Quite often, women are diagnosed with genital herpes during pregnancy. This is a viral disease that can provoke the development of defects in the fetus. According to statistics, in 75% of all cases, genital herpes in a pregnant woman does not manifest itself in any way. The asymptomatic course of the disease becomes the cause of infection of the newborn with this virus. If such a pathology is diagnosed during pregnancy, the mother must undergo comprehensive treatment.
Causes
Genital herpes during gestation occurs due to the herpes simplex virus, which belongs to the second type. From infection to the moment of primary manifestations of infection, as a rule, 2-12 days pass. The conductor for the pathogen is the skin of the genitals, mucous tissues of the urinary system, and genitals. Once the goal is achieved, the infectious agent is sent to the blood, lymph nodes, and nerve cells.
Primary infection
Many people are mistaken in believing that primary infection and relapse of genital herpes are the same thing. These are completely different concepts. The first infection means that the pregnant woman’s body has not yet developed antibodies to the virus, that is, this is the first time she has encountered it.
Relapse means that antibodies to the pathogen already exist in the blood. A short conclusion suggests itself here: becoming infected for the first time is much more dangerous than reactivating the virus.
The causes of the first infection are:
- sexual contact with a sick person;
- contact with biological material of an infected person;
- kisses;
- aerogenic route, that is, the spread of infection with droplets of sputum belonging to an infected person (coughing, sneezing).
Recurrence of herpes
After penetrating nerve cells, the virus remains there and goes into latency, that is, into a sleeping state. As soon as factors favorable for its awakening appear, it is activated. The main causes of herpes are:
- weakened immunity caused by pregnancy itself;
- hypothermia;
- stress, emotional lability;
- lack of sleep, poor sleep;
- improper and irrational nutrition;
- chronic diseases.
The intensity of manifestations directly depends on the activity of the immune system. If the body's defense produces a large number of immunoglobulins - antibodies to the virus, then the likelihood of symptoms occurring is low.
The initial detection of the disease can occur during pregnancy. This is why tests to detect infection are so important.
It is worth noting that relapses of genital herpes during pregnancy are less dangerous than infection for the first time. If the restoration of the viability of the virus occurred even before conception, then the body has already managed to produce specific globulins. This means that the baby will be protected by the immunity of the expectant mother and the probability of transmission of infection in this case is small - only 0.02%.
What provokes an exacerbation of pathology during gestation?
If there are rashes in the intimate area during pregnancy, this may indicate activation of the herpes simplex virus type 2. Infection with this infection occurs through contact. Most often, the virus is transmitted through sexual intercourse. However, using a condom does not guarantee protection against the disease. This is due to the presence of rashes. If the mucous membrane of the genital organs comes into contact with erosions on the body of a sick person, then infection occurs with a 99% probability.
Once the herpes simplex virus type 2 enters the body, it is impossible to completely get rid of it. With the help of medications, symptoms are removed and the concentration of pathogens in the blood and other biological fluids is reduced. Thus, the virus goes into a latent form.
Recurrent genital herpes is often observed in women who bear children. It is not as dangerous as the primary one, but it brings a lot of unpleasant symptoms. Exacerbation is possible due to the following negative factors:
- exposure to stress and emotional turmoil;
- weakening of the body due to concomitant infectious diseases;
- presence of human papillomavirus;
- weakened immunity;
- lack of proper rest;
- unbalanced diet;
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- contact with a person who has an acute form of the virus.
During sexual contact with a carrier of the virus in acute form, a pregnant woman may experience a relapse. A large amount of pathogenic microflora enters the mucous membrane of the external and internal genital organs, which begins to actively multiply. To restore normal acidity levels and reduce the concentration of the virus, drug therapy is used.
Symptoms
Herpes in the intimate area during pregnancy leads to various symptoms. Their intensity will depend on the degree of functioning of the protective function. In addition, when the woman was infected with the virus will play a key role.
General symptoms
One of the obvious symptoms indicating the development of vaginal herpes is the appearance of a rash in the area of the external genitalia. Their occurrence may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the head, muscles, lymph nodes in the groin area;
- malaise;
- weakness;
- vaginal discharge;
- burning, tingling sensation in the affected areas;
- frequent urination.
