IN THIS ARTICLE:
- What is herpes in children and what are its symptoms?
- Causes of herpes in children
- What symptoms does herpes cause in children?
- How dangerous is herpes for a child?
- How to treat herpes on the lip of a child?
- Prevention of herpes on the lips in children
Herpes is a harmless disease, the main symptom of which is blisters on the lips. But young children may have a hard time with their first herpes infection and will need a doctor. Children can also infect their eyes with the virus, which can lead to blindness. To avoid the dangerous consequences of this disease, we talk about the symptoms and how to treat herpes on the lip of a child. We will also talk about methods of infection, prevention and how to quickly get rid of the sore at home.
General information about herpes type 1
Humanity knows 80 representatives of the herpes virus family. Of these, 8 are highly pathogenic for humans. The most common of these is herpes simplex virus type 1, or HSV-1. A distinctive feature of this pathogen is that it primarily affects the upper half of the body, especially the face: mucous membranes (lips, cheeks, pharynx, eyes) and skin. In this regard, the virus is also called orofacial - affecting the mouth and face. It multiplies and persists (constantly located) in the spinal nerve ganglia.
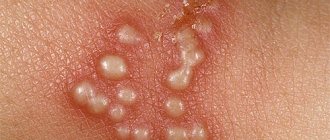
Isolated symptoms of the disease (blisters on the lips) characteristic of herpes virus type 1 can be first encountered in a child 3 years of age or older. It is at this age that immune cells (T-helpers) in their functional activity correspond to that of an adult, do not allow the development of generalized forms of the disease, preventing multiple lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. Up to 3 years of age, the external symptoms of the disease are always multifocal, and it is extremely rare to encounter, for example, a separate herpes on the lip of an infant, as the only manifestation of a herpes virus infection.
At the age of 10 years and older, type 1 herpes manifests itself mainly as vesicular-erosive rashes and disorders of the general condition of varying degrees of severity.
How does herpes infection occur?
The cause of the disease is infection. The source of infection with the herpes virus type 1 is always a sick person. The pathogen is contained in almost all secretions and fluids of the carrier: vaginal secretions, amniotic fluid of a pregnant woman, saliva, bronchial and nasopharyngeal mucus, conjunctival fluid, blood, sperm, urine. Contact with any of these biological substrates leads to the virus entering the body and persisting in its nervous structures. Typically, infection occurs during childbirth, through everyday life in the maternity hospital, while caring for a baby, in kindergarten, through the common use of kitchen utensils, through kissing through the mucous membrane of the lips, etc.
The characteristics of the child’s immune defense also contribute to herpes infection. For example, skin and mucous membranes covered with secretions in adulthood are a reliable barrier to the virus. Special substances contained in the blood of an adult - immunoglobulins - reduce the severity of symptoms (sometimes the disease is limited to mild general manifestations) and partially prevent relapses. The so-called secretory immunoglobulin A of saliva and other secretions prevents the penetration of the virus when it comes into contact with the mucous membranes of the mouth - lips, cheeks, soft palate.
In children under one year of age, the skin is easily injured, often itself has areas permeable to infection (diathesis, diaper rash, mechanical injuries), and therefore is not a barrier to the pathogen. The mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks is thin, loose, and also does not provide adequate protection. Of the immunoglobulins, a child under 5 months has only those that were inherited from the mother at birth. In a one-year-old child, immunoglobulins only begin to acquire functional activity and fully “start working” only at 5 years of age.
Preventive actions
Herpes in newborns can be prevented by proper preparation for conception. Herpes is classified as a TORCH infection - a potential trigger for the development of complications during pregnancy.
If a pregnant woman has never experienced symptoms of a herpes infection, she needs to be tested in advance to find out whether she has antibodies in her body that will protect her and the fetus from infection. A virus that enters the body for the first time during pregnancy is very dangerous and fraught with complications.
If the necessary antibodies are present in the body, a woman should still avoid re-infection: carefully observe personal hygiene, maintain the functioning of the immune system through a healthy lifestyle.
