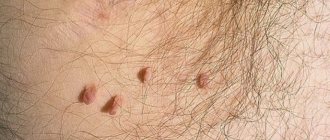
Warts and papillomas on the pubis are benign formations that are caused by the human papillomavirus, most often formed on the skin or mucous membranes. The location can be very varied. In addition to aesthetic discomfort, warts and papillomas can also cause physiological discomfort. As mentioned, a wart is associated with the papilloma virus, and therefore is a viral disease. In people with normal immunity, the body copes with the virus itself, and the presence of warts often indicates a weakened immune system.
Ways of infection with genital warts
Intimate papillomas are a type of skin disease, but there are several ways of infection:
- sexual intercourse;
- after touching the genitals during oral-genital contact, petting, hygiene procedures;
- in a household way;
- from an infected mother to a baby during childbirth.
The virus can persist in the air for some time, so there is a possibility of papillomas occurring as a result of self-infection through personal belongings (underwear, towels) and similar household items. Pubic warts more often appear in men and women who shave their private parts and do not follow proper hygiene rules - small lesions on the skin are very easy to get infected.
As it turns out, pubic warts appear faster when conditions are created that are conducive to their development. Among them are:
- period of bearing a child;
- postpartum period;
- breast-feeding;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- long-term use of contraceptives;
- frequent stress;
- imbalance of the microflora of intimate organs.
People who began to be sexually active early and regularly change sexual partners are more susceptible to infection with the papilloma virus.
Removal by radio method
This is the so-called radio wave method, quite modern, with a number of advantages. For such procedures, the new Fotek device is often used. The main positive feature of this removal is the absence of injury to delicate areas. The use of a radio wave knife when removing papillomas in intimate places allows you to avoid touching the skin or mucous membranes. In this case, the neoplasms are evaporated. Using the method, not only papillomas with legs are removed, but also smooth growths. Within just a few seconds, all growths can be eliminated. Scars do not form after surgery.
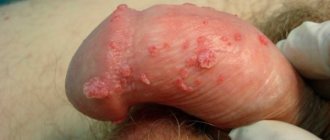
Types of papillomas
All warts in the pubic area can be combined into two main types:
- Pointed, the size of which does not exceed a couple of millimeters. They look like small nipples. The danger of genital warts is that they can lead to cervical cancer in women, and the risks for men include damage to the urethra. Detection of condylomas in the pubic part of men is more often likely to be on the genital organ, often on the foreskin. In women, they are found on the labia, pubis and vagina.
- Thread-like. The size of growths of this type is no more than 5 mm. There are single papillomas or warts, but with the same degree of probability there are multiple ones. Again, a decrease in immunity can lead to their additional growth.
How not to get sick
- The HPV vaccine protects against the types of virus that cause anogenital warts. Ideally, you should get vaccinated before you become sexually active.
- Using condoms during sexual intercourse. They protect against HPV at least partially. Also, this method of protection helps to recover from warts faster if both partners are infected with HPV.
- Smoking is a risk factor for HPV infection. But there is currently no evidence that quitting smoking helps cure warts.
- The fewer sexual partners you have, the lower your risk of developing warts.
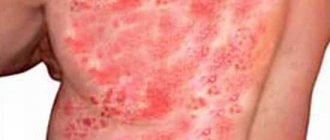
Symptoms of pubic warts
Warts on the pubic area do not immediately make themselves felt and for some time you may not even suspect their existence.
To prevent complications, at the slightest suspicion of an intimate mass, consult a doctor.
When their number increases, the following symptoms appear due to contact with linen:
- pain;
- burning and itching;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor due to inflammation of growths;
- blood when the formation is injured.
It is important to detect the problem in time, which external manifestations of papillomas will help with:
- hyperemia (redness) of the skin;
- specks of gray, whitish or pink color;
- thickening of the skin.
Description of the procedure for removing condylomas with a laser
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. First, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic, after which an anesthetic drug is applied. When the anesthesia takes effect, the doctor begins the procedure. Using a laser (without direct contact), evaporation (vaporization) of the condyloma is performed. Laser beams act exclusively on the formation itself without damaging surrounding healthy tissue.
After the procedure, the skin is treated with an antiseptic, and a local antibiotic is applied to the treated area, which reduces the risk of infection. The duration of the procedure is 15–20 minutes, depending on the number of tumors that need to be removed, their location and size.