Often a pregnant woman loses her appetite and sleep becomes interrupted.
External manifestations
The manifestations of vaginal herpes during pregnancy depend on the time at which the infection occurred.
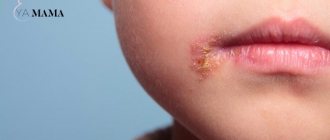
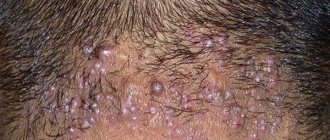
If this is a primary infection, then the pimples will appear in the form of vesicles or small nodules. They can group. Their appearance causes severe itching, burning and tingling, pain in the perineum when urinating.
The rash usually goes away within 6-13 days. On days 2-4, the blisters burst, forming ulcerated areas, which subsequently become covered with crusts. Then they fall off, and in their place there are pigment spots that disappear after a few days.
The maximum severity of symptoms is observed in the first 2-3 days. The discharge of mucus from the vagina bothers the woman for about 5 days. Within a week, if no secondary infection has occurred, the symptoms disappear without a trace.
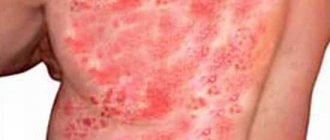
When herpes recurs, the same symptoms are observed, only they are less pronounced than when infected for the first time. Periods of exacerbation occur on average once every 3 years. Herpes is localized on the labia during pregnancy, mucous tissues of the urinary and reproductive systems (causing urethritis, adnexitis, colpitis, etc.).
If the disease lasts for years with regular exacerbations, then the woman experiences pigmentation of the mucous membranes and skin in the affected areas.
With frequent relapses of genital herpes during pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen, perineum, sacral region, severe burning, itching at the site of the inflammatory focus, neuroses, and irritability may be observed. The disease recurs most often in the 1st and 3rd trimesters.
Herpes in the intimate area: symptoms and prevention
The first symptoms of herpes simplex type 2 may appear as a cold.
The woman experiences symptoms such as:
- Aches all over the body,
- Slight increase in temperature (up to 38 degrees),
- Headache,
- Nausea,
- Lack of appetite,
- Increased fatigue
- Insomnia,
- Bad mood.
Diagnostics
If a woman complains that there is severe itching, burning and pain in the perineum, then the doctor will suspect genital herpes first. The doctor will conduct an external examination and take a scraping from the cervical canal. In some cases, tests for other sexually transmitted infections may be prescribed.
Clinical tests for the presence of herpes virus in the blood of a pregnant woman are mandatory, since in most cases the infection can be asymptomatic. To identify it, the following tests are prescribed:
- Culture method. It consists in taking liquid from the bubbles that appear using a syringe. Biological material is implanted onto a growing chicken embryo. If he dies, then in this case they talk about genital herpes during pregnancy;
- PCR. The material is collected using a brush. The pathogen can be detected only during the period of exacerbation of the infection. Diagnostics determines the type of infectious agent;
- ELISA. This requires taking blood from a vein. It is carried out on an empty stomach. An analysis is done to detect antibodies - immunoglobulins to the virus (Ig G and Ig M). If a primary infection occurs, the analysis shows the presence of Ig M, and if the infection recurs - Ig G.
Unfortunately, today there is no study that could confirm or refute the diagnosis of “genital herpes during pregnancy” with 100% certainty. It happens that tests do not provide the final result.
Methods of diagnosis and therapy for pregnant women
A herpes infection should be treated immediately after it is diagnosed. Identifying this disease today is not particularly difficult. The first thing that indicates a virus is the clinical picture. If tiny blisters filled with liquid appear in the area of the labia minora and majora, then most likely this is herpes. These blisters later burst, leaving behind open wounds. Then crusts form at the site of the rash. This is all accompanied by itching, burning and purulent discharge from the vagina.
