Reasons for the development of the disease
There are eczemas for which the cause has never been established, which is why they are called unstudied. But scientists identify the most common factors influencing the development of the disease in pregnant women:
- In the first trimester, immunity decreases. This is due to the fact that the woman’s body seeks to protect the unborn child from harmful factors.
- Allergic reaction to food, medicine, plants or household chemicals.
- Constant stress.
Increased sweating.- Heredity.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and thyroid gland.
- A rare cause is weather change. There is a certain group of people who cannot tolerate high humidity.
- People with asthma, conjunctivitis, rhinitis and other chronic diseases are predisposed to the disease.
- There is a possibility of passing on a tendency to eczema to your child during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Causes of eczema in pregnant women
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a skin inflammation of a neuro-allergic nature. If earlier the disease was more typical for childhood, now it has “matured”.
Due to unfavorable environmental conditions, increased air and water pollution, its cases among adults are inexorably increasing.
Eczema during pregnancy gives the patient a lot of unpleasant sensations and worries. Why does the skin begin to react this way? Is this somehow connected with the special position of women? The answer to the last question is definitely yes.
To date, it has not yet been precisely established why various types of dermatitis appear on the human body. This also applies to eczema. However, it is known that such phenomena are directly related to the immune system.
Human immunity is divided into two types:
- Cellular – dominates and triggers the mechanism of antibody production.
- Humoral - destroys everything foreign that enters the body.
During pregnancy, there is a disruption in the balance of these two immunities, which ultimately ends in the following: skin cells become hypersensitive to both external factors and what is happening inside the body.
What factors can cause the development of eczema during pregnancy? The fact is that in the first trimester, a woman’s immunity begins to decline.
This happens in order to protect the baby from aggression from the body. However, for the mother this is fraught with various ailments.
A weakened body begins to contract various diseases, chronic diseases worsen.
Symptoms
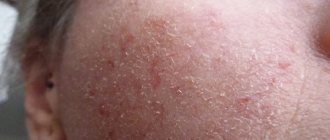
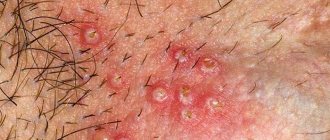
Eczema during pregnancy can form on any part of the body. Experts divide the disease into the arms, legs, face, and so on. You should contact a dermatologist if the following symptoms occur:
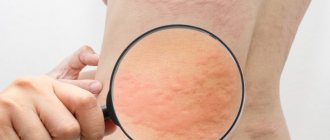
- Itching of the skin.
- Red rash.
Skin is dry and cracked.
- Purple spots that constantly get wet.
- Swelling of the limbs, body and face.
- The appearance of blisters.
- Skin irritation.
- Constant burning sensation in the affected area.
- Redness of the scalp and face.
The most common form of eczema is atopic dermatitis, which is localized in the skin folds and patients report severe itching and flaking of the skin.
It is forbidden to scratch the rash, as this can cause infection in the wound.
Possible complications and prevention
Eczema is not life-threatening, but if the itching is severe, there is a risk of ulcers forming, which can become infected by a bacterial infection. Deep damage to the skin threatens blood poisoning and disruption of internal organs. The condition is dangerous due to termination of pregnancy, and in severe cases can be fatal.
Complications can be prevented with proper, timely treatment. In the future, it is necessary to follow special rules so as not to cause a new relapse of the disease:
- eat well, rest;
- use high-quality detergents (shower gel, soap, shampoo);
- do not wear synthetics;
- adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
- avoid stress and physical overload.
Remember, eliminating the allergen and provoking factor is the main condition for a quick recovery.
Eczema is a consequence of poor diet, lifestyle, and frequent stress. If you have a predisposition to the disease, try to protect yourself from problems during pregnancy, give preference to wholesome, healthy food, walk more, relax, enjoy the new state of mind and body. Remember that now you have reduced immunity, there is a dangerous period for various exacerbations. Any factor can influence health. Elena Malysheva advises not to delay treatment of eczema in pregnant women, but to choose safe, effective remedies and not to self-medicate.
>
Effect on the fetus
Eczema does not affect the development and health of the baby because it does not penetrate the placenta. The disease only causes discomfort to the expectant mother.
It is this factor that influences the course of pregnancy, because the woman becomes irritable, and even the calmest nervous system malfunctions.
