Candidiasis in the nose - how to treat nasopharyngeal thrush
Every person experiences a runny nose in their life, but not everyone knows that this phenomenon can be caused not only by viruses, but also by fungus. This condition is called candidiasis in the nose. Although this pathology is rare, its presence cannot be completely excluded. This disease can be caused by frequent colds, viral infections and chronic pathologies, since the immune system is very weakened and is easily affected by thrush.
Prevention and prognosis
By taking care of your health and following the rules of personal hygiene, such a problem as thrush can be completely avoided. To do this, you should follow a number of simple rules:
- carry out hygiene procedures in the oral cavity and nasopharynx;
- treat thrush before conception;
- strengthen the immune system with well-known procedures;
- do not abuse sweets;
- allocate the required number of hours for sleep and rest;
- disinfect household items and baby supplies.
If infection does occur, then with timely treatment, the prognosis is positive. The candida fungus stops actively reproducing, but remains a “resident” of the body until the immune system fails again.
Causes
A harmful fungus enters the nose due to the fact that this organ is open to access. Thus, in addition to air, viruses and fungi easily penetrate there. This occurs through the standard airborne route from a carrier of the disease, and it is difficult to diagnose the presence of this particular pathology.
If a person is completely healthy, then candidiasis in the nose is absolutely not scary for him. But in the case of a weakened body, the fungus quickly multiplies throughout the body.
Although, a person who has never had contact with a sick person can detect the presence of this pathology. Since Candida is present in most people and is not always active.
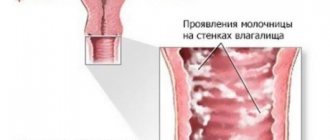
Interestingly, these fungi are normally found in healthy genitals and intestines, without causing any inconvenience to their owner. But under favorable conditions, they migrate throughout the body, which leads to infection of other mucous membranes, which include the mouth and nose.
The disease can become more active if the body is weakened as a result of such diseases and pathologies:
diabetes;
- ARVI or acute respiratory infections;
- previously diagnosed thrush on the genitals;
- AIDS;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- exacerbation of nasopharyngeal diseases;
- flu;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- recent illness;
- hypothermia;
- nasal injuries.
Nasopharyngeal candidiasis is transmitted in the following cases:
- During treatment in a hospital, where the patient is given intravenous catheters, hemodialysis is prescribed, or he is fed through a vein. In this case, the reason is the lack of sterility of devices or instruments.
- In everyday life, when infection occurs through a normal handshake or through the common use of personal items.
- The use of non-thermally processed foods.
- During pregnancy, when the fungus passes from an infected mother to a healthy baby.
Also, this pathology develops after taking a course of antibiotics or hormonal drugs, after suffering stress, in pregnant women and the elderly.
How does fungus appear in the nose?
It is not difficult for fungi to get into the nose: the organ of smell is always open. Along with the inhaled air, pathogenic microbes and, as in our case, fungi also enter it.
They can be transmitted by airborne droplets or during physical contact with a carrier of the disease. At the same time, a person who “blesses” others with an unpleasant disease may not even realize what a threat he poses. Nasopharyngeal candidiasis is quite difficult to diagnose.
However, for a strong, healthy person, Candida is not dangerous. The body is able to suppress them, prevent their reproduction and completely cleanse itself of this scourge.
For a weakened person, everything can end much sadder: without meeting adequate resistance, the fungi, once on the nasal mucosa, will begin to rapidly multiply, forming entire islands in different layers of the epidermis. The unpleasant symptoms that follow will certainly force you to consult a doctor and begin treatment for nasopharyngeal candidiasis.
However, even those who have not had contact with patients can detect this disease in themselves. Candida fungi are present in the body of many people, but remain dormant. A certain amount of them in the intestines or in the genital area is normal if they are not active and do not cause concern. However, they can begin to migrate in the body, infecting other mucous membranes, including the nasal and oral cavities.
An outbreak of disease can occur when the body is weakened . The most susceptible to fungal diseases of the nasopharynx are:
- patients with influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections,
- diabetic patients,
- AIDS patients,
- people who have recently had any other serious illness,
- patients who have undergone antibiotic treatment,
- injured nose: severe bruise or fracture,
- aged people,
- pregnant women.
Nasopharyngeal candidiasis: symptoms
People should know that nasal thrush is similar to a viral infection and a cold. Thus, without appropriate diagnostics, it will not be possible to determine the presence of this particular pathology.
A fungal infection in the nose not only affects the mucous membrane of this organ, but also the throat. But in this case, the symptoms of candidiasis of the sinuses are no different from the usual disease.
Thus, a prolonged runny nose, which cannot be cured with standard antiviral drugs, gives confidence that a fungus is actively multiplying here. But it will not be possible to stop this process without using special means.
Thrush in the nose in adults is characterized by the following clinical picture:
- Congestion.
- Plaque in the form of films in the mouth and nose.
- Copious discharge of whitish or yellowish mucus. If a person has difficulty swallowing, then most likely mucus has accumulated there. Nasal drops do not help in this case, and meanwhile Candida multiplies faster and faster, which causes more congestion.
Sneezing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Unbearable itching.
- Swelling.
- Symptoms of a prolonged cold. If a runny nose lasts for a very long time and after using very strong antiviral medications, then this is a clear symptom of thrush.