After childbirth, in the first years of life, you need to protect the baby from contact with carriers of the virus, and do not allow everyone to kiss the baby. You cannot feed him from your spoon or play with other people's toys. Infection with herpes will happen one day, but the stronger the child’s own immunity by that time, the lower the risk of complications and the development of pronounced symptoms of the disease.
If a young mother discovers that she has symptoms of herpes, she must observe quarantine so as not to harm her baby.
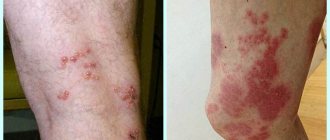
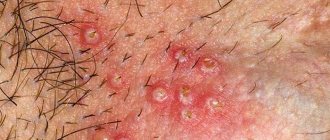
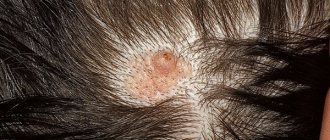
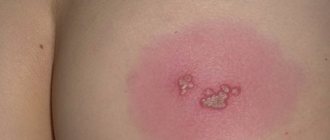
Types, stages and symptoms of the disease
The herpes simplex virus causes various types of lesions in children. The forms of the disease and their symptoms differ in children of different ages. They depend, among other things, on the state of immunity.
In infants and children 2 years of age (sometimes at an older age - at 7 years of age) a primary herpetic infection develops. It may be asymptomatic or have “vague” signs, reminiscent of an episode of pharyngitis or other infectious lesions of the upper respiratory tract. In this case, herpes on the lips of a baby may be the only sign of infection. Only a third of children of this age have acute herpetic stomatitis, accompanied by blistering rashes on the inside of the lips, in the cheeks, soft palate, and less often on the tongue and gums. The severity and duration of the disturbance in the general condition, the prevalence of local changes in the mouth and on the skin determine the mild, moderate or severe form of this disease.
Light form
A characteristic symptom is a relatively small number of lesions (3-5), located mainly in the mouth, very rarely on the lips. The temperature does not rise above 37.5°C, the general condition suffers little or remains unchanged. Bubbles in this form of the disease appear once on days 2-3 and burst almost immediately, leaving erosions that begin to heal on days 4-5. Symptoms of a mild form of infection last 5-7 days.
Medium form
The moderate course of herpes begins with a disturbance in the general condition, which is manifested by the child’s anxiety, loss of appetite, lethargy, moodiness, and signs of sore throat (redness of the throat, crying after swallowing food). On the 2-3rd day of the disease, general symptoms increase: the temperature rises to 38-39 ° C, chills, nausea, headache appear, lethargy and fatigue increase. At the peak of the temperature in the mouth - on the lips and cheeks - multiple erosions form (the bubbles burst immediately after they appear). Up to 25 damaging elements. Saliva is viscous, gums are inflamed. After the rash appears, the body temperature drops.
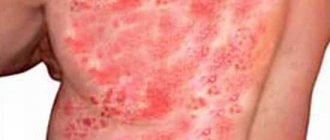
In moderate forms of the disease, the rashes recur and can merge into large erosive areas that are painful and sometimes bleed on contact.
Severe form
This form of herpes is quite rare among all cases of primary herpetic infection, since it is caused by severe immunity disorders. What herpes looks like in severe form depends on the degree of suppression of the body’s immune forces.
The main symptoms of a severe form of the disease are a sharp disturbance in the general condition of the child. The body temperature rises in waves to 40°C: it increases from 38-38.5°C to 40°C and higher, and with the appearance of rashes it decreases, after which it slowly increases again and decreases when a new “portion” of bubbles appears. Such fluctuations can last for quite a long time, which exhausts the baby. His face takes on a mournful expression, his eyes are sunken, his lips are dry, and he has no appetite.
Herpes in a child is often more severe than in an adult and can cause serious consequences. Complications of herpes in children can include serious damage to the nervous system and various disturbances in the functions of internal organs.