To confirm herpes, PCR diagnostics are performed. In some cases, a woman must be tested to detect antibodies and immunoglobulins. If these substances are few or absent at all, then primary herpes is diagnosed. It is incredibly dangerous for a child. If the level of antibodies is high, then we are talking about a latent infection or an exacerbation of the virus.
An intravenous drip for a pregnant woman is prescribed in the second trimester.
In pregnant women, treatment is carried out depending on the trimester. This is necessary in order not to harm the child. In the first trimester, antiviral therapy is mandatory. This allows you to reduce the level of herpes infection in the blood. In addition, a woman should take immunoglobulins and drugs that strengthen the immune system. Sometimes IVs are prescribed to cleanse the blood. The rashes should be lubricated with brilliant green or any other drying antiseptic.
In the second trimester, intravenous drip antiviral therapy is prescribed. Immunoglobulin is necessary so that the baby’s body can resist the virus. Sometimes Viferon-1 rectal suppositories and Acyclovir cream are used. After 4 weeks, a repeat PCR diagnosis is carried out. The further treatment plan will depend on the results of the clinical trial. If PCR diagnostics showed that the virus is still active and can harm the fetus, then during the entire 3rd trimester until birth, the same therapeutic course is carried out as in the second trimester.
Women who have type 2 herpes are recommended to have a cesarean section. Natural childbirth is possible only if the level of pathogenic cells in the body is minimal and there are no rashes in the birth canal area. Otherwise, even a healthy child can become infected while passing through the vagina.
Tweet
Pin It
Tags:Pregnancy, Intimate herpes
- Does herpes occur on the palms?
- Shingles in men and women: consequences
- How to treat herpes on the face of a child
- Effective treatment of herpes zoster with folk remedies
How to treat genital herpes during pregnancy
Genital herpes in pregnant women is treated only under the strict supervision of a doctor, since many drugs are prohibited for use during this period.
Medicines for oral administration
Genital herpes in early pregnancy cannot be treated with systemic medications - only with local ointments, gels and solutions.
Starting from 12-13 (2nd trimester) weeks, tablets containing acyclovir and interferons in the form of rectal suppositories are prescribed - “Viferon”, “Cycloferon”, “Genferon”. Recurrent infection before childbirth is treated with immunomodulators. Acyclovir is prescribed during this period in extreme cases.
Local therapy
Treatment with local agents can be carried out in early and late pregnancy. Ointments with a healing, anti-inflammatory, drying effect, as well as antiseptic medications are prescribed:
- Furacilin solution.
- "Miramistin".
- "Chlorhexidine."
- Decoction of oak bark, chamomile.
- Hydrogen peroxide.
These drugs are allowed in the first trimester. Starting from the second, it is recommended to use:
- "Virolek."
- "Panavir".
- "Zovirax".
- "Levomekol".
- "Bepanten."
- Calendula extract.
- "Solcoseryl".
- Oil of fir, rosehip, sea buckthorn.
The following are used as drying agents:
- Zelenka.
- Baby powder.
- Zinc paste.
- "Fukortsin".
- Methylene blue.
Vitamin complexes and nutritional supplements (“Tratsmel-S”, “Engistol”) are also prescribed.
What causes relapses?
Excessive loads can cause whitening.
The following factors can provoke recurrent vaginal herpes:
- Exhaustion of the body due to physical activity. Sometimes it happens that conception has already occurred, but the expectant mother still does not know about it and continues to exhaust herself with physical labor. The body is gradually depleted, the immune system weakens and the herpes infection recurs.
- Various complications of pregnancy: polyhydramnios, unplanned birth, toxicosis in the first weeks of pregnancy.
- Ultraviolet radiation. Visiting a solarium and prolonged exposure to sunlight affect the activation of the virus even after treatment.
In addition, recurrence of genital herpes during pregnancy is sometimes caused by the use of certain medications.
Why is genital herpes dangerous during pregnancy?
Despite the fact that the baby has antibodies to the virus transmitted from the mother, no one can give one hundred percent guarantees that it will not affect its development in any way. This is why doctors are very wary of herpes. It is worth noting that the infection can recur with different frequencies. If exacerbation occurs rarely, it is unlikely to cause any harm to the child. If relapses occur more than 3-4 times throughout pregnancy, the risk of fetal infection increases by almost 50%. In addition, the manifestation of genital herpes during pregnancy on the mucous tissues of the genitourinary and reproductive systems is considered dangerous.