Naturally, the stressful state of a pregnant woman negatively affects the fetus, so you should immediately make an appointment with a dermatologist. It is the specialist who will select treatment that does not affect the child’s development.
The use of hormonal drugs during gestation
Eczema does not have a direct effect on the fetus. It is also not a problem to get pregnant. The main negative effect on a pregnant woman’s body is a feeling of constant itching, which can cause insomnia. A mother's nervousness can harm the health of her unborn baby.
During pregnancy, not all medications prescribed for eczema are allowed. If dermatosis does not go away, you should first analyze whether allergenic foods are present in your daily diet. However, having excluded them, you need to make sure that the woman’s diet is still varied and balanced. A poor diet can also negatively affect the health of the unborn child.
Drug therapy is prepared according to an individual regimen for each patient. During the treatment of dermatosis, complexity is important, therefore, along with medications to eliminate external symptoms on the skin, the attending physician will prescribe the pregnant woman an examination with other highly specialized specialists in order to determine the cause of the disease.
For example, an otolaryngologist will confirm with his conclusion the absence of chronic infections in the ENT system, a gastroenterologist will exclude the possibility of developing chronic pathologies of the abdominal cavity, the gastrointestinal tract, a urologist and a gynecologist will examine the urinary system of the expectant mother. If it is necessary to use potent drugs, a patient with eczema is hospitalized, and therapy is carried out according to indications under the supervision of medical personnel.
To achieve a quick therapeutic effect, patients with eczema are prescribed corticosteroids, not only for local, but also for general effects on the body. During the gestation period, tableted hormones are not used under any circumstances, since these drugs can negatively affect the condition of the fetus.
When including corticosteroids in the list of drug prescriptions, the doctor must take into account several key points:
- specificity of drug metabolism;
- permeability of drugs through the placenta;
- trimester of pregnancy.
Experts can recommend certain hormonal ointments for pregnant women only on an individual basis, and only if external therapy with safe medications does not produce the expected result.
Among the steroid ointments for expectant mothers, the following should be noted:
- Lokoid;
- Afloderm;
- Flucinar.
Treatment of eczema during pregnancy is prescribed by a specialist.
The disease itself is not dangerous and cannot be transmitted to the fetus. However, the symptoms inherent in eczema can greatly worsen the physical and emotional state of the mother. Due to the incessant itching, the expectant mother becomes irritable, sleep disturbances and loss of appetite may occur.
Eczema can be one of the signs of an inflammatory process in a woman’s body, which can negatively affect the fetus. Therefore, it is extremely important to timely determine the true cause of the disease and begin treatment.
If you were diagnosed with eczema during pregnancy?
When the disease is confirmed, in addition to drug treatment, pregnant women need to pay attention to their lifestyle. The following rules will apply to the period and after childbirth, when breastfeeding:
- Underwear and clothing in contact with the body should be made from natural fabrics.
- Take frequent walks in the fresh air and ventilate the room at least 3 times a day.
- The house must be wet cleaned daily.
Minimize contact with pets.
- Buy household chemicals on a natural basis; they should be marked as hypoallergenic.
- Clean and wash dishes only with rubber gloves.
- Do not eat foods that may cause allergies.
- Deal with stress - get proper rest and sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Do not stay in direct sunlight for a long time.
- Follow all instructions prescribed by your doctor.
Physiological characteristics of the female body
To effectively combat skin diseases, modern medicine offers a huge number of different medications that can be used both externally and internally.
In the vast majority of cases, the following medications are used to treat eczema:
- Antihistamines.
- Diuretics.
- Tranquilizers.
- Sedatives.
- Calcium preparations, ascorbic acid.
But since most of the above medications are prohibited during pregnancy, the treatment tactics for eczema are determined individually. Most often, to eliminate rashes, itching and burning in pregnant women, topical medications are used - ointments, creams, lotions, solutions.
Zinc ointment should be applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin of the face and body, leave the product to dry for 2.5-3 hours, then rinse off the remaining ointment with warm water. Zinc medicine should be applied 3-4 times a day.
Your doctor will tell you how to treat eczema during pregnancy. It is imperative to contact him, even if the disease manifested itself before the “interesting” situation, and the ways to combat it seem to be known. The thing is that many previously tested methods during pregnancy are unacceptable, so it is strongly not recommended to engage in amateur activities.
