The saying “it’s better to be covered in sweat seven times than frost once” is especially true for people suffering from cold urticaria. In severe cases of this disease, the figurative meaning of this joke can quickly become literal.
Is there an allergy to cold? What are its symptoms? Cold urticaria (CU) is a disease characterized by the appearance of blisters and/or angioedema after general or local exposure to cold, one of the forms of physical urticaria. ICD-10 code: L50.2 (urticaria caused by exposure to low or high temperature).
Classification
- Acquired HC
- primary (contact, idiopathic)
- secondary (with cryoglobulinemia, infectious diseases, tumors; arising after taking medications, insect bites, etc.).
- Atypical HC
- systemic acquired HC
- slow HC
- local HC
- cold erythema
- cold-dependent dermographism
- cold-induced cholinergic urticaria
- Hereditary HC
- Cryopyrin Associated Periodic Syndromes (CAPS): familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, Muckle-Wells syndrome (urticaria, deafness, amyloidosis), Chronic Infantile Onset Neurologic Cutaneous Articular Syndrome/Neonatal Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease – CINCA/NOMID)
- Familial atypical HC.
Prevention methods
The development of cold urticaria on the legs, arms and other parts of the body can be prevented if certain preventive measures are followed.
Measures:
- Dress according to the weather, do not forget about warm underwear, hats and scarves.
- It is recommended to use special protective agents and apply them to exposed areas of the skin.
- If signs of hives occur, immediately go to a warm place.
- Particular attention is paid to proper nutrition; the diet should not contain foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
- If possible, try to avoid contact with the allergen.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner - infectious, viral, fungal.
Cold urticaria is an unpleasant disease that disrupts a person’s normal lifestyle. It is not possible to cure the disease completely, but following the instructions will allow you to achieve stable remission.
All data in the article is provided for informational purposes and we do not encourage self-medication options. For more detailed answers, consultation with a specialist is required.
Epidemiology
Allergy to cold can occur in both adults and children. However, it is more common in young people (18–25 years old). This is a relatively rare condition, with an incidence of about 0.05–0.1% of all cases of urticaria. In cold climates it naturally develops a little more often. More than half of patients with chronic hyperplasia suffer from other allergic diseases.
In most cases (> 90%), primary acquired CU develops. Hereditary forms are extremely rare (≤1: 360,000–1,000,000), inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, and persist, as a rule, from early childhood.
What is cold urticaria
The disease is an allergic reaction of the body to cold. Skin exposed to low temperatures becomes covered with red, itchy, small blisters.
Symptoms of diseases vary. Most people react normally to cold weather. Others experience severe symptoms of the pathology. The most common cause of allergies is immersion in water with low temperatures. It can cause shock, fainting, low blood pressure, and death.
The disease is most common in children over five years of age and in people from 17 to 26. If the symptoms of urticaria do not go away within 42 days, experts diagnose a chronic course of the disease. In most cases, urticaria disappears spontaneously after a few years.
If symptoms of urticaria appear, you should visit a dermatologist and allergist. Try to avoid exposure to cold during this period.
Causes of cold allergies
The significant factors and causes of primary acquired cold urticaria are unknown. Secondary acquired chronic disease can develop in patients with infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, HIV infection, infectious mononucleosis, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, borreliosis, etc.), tumors, after the use of medications, including serums and vaccines, hymenoptera bites. Cryoglobulins (serum proteins that change their structure and precipitate when the temperature drops; are formed in tumor, infectious and systemic inflammatory diseases) were detected in the blood of 3–4% of patients with chronic chronic disease. Isolated cases of secondary CC that arose against the background of allergen-specific immunotherapy and after allergological skin tests have been described.
Hereditary CC develops as a result of mutations in the gene encoding the cryopyrin protein, which is involved in the regulation of the production of proinflammatory cytokines, primarily interleukin-1 (IL-1).
Diagnosis of urticaria
The diagnosis is made in specialized institutions. To detect a reaction, they do a test for the skin's perception of cold - a piece of ice is passed along the epidermis at the bend of the elbow. If a rash occurs, we can talk about the presence of urticaria.
If necessary, a variety of studies are used.
Methods:
- Blood and urine tests
- Allergen tests
- Immunological studies,
- Tests for the presence of parasites,
- The use of radiography and computed tomography,
- Research of the thyroid gland.
