The human papillomavirus, which causes condylomatosis - pointed growths on the mucous membranes of the body - lives hidden in the body until changes begin to occur in it. As a rule, these changes are associated with a weakening of general immunity and hormonal imbalance. In women, such changes usually occur during pregnancy. And here questions arise: are condylomas dangerous during pregnancy, what should a woman do in this case? The pathology is not dangerous for the baby while he is in the womb. Therefore, sooner or later, a pregnant woman will have to consult a virologist with this problem.
Epidemiology
Pointed condylomatosis is an infectious viral disease found in venereological clinics, 3 times less often than gonorrhea in both sexes, but 9 times more often in men and 25 times more often in women than infectious syphilis. Consequently, genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases characterized by ulceration or tumorous manifestations. Statistically in our country, condylomatosis acuminata is not taken into account, and therefore its distribution among the population can only be judged by relative data.
The disease is diagnosed most often at the age of 20-25 years (from 52 to 54.8 percent). at the age of 26-30 years (from 9.7 to 12.3 percent). less often at the age of 13-19 years (about 10 percent) and 15-17 years (from 5.3 to 7.9 percent). However, the disease is possible in early childhood and old age. It is more common among prostitutes and women who have had a large number of sexual partners.
The causative agent of genital condylomatosis is a filterable virus from a group of viruses that are morphologically identical to one of them that causes the development of warts on the skin, but differs from it in antigenic composition. The disease is contagious, and eutoinoculation is often observed. The development of genital warts is promoted by various local irritants, heat, moisture, and skin maceration.
A combined disease is often observed, or rather the development of condylomas in patients with sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and others) and accompanied by copious discharge from the urethra, cervix, vagina, rectum. I believe that genital warts develop more often in women, especially during pregnancy, and in case of poor hygiene of the genital organs (accumulation of smegma in men, contact of genital discharge on the surrounding skin in women), and with existing immune disorders.
Indications for removal
Many women ask whether it is possible to remove growths during pregnancy. This problem is solved individually. The need for radical therapy depends on the stage of the lesion, the stage of pregnancy and the patient’s health status.
Condylomas must be removed in the following cases:
- The widespread distribution of growths has caused a loss of elasticity of the mucous membrane, which can lead to rupture of the genital tract or its blockage.
- Difficulty urinating negatively affects the condition of the body as a whole.
- The danger of education transitioning into oncological pathology.
- Condylomas covering the birth canal can pose a threat of infection to the fetus.
The treatment method is selected by the gynecologist after a comprehensive examination, depending on the condition of the patient and the fetus.
Clinic
The incubation period of condylomas varies - from 1 to 6 months. usually 2-3 months
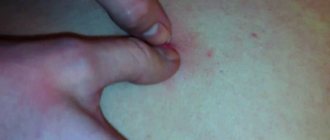
Genital warts are most often localized in women - on the inner surface of the labia majora. on the labia minora, in the clitoris area, the entrance to the vagina, on the perineum and around the anus. In obese patients, condylomas can also develop in the inguinal-femoral folds, armpits, in the navel area, submammary glands. The disease is more often diagnosed in men than in women, and even much less often in children and the elderly. In children, growths in the vulva area and in the inguinofemoral folds are more common.
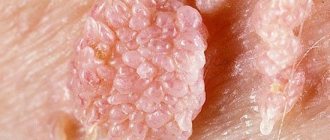
The incubation period varies - from 1 to 6 months. usually 2-3 months. Initially, small single papillary villous growths appear in the form of pink nodules in unlimited areas, then they are grouped, resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower on a narrowed base that resembles a stalk. Single condylomas are observed only in a small part of patients; in general, multiple growths are observed; less often, growths, merging into conglomerates, reach large and gigantic sizes.
This type of lesion is observed more often in patients with pronounced subcutaneous fat and in pregnant women. The elements acquire a bright red color with a cyanotic tint on the surface, are macerated, eroded, painful when touched, and bleed easily. Serous-purulent exudate accumulating between the lobules of condylomas, decomposing and combining with sweat, emits an unpleasant odor.
A serious complication, mainly of large and giant condylomatosis, is malignancy. Cases have been described, more often in elderly people, of transformation into warty cancer, so histological examination is necessary in such cases.
Sources of condylomatosis infection
Reduced immunity during pregnancy is one of the main causes of condylomatosis
It is possible to become infected with HPV through sexual and household contacts. Women who frequently change sexual partners may become infected. Representatives of the fair sex who are at risk may experience various disorders in the body, namely:
- reduced immunity;
- infectious diseases;
- fungal infections at the time of HPV infection (gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc.), sexually transmitted;
- emotional overload due to frequent stress;
- tendency to smoke and drink alcohol frequently;
- lack of vitamins due to poor nutrition;
- consequences of abortion.