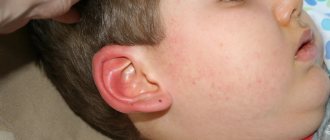
The oral mucosa is inflamed, swollen, erosions can number up to 100 or more. Bubbles are located on the lips, eyelids, and earlobes. When the lesions merge, huge erosive surfaces are formed, which quickly acquire an ulcerative-necrotic character due to the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. There is a strong putrid odor from the mouth.
Relapses after a severe form are characterized by a smaller number of lesions on the lips, cheeks, palate, their smaller size and the preservation of a relatively satisfactory general condition.
Features of treatment
In most cases, the herpes virus in newborns is severe, so hospitalization in a hospital is required, where the little patient will be provided with round-the-clock medical supervision. In mild cases, herpes can be treated at home, but all prescriptions must be made by a doctor. Self-medication and the use of traditional medicine methods are not allowed.
To combat the virus, Acyclovir is used, which is administered intravenously through a drip. If the patient is older than 3 months, therapy is supplemented with the use of an ointment with the same name applied directly to the rash.
Treatment of rashes requires the use of local antiseptics (Miramistin), wound healing drugs: Fukortsin, brilliant green.
The remaining drugs are prescribed for symptomatic therapy if indicated:
- For fever: Ibuprofen or paracetamol, tablets, rectal suppositories.
- For itching - antihistamines: Suprastin.
- For convulsions - anticonvulsants.
Typically therapy takes 3 months. The onset of recovery can be accelerated if you provide the patient with peace, ventilate the room, and maintain the room temperature at 20 degrees.
Important! After recovery, you need to reschedule vaccinations to a later date until the body has fully recovered.
Complications and relapses
Of all the possible complications of herpes, the most severe can be considered the development of herpetic encephalitis, meningoencephalitis and the transition of the disease to a generalized form with developed viremia. Viremia is high concentrations of the virus in the blood, affecting all or most organs. In an organism with an adequate state of the immune system, herpes infection has a mild course with relapses of varying frequency and lasts 10-14 days without treatment. It ends with suppression of viral replication and recovery. In a baby, especially one year old or less, and with immunodeficiency conditions, viral reproduction continues for more than 2 weeks, causing severe conditions.
The frequency of relapses of herpes in a child, as well as the development of complications, is determined by the state of the immune system and the activity of the virus itself. HSV activity can change under the influence of various drugs, against the background of stress, acute and chronic diseases, malnutrition, and dehydration.
Symptoms of herpes in children
The disease begins with a minor malaise, since any infection that enters the baby’s body causes a weakening of the immune system and a decrease in well-being. For a child over 1 year old, the most common type is herpes of the first three types. However, the sixth type is also often found.
The main symptoms of any herpes are:
- fatigue;
- fever;
- nervousness and irritability;
- poor appetite;
- burning and itching at the site of future ulcers and spots;
- body redness;
- sometimes nausea and vomiting.
From the very first minutes of damage to the body, you can notice a slight tingling (for the first types) and redness of certain areas of the body (if infected with type 6). Because of this, experienced patients often successfully attempt to block the effect of the infection through the use of active medications.
It is possible to determine the presence of the virus in a child through a blood test, since this is where a significant part of the bacteria is localized. To determine the degree of infection of the body, a general analysis is performed, which can be done in any children's department.
Diagnostics
In order to detect and clarify what type of herpes virus on the lip, the following is carried out:
- laboratory examination of smears from lesions - immunofluorescence analysis;
- PCR - polymerase chain reaction, which has a sensitivity of 90%, can detect even 1 molecule of viral DNA;
- sowing the material collected from the lesion elements onto chicken embryos;
- direct fluorescence analysis method.
Based on the data obtained and the results of a clinical study, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe rational treatment for the disease.
Consequences
Herpes in newborns can cause severe damage to internal organs, and multiple organ failure is fatal.
The most common targets for the virus are:
- Heart.