- Persistent congestion.
- A characteristic whitish coating appears on the tongue and cheeks.
- The same plaque on the tonsils.
- An extremely unpleasant odor of nasal discharge, which is a distinctive feature of a fungal infection from another disease.
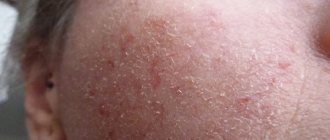
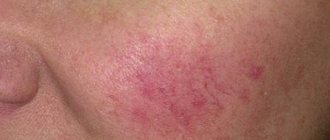
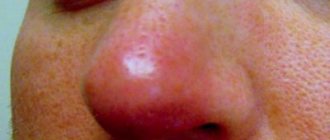
In addition, candidiasis of the nasal mucosa can be recognized due to the fact that there are characteristic white dots in the nasal cavity that are visible to the naked eye.
It is important that the examination is carried out on time, since otherwise the pathology becomes chronic.
Types of fungal rhinitis
- itching in the nasopharynx;
- cottage cheese-like discharge;
- sour smell from the nasal mucosa.
- burning in the sinuses;
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- tumors of a malignant and benign nature.
- polyps;
- destruction of bones and cartilage of the nose.
- nosebleeds;
- change in voice intonation;
- copious mucous discharge.
- pain in the nose;
- formation of wounds and erosions on the mucous membrane.
Treatment
Treatment of nasal candidiasis takes place in several stages. Initially, the specialist determines the type of Candida fungus, after which he prescribes treatment, which is carried out in a course.
How effective the treatment process can be determined independently, that is, if white flakes become noticeable in the secreted mucus, then healing is already taking place. Candida dies at this time, that is, the fungus leaves the body with mucus.
It is important that, together with medications, appropriate measures are taken to increase immunity, since a weakened body will not be able to cope with the disease completely. This is due to the fact that topical agents are designed to destroy colonies of the pathogenic fungus, and additional forces will be required to ensure that outbreaks do not recur.
The treatment procedure begins with the use of antifungal agents that act locally. As a rule, treatment of nasopharyngeal candidiasis includes the following procedures and means:
- ointments and creams;
- rinsing the nasal cavity;
- nasal drops for thrush;
- rinsing with furatsilin, soda, and so on;
- folk methods.
Classification of pathology
Another name for candidiasis is thrush. This emphasizes that the fungus leads to the appearance of cheesy white deposits on the affected mucous membranes with a characteristic sour-milk odor. This is a pathognomonic symptom. According to the localization of the process, candidiasis is distinguished:
- Cheilitis is a fungal infection of the red border of the lips.
- Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue.
- Sore throat.
- Stomatitis is a lesion of the oral mucosa.
- Seizures in the corners of the mouth.
- Laryngitis - the larynx may be affected. Depending on the degree of damage, the process is distinguished between superficial and deep. According to the course - acute and chronic.
Today, there are 170 known species of this microorganism, which is distributed everywhere, on all surfaces around, and 10 of them are parasitic in the mouth. But the three most common are: C. albicans - 60% of cases; C. Parapsilosis (oral thrush in children) and C. Glabrata (higher percentage of detection in the elderly). Fungi feel good at temperatures of +27...+37°C.
Prevention
Avoiding the occurrence of this disease is quite simple; for this you need to:
monitor the cleanliness of the nasal mucosa;
- promptly treat ENT diseases that could cause this disease;
- do not allow dirty hands, handkerchiefs, napkins and other foreign objects to come into contact with the nasal cavity.
If, due to the nature of your work, you have to be in a room where there is a high content of dust or other small substances, then it is more advisable to wear a mask or respirator.
The risk of developing candidiasis of the nasopharynx is especially high if this pathology of other organs is present.
It is very important to take vitamin complexes during the period of vitamin deficiency, exercise hardening and eat a balanced diet.
You should not skip scheduled visits to the dentist, who can determine the presence of an infection in the early stages.
What is respiratory tract candidiasis
Respiratory tract candidiasis is an infectious disease caused by opportunistic fungi of the genus Candida, and accompanied by damage to the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract (oropharynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs).
The main causative agents of pulmonary candidiasis are C. albicans (seventy percent of cases) and C. tropicalis (less common, but more severe and less treatable).
Pulmonary candidiasis caused by C. Glabrata occurs predominantly in patients with decompensated diabetes mellitus and in HIV-infected patients. Other types of candida rarely cause respiratory tract candidiasis.
Attention. In the first stages, the symptoms of the disease resemble ordinary bronchitis (cough, fever). However, if untreated, severe candidal bronchopneumonia, respiratory failure, allergic and toxic shock, as well as candidal sepsis may develop.
Nasopharyngeal candidiasis - causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention, photo
Fungal infections of the nose are pathologies that are transmitted by airborne droplets. This happens at the moment of physical contact with an already infected person. One of the manifestations of this group of diagnoses is thrush.
The bacteria that infect the body are called Candida; the disease itself in medical terminology is interpreted as nasopharyngeal candidiasis. The specificity of the disease lies in its complex diagnosis and relapses that occur when treatment is ignored for a long time.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment is prescribed by an otolaryngologist and includes a whole range of measures: medication and physiotherapy, the use of traditional medicine methods, and diet. If all of the above instructions are followed, thrush will be completely cured, but the fungus will remain in the body.
