Prevalence in nature
The fungi that cause the disease are ubiquitous. Favorable conditions for their life are created in regions with a warm, humid climate.
Zoophilic, anthropophilic, and geophilic Microsporum fungi are found in nature; almost all types are dangerous to humans.
Geophilic fungi live in the soil; infection occurs when working with soil in summer cottages. Anthropophilic fungi are found on human skin.
Zoophilic fungi are spread by animals. Homeless animals pose a danger of microsporia infection to humans.
The zoophilic fungus Microsporum canis, which parasitizes mainly cats, has recently become almost the only cause of microsporia in humans, for which it has received the name cosmopolitan fungus.
How does infection occur?
Carriers are domestic or stray animals (usually cats and kittens) and people. Microsporia is transmitted through direct contact of a child with an infected kitten, puppy, or through objects that have come into contact with fungal spores and animal fur. The fungus is widespread and susceptibility to it is very high. Children's skin is thinner than that of adults, and until puberty it does not produce substances that kill the fungus.
It is noteworthy that red-haired children do not become infected with microsporia.
Infection is promoted by reduced immunity, hypovitaminosis, microtraumas, increased sweating, as well as neglect of hygiene and sanitary standards in children's institutions. The peak of infection occurs in May-June, September-November. This is explained by the birth of more kittens and the frequent communication of children with animals at this time.
Epidemiology, routes of infection with microsporia
Mostly children suffer from fungal infections; there is an increase in the number of cases of microsporia in newborns.
Adults practically do not suffer from microsporia of the scalp, and when infected, they heal themselves due to the presence of organic acids in the hair that have antifungal activity.
Mostly young women, as well as people suffering from chronic diseases that cause a decrease in immunity, become ill in adulthood.
The percentage of adults suffering from microsporia has been increasing recently and this is associated with the increase in neuroendocrine diseases and HIV-infected people.
With inadequate treatment, the disease becomes chronic with sluggish, erased symptoms. This leads to the spread of infection.
Infection of both children and adults with microsporia most often occurs from a sick animal, usually a kitten, less often from a sick dog.
Preventive actions
Preventive measures for microsporia include sanitary and hygienic measures, incl. compliance with personal hygiene measures, and disinfection measures (preventive and focal disinfection). Focal (current and final) disinfection is carried out in places where the patient is identified and treated: at home, in children's and healthcare institutions. Preventive sanitary-hygienic and disinfection measures are carried out in hairdressing salons, baths, saunas, sanitary checkpoints, swimming pools, sports complexes, hotels, hostels, laundries, etc. Anti-epidemic measures
|
The problem of ringworm will apparently always be relevant. The issues of predicting morbidity, the strength and degree of correlation of these rises with solar activity cycles, reducing the duration of treatment, finding new methods of external therapy to avoid the occurrence of irritant dermatitis remain unresolved... The list of questions can be continued for quite a long time.
One of the most pressing problems in the search for new methods of therapy is the study of the dynamics of the emergence of fungal resistance to antifungal agents, including the so-called xenobiotics - substances synthesized by humans that are not found in nature.
Antifungal agents include all azole compounds (itraconazole, clotrimazole, fluconazole, etc.). Another problem of superficial dermatomycosis of the skin is finding ways to form specific resistance of the body against the fungal agent.
Thus, the development of immunotropic drugs for the treatment of skin mycoses continues, although it is only of an adjuvant nature in microsporia treatment programs.
The third modern problem concerns the organization of secondary medical and social prevention of skin mycoses among all age groups of the population. This problem lies mainly in the organization of interaction between medical and veterinary services, which in our time are significantly separated.
The solution to these problems should serve as the key to successful treatment of dermatomycosis, reducing morbidity, and increasing mycological safety. It is the term “mycological safety” that best characterizes the entire complex of measures for the identification, treatment, medical examination and prevention of mycoses, and not only of the skin.
Page 3
Medicine Microsporia: etiology and treatment
| Source: //studwood.ru/1617336/meditsina/profilakticheskie_meropriyatiya |
Symptoms
Up to 97% of microsporia infections are caused by the zoophilic fungus Microsporum canis.
The incubation period of this fungus is the time from the penetration of fungal hyphae into the skin until the appearance of symptoms of microsporia, lasting 7 days. The smooth skin of the trunk, limbs and scalp are most often affected.
