Reasons for the formation of the disease
In practice, eczema, both in infants and children under one year old, and in adults, is caused by several factors. In addition, the disease itself can have different origins.
Below we will consider the immediate causes of the formation of eczema.
Allergic reaction
Allergies are perhaps the main cause of the formation of eczema on any part of the body.
It develops as a result of an immune response when an allergen comes into contact with the skin. The body's defense system mistakes a harmless substance for a dangerous intruder and initiates a response that leads to the destruction of basophil mast cells and the release of large amounts of histamine, ultimately leading to the manifestation of allergy symptoms, including on the skin.
The antigen can be:
- plant pollen,
- animal fur,
- food (endogenous development path),
- other substances.
Allergy tests will help find the provocateur of the reaction.
Worm infestations
Causes vitamin deficiency and metabolic disorders. This increases the risk of developing an infectious skin lesion, since the immune system weakens along the way.
Skin damage from infectious agents
Photo: Herpetic eczema on the face at the initial stage.
It occurs quite often.
Human skin is a real breeding ground - we have been living next to us for a long time:
- staphylococci,
- streptococci,
- coli,
- herpes viruses,
- adenoviruses,
- rotaviruses.
This is only a small part of the “satellites”.
As a result of weakened immunity, activation of pathogenic flora is possible. After all, only the protective system keeps all the wild color in check.
Other reasons
- Fungal infections. The most common culprits are candida fungi (both protozoan, yeast, and hyphal varieties).
- Insect bites. Result in infection of the wound surface.
- Hereditary factor. It doesn’t play a big role, but it has been proven that if there is a person in the family who suffers from eczema, the risk increases by almost one and a half times. Including when it comes to facial damage.
- Skin injuries. They lead to the same infection as with the bite of bedbugs, bees and wasps.
- Systemic autoimmune diseases, problems with the digestive tract, endocrine pathologies.
Development mechanism
Seborrheic eczema is a joint result of:
- congenital disorders of the immune response;
- sensitization (hypersensitivity) to allergens;
- activity of the opportunistic microorganism Pityrosporum ovale.
The human immune system includes various cells, the function of which is strictly defined in the overall functioning of the immune system. Any disturbances in the cellular composition lead either to insufficient protection - immunodeficiency, or to excessive aggression - allergies. Patients with seborrheic eczema have an innate tendency to develop delayed-type allergic reactions, which, in essence, is their disease.
The yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum ovale normally lives on the hairy areas of the human body and is a representative of the skin microflora. A healthy epithelium is an insurmountable barrier for a microorganism, but it can penetrate into the deep layers of the skin due to any violation of its protective system. There he meets local immune cells, which destroy the alien and remember its antigenic composition - they become sensitized.
Forms and types of eczema in the video:
Repeated entry of the fungus into the deep layers of the epidermis leads to the development of a delayed allergic reaction. Sensitized cells release inflammatory substances into the tissue, under the influence of which the blood vessels dilate and local edema forms. Normally, this reaction should stop after the pathogen is destroyed, but an excessive immune response maintains it for a long time.
A feature of seborrheic eczema is the increased production of sebum in the area of inflammation. Its excess glues the skin scales together - this is how fatty yellow flakes are formed. The skin underneath becomes more wet, which complicates healing and increases the duration of the disease.
Risk factors and groups
In addition to the immediate causes, there are factors that increase the risk of developing the disease described:
- Weakening of the immune system. Why this is so is already clear.
- A history of infectious diseases. Especially pathologies of the dermal cover.
- Stress, nervous tension. Eczema may develop due to nervousness.
- Often the disease begins during pregnancy. This is associated with a whole complex of endocrine and neurological problems.
The list of possible reasons is wide. Contrary to popular belief, the disease is not always of an allergic nature, although this happens in the vast majority of cases (about 70-80% of all visits to a specialist).
Symptoms of eczema on the face
Characteristic symptoms depend on the form of the disease. There are several types of damage.
Information about eczema on the fingers, hands and feet may also be helpful.
True eczema
Photo: Dry eczema
It is also idiopathic, also called dry eczema on the face.
Most often, the first symptoms of true eczema develop as a result of an immune reaction. Among them are:
- redness of the skin,
- minimal swelling
- itching feeling.
The trigger is exposure to an allergen on the skin.
If the allergen acts on the skin for too long, the clinical picture of allergic eczema worsens. When scratching, so-called wet eczema is formed. This is a secondary infectious process, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- many vesicular formations filled with exudate develop on the skin of the face;
- a reddish rash appears;
- after opening the vesicles, a weeping, crater-shaped wound surface remains.
The vesicular ulcers then resolve with the formation of a crust. The disease again turns into a dry form. The pathogenic process, as a rule, has a descending character.
Can eczema move from your hands to your face?
This is extremely unlikely.