Drug therapy
It is important to stop the inflammatory process and destroy pathogenic microflora, so treatment begins with antifungal drugs (antimycotics): Nystatin, Mycostatin, Fluconazole, Futsis, Mikosist, Flucosist, Levorin and others.
The drug and its dosage are selected by the doctor taking into account the severity of the disease. In some cases, taking antifungal drugs is not limited to one course; to achieve the effect, the drugs are used in 2-5 doses.
Along with antimycotics, the doctor prescribes:
- Antihistamines of the latest generation: Zodac, Zyrtec, Loratadine.
- Immunomodulators that stimulate the immune system: Lykopid; Imunorix, Polyoxidonium, Echinacea.
- “Vitamin cocktail”, of which vitamin C and representatives of group B are especially important.
- General strengthening natural remedies for immunity: tinctures of ginseng, eleutherococcus, aloe.
- Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, since thrush is accompanied by dysbacteriosis.
- Antiseptics with a spray for the oropharynx: Tantum Verde, Chlorhexidine, Fukortsin.
- Antiseptics for gargling: Chlorophyllipt, Hexoral.
It is undesirable to use antibiotics aimed at destroying bacteria while treating a fungus. This is acceptable in the case of mixed infections as an exception. First, a course of antibiotics is carried out, and then antimycotics are administered.
See also
What to do if adults and children feel nauseous and have a sore throat after vomiting, causes and treatment methods
Read
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary to improve immunity and eliminate the inflammatory process. They help consolidate the obtained therapeutic result. Herbs and foods help:
- collection of calendula, chamomile, sage for gargling;
- tincture of lemon and goldenberry juice (1:3) to treat the throat;
- decoctions of rosehip and echinacea for internal use;
- lubricating the throat with a decoction of flax seeds;
- rinsing with a solution of soda and salt.
Treatment and rinsing will be most effective when applied three times after meals.
Honey is not used to treat throat infections due to thrush. It promotes the spread of infection because fungi readily feed on it.
Physiotherapy
Includes the following procedures:
- UFO of the pharynx;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis with potassium iodide solution.
Other techniques are also used in the treatment of the oropharynx, but in the case of mycoses they are contraindicated.
Diet therapy
With candidiasis, it is important to adhere to a certain diet, which includes lean meat, cereals, and vegetables. Natural juices and dairy products are beneficial. Dishes must be steamed. Eating fried foods and smoked foods aggravates the disease.
You should not include sweet fruits, sugar, grain porridges, yeast and fermented milk products in the menu, which contribute to the growth of fungi. If you have a sore throat, avoid solid foods so as not to injure the inflamed mucous membrane.
Features of the treatment of candidiasis in children
With minor manifestations of candidiasis at the first stage of the disease, it is sufficient to use local therapy, in which the affected areas are treated. If the disease is advanced, then complex therapy cannot be avoided. It is carried out in a hospital, where the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen and monitors its implementation. The following treatment procedures are usually recommended:
- taking antimycotics;
- the use of ointments and creams containing clotrimazole;
- taking medications with live bacteria that suppress pathogenic microflora;
- introduction of brewer's yeast and vitamins into the diet;
- use of traditional medicine to improve immune status;
- dieting.
In case of thrush, breastfeeding is maintained, but the nipple areolas must be treated with antiseptics, and the baby’s hygiene items must be sterilized.
Symptoms of nasopharyngeal candidiasis
Thrush of the nasopharynx is characterized by a rather poor clinical manifestation. At the initial stages of the formation of the pathological process, the patient may complain of general weakness, lethargy, and physical malaise. This symptom, as a rule, is not associated with the diagnosis discussed in the article, and therefore is ignored.
Quite often, people diagnosed with nasal candidiasis suffer from a sharp decrease in appetite. This occurs against the background of pronounced loss of body weight - in a fairly short period of time, the patient can lose up to 10% of the initial weight.
Symptoms
When the oropharynx is affected by the waste products of the fungus and its enzymes, the following symptoms occur:
- the throat is dry, the mucous membranes are not sufficiently moistened;
- an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth;
- the larynx swells and turns red;
- the oral cavity becomes less sensitive;
- there is soreness in the mouth and throat;
- itching, soreness or burning occurs in the throat.
In rare cases, low-grade fever, increased volume of tonsils, and loss of appetite are possible. If you eat spicy, salty or hot food during the course of your illness, the symptoms of candidiasis will worsen.
When examining the mouth and throat, cheesy white accumulations are visible. They can be in the form of dots, grains, which are clearly visible against the background of the red, inflamed mucous membrane. Another option is possible in the form of white films or plaques, which gradually merge with each other.
Causes of nasopharyngeal candidiasis
This anomaly is a consequence of infection of the mucous tissues of the larynx by Candida fungi. The main risk group is patients of the older age group and young children.
Factors that can provoke the development of pathology:
- previously suffered infectious diagnoses that occur in a severe form;
- drug or alcohol addiction;
- a consequence of radiation or chemotherapy during the treatment of oncological tumors.