Microsporia of smooth skin
The maximum number of infections in children is observed in early summer and autumn, which is associated with the time of birth of kittens, which are more susceptible to infection than adult animals, and the time of return to school.
The first symptoms of smooth skin microsporia in children appear on the skin in the form of a red spot (as shown in the photo) at the site of infection. Adults can also become infected with a fungal infection, and the number of such cases is growing.
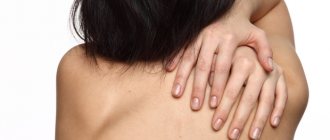
The localization of the manifestation of symptoms of smooth skin microsporia corresponds to contact with a sick animal, usually the skin of the face, hands, neck (see photo).
Unusual places of microsporia foci are also noted, for example, foci of infection are observed on the skin of the palms, feet, legs, penis, pubis, labia, and on the nail plate.
The number of patients with microsporia with genital lesions has increased over the recent period of time. You can become infected not only through direct sexual contact, but also through a washcloth, soap, or towel.
The peculiarity of microsporia of smooth genital skin is the abundance of blood vessels in this area, which contributes to the spread of the process deeper and complicates treatment.
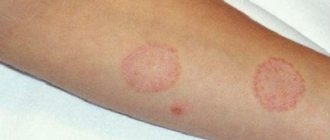
A symptom of microsporia in humans is the appearance of redness (see photo). The spot is swollen, rises slightly above the surface of the skin, and has clear outlines.
Gradually, a roller is formed along its border, consisting of crusts, bubbles, nodules, and the spot takes on the appearance of a ring. The central part of the spot becomes pale pink, and the skin on its surface peels off.
The size of the ring reaches 3 cm, the number of foci of infection does not exceed 3. The foci of infection do not bother the patient; some discomfort is caused by itching in the affected area.
In people suffering from atopic dermatitis, the fungus cannot always be recognized in a timely manner, since it has similar manifestations to atopy, and the use of corticosteroid ointments only increases the spread of fungal infection.
Such patients have papular-squamous microsporia of smooth skin, rashes on the chest, back, face, accompanied by severe itching and significant peeling of the skin.
The skin of the lower leg can also be affected by microsporia, with deep lesions up to 3 cm in diameter; the disease is more common in young women. Microsporia of the feet (shown in the photo) is manifested by characteristic rashes on the soles.
The fungus Microsporum canis can cause onychomycosis, which causes damage and destruction of the nail. The first symptom of infection is the appearance of a dull spot on the nail plate close to the nail bed.
Gradually, the stain becomes white, softens, and collapses. Microsporic onychomycosis is difficult to diagnose in a timely manner, since it practically does not bother the patient, the disease becomes a chronic source of infection.
Microsporia of the scalp
Microsporia of the scalp, caused by the zoophilic fungus Microsporum canis, most often affects children aged 5-12 years.
The exception is red-haired children. For them, protection against infection is provided by the special chemical composition of organic acids in the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the scalp.
The same acids are found in the hair of adults, which explains cases of spontaneous recovery of children with microsporia upon reaching adulthood.
Foci of microsporia infection in children are located on the crown, crown, and temporal region (see photo). Initially, the hyphae of the fungus penetrate the hair follicle and create a kind of cuff around the hair.
After the incubation period, changes become obvious: the hair in the area affected by the fungus breaks off, leaving stumps 4-6 mm high. Usually there are no more than two lesions, the diameter is up to 5 cm.
The stumps of broken hair look as if they have been trimmed, which is why the disease got its common name “ringworm.”
The hair stumps are dull and covered with a gray coating. If the hair on the infected area is stroked, it becomes deflected and does not restore its original position.
The affected area exhibits swelling, redness, and peeling of the skin. Near the main source of infection, small dropouts of the fungus, small pockets up to 1.5 cm in size, are often observed.
Microsporia caused by anthropophilic fungi
The clinical picture of microsporia of the scalp when infected with an anthropophilic fungus is somewhat different (shown in the photo). The lesions are small, multiple, with unclear boundaries.
The areas of infection are localized on the marginal zone of hair growth of the scalp; often one focus is located in the scalp, and the other on the smooth skin of the face.
Rare types of microsporia of the scalp
Atypical cases of microsporia include seborrheic, deep, trichophytoid, exudative forms of the disease.