There are typical and atypical forms of cold urticaria. In the first case, urticaria is acquired; to diagnose it, a skin biopsy is performed.
The atypical form is a hereditary disease and is diagnosed using a blood test. Once an accurate diagnosis is made, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Pathogenesis
Local and/or general exposure to cold on the skin or mucous membranes leads to changes in tissue antigens and/or antibodies. Contact of these altered molecules with mast cell receptors leads to the release of histamine and other allergy mediators from the latter. Under their influence, capillary permeability increases, swelling and inflammation quickly develop.
In hereditary forms of CC, an uncontrolled increase in the expression of IL-1 leads to the development of a systemic inflammatory process in many organs and tissues of the body.
Treatments for Cold Rash
When the first signs of urticaria appear, the person is placed in a warm room, and a warm bath can be provided. Subsequently, medications and traditional medicine are used for treatment.
Medicines:
- Antihistamines - Claritin, Tavegil, Suprastin - reduce the production of histamine in the blood and reduce the negative reaction on the skin.
- External agents help relieve inflammation, reduce swelling and itching. They are found in the form of creams, gels, ointments - Fenistil, Skin-cap, Gistan.
- In severe cases, drugs containing hormones - Hydrocortisone, Elokom, Advantan - may be prescribed. The products help well, but they have certain side effects and are prohibited for use for a long period.
- In case of Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock, it is necessary to provide emergency assistance to the victim and call a team of doctors. In such a condition, the patient is given epiniphrine, one ampoule of antihistamine and decongestant medication.
Medications are prescribed by a specialist; independent selection of medications can provoke an exacerbation of urticaria. To treat nettle fever from cold, it is allowed to use folk remedies and methods.
Folk remedies:
- Drink one small spoon of freshly squeezed celery juice three times a day before meals.
- Squeeze a small amount of juice from an aloe leaf onto a gauze napkin. The compress is used on inflamed areas of the skin for cold urticaria.
- Three hundred grams of nettle leaves are poured into three hundred milliliters of boiling water. Insist during the day. Filter and take one glass before bedtime.
- A good preventive remedy for hives on the body is raspberry jam. You should consume several spoons of it per day.
- For herbal infusions, chamomile, calendula, and burdock are used. The prepared product is used to wipe the inflamed areas of the skin.
- Two hundred grams of fresh blueberries are ground and applied to affected areas. The procedure is carried out once a day for seven days.
- One hundred and fifty grams of pine needles, cones and twigs are poured with boiling water. The prepared solution is used for allergy baths.
Folk remedies can cause exacerbation of urticaria, so they are used after consultation with a specialist.
Nutrition should be balanced. Avoid foods high in histamine, enzymes and artificial colors. Preference should be given to fermented milk products, hypoallergenic fruits and vegetables.
Symptoms of an allergy to cold
How does an allergy to cold manifest itself? The triggering factor is general or local cooling: cold air, in severe cases, sometimes a draft or flow from an air conditioner is enough, immersion in cold water, ingestion of cold food and drinks, contact with a cold object. Cold-induced cholinergic urticaria develops after exercise in the cold.
Patients with cold allergies complain of symptoms such as:
- typical urticarial rashes,
- rounded or irregularly shaped elements rising above the surface of the skin, accompanied by itching or burning,
- possible swelling of the lips, mucous membranes of the oral cavity,
- itching in the mouth, throat.
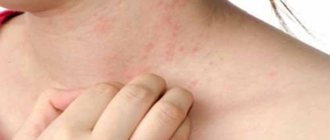
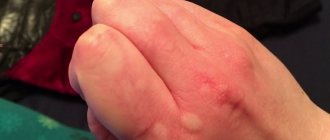
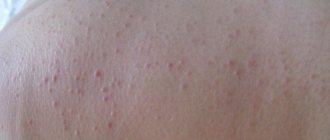
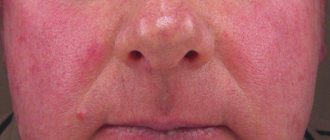
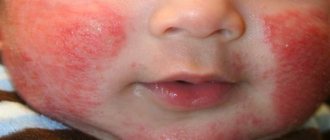
A rash with an allergy to cold usually appears within a few minutes on the arms, legs, face or other areas of the skin exposed to cold, less often around them or on “insulated” parts of the body (reflex CU). With cold erythema, there are no characteristic urticarial elements, the cooled area turns red, and pain appears.