The main causes of infection are also:
- inflammation of the adenoids and progressive caries - these factors create an ideal environment for the development of pathogenic fungal bacteria that form candidiasis in the nose;
- serious diseases of the most important systems of the body's functioning in their chronic stage. These are diabetes mellitus, autoimmune dysfunction, respiratory damage;
- long-term use of drugs with an immunomodulatory spectrum of action, cytostatic group, and hormone-containing drugs. All this at a certain stage of use can cause candidiasis of the nasal mucosa;
- chronic exhaustion of the body, accompanied by decreased immunity, anorexia;
- excessive physical activity;
- HIV infections and AIDS.
Throat candidiasis
Throat candidiasis , or in other words pharyngomycosis, is a group of pathologies that leads to inflammatory fungal infection of the mucous membranes. The main causative agent is yeast fungi of the genus Candida (candida albicans is most often identified).
This fungus is always present in the human body in minimal quantities, without causing any inconvenience. However, when the immune system is weakened or any other unfavorable combination of circumstances, the disease makes itself felt.
General practitioner: Azalia Solntseva ✓ Article checked by doctor
Throat candidiasis - what is it?
Candidiasis is an infection caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Candida albicans is the most common causative agent of the disease.
People with oral and throat thrush usually have a positive HIV infection, dentures, diabetes, or recent use of broad-spectrum antibiotics or inhaled steroid medications.
The main manifestations of the disease:
- inflammation and pain in the mouth;
- burning;
- problems with swallowing;
- white, dense plaques on the mucous membranes.
Upon examination, extensive redness and a whitish coating are diagnosed on the inside of the cheeks, in the throat, on the tongue and gums.
There are 5 possible forms of oral and throat candidiasis:
- Membranous candidiasis is one of the most common forms. Characterized by curdled white plaques on the oral mucosa.
- Chronic atrophic candidiasis (prosthetic stomatitis) is also a fairly common form. Symptoms include severe redness and swelling of the part of the roof of the mouth that touches the dentures.
- Acute atrophic candidiasis (Erythematous) - pronounced redness on the hard and soft palate.
- Seizures (Angular cheilitis) - an inflammatory process with redness, soreness and cracking in the corners of the mouth.
- Mixed form is a combination between several of the above types.
emedicine.medscape.com
How to treat or treat candidiasis
Treatment for throat candidiasis depends on age and overall health. The goal of treatment is to stop the fungus from growing and spreading.
How to treat pathology:
- fluconazole is an oral antifungal agent;
- clotrimazole in oral lozenges;
- nystatin, a mouthwash followed by oral administration;
- itraconazole, a drug for people who are resistant to conventional treatment or who have HIV or AIDS.
- amphotericin is used for severe infections.
Treatment at home:
- brushing your teeth with a soft toothbrush without touching the damage;
- use a new brush every day until the infection is completely eliminated;
- avoiding sprays and commercial mouthwashes;
- rinsing your mouth with water and salt;
- maintaining normal blood sugar levels in diabetes;
- eating unsweetened yoghurt to restore and maintain good microflora.
If an infection is detected in breastfed newborns, both mother and child must be treated to prevent transmission of the virus in a circle.
In these cases, the following treatment is necessary:
- antifungal medicine for the baby and antifungal cream to apply to the mother's breast;
- Disinfect nipples, bottles, breast pump parts in a solution consisting of half water and half vinegar, after which they must be given time to dry;
- Using bra pads to prevent infection from spreading to clothing.
Once treatment is started, candidiasis usually goes away within a few weeks.
healthline.com
Main symptoms of throat candidiasis
Initially, symptoms of oral candidiasis may go unnoticed.
The main symptoms of throat candidiasis include:
- whitish coating on the tongue, inside of the cheeks, palate, gums and tonsils;
- raised, curd-like plaques;
- redness, burning and dry mouth, problems with swallowing;
- redness and slight bruising;
- redness and cracking in the corners of the mouth;
- taste of cotton in the mouth;
- taste disturbances;
- redness, irritation and burning under dentures (denture stomatitis).
In severe cases, with cancer or a weakened immune system, the lesions can spread into the esophagus, a long muscular tube that runs from the back of the mouth to the stomach. In this case, you may experience difficulty swallowing, pain, and a feeling of a lump in the throat.
Babies and nursing mothers
In addition to having the characteristic whitish plaques, babies may also eat less well or act restless and irritable. During feeding, they can transmit the infection to the mother. Subsequently, the circulation of the virus from mother to child and vice versa is possible.
Women with breast candidiasis may have the following symptoms:
- red, sensitive nipples with cracks and itching;
- shiny, scaly skin on the areola;
- pain between feedings or during the process itself;
- stabbing pains deep inside the chest.
When to see a doctor
Candidiasis is not typical for preschool children, adolescents and adults, therefore, if it develops, consultation with a specialist is necessary to determine the possible causes.
mayoclinic.org
How to gargle when you are sick
There are many natural remedies for the disease.