With seborrheic microsporia, the hair thins and becomes covered with yellowish dandruff flakes, under which broken hair is found.
The trichophytoid form of microsporia is more common in older people and is characterized by low broken hair (1-2 mm above the skin) and the presence of long hair in the lesion.
With exudative microsporia, bubbles with exudate form at the site of infection. Serous fluid permeates the flaking scales, sticking them together, forming crusts.
With a deep suppurative form of microsporia, the site of infection acquires a red-bluish color, becomes inflamed, and when pressure is applied to it, pus is released.
With this form of microsporia, a person (as in the photo) may experience symptoms of intoxication of the body, which requires complex treatment.
Microsporia in children: how long is the incubation period and how to treat the disease, what is the quarantine period
Microsporia is a fungal disease that affects the skin and hair follicles.
It may be caused by various fungi of the genus Microsporum: zoophilic or anthropophilic. Zoophilic diseases are transmitted from domestic animals , mainly cats. Anthropophilic ones get on the skin through contact with people and objects touched by an infected person.
This lesion is easily transmitted between people and can break out in epidemics. If microsporia is detected in educational institutions, quarantine is introduced according to SanPiN standards.
What is microsporia of smooth skin
Microsporia is an inflammation of certain areas of the skin, hair, and rarely nails, caused by a pathogenic fungus of the genus Microsporium (more than 20 of its varieties are known). This lesion is often diagnosed in pediatric practice. Children get sick between the ages of 6 and 14 years.
Among adults, this pathology is registered in 9-25% of cases annually. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of reports of the identification of foci of infection in families affecting adults and the elderly.
In the last decade, there has been a trend towards a decrease in scalp microsporia and an increase in the number of smooth skin mycoses with additional inflammation of vellus hair - smooth skin microsporia.
Is there a vaccine for ringworm?
In general, vaccination against ringworm is not done - thanks to developed medicine, this disease has been learned to be easily and quickly treated after infection.
However, a vaccine against lichen still exists, although it is very difficult to find, and you are unlikely to be able to buy it at any pharmacy.
As a rule, children who are constantly in the hotbed of infection - among sick dogs and cats - need vaccination and have daily contact with them, risking infection. In other cases, simple adherence to hygiene rules is sufficient.
Find out whether children need to be vaccinated with DTP, Mantoux test, as well as against diphtheria, polio, and pneumococcal infection
Routes of infection
To protect yourself from pathology, it is important to understand how microsporia is transmitted. It is noteworthy that the fungal pathogens are extremely viable. They remain vitally active even when outside the human or animal body. The causative agent of this pathology is the fungus Microsporum.
- stray cat or dog;
- an infected person;
- personal belongings or common household items with a patient with microsporia;
- due to the use of a shared towel, comb or utensils.
This pathology is transmitted so quickly and actively that if one of the children is diagnosed with the disease, a quarantine is declared in the kindergarten.
It is noteworthy that SanPiN for microsporia implies the closure of a preschool institution for a period of three weeks.
But in practice this is not always the case. Most often, an infected child is isolated from the group and treated. The remaining children are carefully examined and preventive measures are taken to protect them.
SanPiN for school
The same measures are being taken in secondary schools as in preschool institutions. Quarantine is established, children are regularly examined by a dermatologist .
An SES worker is involved. Based on his decision, final disinfection of upholstered furniture, walls, floors and ceilings, as well as other things, is carried out.
Final focal disinfection eliminates fungal spores and makes the premises safe for children and working personnel.
The causative agents of the disease and how long the incubation period lasts
The main causative agents of microsporia in humans are:
- The zoophilic fungus Microsporium canis - about 98% in the European part of Russia - is transmitted to humans from a sick animal;
- The anthropophilic fungus Microsporium ferrugineum - about 1% - is transmitted from person to person;
- In the territories of Siberia and the Far East, on the contrary, the pathogen Microsporium ferrugineum is more widespread.
The incubation period is the time from the first contact of the fungus with the skin until the onset of clinical manifestations of the disease. The duration of this period for microsporia is: 7 days in the case of a zoonotic infection caused by Microsporium canis. In anthroponosis - the causative agent is Microsporium ferrugineum - longer, about 45 days.
Types of lichen
Ringworm is a general name for a whole group of diseases, mainly of a fungal nature.