Mycotic eczema
It is provoked by fungal pathogens. The candidal nature of the disease determines the specificity of the course.
The mycotic variety is characterized by clearly demarcated lesions. Otherwise, the symptoms are identical.
Infectious eczema
Microbial eczema is provoked by staphylococcal and streptococcal pathogens. There are two main types of disease:
Photo: Microbial eczema
Plaque eczema
Develops in areas of skin lesions. It is characterized by:
- areas of redness and peeling of the skin;
- itching, burning.
If the lesions are constantly subjected to combing, there is a high risk of the formation of the true form.
Near-wound form
It is difficult to differentiate from the plaque type.
Seborrheic eczema
Most often it forms on the scalp. If left untreated, it spreads to the face.
Photo: Seborrheic eczema
The initial stage of seborrheic type eczema is characterized by:
- the appearance of yellowish, greasy spots covered with flakes of dead skin;
- formation of papules filled with serous fluid occurs;
- when moving to the face, the skin peels off, signs of true eczema appear.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema never occurs on the face, so you should not be afraid of this form. It affects the soles of the feet and hands.
Sycozyform eczema
Has all the manifestations of weeping eczema. Develops in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
Kaposi's eczema
Photo: Kaposi's eczema
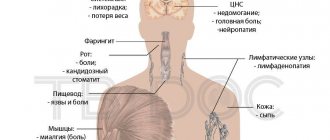
Most often affects young patients. Develops as a result of exposure to the wound surfaces of a herpetic pathogen. Characterized by:
- increased body temperature;
- massive crimson rashes merging into a single focus;
- inflammation of nearby lymph nodes
What does eczema look like on the face when it comes to this type of pathology? It spreads evenly over the entire face. It looks like bright crimson rounded plaques that form large lesions over time. The surface is covered with crust. Over time, the crust comes off and so-called wells: ulcerative defects.
It is important to carry out a differential diagnosis with streptoderma.
Contact eczema
It is not considered an independent variety. Considered to be a form of true eczema, triggered by wearing scarves, hats and other clothing that touches the face.
Prevention of exacerbations
To avoid having to select a suitable treatment method for eczema, it is better to prevent the disease altogether. As a preventative measure, experts recommend adhering to several rules:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits, normalize your daily routine, include moderate exercise, eat right, excluding sweet, starchy, spicy foods, as well as smoked meats, sauces, etc.
- Monitor your weight and avoid obesity, as it directly affects the functioning of the entire body.
- Observe personal hygiene rules; scalp problems often arise if you do not wash your hair on time.
- Pay careful attention to the selection of cosmetics. Gentle shampoos, conditioners and shower gels are safer for people. Aggressive components in the composition increase the risk of a negative skin reaction to the products.
- Take responsibility for your health and treat chronic diseases, especially for problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
At the first signs of seborrheic eczema, you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible, which will allow you to quickly begin treatment and get rid of skin rashes.
Stages of the disease
| Stage | Characteristic |
| Stage 1 (initial stage, erythematous eczema) | It is characterized by redness of the skin, burning and itching sensations. By nature it is the same dry form. |
| Stage 2 (developmental phase or papulovesicular eczema) | Microvesicles filled with serous fluid are formed. |
| Stage 3 (wetting eczema) | Ulcerative defects develop. |
| Stage 4 (resolution or phase of secondary dry eczema) | Everything comes back to the first stage. The vesicles heal, crusts form, and later scar marks. |
Diagnostic measures
Who should I contact with the described problem? Eczema is treated by dermatologists or dermatovenerologists. The initial consultation begins with an oral interview with the patient regarding his complaints and their nature.
The more thoroughly the patient or his parent answers, the less time it will take to carry out the diagnosis.
Then the doctor collects anamnesis (finds out what the patient has been ill with throughout his life). It is extremely important to establish the supposed factors that influenced the development of the disease:
- interaction with allergens,
- presence of open wounds, etc.
Diagnosis itself is not a problem. It is necessary to take a scraping from the affected skin - this will help identify the pathogen. It may also happen that the study does not yield any results. In this case, the source should be sought in an allergic reaction: stress tests and allergy tests are indicated.
In the course of these studies, the disease is distinguished from streptoderma and other similar pathologies.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Seborrheic eczema is easily identified by the appearance of the rash. But sometimes additional examination is required. It includes:
- dermatoscopy - examination of the skin using special optical equipment;
- luminescent diagnostics - under the influence of ultraviolet waves (range 360-370 nanometers), the affected areas glow in a certain color;
- taking hair and skin scrapings - examination under a microscope;
- bacterial culture if a secondary infection is suspected.
A differential diagnosis is carried out, the main task of which is to distinguish the disease from true and occupational eczema. The first type is characterized by the presence of a larger number of weeping areas, and occupational eczema regresses in the absence of exposure to an irritating factor.