Pregnant women and nursing mothers are more susceptible to HPV infection. Regular sexual relations with the same partner lead to a reduction in risk. You can become infected through extrasexual contact at home. Using only your own personal belongings allows you to avoid infection if you have to live in a dormitory, communal apartment or rent an apartment, since there are always strangers there. You cannot use the personal belongings of infected or strangers.
You can become infected with HPV through contact with the secretions of a sick person in public places. For example, if disinfection rules were violated in the pool, then the risk of getting HPV in it is high. Particular care should be taken when visiting public toilets, otherwise you can become infected not only with the virus, but also with other dangerous diseases. HPV is also transmitted through a friendly kiss upon meeting. The risk of acquiring HPV in a bathhouse or sauna is reduced due to the high temperatures that cause the death of the infection.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Genital condylomas are one of the forms of papillomatosis. The culprit of this disease is the human papillomavirus or HPV. Infection occurs exclusively through contact.
The favorite location of condylomas is the reproductive organs of both women and men, the perianal fold, the anus and urethra, the rectum, the inner part of the urethra, the buttock area, the cervix and, in rare cases, the tongue and larynx.
Symptoms of the disease:
- severe itching at the site of virus penetration;
- pain in the area where condylomas appear;
- problems urinating or defecating if the wart appears in the rectum or urethra;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- bleeding when tumors are damaged.
In appearance, condylomas resemble broccoli or cauliflower inflorescences. The color of the neoplasms ranges from flesh-colored to pink on the mucous membranes to brown on the skin in the anal area. The size of a single vegetation does not exceed 0.7 cm. If several neoplasms merge, the diameter can reach several centimeters. If growths or any alarming symptoms appear, you should contact your local gynecologist.
Diagnosis of condyloma in pregnant women is carried out according to standard medical protocols:
- Visual examination by a doctor of the external intimate organs and examination of the internal walls of the vagina and cervix in the mirrors.
- Smear test for sexually transmitted diseases to rule out bacterial infections.
- PCR analysis to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of virus. There are 2 types of HPV - low-oncogenic strains - that is, the likelihood of degeneration into a cancerous tumor is insignificant and highly oncogenic strains. The latter provoke the development of cervical cancer pathologies.
An indirect sign of a highly oncogenic formation is the location of the tumor - on the cervix - and its appearance. If a classic pointed papilloma is detected, then the risk of degeneration is low, since such neoplasms are caused by low-oncogenic strains. If a flat, wide wart is diagnosed that grows deep into the tissue, then a biopsy of the tumor is indicated to determine the nature of the growth. The likelihood of developing cervical cancer in this case is extremely high.
Why and how the virus appears
A woman can avoid the disease if she knows how it occurs. You can become infected in the following ways:
- One of the most common ways of infecting the female body is through sexual intercourse. Keep in mind that even contraceptives will not protect you from the virus if your partner has it. So be careful and careful when making contact.
- Much less often, but it is still noted that a newborn child becomes infected from the mother when she passes through the birth canal if she had a virus. Of course, this is extremely rare, but still, as a precaution, it is recommended to be treated in advance, even before giving birth.
- There are types of papilloma virus (and there are a lot of them) that are transmitted not only by sexual contact, but also by oral contact - this means that infection is possible through an innocent kiss.
Turning to the statistics, one can be amazed: the vast majority of people infected with the virus are women. But pregnant women should not worry too much, because there are more than ninety types of infection, and only a few of them are truly dangerous - condylomas lata and acuminata.
Condylomas in the form of growths
If partners do not use such a well-known method of contraception as a condom during sexual intercourse, then infection can pass from one person to another. At the same time, this remedy is not always able to protect, since HPV is localized not only on the male genital organ, but also in the anus, on the scrotum, etc.
Contact with infected areas of a partner’s body as a result of sexual intercourse is dangerous to a woman’s health. She can avoid this if she arranges for her partner to get tested for HPV in advance. An intimate relationship with this person will be safe if the result turns out to be negative.
Condylomas in women, the causes of which are related to intimate relationships, mainly form in the vagina and on the labia. According to statistics, vulvar condylomas are more common, but the papillary type of growths can also appear in the anus. The perianal type is formed near the anus, and the development of anal formations occurs directly in the rectum.
The growths can be either single or multiple. Single - divided into large and small. Multiple growths may look like cauliflower, but this type of growth can be hidden. Pathology therapy should be carried out by a proctologist. The existence of anal and perianal condylomas in the human body is characterized by symptoms such as itching and bleeding. If there is no treatment, the formations begin to grow and become malignant.
The active development of condylomas causes problems not only with physical, but also with mental health. Growths on a sexual partner, which cause a lot of unpleasant emotions, develop an inferiority complex in a woman. If the formations begin to grow, then the partners can no longer lead a full sex life.