In warm conditions, skin manifestations usually regress within 1–24 hours, but may persist for up to several days.
In severe cases of the disease, disturbances of consciousness, headaches, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain are possible.
In addition to the individual sensitivity of the patient, the severity of signs of cold allergy depends proportionally on the operating temperature, the area being cooled and the duration of exposure.
Prevention
In order to avoid exacerbation of cold allergies, it is necessary to follow a number of simple rules.
All exposed areas should be protected as much as possible with a scarf, gloves, mittens, and thermal underwear. Outerwear must have a hood that protects the head and face from wind and cold.
About half an hour before going out, your face should be lubricated with a rich, nourishing cream that protects the skin well from frostbite. Before going outside, you need to drink warm tea. On the street it is better to breathe only through your nose, this will protect the body from premature hypothermia and avoid the development of cold allergies.
In addition, during the cold season, you need to strengthen your immunity and try not to catch a cold.
Good health to you!
Diagnostics
In most cases, characteristic complaints, medical history and examination results are sufficient to make a clinical diagnosis of CU. To confirm it, a provocative test is performed: an ice cube packed in polyethylene is placed on the skin of the anterior surface of the forearm for 10–20 minutes, after which one or more urticarial elements appear at the site of contact or around it for 30 minutes. Antihistamines must be discontinued at least 48 hours before the test.
In case of a negative ice test, it is possible, but modern guidelines do not recommend - due to the risk of developing systemic reactions - a modified cold test: the forearm is placed in very cold water (5 ° C) for 10 minutes.
For the same reason, as well as from humanism, the third test is not recommended for use: a person stripped to his underwear is placed in a room with a refrigerator temperature of +4 °C for 20–30 minutes. This truly Gestapo method allows you to identify HC, which manifests itself only with general cooling.
In civilized countries, to assess the severity of chronic cold, the temperature sensitivity threshold is also determined using a special device, but it is not used in the daily practice of domestic allergists.
Using laboratory and instrumental methods, the presence of pathological conditions that may be associated with the development of secondary chronicle disease is excluded or confirmed.
Signs of the disease
How does cold urticaria manifest? The symptoms of this type of urticaria are no different from those of other types.
The reaction to the stimulus appears within five to twenty minutes. In some cases, symptoms may occur within a few hours. What is characteristic of cold fever?
Symptoms:
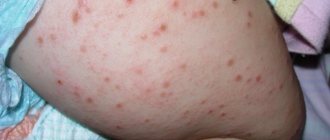
- Red blisters on the epidermis, single or multiple, can merge into large spots,
- Severe itching, intense, sometimes unbearable,
- Poor health, weakness,
- Painful sensations in muscles, joints,
- Head pain, dizziness,
- Pre-fainting or fainting state,
- Swelling of tissues in contact with cold
- Difficulty breathing, runny nose, watery eyes,
- Nausea, in rare cases, gag reflex,
- Swelling of the mucous membranes, anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema.
Symptoms appear quite quickly. disappear gradually upon returning to a warm environment. Cold urticaria is divided into several types.
Types:
- Spicy. It is characterized by a sharp manifestation of symptoms, in rare cases severe reactions occur. The signs also disappear quickly.
- Reflex. An allergic reaction is present only in areas of the epidermis that come into contact with cold.
- Recurrent. Characterized by a seasonal manifestation, urticaria may not appear for a long time, after which it again affects the skin.
You can see what urticaria looks like in the photo.
Treatment of cold allergies
How to treat allergies to cold? Patients with HC should, if possible, avoid exposure to low temperatures: dress warmly, wash with warm water, do not drink cold drinks, swim with great caution or not swim at all. During the cold season, it is recommended to use cosmetics that prevent the skin from cooling.
The main treatment for cold allergy symptoms is second-generation H1 antihistamines. If necessary, it is possible to increase the daily dose up to 4 times, but for this it is necessary to obtain the informed written consent of the patient.
The effectiveness of leukotriene antagonists is not shown in all cases. Systemic glucocorticosteroids are often ineffective.