Diagnostics
Without the intervention of a specialist, it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, unless the size of the growths is very large and there is no doubt that these are condylomas. The following doctors can professionally solve the problem:
- gynecologist;
- urologist;
- dermatovenerologist.
Diagnosis of the disease takes place in several stages:
- examination of the patient;
- taking blood for analysis to determine the presence of a sexually transmitted disease;
- conducting a PCR test (in some cases).
In some cases, the circle of doctors expands to include an oncologist if there is a suspicion of malignancy.
How is the rehabilitation period after laser removal of condylomas?
During the procedure, laser beams stimulate the process of tissue regeneration, so recovery after laser removal of condylomas is quite fast. To avoid the development of adverse complications, several rules should be followed during the rehabilitation period:
- during the first days, treat the removal area with an antiseptic drug (as prescribed by a doctor);
- do not engage in intimate relationships;
- during the first 24 hours, refuse hygienic water procedures;
- avoid intense physical activity;
- do not visit the sauna, swimming pool and solarium;
- do not take hot baths.
Laser therapy is aimed at eliminating only the external manifestations of the disease, and not its cause. To avoid re-formation of condylomas, drug treatment is prescribed after laser removal. It involves taking antiviral and immunoprotective drugs. Properly selected drug therapy can stop the spread of infection and increase the body's protective functions.
Treatment of growths on the pubis
Therapy for warts in intimate places, like most other diseases, includes:
- medication treatment;
- surgical removal of condylomas;
- traditional medicine methods.
Drug therapy
Pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed only by a doctor. If there is only one wart and is small in size, then antiviral ointments are used as therapy, which are applied to the growth itself and the area of skin around it.
One of the most important points when treating warts is strengthening the immune system!
When there is no result or there is more than one wart, treatment is aimed at strengthening the immune system of the sick person. Immunostimulating drugs are prescribed along with vitamins and proper nutrition, because the approach must be comprehensive. Weak immunity is not able to resist infection, including the papilloma virus.
Removal in the clinic
The most effective method of getting rid of growths is mechanical removal. When contacting the clinic, the patient will be given several options for removing genital or filiform condylomas:
- excision with a scalpel is a traumatic option, but available to every patient; it is more often used when a large area of skin is affected;
- laser method, when warts are removed layer by layer using a heat beam;
- electrocoagulation, when the growth is exposed to electric current;
- freezing papillomas using liquid nitrogen;
- cutting off the growth with a radio knife is a method that has the least trauma.
There is no single best way to remove papillomas among those presented. Each of them has an efficiency of about 90%.
After removal, you will need to undergo antiviral and immunostimulating therapy to prevent relapse.
We treat warts in intimate places with folk remedies
Treatment of warts in some cases is acceptable at home. The plants around us contain components that can burn out growths and remove papillomas. Before starting home treatment, it is better to consult a doctor.
Let's consider the most effective methods of traditional medicine:
- Celandine juice. The plant is easy to find in any yard in the summer. Fresh juice should be applied to the growth several times a day. In winter, it is recommended to use plant extract from the pharmacy.
- Fir oil has the same effect. Twice a day you need to lubricate problem areas with it until the condyloma disappears.
- Raw potato juice, when applied daily to a wart, will get rid of the growth within a month.
- Garlic compresses also solve the problem. The clove is crushed and mixed with cream in equal proportions, applied to the problem area and left for several hours.
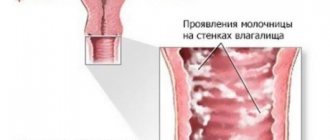
Condylomas in women
For those who do not yet know, intimate condylomas are warty, papillary growths on the mucous membrane and skin of the genitals. Caused by the human papilloma virus - HPV, they are more common in adults, regardless of the presence or absence of sexual intercourse, as well as in children, adolescents and virgin girls.
In women, intimate condylomas are most often seen by the gynecologist during an external examination of the genital organs. Although it is not uncommon for small genital warts to be undetected due to insufficient physician care. When a certain size is reached, the growths on the labia begin to be felt by the woman herself, which manifests itself in the form of a vague feeling of the presence of “something extra” between her legs.
Where do condylomas grow most often in women:
- labia,
- Vaginal walls,
- Hymen,
- Entrance to the vagina
- Cervix,
- Anus (usually during anal intercourse),
- Urethra, clitoral area.