If the infection occurs with only a slight sensation of pain and small areas of rash, then the child will not be affected. Antibodies in this case work harmoniously and are sufficient to resist the virus.
Consequences for the fetus
The most dangerous thing for the fetus is primary infection with the herpes virus. Serious complications are usually observed in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. Let's consider what the virus can mean for a child in the early stages and after conception:
- severe developmental defects;
- stop in development;
- fetal freezing;
- miscarriage;
- anembryony (absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg).
Consequences of infection in the second trimester of pregnancy:
- intrauterine infection - as a result, diseases of the brain, lungs, and liver can develop;
- death in the first days of a child’s life.
Dangers in the third trimester:
- with primary infection - 1 month before birth - the child can be infected in 50% of cases, with relapses - in 0.2% of cases;
- premature birth.
As a result of infection, the likelihood of a child being born disabled, with cerebral palsy syndrome, deafness, blindness, etc. increases. If the infection affects the child’s nervous system, then the risk of death increases to 50%.
How dangerous is the virus for pregnant women?
With frequent reactivation, genital herpes becomes the cause of hormonal imbalances and blood poisoning in a pregnant woman. In addition, the infection can become a source of constant itching (here the likelihood of secondary infection increases, that is, the addition of a bacterial infection), cervical erosion, cancer of the genital organs, and the spread of infection to internal organs.
How is pathology transmitted?
Genital herpes is a common disease. In general, the virus can lead to damage to any skin and mucous membranes.
In the absence of timely treatment, genital herpes can spread to other organs, in advanced cases, disrupting their functionality.
The provocateur of the pathology can be a virus of the second and first types. Both infections belong to a large group of herpes viruses.
The pathogens are extremely viable and this allows them to remain active on open surfaces for a long time.
In medicine, there are two types of herpes - recurrent and primary. In case of relapse, the clinical picture may be blurred or completely absent.
At this moment, a person is often unaware of the presence of the disease and unintentionally infects his sexual partner.
Primary infection is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture; the rash appears several days after infection.
Genital herpes occurs in 85% of cases as a result of sexual contact with an infected individual. But we cannot exclude the possibility of the disease manifesting itself in people who are not sexually active.
Among the main methods of infection are the following:
- Household . Using a towel or soap that has been used by an infected person.
- Sexual intercourse . You can get the herpes simplex virus from any type of sex, including oral sex.
- Perinatal . The disease can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth or in utero.
- Inoculation . The patient, due to personal inattention, transfers the manifestations of the disease from one part of the body to another.
The incubation period can last from several days to several months.
This moment has the opportunity to play a cruel joke, because herpes can appear in an intimate place in a pregnant woman immediately before childbirth. Then the only option is a caesarean section.
Attention ! As immunity decreases, the risk of relapse of the disease increases. This is why it is important to pay special attention to strengthening the immune system.
If herpes occurs during pregnancy, you should immediately consult a specialist. Only correct and timely treatment can be the key to successful recovery and reducing the risk of infection in the baby.
Prevention
Since the infection in women carrying a child occurs due to weakened immune functions, the prevention of herpes consists of strengthening them. If you follow the following recommendations, then relapse, as well as primary infection with the disease, can be avoided.
- If a partner is diagnosed with genital herpes, then during treatment you should avoid intimacy and any tactile contact with him.
- You must not touch, let alone use, personal hygiene items belonging to an infected person.
- Avoid hypothermia, overheating, dress appropriately for the weather.
- Eat properly and rationally, take vitamin complexes.
- Walk more, get enough sleep, worry less.
Genital herpes in girls carrying a child can affect the course of pregnancy, childbirth, the physical and intellectual development of the child, and in rare cases is even an indication for termination of pregnancy. However, if you start treatment on time and monitor the maintenance of immunity, complications can be avoided.