How to cure eczema on the face?
Therapy is prescribed from the first day of the disease. Practice shows that the greatest results can be achieved by combining traditional therapy (various drugs) with traditional methods of treatment. Among the classic remedies are:
Antihistamines
They are prescribed only by a doctor and help relieve itching and burning. Relieves the allergic component.
The use of drugs of all three generations is indicated:
- Pipolfen,
- Tavegil,
- Suprastin,
- Zyrtec,
- Tsetrin,
- Claritin.
However, it is recommended to be careful with second-generation drugs. They give more side effects, in particular, they “hit” the cardiovascular system. It is recommended to use it in the form of ointments (Fenistil and others).
Non-hormonal ointments
You can recommend classic zinc ointment. This is a kind of panacea for dermal problems:
- promotes rapid healing of wounds,
- relieves inflammation, itching,
- disinfects the surface of the skin.
Additionally, the use of salicylic ointment is recommended. It has powerful anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
However, it is recommended to use a similar ointment for eczema on the face if the disease is non-allergic.
Such products together provide an answer to the question “how to remove redness?”
Hormonal ointments
First of all, hydrocortisone. Prescribed to relieve inflammation and allergic reactions as part of complex therapy.
Detailed information about creams and ointments for eczema on our portal.
Antiseptic drugs
Will help dry out weeping eczema. Among them:
- Fukortsin,
- brilliant green,
- Tsindol,
- Calamine.
Prescribed for the treatment of eczema and other skin lesions. Helps dry wounds. Additionally, within the framework of antiseptics, we can mention Zinocap. It relieves inflammation, eliminates infectious pathogens, and protects the skin.
Antibiotics
Wide spectrum of action.
It is possible to restore the skin and prevent the development of ulcerative and scar defects through the use of Retinol (vitamin A) in the later stages, injections of novocaine with hydrocortisone subcutaneously. Additionally, ointments Kontaktubex, Mederma and their analogues will help.
How to make the treatment as effective as possible?
You should follow simple rules:
- Follow your doctor's recommendations.
- For the first week, you should not wash your face with soap or aggressive substances. Only warm water.
- You need to adjust your diet. Nothing spicy, sour or sweet. Limit consumption of fatty and fried foods.
Treatment: what drugs are used
Seborrhea treatment is almost always carried out at home. Depending on the specific case, several types of drugs and ointments are used in the fight against eczema:
- anti-allergic – act on histamine, reducing swelling, some drugs have a sedative effect, which also has a good effect on the patient’s condition, but it should be remembered that you should not drive or do work that requires increased concentration;
- sedatives - help cope with psycho-emotional stress and normalize sleep, especially if stress has caused rashes, for example Novopassit or Adaptol are suitable for this;
- antifungal – affect the cellular structure of the fungus: Clotrimazole, Nystanin;
- antibiotics - usually prescribed only for secondary infection in cases of bacterial infection;
- vitamins – vitamins B1 and B6 will be especially useful; they will help quickly restore damaged skin on the head or other areas.
Treatment with various means is often recommended as local therapy:
- sulfur mash;
- greenery;
- solution with alcohol;
- white mercury ointment;
- salicylic ointment;
- powder with resin or sulfur.
To relieve the inflammatory process, corticosteroid drugs are used, for example: Hydrocortisone, Diproslan or Prednisolone.
Various physiotherapeutic procedures also have excellent effects:
- laser exposure;
- cryomassage;
- magnetic therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- Darsonvalization.
If you use the above procedures in combination with basic drug treatment, you will be able to increase their effect and get rid of unpleasant symptoms faster.
For seborrheic eczema on the head, it is recommended to use special medicated shampoos: Nizoral, Friederm, Sebiprox, Sulsena. When choosing a shampoo, you should pay attention to its purpose or consult with your doctor so that you can choose the most suitable product.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are prescribed with caution. No herbs, only mildly active ingredients.
Sea salt
- 3 liters of water,
- 1 tbsp. sea salt.
Bring water to a boil and leave to cool slightly. When the temperature of the liquid reaches 70 degrees, add a glass of sea salt.
Soak a cotton swab or gauze in the cooled solution and apply to the affected area. Fix and hold for half an hour. It is necessary to repeat the procedure daily, 10-15 times.
Celandine juice
Lubricating plaques and lesions with concentrated celandine juice is also effective. It relieves inflammation, disinfects the surface and normalizes metabolism. These two methods can be treated at home.
Essential oils for eczema on the face, as well as homeopathic remedies, are not recommended. In the first case, there is a high risk of getting an allergy, and in addition, chemical burns. Homeopathy is generally recognized as a pseudoscientific practice.
How long does it take to treat eczema on the face?
The duration of the course varies from 10 to 21 days in the acute phase. Relapses of chronic eczema last about the same amount of time. A continuous course with vague symptoms is possible.