How to gargle for candidiasis:
- Rinsing your mouth with salt water. Salt attacks bacteria and changes the acidity in the mouth, making it unsuitable for the fungus C. albicans to grow. It helps to cope with candidiasis, but using this method alone is not as effective as, for example, using fluconazole or coconut oil. However, if you combine this method with others, you can significantly speed up the healing process. To prepare this solution, you need to dissolve half a spoon of salt in a glass of water (250 ml) and rinse your mouth with it. Repeat the process 2-4 times a day until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
- Rinse with Nystatin oral suspension (100,000 units/ml) 5 ml 4 times a day for 2 minutes, after which it must be spat out. Please be aware that this commercial product may contain sweeteners that are known to cause tooth decay.
thrushtreatmentcenter.com
jcda.ca
Disease in a child - signs and treatment
The main manifestation of candidiasis is whitish plaques on the child’s tongue and in the oral cavity in general. The plaques may resemble cheesy deposits and are usually difficult to separate. If a child has a white coating on the tongue that is easily wiped off, most likely it is just milk and not a fungus.
Usually, candidiasis does not particularly bother children, but the child may begin to eat poorly and “not latch” on the mother’s breast during feeding. Diaper rash may also occur due to the same infection and require treatment.
If your child's doctor decides it is necessary to prescribe treatment for your child, he will most likely prescribe antifungal medications.
The 2 main antifungal medications for treating oral candidiasis in children are:
These drugs are used 4 times a day and are most effective if used immediately after feeding the baby. The drug must be used for another 2 days after recovery from the infection in order to prevent its return.
If a child has an infection, there is a risk of transmitting it to the mother during breastfeeding. The fungus can infect the nipples or breasts, leading to nipple candidiasis. After each feeding, apply antifungal cream to the nipples and remove it before the next time.
nhs.uk (Signs of oral thrush in babies, Treating oral thrush in babies, Advice for breastfeeding mothers)
Why does my throat hurt with candidiasis?
The fungus that causes the disease, Candida albicans, is often found normally in the mouth and throat. When the environment in the mouth changes (usually due to an immature or weakened immune system), the fungus can grow, causing symptoms such as burning, redness and pain.
It can sometimes occur in people taking antibiotics and steroid hormones (for example, prednisolone). More often, the throat hurts already at the initial stage of the disease.
Sore throat and other flu-like symptoms are also diagnosed with HIV infection.
People living with HIV may suffer from chronic or recurring sore throat due to a secondary infection. In addition to the fungus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), a common viral infection that causes serious consequences, can also be associated.
Candidiasis and cytomegalovirus can appear in absolutely any person, but most often they are associated with a weakened immune system.
hmedicinenet.com
mayoclinic.org
Complications and consequences in adults
Oral candidiasis rarely causes complications in people with good immunity. It appears only when the immune system is weakened due to past illnesses or after taking certain medications.
Extensive involvement of the trachea (tracheitis) and esophagus (esophagitis) can lead to problems with swallowing and breathing in previously healthy people. There are known cases of bronchopulmonary candidiasis.
Esophageal candidiasis and systemic spread of the fungus most often occur in patients with a weakened immune response.
healthline.com emedicine.medscape.com
Correct diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of candidiasis depends on its location and cause.
If the fungus is limited to the mouth, to diagnose the disease, the doctor or dentist may:
- examine the mouth for whitish lesions;
- take a small scraping from the lesions for subsequent examination under a microscope;
- If necessary, conduct blood tests to detect concomitant diseases that can lead to the development of candidiasis.
If the fungus is in the esophagus, determining esophageal candidiasis may require:
- A biopsy to determine which fungus or bacteria is causing the symptoms.
- Endoscopic examination. Using a special flexible tube with a camera and a light on the end, the doctor examines your esophagus, stomach, and upper intestine (duodenum).
- Physical examination. If necessary, a blood test may be prescribed to determine concomitant diseases.
mayoclinic.org
Treatment of nasopharyngeal candidiasis
A fungus that can cause candidiasis of the nasal mucosa should be treated only after a thorough laboratory diagnosis. It is not only able to confirm the presence of the disease, but also to identify the presence or absence of yeast-like pathology in the body.
It is important to understand that regardless of which of the methods discussed below is chosen as a priority, it will take quite a long time to treat candidiasis in the nose.
General scheme
The treatment regimen, taking into account the stage of progression, is as follows.
First, the patient is prescribed topical drugs. At the stage of disease formation, this is often enough. This includes antifungal syrups, compositions for irrigation of the tonsils and residual mouth, and tablets for slow resorption. In addition, the patient may be recommended a course of antifungal injections.
If such therapy is not effective enough and the course of treatment does not bring positive dynamics, complex treatment is used as an additional stimulating factor.
Nasal drops for candidiasis
Nasal drops for candidiasis should have a pronounced antifungal effect. Protargol has proven itself to be excellent - the composition is brown, odorless, and has a bitter aftertaste. Qualitatively neutralizes pathogenic organisms. Inhibits the progression of atypical processes. Has virtually no side effects. The drug is dripped twice a day for 7 – 10 days.
Other drugs
Medicines with antifungal effects are produced based on components of the azole group. This:
- Fluconazole;
- Ketonazole;
- Clotrimazole.
Yeasts that cause the disease are extremely sensitive to the effects of polyene class antibiotics - Nystatin, Levorin. The products are effective both for external use - produced in the form of ointments, and for internal use - in the form of tablets. Which option is preferred is determined by the doctor, taking into account the clinical situation of the pathology.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- Mycostop;
- Futsis;
- Nizoral.
In the form of creams and ointments, the following is indicated:
- Mycogel;
- Ketodin;
- Dermazole.
Miramistin is ideal as a disinfecting solution.