Dreadful complications of a simple virus
Herpes is considered a dangerous viral pathology of pregnant women, especially when it comes to the sexual manifestation of the infection. Most often, the virus affects the outcome of pregnancy by causing:
- frozen pregnancy;
- early spontaneous abortion;
- premature birth in the second half of pregnancy;
- stillbirth.
A complication of genital herpes, which threatens not only the fetus, but also the mother, is considered to be a frozen pregnancy. This pathology occurs in the first trimester: against the background of successful fertilization, the embryo does not develop, only the amniotic membranes develop.
The woman feels good and does not suspect a serious problem in her body. The decay products of the embryo cause general intoxication of the body, which can lead to sepsis and death of the mother herself.
Treatment of the virus with local folk remedies
Vaginal herpes cannot be cured, experts warn about this. But even traditional medicine can significantly reduce the risk of frequent relapses and speed up the recovery process. For women expecting a child, local lotions and compresses are considered the safest folk remedies.
A few drops of geranium, lavender or eucalyptus essential oil are diluted in a glass of warm water. A napkin soaked in the solution is applied to the rash on the labia and held for several minutes, moistening the napkin from time to time.
Pain and burning on the labia caused by herpes rashes can be relieved with cold compresses. A sterile napkin is moistened in very cooled boiled water and applied to the sore spot.
Places where rashes are localized on the labia, thighs, and anus are lubricated with oxolinic ointment several times a day. You can also make compresses with ointment applied to a small piece of gauze.
More: How to treat genital herpes during pregnancy
Treatment of genital herpes with local folk methods during pregnancy must be agreed with the doctor observing the pregnant woman. It is impossible to independently understand the possible risk to the fetus from such treatment, so it can harm the baby.
Drug antiviral therapy
The treatment regimen for herpes virus during pregnancy is based on the following therapeutic goals:
- weakening of symptoms, shortening the period of virus activation;
- accelerating the process of restoration of damaged tissues;
- reduction of viral secretions on the labia;
- minimizing the number of disease relapses.
The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the timing of the start of therapy: the earlier the antiviral attack on herpes begins, the greater the chance of a successful pregnancy outcome and the absence of complications.
Antiviral therapy is considered the main method of treating herpesvirus infection in pregnant women.
In severe cases of the disease and deep damage to the genital organs by rashes, including rashes on the inner labia, doctors prescribe acyclovir and its derivatives internally:
- Acyclovir tablets - 200 mg three times daily for 5 days (for frequent and extensive rashes);
- for any lesions - ointments based on acyclovir, they are applied to the affected area on the labia and nearby tissues every three hours;
- treatment with antibacterial and analgesic ointments.
Consequences in the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester, herpetic rashes can often bother a woman due to the increasing load on the immune system. The middle of pregnancy or the 2nd trimester is characterized by fully formed systems, but developing organs, so the penetration of virions into fetal tissues can have a negative impact on the organs, leading to developmental abnormalities.
The following possible outcomes of infection in the second trimester:
- stillbirth when the fetus is infected at the beginning of the 2nd trimester or when the mother’s body is severely weakened;
- damage to nerve tissue and brain - microcephaly, hydrocephalus;
- damage to the hearing organ in the form of deafness;
- blindness;
- atresia of the rectum, esophagus, vagina in girls.
If developmental anomalies are detected, a pregnant woman has the right to either keep the child or agree to an artificial birth from 23 weeks, or to an abortion until 22 weeks.
Important!
Frequent exacerbations of the genital type of infection during pregnancy lead to intrauterine infection in 2-25% of cases.
Viral threat to the baby
No less serious are the consequences of the penetration of herpes infection through placental tissue to the fetus. Herpes causes serious complications in a fragile small body:
- malformations of the fetal cardiovascular system;
- delayed physical development;
- prolonged jaundice;
- damage to the central nervous system of the fetus;
- loss of vision, hearing;
- hydrocephalic syndrome;
- epileptic syndrome;
- internal and external bleeding in a newborn.
Experts note that the likelihood of infection of the fetus, fortunately, is low, especially if the mother follows all the recommendations of the gynecologist observing her.