate it is to influence the human nervous system. Stress can be relieved only by removing its source, accelerating the onset of a positive effect with the help of sedatives: Valocordin, Tricardin, Barboval.
Blisters in the groin due to heat rash
Miliaria is a reaction of the groin skin to overheating.
There is a blockage of the sweat glands.
Miliaria can be crystalline and red.
In the case of crystalline prickly heat, blockage of the sweat glands occurs at the level of the stratum corneum of the skin.
In this case, small bubbles with transparent contents are formed.
Usually they do not exceed 1 mm in diameter.
Miliaria rubra is an even deeper process.
Therefore, in addition to the blisters, papules appear.
Miliaria itself is not considered a disease.
This is nothing more than a skin reaction to overheating and humidity.
After eliminating the pathogenetic factors, the skin is restored without treatment.
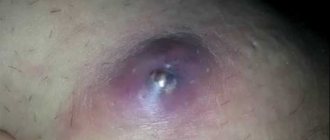
But prickly heat is a predisposing factor for secondary infections.
If bacterial flora attaches, sweat gland abscesses can form.
They require surgical treatment.