A very common place for intimate condylomas to occur is the skin around the anus. In women, this place is often injured during anal sex, the use of rough toilet paper, and some diseases of the anus, so condylomas quickly spread deep into the anal canal through microtrauma. In a similar way, papillomas can also occur in those girls who, wanting to remain virgins, allow sexual intercourse in the rectum. Using a condom during anal sex cannot always protect against infection - HPV can penetrate through the micropores of the product, and the product itself can break due to excessive stress due to the relative narrowness of the anus. It is best to remove condylomas around the anus using the radio wave method in order to minimize the impact on sensitive areas.
How can you get infected with them?
If you have been diagnosed with genital condylomatosis or HPV carrier status, don’t be surprised! The presence of this virus in the body is a more expected thing in gynecology than its absence, since it is quite easily transmitted. The asymptomatic course is the reason that papillomas in many cases are an “accidental finding” during an examination by a gynecologist. In this case, it is difficult to accurately determine the route of HPV infection and the duration of the disease.
The virus that causes condyloma lives and manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes and is transmitted from these areas by touching them. Thus, HPV and intimate papillomas not a disease transmitted exclusively through sexual contact! Yes, of course, sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal) is also a method of transmission, but not the only one: it could also enter the body through everyday means. Therefore, the lack of experience in sexual relations ☛ does not guarantee virgin girls the absence of HPV and genital warts. Therefore, it is important for all representatives of the fair sex from the age of 16 to regularly undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist and at least have smears for flora.
Photos of condylomas in women
| Intimate papillomas | Vaginal condylomas | Condylomas on the labia |
| Papillomas of the hymen and urethra | Papillomas of the labia minora | Growths on the labia |
Do you want to be checked for intimate warts? Do you want to see everything with your own eyes, just as a gynecologist sees it? We invite you to do a video colposcopy!
Do condylomas need to be removed?
Cauterization of condylomas in intimate places (vagina, cervix, urethra, anus and anal canal, labia, etc.) is a mandatory procedure in gynecology. As well as preliminary diagnosis of carriage - tests for HPV infection in the body. If it is detected, simultaneously with the elimination of all formations, it is necessary to treat the virus. Only in this way can one prevent the progression of the process, the spread of papillomas to other parts of the body, transmission to a sexual partner or family members, and infection of the newborn during childbirth.
And, in the end, for a girl to wear and not remove warts on the genitals and various growths on the labia minora is simply unaesthetic.
Reviews about genital wart removal in the clinic
1. Recently discovered HPV and warts on the labia. Growths in the intimate area appeared several weeks ago. Where is the best place to remove condylomas in Moscow, by what method, so as not to hurt and is effective, I knew firsthand, because... two of my friends went to this clinic. I would like to note the high level of service and professionalism of the gynecologist who worked with me, namely Diana Andreevna Vakhrusheva. I also liked the conditions at the clinic! I made an appointment through their website and was accepted almost on time. They looked at everyone, took tests, and explained my further actions. After receiving the results, I came to the center to have condylomas cauterized, and during colposcopy the doctor also found one on the cervix, and they are known to be the most dangerous... They removed everything at once, with an injection, it didn’t hurt, I only groaned once) In general, very attentive staff, nice nurses. I have already and will continue to recommend your center to all my friends and acquaintances. Thank you! — Maria, 29 years old, Moscow
2. I tried to remove papillomas in intimate places and in the urethra 2 times, each time they grew back. I was tired of self-torture and decided to go to another center. I found positive reviews on the Internet about the removal of condylomas, which is carried out by this specialized clinic on Kutuzovsky Prospekt. I would like to express my deep gratitude to the gynecologist Bezyuk Laura Valentinovna, who devoted a lot of attention and time to solving my problem. It was only from her that I realized that before I had not carried out the treatment quite correctly, i.e. I simply burned out the condylomas, but did not get tested for viruses, and this is important. After all, if you do not get tested for HPV and do not treat it if it is present, then the papillomas will return again. In my case this was the case. But this time we did everything right, underwent treatment for HPV (types 33 and 18), removed condyloma in the urethra and there were many around. The doctor did everything with pain relief, I didn’t feel anything, only then there was slight discomfort for several days. Thanks for your help! — Sabina R., 31 years old, Moscow
3. There were a few condylomas in the intimate area (near the clitoris). Cauterization with Solcoderm, done by the doctor at this clinic, helped the first time. After a week, everything was practically healed and now there is no longer a trace left. Thank you to the doctor and all the staff! — Olga, 21 years old, Moscow. region
Here you can see all reviews about gynecologists.