But you can and should change your lifestyle. First of all, this concerns diet. If it turns out that eczema is allergic in nature, potentially dangerous foods should be excluded from the diet:
- nuts;
- honey;
- chocolate;
- red and orange vegetables and fruits;
- products containing gluten;
- selected seafood (for example, shrimp).
In addition to diet, there are other requirements for the behavior of a pregnant woman with eczema. So, for example, she should:
- wear clothes and underwear made from natural materials (preferably loose-fitting);
- regularly ventilate the room and do wet cleaning;
- avoid contact with household chemicals (it is especially important to use detergents and cleaning products with rubber gloves if hand eczema is diagnosed during pregnancy);
- spend at least a few hours outdoors every day;
- avoid stress;
- use hypoallergenic powder for washing;
- limit exposure of ultraviolet radiation to affected areas of the body;
- sleep on hypoallergenic pillows (down excluded);
- keep diseased areas away from contact with cold and hot water.
If eczema occurs in pregnant women, treatment should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, who will conduct a full examination of the body and select the most effective, but safe and mildly acting medications.
First of all, you need to take care to eliminate as much as possible all external and internal irritating factors. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of nutrition - you should try to completely eliminate all foods that can provoke the development of an allergic reaction.
You also need to remember and follow several important rules:
- A pregnant woman is recommended to wear clothes and underwear only made from natural, breathable materials.
- All items of clothing should be washed only with special hypoallergenic washing powders.
- A mandatory rule is daily wet cleaning and systematic ventilation of the room.
- Expectant mothers need to pay special attention to the cosmetic and hygiene products they use, choosing only products with a hypoallergenic composition.
- Pregnant women should try to avoid direct contact with chemical and synthetic substances, as well as household chemicals.
When contacting household chemicals, you must use special protective rubber gloves that will protect the delicate skin of your hands from their aggressive effects.
Since the most common location of pathological rashes is the skin of the hands, it is worth paying attention to the advice of dermatologists on how to treat eczema. During pregnancy, in addition to the characteristic papular-vesicular rash and erosive areas, women may experience more pronounced swelling of the palms and fingers, and severe itching.
To treat dermatosis on the hands of expectant mothers, the following therapeutic complex can be used:
- Make lotions and baths based on chamomile or plantain infusions.
- For antibacterial external treatment, solutions of Furacilin, Resorcinol, and Ethacridine are usually used.
- It is advisable to lubricate wet hands with Fukortsin.
- Avoid exposing eczematous areas to direct sunlight.
- Do not come into contact with cold or too hot water.
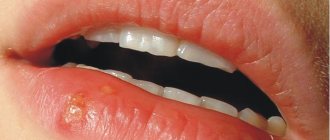
Eczema can also occur on the chest of a pregnant woman. This type of dermatosis is characterized by inflammation in the area of the areola and nipples, the epidermis acquires a crimson tint, and scales and crusts appear. During pregnancy, before childbirth and the onset of lactation, you can be treated with non-hormonal medications and moisturize the skin with natural oils. It is equally important to follow the basics of a hypoallergenic diet and eliminate external irritants from everyday life.
Eczema on the legs during pregnancy is most often a consequence of varicose veins. If there is insufficient blood circulation or venous expansion, expectant mothers are advised to wear elastic underwear and use external products that do not contain steroids. In any case, you should use ointment or cream for eczema during pregnancy only as prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment for eczema during pregnancy most often lasts less than two months.
In general, the prognosis for the recovery of the pregnant patient is positive. In rare cases, treatment lasts more than 2 months. If you follow all medical prescriptions, you will be able to get rid of the symptoms of the disease long before the long-awaited baby is born. But even if the manifestations of dermatosis partially persist after the birth of the baby, it will now be much easier to cope with the disease.
Features of eczema in an expectant mother:
- the disease worsens in the 1st and 2nd trimesters,
- Most often, eczema occurs on the arms in the area of the hands,
- a rare form of the disease may occur - nipple eczema,
- When treating pathology during pregnancy, doctors give preference to ointments and other local remedies.
From the first day of pregnancy, the female body begins the amazing process of creating a new life. He is the first to try to protect the growing fetus from aggressive influence from his defense system.
At the same time, all his forces are redirected to the unborn child to the detriment of his own interests.