Risk factors
According to statistics, one third of the number of people who are carriers of HPV are unaware of its presence in the body. You can catch the disease through scratches and wounds even in childhood, attending clubs and kindergartens. Factors in the development of the disease are a whole group of viruses.
Provoking causes of the development of condylomas:
- frequent change of sexual partners,
- early onset of sexual activity, when constant disruptions of the immune system occur in the not yet formed body,
- dysbacteriosis in the vagina and changes in the microflora of other organs,
- the presence of infections such as herpes, gonorrhea and chlamydia,
- lack of barrier contraception.
Lack of vitamins and stressful situations also play a huge role, which entail an additional risk of infection and lead to a decrease in immunity.
Causes of condylomas during pregnancy
Why do ridged growths appear during pregnancy? Indeed, sometimes, for a number of indications, sexual activity is prohibited during this period. And the husband or father of the child did not have any growths or complaints. A man’s immunity is initially stronger than a woman’s, and for many years a loved one is a carrier of the disease. He has no clinical manifestations of the pathology, but he infects his partner.
Papillomavirus is an insidious disease. For a long time, provided there is a strong immune response, it can remain in the body and not show itself in any way. Until at some point the protective forces weaken, and the virus begins to cause a mutation in the cells of the epidermis.
In this case, the mechanism of cell division is disrupted. They begin to divide chaotically, and a condyloma appears at the site of virus penetration.
During pregnancy, the reason for the appearance of condyloma is a physiological decrease in immunity during this period. The body considers the fetus a foreign body and will strive to get rid of it. Therefore, for 40 weeks, a woman’s defenses decrease in order to preserve future offspring. In addition, physiological hormonal imbalance develops during pregnancy. This is also a factor that triggers the onset of the virus attack.
Possibility of getting pregnant with condylomatosis
Many women wonder whether it is possible to get pregnant with HPV. The presence of the disease will not interfere with conceiving and bearing an absolutely healthy child.
But there are exceptions when papillomavirus of the oncogenic group is detected. In this case, it is necessary to take a cytology test and find out which type is present in the body and how dangerous it is. If the results are within normal limits, you can begin to conceive. But if changes in the cervix are detected, you need to undergo a course of mandatory treatment, and only after that plan a pregnancy.
The danger of condyloma during pregnancy
If we talk about the effect of condyloma during pregnancy on the fetus, then there is only one danger - laryngeal condylomatosis of the newborn
If we talk about the effect of condyloma during pregnancy on the fetus, then there is only one danger. As the baby passes through the birth canal, he may take his first breath prematurely, and if the condylomas are located directly in the vagina, he may become infected with a virus, which can lead to the development of a rare disease - laryngeal condylomatosis of newborns. To avoid infection of the child, women with vaginal condylomas are recommended to deliver by caesarean section.
If condylomas during pregnancy are not located in the vagina, there is no risk to the baby. However, any manifestations of HPV weaken the immune system, which can lead to undesirable consequences for both the child and the pregnant woman.
What should an expectant mother remember?
It is much more difficult when the virus is type sixteen or eighteen. Then the doctor will advise you to start treatment already during pregnancy, but this is not scary, but the child will be born in a healthy body.
The deadline for the removal of type eighteen or sixteen condylomas is: the third trimester, and all because it is necessary to ensure the safety of the child (in order to avoid problems with the growth and development of the baby).
You need to know that sitting at home you will not be able to determine the type of infection. This is not something to joke about. If you are offered any tests, etc. on the Internet, do not believe them. Because you can find out the type only after undergoing an analysis, which will be carried out by a professional doctor.
Is it possible to give birth with condylomas?
If condylomas appear in a pregnant woman, even if the results of PCR analysis indicate the presence of a highly oncogenic strain, then there are no indications for abortion. There is no risk of intrauterine infection of the child.
method of delivery together with her gynecologist:
- if genital warts appear on the skin in the anus and on the external genital organs, natural childbirth is recommended;
- if the tumor is located in the vagina or cervix, or in the presence of highly oncogenic condylomas, the doctor will recommend surgical delivery.
After removal
After the procedure, the expectant mother undergoes regular examinations by a gynecologist. Regardless of the chosen treatment method, a woman must adhere to a special regimen for about two weeks. Restrictions are necessary to prevent injury to the treated area of the mucosa and epithelium.
Instructions from the gynecologist:
- In the first week after the procedure, you should not have sex or take a hot bath. This time will be enough to restore damaged tissue.
- Particular attention should be paid to the hygiene of the intimate area.
- Stop promiscuous sex, especially without the use of barrier contraceptives.
A relapse of the pathological process is possible, so a woman needs to constantly strengthen her immunity.
Treatment of condylomas in pregnant women
Treatment of HPV and condylomas must be carried out in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Treatment of HPV and condylomas must be carried out in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. In the presence of exophytic forms, their removal is indicated, since their rapid growth can be expected at a later date. This is fraught with various complications during further pregnancy and childbirth.