Tolerance induction with the patient's own serum is used to a limited extent due to the relative complexity and labor-intensive nature of the procedure. From a patient with an exacerbation - usually after a walk in the cold - 20 ml of blood is taken, the serum is isolated, diluted with saline and gradually increasing concentrations are injected subcutaneously over two weeks. In some cases, this method has a good temporary or permanent clinical effect in the treatment of cold urticaria.
In rare cases, when life-threatening conditions occur and the disease is severe, hospitalization is indicated. In case of secondary chronic disease, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary.
Relationship between atopic allergic manifestations and cold urticaria
After exposure to cold, allergic manifestations become stronger, worsening against the background of other diseases, for example, atopic dermatitis. Almost half of patients suffering from dermatitis or asthma experience cold urticaria.
On this topic
- Hives
The best treatments for generalized urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 18, 2020
It is almost always accompanied by allergic rhinitis. In patients with concomitant diseases, a local form of allergy is observed. Systemic reactions of the body that cause serious health consequences occur mainly in people who do not suffer from allergies.
During the cold season, urticaria worsens in people with allergic rhinitis. If a person does not have allergies, then cold urticaria can occur at absolutely any time. In this case, the temperature difference is of particular importance, and not the low ambient temperature.
Causes
A weakened immune system can cause allergies.
Obviously, cold urticaria occurs from the cold. Many years of work by researchers to identify the causes have yielded results, but the 100% source of the disease has not been identified. It is believed that this is not one irritant, but a combination. It is known that there are circumstances that provoke the development of the disease:
- presence of food allergies;
- weakened immune system. It may weaken as a result of previous illnesses, operations, or after taking potent drugs;
- helminthic infestations;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic diseases;
- inflammatory processes.
Read also:
Symptoms and treatment of cold dermatitis
Against the background of the above factors, cold urticaria occurs much more often than in their absence. Any of the listed conditions can provoke the onset of the disease or its exacerbation.
Complications
Complications of cold allergies:
- Injury to the epidermis due to itching. This leads to harmful microorganisms entering the body through damaged skin;
- Swelling of the larynx. This condition leads to suffocation, which can cause death;
- Anaphylactic shock. If this condition continues for more than 5 minutes, it can also lead to death of the patient;
- Bronchial spasm. At the same time, the person begins to choke, and the lack of timely assistance leads to death.
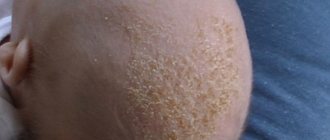
Photo of cold urticaria
The photo shows the external manifestations of cold allergies.
Cold allergy is a pathology that has several varieties and several stages of progression. If you suspect a pathology, it is important to consult a doctor to prescribe therapy. This will help avoid complications, and in some cases even death.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures will help avoid the occurrence of signs of the disease.
General recommendations
Patients diagnosed with cold allergies should not be allowed to suffer from hypothermia. It is not recommended to take walks in windy and cold weather, swim in bodies of cold water, or consume cold food and drinks. The following preventive measures will also help to avoid the development of pathology:
- taking immunostimulants to increase the body's defenses;
- applying protective drugs to the epidermis before going outside;
- wearing warm clothes made from natural fabrics.
Hardening
Doctors do not agree on the question of whether it is necessary to harden for this form of reaction of the body or not. Experts are unanimous in only one aspect - children from birth to three years old should not be hardened, as this can lead to dire consequences.
As for adults, hardening is recommended to be carried out gradually. First, you should wipe your face and hands with water. If there is no reaction, proceed to washing and rinsing your hands with water, gradually reducing the temperature.
If no signs of illness appear, you can proceed to hardening the whole body, but also gradually. First, take a slightly cool shower for a couple of seconds. If the body has responded normally to the procedure, you can begin to reduce the temperature and increase the duration of hardening. When symptoms appear, all manipulations are stopped immediately.
Causes of cold type allergies
In people who are sensitive to temperature changes and suffer from cold allergies, frosty air causes an effect on mast cells.
These cells are located on the surface of the skin. They give a signal, and a reaction occurs, accompanied by the release of histamine. The body, experiencing an excess of the above-mentioned hormone, responds with an allergic reaction.
People who are sensitive to weather changes should think about what the body’s reaction to a drop in ambient temperature is and what treatment is required.
There is a high probability that a disease is hidden in some part of the body, the development of which a person may not be aware of.