The basic rule is to eliminate mucus as thoroughly as possible, relieve swelling and itching in the nasal passages and in areas where ulcerative formations are localized
For maintenance therapy, vitamin complexes and immunostimulants should be taken.
Folk remedies
Treatment of nasopharyngeal candidiasis, if the progression process is not yet too advanced, is possible with the use of traditional medicine. However, in most cases, their effectiveness occurs only with an integrated approach to the treatment process.
The most popular methods are:
- rinsing the nasal cavity
is carried out with a water-salt solution (one teaspoon of components per glass of warm water). It is necessary to rinse the lesions at least 4 times a day; - irrigation of mucous tissues
- decoctions based on chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus. Lotions based on oak bark or St. John's wort are effective. These components have a pronounced antimicrobial effect, have antibacterial and restorative properties; - treatment of the internal surfaces of the larynx with sea buckthorn oil or tea tree extract.
The composition should be applied slightly warm; - lubrication with natural juices
is an ideal solution - beets, carrots. The procedure is carried out using a syringe or a small syringe.
Applications of aloe juice, vitamin A and olive oil will help make the microflora of the mucous membrane softer.
Fungal rhinitis. Methods of effective treatment, folk remedies
Fungal rhinitis, or mycosis, often affects the membranes of the olfactory organ. The disease is characterized by damage to the nasal mucous membranes, where a fungal infection penetrates, causing a prolonged runny nose.
Causes and development factors
In a healthy person, the nasal mucosa is always moist. This feature protects the airways from aggressive external irritants. Under the influence of various factors, the mucous membrane can dry out. This leads to the formation of small wounds into which pathogens of fungal infections penetrate.
Fungus can get into the nose for a number of reasons that negatively affect the general condition of the human body. These include:
- avitaminosis;
- colds, flu;
- nasal injuries;
- diabetes;
- taking hormonal medications;
- long-term intestinal dysbiosis;
- weakened immune system;
- deviated nasal septum;
- frequent viral diseases;
- nasal polyps;
- dental caries;
- taking antibiotics.
A fungal infection in the nose can occur as a result of frequent swimming in dirty natural bodies of water. Abuse of medications for the common cold is also a provoking factor in the development of the disease. This happens because nasal medications can reduce the body’s protective functions.
Types and pathogens of mycoses
There are several types of fungal pathogen. Clinical manifestations depend on the type of fungus parasitizing the nasal mucosa.
Staphylococcus aureus
The disease affects the nose and throat. Over time, nasal mucus completely clogs the sinuses, and the following symptoms appear:
- yellow-green mucous discharge;
- ulcers, redness in the nasal cavity;
- impaired sense of smell (weak sense of smell);
- hoarse and nasal voice;
- there is no nasal breathing, the person breathes more often through the mouth;
- The acute form of rhinitis is characterized by an increase in temperature.
Staphylococcus aureus has developed immunity to many antibiotics and to drugs that reduce sensitivity. Therapy is due to long-term use of drugs of various groups.
Candidiasis of the nasopharynx
The disease directly depends on yeast microorganisms of the genus Candida. They are constantly present in the body, but under the influence of certain circumstances their number increases sharply.
Symptoms of nasopharyngeal candidiasis are similar to those of a cold. Therefore, a person begins to treat himself, using nasal drops. The following signs indicate the presence of fungus in the nose:
- whitish coating on the nasal mucosa and in the oral cavity;
- discharge of a large amount of yellowish or white mucus;
- difficulty breathing through the nose due to constant nasal congestion;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Often during diagnosis, the fungus is found not only in the nasopharynx, but also in other systems of the body.
Aspergillosis of the mucous membranes
The pathology is caused by moldy fungi, which, when inhaled, first settle in the lung tissues. Gradually they spread, causing ulcers to appear. Inhaling large amounts of fungal spores can cause pulmonary inflammation even in a healthy person.
Symptoms of mucosal aspergillosis:
- the sinuses, which initially have varying thicknesses of mucus, are constantly blocked;
- allergic rhinitis that does not go away after taking antihistamines;
- headache;
- attacks of suffocation;
- heat;
- proliferation of nasal polyps;
- bleeding from the nose.
The acute course of this disease is characterized by necrotic processes that can spread to the bones of the face and skull.
The risk of infection is high among agricultural workers, as well as among people involved in paper spinning and weaving production. Various invasive procedures are another possible cause of development.
Treatment
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor decides on treatment tactics. If the treatment was chosen correctly, then the signs of the disease disappear after 2-3 weeks.
Medication
To treat fungus in the nasopharynx, antimycotic medications are used for internal and external use. These include the following drugs:
- Nystatin;
- Levorin;
- Amphotericin;
- Clotrimazole;
- Fluconazole;
- Bifonazole and others.
Antimicrobial tablets must be taken according to the regimen determined by the attending physician. Medicines in the form of ointment or gel are used every day. In order to increase immunity, vitamin complexes and general strengthening agents are prescribed.
Surgical intervention is indicated for the development of mucormycosis and histoplasmosis. For rhinosporidosis, excision (cauterization) of polyps is recommended.
To avoid unwanted consequences from taking medications, they should be taken strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Prevention of fungal rhinitis
To prevent the development of a fungal infection from being taken by surprise, it is necessary to follow preventive measures to prevent infection. It is recommended to follow these simple rules:
- adhere to a balanced and proper diet;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- be sure to treat any diseases;
- carry out the prevention of dysbacteriosis.