Therefore, a woman in the first trimester experiences a significant decrease in the level of immunity and hormones. Having lost its usual position, the immune system, in order to restore its previous state, begins to actively react to various irritants - allergens.
As a result of this titanic work, biologically active substances begin to intensively enter the blood in excess quantities, which along the way suppress not only other people’s cells, but also their own.
As a result of this process, eczema begins to develop in certain areas of the woman’s skin.
Treatment
Only a dermatologist should treat eczema during pregnancy and lactation.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, as many drugs can harm the child’s health.
Before prescribing treatment, a specialist must identify the cause of the disease. In most cases, pathology develops after errors in diet or bodily contact with allergens.
Pregnant women should avoid the following foods:
Citrus.
- Eggs.
- Meat.
- Seafood (shrimp, mussels, etc.).
- Nuts.
If the diet is chosen correctly, an improvement in the condition of the expectant mother is noted. In acute cases of the disease, a strict diet is prescribed for 3 days. Also during treatment, medications containing enzymes are prescribed. To avoid dysbiosis, it is recommended to take a course of probiotics.
General principles of treatment:
- Carry out therapy in stages.
- Treatment cannot be interrupted.
The regimen is selected for each patient individually.
- An integrated approach is needed, which involves the use of drugs with different mechanisms of action.
- In case of chronic diseases of the ENT organs, gastrointestinal tract and excretory system, they must be treated and the woman’s health status must be constantly monitored.
- Potent drugs are used only in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
- Antiallergic drugs are used.
Before prescribing external medications, the dermatologist determines the form and stage of the disease. Be sure to take into account:
- The ability of a drug to cross the placenta.
- Gestational age.
Diet
Often, eczema appears in response to poor nutrition of the expectant mother. During pregnancy, you need to plan your diet wisely, eating as much fresh herbs, vegetables and fruits as possible, avoiding foods that can cause allergic reactions.
List of products that can cause allergies:
- chocolate,
- bakery,
- oranges, lemons and other citrus fruits,
- nuts,
- whole cow's milk,
- seafood,
- red vegetables and fruits - tomatoes, apples, carrots, etc.,
- berries – raspberries, strawberries, currants,
- honey.
To maintain health, a pregnant woman needs to ensure that the body receives the optimal amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Food products should be moderate in calories and easily digestible.
Medicines for external use
The specialist will select an ointment for eczema that can effectively cure the disease and not affect the course of pregnancy. Local treatment depends on the affected area and the severity of inflammation.
If the patient has a chronic disease, then before treatment the crust should be removed and then the affected area of skin should be treated. To make this procedure painless, compresses with vegetable oil are first applied.
You can make your own ointment for eczema. For the microbial form, take 4 parts of zinc ointment and 1 part of Wilkinson's ointment, mix everything and apply it to the inflamed skin. After the redness decreases, it is recommended to use sulfur, ichthyol or tar ointment.
For hygiene procedures, it is imperative to purchase hypoallergenic soap and avoid contact of the inflamed area of the body with hot water. Therefore, if you have eczema on your hands, it is recommended to use rubber gloves.
Proper treatment and compliance with all recommendations allows you to get rid of eczema in 1.5-2 months. In rare cases, the disease remains after childbirth. But then it becomes easier to get rid of it, since the list of drugs approved for treatment is significantly expanded.
How to alleviate the condition and get rid of the disease?
Eczema during pregnancy always gives the expectant mother a lot of unpleasant moments. And if the external factors of the disease do not directly affect the fetus, then the accompanying itching bothers the woman very much, causing her irritation, nervousness, and the inability to get a good night’s sleep or rest.
Therefore, this reason may affect the future child in the formation of his nervous system.
From this it follows that it is necessary to treat eczema. At the same time, doctors should definitely approach this treatment comprehensively, relying on safe folk remedies, paying special attention to nutrition, and using a minimum of medications.
Since during this period it is not advisable for a woman to use traditional hormonal drugs, so as not to harm the unborn child. Therefore, first of all, she needs safe methods to soothe itching and relieve skin irritations. Let's look at these positions in more detail.
What can you eat?
Organizing a healthy diet for an expectant mother suffering from eczema should be at the forefront of basic treatment. Her diet should be rich in natural products. The emphasis here should be on:
- Vegetables;
- Greenery;
- Fresh fruits;
- Berries;
- Goat milk.