- Hematopoietic system.
- Liver.
- Vision.
- Hearing.
With genital herpes, the bladder and ureters are usually the first to be affected.
Life-threatening consequences can be prevented by starting treatment in a timely manner. Despite the fact that the herpes virus is extremely common, it can be dangerous for people whose defense system is not able to cope with the infection due to the presence of diseases, the use of cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids, and age.
How and how to treat herpes on the lips in children of different ages
Treatment of herpes on the lips in children should begin immediately after diagnosis, especially in premature infants, newborns, infants and patients with immune pathologies.
The drug of choice is Acyclovir. For newborns and premature infants, the drug is administered intravenously for any severity of infection, 3 injections per day with an interval of 8 hours. Duration of therapy is 14-21 days. Further, oral administration in tablets is recommended, in the same dosages, for 10 days. This approach makes it possible to relatively quickly cure mild herpes and relieve the severity of symptoms in severe cases.
How to cure herpes in children who have only local manifestations depends on the prevalence of the symptoms. Single rashes are lubricated with Zovirax, Viralex, Tebrofen ointment, Florenal. For multiple rashes, intravenous or oral administration is added.
Today, therapy for herpes infections is diverse. It includes a large number of different drugs and medications.
You can treat herpes on the lips at home using antiviral ointments and taking tablets based on acyclovir, Viralex, Zovirax. It is advisable to carry out home treatment only after consultation with a doctor and in case of a mild or moderate form of the disease.
Reasons for appearance
The baby develops a disease for the following reasons:
- Infection of a child. Occurs in everyday situations through contact and airborne droplets. The virus makes itself known only when immunity decreases.
- Lack of vitamins . If a child’s body lacks vitamins, the immune system is weakened, and the likelihood of illness is high.
- Hypothermia , colds. They weaken the child’s body, making it vulnerable to herpes.
- Protracted allergic reaction. If allergy symptoms do not go away for a long time, it is quite possible that this disease will appear.
- Stress . Being in stressful situations makes the baby's body weak; for this reason, herpes occurs quite often.
How to treat gingivitis in children? Find out about this from our article.
Features of nutrition during illness
Caring parents are always looking for what else to do to alleviate the baby’s general condition and local symptoms. Adequate nutrition during the period of the height and resolution of the disease brings invaluable benefits. If a child has herpes, the following should be excluded from the diet:
- Arginine-rich foods - legumes, nuts, chocolate, peanuts;
- sugar and salt;
- carbonated drinks;
- fat meat.
Inclusion in the diet has a positive effect on the patient’s condition:
- vegetables and fruits;
- lean meat;
- seafood;
- dairy products;
- greenery;
- eggs
With moderate and severe forms of herpes, dehydration often develops, so it is imperative to increase the amount of fluid consumed.
Prevention of further relapses
The high dependence of the frequency of herpes relapses on the state of immunity makes the correction and maintenance of the latter the primary objectives of prevention. For this purpose, the drugs Bonafton and Dekaris (allowed at 1 year of age and above) are successfully used to help reduce the frequency of relapses and reduce their intensity. For any form of infection, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes, provide adequate nutrition, and reduce emotional and physical stress (especially in schoolchildren). From the age of 4 years of age, the use of a helium-neon laser is allowed for herpes.
Folk remedies for the treatment of herpes
Along with traditional methods of treatment against herpes, there are many folk recipes. Their use has no special contraindications. However, such techniques are categorically not recommended for treating children under 1 year of age, as they can cause the development of allergies.
The most popular means are recognized:
- fir oil – helps eliminate unpleasant itching and flaking. Initially, after using the product, painful sensations on the wounds may increase, but they quickly pass;
- Earwax allows you to dry and heal ulcers and wounds in a short time. This folk remedy should be applied to a previously cleaned damaged area every 3-4 hours;
- alcohol compresses are considered the most painful way to treat herpes, and are suitable for both the first and sixth types of the disease;
- table salt promotes the speedy healing of wounds