In cases where active manifestations of HPV are detected, including CIN 1 and 2, interruption is most often not performed. After treatment, colposcopy and cytological examination are performed again. If CIN 2-3 is detected in a short period of time, it is optimal to provide termination of pregnancy and appropriate treatment. However, tactics may be different; the decision is made specifically in each case based on the duration, age of the patient, clinical picture and examination. In this case, consultation with an oncologist is required. It is possible to perform microconization of the cervix with subsequent delivery by cesarean section.
In the presence of cervical cancer, provided that the depth of tumor invasion does not exceed 3 mm, conization of the cervix (shallow) is performed. The removed part is subjected to histological examination. Tactics are determined after receiving histology data together with an oncologist.
Radical operations are performed 4-6 weeks after birth. It is worth saying that there is no absolutely uniform tactic in such cases and the decision is made individually.
I would like to emphasize one more important aspect of this viral infection. Transmission from mother to newborn is also possible when the baby passes through an infected birth canal during birth. As a result, the baby may develop a very serious disease of the larynx - recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. It is very difficult to treat, and often these children become disabled. Fortunately, this disease is rare.
Danger to the fetus
There is a high risk of transmission of HPV from mother to child.
It consists of the following factors:
- The human papillomavirus can be transmitted to the baby during childbirth and during fetal development. This occurs when the infection passes through the membranes, or enters the placenta along with the blood.
- Condylomas during pregnancy can negatively affect the development of the fetus. Under the influence of the disease, the placenta begins to change, its walls become thicker and quickly age. This leads to malnutrition of the fetus, and the child is born with low birth weight. The risk of another infection entering through the altered placenta increases.
- HPV changes the healthy composition of the vaginal microflora, which provokes the occurrence of dysbiosis. Chronic infections worsen and bacteria multiply, which can also lead to infection of the newborn.
Other treatments
Doctors are often faced with the fact that they have to treat the consequences of self-medication and the use of traditional medicine. Herbalists and traditional healers offer a number of effective ways to get rid of condylomas on the butt and genitals.
What manipulations should not be performed during pregnancy:
- Cauterization with aggressive substances – feresol, solcoderm. Due to the peculiarities of a woman’s physique during pregnancy, it is impossible to independently treat neoplasms efficiently and accurately. The risk of chemical burns and mucosal atrophy is extremely high. It is prohibited to use such products to treat the inner surface of the vagina.
- Celandine juice and preparations based on it.
Celandine is a poisonous plant. Moreover, all parts are toxic, including flowers, roots, stems, and leaves. During pregnancy, it is dangerous to even inhale the fumes of this plant.
- Tar soap is a safe thing, but also useless. Any soap has an alkaline environment, while the mucous membranes of the reproductive organs are acidic. Using soap is unlikely to get rid of condylomas, but it will certainly disrupt the natural microflora of the genitals. In conditions of reduced immunity during pregnancy, the risk of developing inflammatory diseases of the genital area increases.
ethnoscience
The use of folk remedies for the treatment of condylomatosis is acceptable, but it must be remembered that self-medication is strictly prohibited.
To prevent skin burns, the doctor must supervise the treatment. Folk remedies are effective in any type of treatment, but their use in the genital area is not recommended.
Tools used:
- garlic juice,
- chicken protein,
- castor oil,
- ammonia,
- dandelion juice,
- Kalanchoe leaves,
- celandine tincture,
- decoctions of celandine and string.
Any therapeutic actions must be carried out after consultation with a doctor. Only he will tell you what can be done at home.
Prevention measures
The best prevention of condylomatosis is to be vaccinated with specialized drugs before the age of 13 years.
Important criterion! A girl should not be sexually active! The HPV vaccination is not included in the list of mandatory ones, so parents should take care of their daughter’s safety.
Adult women and men are advised to maintain sexual hygiene and selectivity. There are no other preventative measures.
- Is it possible to get pregnant if you have the virus? Papillomas on the genitals are not a contraceptive. If you have a history of highly oncogenic types of HPV, then when planning a pregnancy, you should be examined and discuss all the risks with a gynecologist.
- During pregnancy, you do not need to do questionable manipulations in intimate places on your own and without a doctor’s prescription.
- The appearance of condylomas is not a sign of betrayal by a beloved man. He could have been infected long before meeting you.
Sources:
- https://www.doctorbest.ru/kondilomy-pri-beremennosti.html
- https://www.women-medcenter.ru/kondilomy_pri_beremennosti/
- https://coriummed.ru/kondilomy/vidy-k/ostrokonechnye-pri-beremennosti.html
- https://www.goodoktor.ru/21.html
- https://dermainfo.ru/papilom/kondilomyi-u-zhenshhin.html