If signs of illness appear, you should visit a doctor. If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. With treatment, a fungal runny nose quickly goes away and never returns.
Source: //nosoved.ru/zabolevanija-nosa/rinit/lechenie-gribkovogo-nasmorka.html
Candidiasis in the nose - causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Fungi of the genus Candida are part of the opportunistic human flora and are not dangerous to health.
But under certain factors, they begin to actively multiply in the body: on the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, genitals, in the digestive tract, causing discomfort. Most often, nasopharyngeal candidiasis, like any other type of disease, occurs in young children and adults with chronic and autoimmune diseases. People with weakened or imperfect immunity are at risk.
It is important not only to treat a fungal infection - it is necessary to look for the cause of its occurrence, otherwise a relapse of the disease is possible.
Symptoms of appearance
A distinctive feature of a fungal infection is that the runny nose caused by it does not go away for a long period of time (from 14 days or longer). Fungal congestion is not relieved by vasoconstrictor medications. Antiviral medications have no effect on the fungus. Other symptoms of candida in the nasopharynx include:
- dry mucous membrane;
- pain in inhalation and exhalation through the nose;
- white discharge with a stable consistency throughout the course of the disease;
- feeling of pressure in the paranasal sinuses;
- itching of the mucous membrane.
Return to contents
Causes
The main cause of nasopharyngeal thrush is a malfunction of the human immune system when pathogenic microorganisms get out of control.
It occurs due to the following factors:
- Lack of vitamins or banal malnutrition;
- Uncontrolled treatment with antibiotics, hormone-containing drugs;
- Treatment of cancer using chemotherapy;
- Presence of carious teeth;
- Chronic diseases of the nasopharynx (tonsillitis, pharyngitis);
- Colds;
- Disturbed balance of opportunistic intestinal flora;
- Nasopharyngeal injuries;
- Neglect of oral hygiene.
In some cases, the disease can be transmitted through the external environment: the saliva of a sick person, common objects, and in newborns - during childbirth, passing through the infected birth canal of the mother.
Brief description of the pathology
In such favorable conditions, the Candida fungus in the throat unfolds vigorous activity: it buds, multiplies in colonies, penetrates the mucous membrane of the throat, and begins to destroy epithelial cells. In addition, the metabolite substances released in the product of its vital activity are toxic to humans.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis is a rather comprehensive concept, because it includes not only the nasopharynx. Fungi affect the entire oral cavity and upper respiratory tract. The locations of the lesions are different at different ages, but there are also common symptoms. Despite the fact that after 18 years of age, the fungus usually affects the urogenital organs, candidiasis in the throat can also occur in young people, as a result of other inflammatory processes, taking antibiotics, etc.
The fungus is quite contagious and can be transmitted through contact, kissing, and hygiene items. A newborn can become infected with the pathogen from the mother when passing through the affected birth canal.
Nasal candidiasis: symptoms
Due to its great similarity to a common cold, nasal candidiasis can only be diagnosed by a specialist. However, if nasal discharge does not go away for a long time, it is difficult to treat with antiviral drugs - this may be a sure sign that the Candida fungus has “woke up” and has begun to actively multiply.
Symptoms of nasal candidiasis include:
- Congestion that does not go away even after using vasoconstrictor drugs;
- Discharge of a large amount of mucus with an unpleasant odor;
- Itching, frequent sneezing;
- Pain in the nasopharynx.
Since a person’s nose and mouth are closely connected, candidiasis of the nasal cavity is often transmitted to the oral cavity. In adults, an inflammatory process begins in the area of the nasal septum, which can subsequently affect the paranasal sinuses; in children, on the inside of the cheeks, tonsils and tongue. The appearance of white plaque in places of inflammation is characteristic. In the absence of timely treatment, the affected areas increase in size and painful ulcers appear.
Symptoms and signs
Only a specialist can diagnose candidiasis in the nose, since it has common symptoms with a cold.
Patients should consult a doctor if there is heavy nasal discharge for a long time and antiviral medications are ineffective.
Nasal candidiasis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Congestion. Difficulty breathing remains even after vasoconstrictor medications.
- Mucus discharge. Clots constantly appear from the nose; they may have an unpleasant odor or may contain blood.
- Pain and discomfort. In the nasopharynx area, a patient with candidiasis will regularly experience discomfort, especially during meals.
- Itching. The patient will regularly want to scratch his nose, this will worsen the condition as dirty hands regularly penetrate the affected area.
- Raid. A white film appears on the mucous membrane. It comes off easily, but quickly reappears.
Some patients develop white lumps from the nose during candidiasis. Because of this, the patient is regularly forced to blow his nose, he becomes irritable and cannot concentrate on anything.
Candidiasis of the nose quickly spreads to the oral cavity. As the disease progresses, inflammation affects not only the nasal septum, but also the paranasal sinuses. If left untreated, ulcers will begin to appear in the affected areas.
Treatment of nasopharyngeal thrush
It is absolutely impossible to treat candidiasis in the nose on your own - the fungus can quickly multiply and spread to internal organs, affecting the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, genitals, kidneys, or can become chronic.