Eliminating the symptoms of a cold reaction is not enough. It is recommended to get rid of the root cause of the disease.
The main causes of cold-type allergies that can lead to complications are the following factors:
- chronic pathologies that a person has suffered from for a long time: sinusitis, sinusitis, caries or tonsillitis;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- weakening of the immune system is often provoked by the presence of helminths in the human body;
- kidney pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and other organs;
- colds, stress and cancer;
- hereditary predisposition;
- infectious diseases, which include: chickenpox, mumps and pneumonia;
- existing problems with an allergic reaction to external irritants: dust, animal hair or pollen;
- long-term use of medications belonging to the category of antibiotics.
Article on the topic: Hay fever - what is it? How to quickly cure this scourge in [y] year?
Rarely, there are precedents in which the above-mentioned type of allergic cold reaction is genetically predisposed. Intolerance to the cold form of allergy sometimes manifests itself in children if one of the parents had similar problems.
The most common type of cold allergy does not occur from cold, but is provoked by windy weather. Its main symptom is not itching, but burning of the skin.
Based on the above factors, it becomes clear that many people are at risk. Therefore, the possibility of acquiring a cold type of allergy cannot be ruled out. Such symptoms require treatment.
Predisposing factors for allergies are sometimes trivial changes in temperature conditions. For example, a person moves from one room to another or goes outside.
The release of histamine can be triggered by contact with supercooled water. This situation can occur when leaving the pool or while swimming in open water. Some people have trouble washing dirty dishes every day.
Symptoms
Urticaria in the cold is manifested by skin allergy symptoms. After exposure to cold, pinpoint rashes of different shades, redness, swelling and itching appear on the skin of the face, arms, legs, and less often other parts. The rash consists of blisters - this is an element that rises above the skin and has different shapes. This is urticaria from the cold (photo). From the moment of exposure to cold until the rash appears, it usually takes from 30 to 60 minutes. After 1 – 2 hours the rash disappears.
Urticaria can be:
- local (local);
- general (systemic).
The symptoms of typical acquired and atypical cold urticaria are almost the same, but each form has its own characteristics.
Typical cold urticaria is characterized by the appearance of a rash on a chilled area. Atypical urticaria differs from typical urticaria in the variability of symptoms and the tendency not only to local symptoms, but also to the body’s general reaction to cold.
Atypical cold urticaria occurs:
- immediate type - the rash appears immediately, but with this form there are no blisters, instead dense nodules or spots form, the skin feels hot to the touch.
- delayed type - the rash is typical, but blisters do not appear an hour later, but 9 - 18 hours after contact with cold, the rash lasts 2 - 3 days.
Typical acquired cold urticaria (photo symptoms and treatment) in adults over 30 years of age may become weaker or stop bothering them altogether. This is explained by changes in hormonal levels, which also affect the reactivity of the immune system and blood vessels. The fact is that there is another variant of the reaction to cold - reflex cold allergy, which occurs due to a violation of nervous regulation. All this can increase the manifestation of cold urticaria itself.
Urticaria on the hands from cold is the most common pathology in adult women.
Cold urticaria in children
Cold urticaria in children has some features. Firstly, the atypical hereditary form is more common in children, and secondly, general symptoms of a cold reaction occur more often. In these cases, in addition to cold allergies, other symptoms of hereditary pathology occur, for example, children may have deafness, damage to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), kidneys, inflammation of the joints, eye damage (swelling of the optic nerve, redness of the eyes).
Typical cold urticaria in children occurs on exposed areas of the skin - face, hands, and symptoms can develop faster because children's skin is thinner.
Urticaria from cold in a pregnant woman
During pregnancy, a reaction to cold may also occur, and cold urticaria may also be accompanied by a cold runny nose and lacrimation from the cold. This also happens due to hormonal changes. Female sex hormones act on blood vessels in almost the same way as the allergic substance histamine. Hormones cause blood vessels to dilate, so an allergic reaction to cold may occur more quickly. A special feature of allergies during pregnancy is that they occur more often on the stomach and chest, due to stretching of the skin in these areas.
The fetus is not directly affected by cold allergy because there is no true allergic reaction in which antibodies are formed. If a pregnant woman’s health sharply deteriorates (swelling of the larynx or a drop in blood pressure occurs), this can reduce the amount of oxygen that goes through the umbilical cord to the fetus.