In this case, allergenic foods such as:
- Fish or seafood;
- Orekhov;
- Citrus fruits, kiwi, pineapples;
- Chocolate or cocoa;
- Coffee or strong tea;
- Red vegetables or fruits;
- Muffins;
- Natural honey;
- Cow's milk.
Here, after the point of our story, we want to protect you from future rash actions after childbirth. The fact is that following a hypoallergenic diet is necessary for a woman not only during pregnancy, but also during breastfeeding.
After giving birth, did you calm down and decide that your eczema, which has been tormenting you for the last six months, is already behind you? Don't relax!
We want to warn you! It is during the lactation period, when the baby receives breast milk, that the symptoms of eczema can spread to him if the mother does not follow a diet and lets the disease take its course.
While you are breastfeeding, be patient, be attentive to your diet, and follow your doctor's advice. The baby's health depends on it!
When treating severe forms of eczema, doctors still resort to prescribing certain dosage forms to patients. It could be:
- Calcium gluconate injections;
- Zinc ointment;
- Fukortsin;
- Panthenol;
- Plant-based gels or ointments.
Nature itself with its folk remedies always comes to the aid of a pregnant woman in the fight against eczema. These can be compresses from:
- Kalanchoe juice;
- Fir oil with baby cream;
- Licorice with sea salt;
- Raw egg, water and vinegar.
In addition, it is very good to wipe the skin in affected areas with tinctures from decoctions:
- Calendula;
- Chamomiles;
- Coltsfoot;
- St. John's wort.
What can you eat?
ethnoscience
During pregnancy, you can use any products and decoctions only after your doctor’s permission.
Recipes:
Garlic ashes are taken and mixed with honey and butter made from cow's milk. The sore spot is steamed and the mixture is applied to it.
- You need to mix a tablespoon of string with the same amount of lingonberries and pour 2 cups of boiling water over everything. The decoction should be left for at least 2 hours. Take 50 ml half an hour before meals.
- An infusion is prepared from 6 tablespoons of ground viburnum berries, which are poured with 750 ml of boiling water. Let stand for 4 hours. Take half a glass orally for 2 weeks, 3 times a day.
- For scalp eczema, salt peeling is done once a week, after 15 minutes you need to rinse the salt with water. Carry out the procedure at least 5 times.
- The skin is sprinkled with crushed raw beans.
- Mix the white of a chicken egg with a spoonful of fresh cream and a tablespoon of medical tar. Apply the resulting mixture to the affected area.
You need tar, yellow sulfur powder and copper sulfate. All ingredients are mixed in proportions 1:1:1. The resulting mass is boiled for 5 minutes, during the process everything is thoroughly mixed. The resulting ointment is used to treat eczema.
- Pour 1 chicken egg into a glass bowl and add 1 teaspoon of chalk. After this, a teaspoon of birch tar is added. Cover the dish with a tight lid and place it in a dark place for 24 hours. Every day before going to bed, apply a compress to the sore spots.
- Make a paste of grapes and apply the resulting mixture to the eczema. After the procedure, you should not wet the skin for 4 hours.
Review of safe drugs
Effective and relatively safe ointments, creams from the category of hormonal products:
- Afloderm is an antipruritic, anti-inflammatory drug. Apply twice a day. The duration of treatment is 2 weeks. Approved for use during lactation;
- Lokoid - helps to quickly get rid of itching, swelling, inflammation. Distribute in a thin layer up to 3 times a day;
- Flucinar is a remedy against inflammation, burning, redness, and other unpleasant symptoms. Apply twice a day to inflamed areas, excluding the face.
Hormonal medication is prescribed in cases where the manifestations of the disease cannot be eliminated by other, safer means.
Anti-inflammatory healing ointments, creams:
- Zinc ointment. An inexpensive, effective drug that can soothe inflamed skin, dry out weeping wounds, and relieve irritation. Forms a protective film.
- Elidel. Anti-inflammatory agent for quick relief of burning and itching. The cream is applied twice a day.
- Bepanten. Moisturizes damaged skin, soothes, accelerates healing.
Ichthyol, sulfur ointment, Desitin, and tar ointment have good properties. Replenish your home arsenal of remedies with them, keep them as an ambulance in case of relapse of the disease. Before use, be sure to study the instructions and contraindications.