If characteristic symptoms appear, you should immediately contact an otolaryngologist. To diagnose nasal candidiasis, the doctor will order laboratory tests, as a result of which he will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medications.
General scheme
Treatment of nasopharyngeal candidiasis cannot be quick - sometimes it takes several weeks or even months until complete recovery. It consists of the doctor selecting special antifungal agents depending on which type of Candida caused the disease.
In the initial stages, thrush responds well to treatment with local medications. In this case, it is appropriate to use ointments: Lamikon, Clotrimazole, Nystatin, Fluconazole. In children, Miramistin or Candide in the form of a solution is widely used to treat affected areas. Antifungal ointments are applied in a thin layer using a cotton swab.
During the treatment period, diet must be followed. The fact is that some foods provoke candidiasis of the nasopharyngeal mucosa, so it is necessary to remove sweets, flour, fatty foods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks from the diet. You cannot eat foods containing yeast: kefir, cheese, bread, yeast baked goods, drink wine and beer.
You need to give preference to white meat, fish, legumes, berries, fruits (with the exception of grapes, watermelon, bananas and melons), vegetables (potatoes, pumpkin are not allowed), eggs. Drinking plenty of clean water is important.
Nasal drops for candidiasis
In the treatment of infants and young children, nasal drops against candidiasis are widely used. Protargol has proven itself well in this regard, which can be used by both children and adults. The silver ions contained in its composition have an antimicrobial effect.
It is important to monitor the expiration date of such medicine and not use an expired one. Candide drops and Pimafucin suspension effectively fight fungus and can be used even in infants. To restore normal microflora in the nose and strengthen the immune system, probiotics Trilact and Bifidum Bug are instilled.
Other drugs
In advanced cases, tablets are also prescribed, which are used strictly according to the scheme. Antimycotic drugs include: Nystatin, Diaflu, Pimafucin, Nizoral, Diflucan. In addition to drug therapy, the nose and throat are treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide and furatsilin. Along with antifungal therapy, vitamin complexes, immunity-correcting drugs, or probiotics are prescribed.
Folk remedies
In some cases, traditional methods of treatment can completely replace drug therapy. They are safe as they contain only natural herbs and are perfect for treating children.
A good addition to standard treatment is rinsing and rinsing the nose with prepared antiseptic solutions:
- A weak solution of soda (per 1 liter of warm boiled water, 1 teaspoon of soda);
- An infused decoction of pharmaceutical herbs. Chamomile, string, St. John's wort, and calendula are suitable. To prepare it, you need to brew 1 teaspoon of the herb in a glass of boiling water and leave for an hour;
- Instillation of aloe juice. Diluted half and half with water. Well disinfects and soothes irritated nasal mucosa.
An integrated approach to treatment
Candidiasis in the nose can be cured only through an integrated approach. The doctor conducts laboratory tests, performs an examination and, based on the patient’s well-being, prescribes drug therapy. Medicines are selected that can regulate the activity of the thrush pathogen in the body, and medicines are used to increase general and local immunity.
If candidiasis is detected in a timely manner, curing the patient will be quite simple. A few weeks are enough to completely eliminate the symptoms of the disorder and improve overall well-being.
To prevent relapses, a re-examination is carried out 4-5 months after treatment.
Therapy includes systemic and local drugs. General therapy involves the use of nystatin or amphotericin B. At the initial stages of candidiasis development, the use of ointments is effective. The most popular of them are lamicol, fluconazole and clotrimazole. Antifungal drugs are applied in a thin layer using a cotton swab. They help quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
To maintain the natural protective functions of the body, vitamin complexes, immunomodulators and probiotics are used. Citrosept is prescribed simultaneously with complex medications; it has a powerful effect on the immune system.
During the treatment of candidiasis in the nose, the patient will have to adhere to a diet, especially if there is coloring of the mucous discharge and an unpleasant odor. Some foods can provoke the rapid development of thrush. Doctors recommend completely abstaining from fatty, starchy and sweet foods for a while. Alcoholic and carbonated drinks should be avoided. Yeast creates favorable conditions for the development of candida, so you will have to give up baked goods, kefir, bread and cheese.
During treatment of candidiasis, the diet should consist of white meat, fish, fresh fruits and vegetables. The only exceptions are grapes, bananas, potatoes and pumpkins. Berries, legumes and eggs are beneficial. Doctors advise patients to follow a drinking regime; the right amount of liquid will help to cope with the disease faster.
What Doctor Komarovsky says
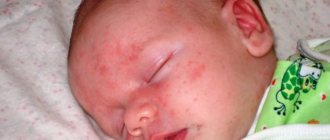
Candidiasis in the nose is often observed in newborns. This is facilitated by the presence of diseases, physiological characteristics and the presence of pathology in the mother. The child experiences discomfort and has difficulty breathing.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends that parents consult a doctor at the slightest discomfort in their baby. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to identify the cause of the disorder and determine the general well-being of the baby.
The pediatrician prescribes nasal drops for small children. Systemic medications can negatively affect the baby’s condition, since his body is not yet strong. Protargol is a safe drug. It is approved for use by adults and children. The silver ions included in the composition have an antimicrobial effect.
Pimafucin and Candida are effective and are prescribed to infants. To normalize the microflora, Dr. Komarovsky recommends probiotics: trilact or bifidum bac.