Prevention of infection
Since the main route of infection with papillomas is sexual transmission, you should first of all give up casual relationships. Also, preventive measures are as follows:
- maintain personal hygiene;
- avoid contact with growths on the skin of other people;
- choose your sex partners carefully;
- use antiseptics in case of cuts, scratches of the skin, etc.;
- use condoms;
- wash your hands often with soap.
Intimate growths are an unpleasant phenomenon for both sexes, but if all preventive measures are taken, the problem can be prevented. The virus attacks weak immunity faster, so try to eat right, take vitamins, and walk more in the fresh air.
Factors in the appearance of benign neoplasms
Growths on the reproductive organs appear due to the human papillomavirus - HPV. The disease is characterized by a long incubation period, and warts appear when a person's immune system is weakened. Papillomatosis should be treated in combination with enhancing immunity.
There are several reasons for the appearance of benign growths in intimate places:
- infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted - herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia,
- promiscuous sex life,
- vaginal dysbiosis,
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals - vitamin deficiency,
- period of bearing a child.
With one sexual intercourse with a partner who is sick with HPV, the risk of infection is only 60%; if sexual intercourse is constant, the result of infection is one hundred percent. The virus enters the body, then penetrates the skin cells of the intimate area, and there it rapidly grows and divides. An inconspicuous neoplasm appears on the skin, which gradually increases in size.
Papillomas: incubation period of the disease
The period of development of the infectious process can be very long and develop in stages.
- Reproductive stage. After the virus enters the body, it is integrated into the genetic apparatus of the cell, and it begins to produce new viral particles. As a result, the concentration of the virus in the body increases.
- Integrative stage. The virus “hides inside the cell” to, for example, protect itself from the harmful influence of the immune system. This condition is called remission. The integrative stage is the initial stage in the development of skin manifestations.
Removal of genital warts using a therapeutic method
Those patients who, for any reason, are contraindicated with hardware removal methods, are offered wart removal with Solcoderm.
"Solcoderm" is a Swiss-made drug in the form of an aqueous solution. Contains nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acids and copper nitrate. This composition has a detrimental effect on the cells of genital warts.
Before the procedure, an antiseptic is applied to the affected area. The doctor applies “Solcoderm” directly to the wart, after which after 3-5 minutes the skin becomes discolored - the neoplasm becomes white-yellow. This sign is evidence of the beginning of the process of mummification (drying) of warts. They finally disappear after a few days.
Symptoms and types of papillomas
The signs of papillomas are quite obvious.
Small pedunculated formations appear on the skin.
They rise significantly above the level of the skin.
The color may be red or flesh-colored.
Blood vessels are visible in them.
Types of skin lesions due to human papillomavirus infection:
- genital warts (the most common variant)
- spots
- papules
- bowenoid papulosis
- giant condyloma
In addition to the formation on the skin itself, other symptoms are possible.
Patients may complain of itching and pain.
Sometimes there is a tingling or crawling sensation.
Painful cracks in the skin may occur.
Side effects of immunomodulators for papillomas
Flu-like conditions often develop when interferons are used.
Body temperature rises, signs of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract appear.
There is a headache.
The higher the dose, the greater the risk of side effects.
They can be relieved by using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
When using cytokine inducers, local reactions may occur.
This is redness, swelling, and the formation of erosions on the skin.
Control tests after treatment of papillomas
After treatment of pubic papillomas, laboratory monitoring is needed.
It is required for:
- viral load estimates
- prevention of recurrence of papillomas (by timely administration of a course of antiviral therapy)
- determining the likelihood of malignant oncological diseases
Control involves performing quantitative studies for human papillomavirus infection.
If it decreases, the virus is likely to be eliminated soon.
In the future, papillomas will not appear.
An increase in the number of papillomavirus DNA copies indicates the need for further antiviral therapy.
Recurrence of skin formations is possible.
In this case, they will have to be deleted again.
In addition, women regularly undergo smears for oncocytology.
This is required if oncogenic HPV types are detected during PCR.