There are such types of lichen:
Source: https://gidroz.ru/gribok/mikrosporiya-u-detej-karantin.html
Diagnostics
Before treating microsporia, diagnostic measures such as luminescent examination of the lesion under a Wood's lamp, microscopic and cultural examination are carried out.
The cultural method allows you to most accurately determine the type of pathogenic fungus that caused microsporia and choose the correct treatment.
Samples of diseased hair and scales from the lesion are applied to a special Sabouraud nutrient medium. In the case of microsporia, the growth of the fungal colony is observed already on the 3rd day. The colony is a white disc covered with delicate fluff, for which the mushroom received the name fluffy microsporum.
How long is quarantine for lichen? Features of different types of disease
In childhood, lichen occurs more often than in adults. Experts associate this fact with the child’s lifestyle.
Children's pityriasis rosea almost always occurs after intestinal or respiratory infections, acute fever or vaccination. The exact cause of this type of disease is not known. However, scientists suggest that its causative agent is the seventh herpes virus. The infection can be transmitted not only by contact, but also by airborne droplets. Typically, pityriasis rosea occurs in children over 10 years of age. Although it can often be observed in adults under 35 years of age.
Depriving quarantine in kindergarten is a mandatory event. This is especially true for cases associated with the occurrence of a ringworm type of disease.
Ringworm has two types (trichophytosis and microsporia). People and animals with a fungal infection are at risk of contracting this disease. It is often transmitted through personal belongings and household items that contain spores.
Versicolor or pityriasis versicolor refers to mycoses caused by three types of yeast-like fungus. The latter can live quietly on the child’s skin and at the same time not cause absolutely any pathological changes. However, infectious diseases, seborrhea, hormonal disorders, hyperhidrosis, leukemia, rheumatism, hereditary predisposition or lymphogranulomatosis often become a kind of impetus for the fungal process.
It should be noted that lichen versicolor is not very contagious. Most often, this disease is observed in adolescents. The most common habitats of this type of fungus are areas with a large number of sweat glands.
The reasons for the development of lichen planus are not well understood. Therefore, experts adhere to several theories (hereditary origin, viral, neurogenic, immunoallergic, intoxication).
Children's shingles - what does it look like? How to treat this disease? In medical practice, this disease is called herpes zoster. Its causative agent is Varicella zoster, which is also the causative agent of chickenpox. As soon as a child has chickenpox, the virus “settles” in the nerve ganglia. In the presence of unfavorable factors (for example, with reduced immunity), it is activated.
As with herpes, shingles is accompanied by a small blistering rash that spreads over the child's body (on the back, stomach, sides). To treat such a disease, you should consult a pediatrician. Usually, when the herpes virus is activated, doctors recommend taking medications containing the active substance - acyclovir.
Treatment of microsporia
The causative agents of microsporia are highly resistant to antimycotics and require the use of large doses of drugs during treatment.
For the treatment of microsporia, griseofulvin and lamisil are mainly used.
Griseofulvin is taken orally with vegetable oil to enhance the secretion of bile and dissolve the drug. Take the medicine with sour juice - apple, lemon, which enhances the absorption of griseofulvin.
Griseofulvin is hepatotoxic; to protect the liver, take Carsil and Liv-52. The course of treatment with griseofulvin lasts up to 2 months according to a special regimen, the maximum daily dose is 1 g.
Lamisil is considered an effective drug for the treatment of microsporia in humans. Lamisil tablets are quickly absorbed in the digestive tract, act specifically on fungal cells, and accelerate recovery even in severe suppurative forms of microsporia.
In addition to taking antimycotics, patients with microsporia are treated with external agents. Every week, hair in the affected areas is removed by shaving or epilation.
The source of infection is treated with alcohol tincture of iodine every day after waking up. In the evening, rub bifosin or sulfur ointment containing salicylic acid and tar into the affected area of the skin.
The affected area is cleaned of pus and crusts using compresses with solutions of licorice root, mumiyo, and ichthyol. They make lotions with gibitan. When treating microsporia in children, 1% mycospora creams, travogen, and lamisil cream are effective.
Types of disease
Have you been trying to cure PAPILLOMAS and WARTS for many years? Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure papillomas by taking it every day...
Lichen Zhibera (lichen rosea)
This type of lichen has a viral etiology, but its causative agents have not yet been fully studied. The patient develops pink, scaly spots up to 4 cm in diameter on the skin. The incubation period of the disease lasts from 2 to 21 days, depending on the person’s immunity.
The duration of the disease is from 1.5 to 2 months.
Shingles (herpes)
The causative agent of this disease is the varicella zoster virus. Children who become infected with it for the first time develop chickenpox, and those who have previously had it develop herpes zoster. In this case, many small itchy blisters filled with liquid form on the skin of patients. As you recover, a crust forms on the skin, which eventually falls off on its own.
The incubation period for shingles varies from person to person. This, as in the previous case, depends only on immunity. Thus, some patients may notice signs of infection within a week after infection, while others may live their entire lives with the chickenpox virus and not even know it. As a rule, shingles goes away after 2-4 weeks, but since the chickenpox virus affects the nerve endings, the itching may persist for a long time after recovery.
Trichophytosis (ringworm)
The causative agent of this disease is the fungus trichophyton or microsporium. The incubation period for ringworm depends on who was the source of infection. So, if a child became infected from another person, the incubation period will last from 2 to 6 weeks.
If the infection occurred from an animal, then it will be shorter - from 5 to 7 days. This is due to the fact that human immunity fights infection much better than animal immunity, so an infection transmitted from person to person is initially more weakened than one transmitted from an animal. Ringworm is the most contagious of all types of pathology.
Symptoms of trichophytosis include the formation of pink spots with jagged edges on the skin. The edges of these spots are white. Slight itching is possible. If hair grows in the affected area, it breaks off almost at the root. It is noteworthy that trichophytosis, unlike other varieties of the disease, can be transmitted not only from person to person, but also from animal to person (and vice versa). In severe cases, the disease may require long-term treatment (up to 2 months).
Despite the development of modern medicine, lichen still remains one of the most common dermatological diseases. According to statistics, about 70 out of 100 thousand people suffer from ringworm, 15 out of 100 thousand - from shingles, and about 5 out of 100 thousand - from Zhiber's disease. It is worth saying that a patient suffering from lichen is considered contagious from the incubation period until the complete disappearance of the skin rash.
For contagious types of lichen, quarantine in the kindergarten should last 45 days.
A folk recipe will get rid of papillomas. Take the simplest...
This is what our grandmothers did. The warts will go away in 10 days. Just take...
Prevention
To prevent microsporia in humans, strict measures are taken to prevent the spread of infection. For each patient with a confirmed diagnosis, a notification in form 281 is filled out.
The patient's family is examined, all persons who came into contact with the patient are also examined by medical workers to detect microsporia infection.
Prevention of microsporia includes examination and treatment, if necessary, of a pet infected with a fungus. A responsible attitude towards stray animals that children or parents themselves bring into the house will help prevent infection.
Even if there are no visible foci of microsporia on the face, ears, or paws, it is necessary to examine the animal at the veterinarian under a Wood's lamp and inoculate hair from different areas of the skin.
Precaution will help protect children from contact with a sick animal and prevent the spread of infection.
Requirements for quarantine for the prevention of deprivation in kindergarten
In preschool and school institutions, after detection of a patient, quarantine is established . The patient is sent home or to a special institution for treatment, and the rest of the children are necessarily examined by a dermatologist.
Employees of the institution are required to notify the sanitary and epidemiological station about the situation so that measures can be taken to reduce risks.
During the quarantine period, children must stay at home and not visit playgrounds, public institutions and classes. They can spread the disease.
Every 5 days, a dermatologist is required to check the condition of kindergarten students (the same group in which the patient studied).
Important!
If microsporia is detected in another child, the quarantine is extended for another 45 days.
If we are talking about a permanent kindergarten, from where children cannot immediately go home, quarantine is also prescribed. Basic Rules:
- remove all soft toys and carpets;
- hard toys must be washed in warm water and soap once a day, in nurseries - twice a day;
- children eat in a separate room, they should not visit public places (canteens, shared bathrooms and toilets, playgrounds);
- children are provided with lockers where they put their outerwear; all lockers must be numbered and signed;
- Other personal items (toothbrushes, combs) are also numbered; teachers ensure that they are used strictly by the owner;
- at the end of each day, mattresses and bed linen are disinfected or vacuumed;
- bed linen and clothes of children in quarantine are washed separately from the linen of children from healthy groups.