Causes of the disease
Mouth fungus most often occurs in newborns and infants
The main cause of fungus in the mouth is the action of yeast fungus of the genus Candida. This pathogen is present in the human body as part of the normal microflora. Under the influence of a number of factors, a disturbance in the balance of healthy microflora occurs and the yeast fungus begins to actively multiply. It quickly affects the most vulnerable parts of the body - the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, the gastrointestinal tract, and the genital organs in women.
Most often, newborns encounter this pathology. Causes of fungus in a child’s mouth:
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- infection with thrush from the mother;
- poor nutrition;
- weak immunity;
- imperfection of one's own microflora.
As a rule, the cause of oral fungus in babies is breastfeeding. The microflora of a newborn's mucosa is still too weak, so any irritant, including milk, can lead to a disruption in its composition. This is how inflammation appears on the mucous membrane and a fungal infection develops.
Causes of Candida fungus in the mouth in adults:
- decreased immunity;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- smoking;
- wearing dentures;
- the presence of a chronic focus of infection;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- corticosteroid therapy;
- metabolic disorders;
- hormone imbalance.
Caries is often identified as a chronic source of infection leading to the development of fungus in the mouth of an adult. The lack of timely treatment for this disease leads to a decrease in local immunity and the accumulation of bacteria that affect the mucous membrane. Against this background, the normal microflora is disrupted and the growth of the fungal colony is activated.
In adults, bad habits can cause fungal infections of the oral mucosa. Cigarette smoke irritates the mucous membrane, provokes a decrease in local protective function and is a favorable condition for the development of fungus.
Fungus in the mouth of a baby over a year old and children over two years old can be a consequence of poor nutrition. The impact of hot and cold food on the mucous membrane, abuse of sweets and a sharp transition to an “adult” diet can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, which is dangerous due to increased growth of fungal flora.
Children can also experience this disease due to poor personal hygiene. Licking dirty fingers can cause fungal spores to enter the oral cavity, which leads to the development of the disease.
Nutritional Features
A diet that eliminates foods that promote the growth of infection will help get rid of it once and for all if you consistently adhere to the right diet.
Highly salted, pickled, spicy and hot foods damage the weak mucous membrane of the oral cavity and worsen the course of the disease. Reducing such dishes in the diet, as well as switching to soft foods for people with a predisposition to stomatitis, is mandatory.
Compliance with diet therapy is necessary after completion of the treatment process for 3-12 months, depending on the degree of damage to the mucosa.
Forms and stages of fungus in the mouth
Fungus in the mouth is accompanied by severe discomfort
The fungus affects the oral cavity, gum mucosa and tongue. This disease looks like stomatitis. With fungus in the mouth, symptoms depend on the type of disease and the stage of its development. There are 4 stages:
- desquamative;
- erythematous;
- infiltrative;
- erosive.
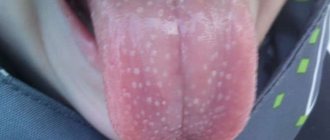
The desquamative stage of mycosis development is characterized by damage to the tongue. It reveals flat seals and a dense white coating. This plaque is quite difficult to remove with a cotton swab and quickly re-forms.
The erythematous stage of the disease is manifested by swelling of the back of the tongue. This is accompanied by difficulty breathing and loss of appetite. The plaque becomes so dense and foamy that it is almost impossible to clean it off yourself.
The infiltrative stage is manifested by a thick coating that affects the tongue, mucous membranes of the lips, cheeks, gums and palate. At this stage there is severe discomfort, significantly worsening the patient's quality of life.
The erosive stage of oral fungus is characterized by a change in the color and consistency of plaque. The entire oral cavity is covered with a thick grayish mass, upon cleansing of which painful ulcers and erosions similar to aphthous stomatitis are discovered.
Additionally, mouth fungus comes in four forms.
- Pseudomembranous fungus is most often detected in infants and older patients who wear poorly fitting dentures. The disease is manifested by dry mouth and the formation of a thick, light coating on the mucous membrane.
- Chronic hyperplastic fungus is characterized by severe swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of a rash and nodules on the tongue. The plaque covers the palate, but practically does not affect the tongue and buccal mucosa.
- Acute atrophic fungus is pronounced swelling and redness of the oral mucosa. Accompanied by severe burning, itching, pain during eating. This form of the disease is characterized by the formation of erosions and ulcers.
- Chronic atrophic fungus is a consequence of improper installation of dentures. The pathology is diagnosed mainly in elderly people. This form of the disease is characterized by pain when eating, severe hyperemia of the mucous membrane, the formation of ulcers and erosions. The white coating characteristic of oral candidiasis is absent.
Any form of the disease is treatable. The fastest way to deal with pseudomembranous and hyperplastic fungus. Atrophic fungus requires long-term systemic therapy.
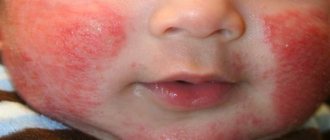
Features of candidiasis in children
Infection of the oral mucosa by fungus is common in children, but they tolerate candidiasis relatively easily and, with timely medical assistance, are quickly cured.
In most cases, infection occurs from the mother during the pregnancy stage. Infection of an infant can occur during care, both at home and in a hospital setting.
The rapid activation of the pathogen and its transition to the growth stage are caused by the physiological characteristics of age:
- the microflora of the oral mucosa is not stable;
- the output of food breakdown products is not formed;
- weak immunity is not able to cope with toxins.
Thrush can be triggered by:
- taking antibiotics;
- failure to comply with the rules for sterilizing items used to feed the baby;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, frequent regurgitation;
- 24/7 pacifier use.
Symptoms of childhood dental candidiasis do not differ from those of adults. However, if the child cannot speak, he will be able to explain what is bothering him.
An infant reacts to any painful sensations by refusing to eat and becoming very moody. The temperature rises to 39-40 degrees.
General symptoms
Oral candidiasis is a fairly common disease.
Manifestations of fungus in the mouth in adults, the symptoms and treatment methods of which everyone should know, are associated with food intake. When eating spicy and sweet foods, there is a strong burning sensation and pain in the mucous membrane. Common signs and symptoms of oral fungus in children and adults:
- light coating on the tongue;
- decreased appetite;
- discomfort while eating;
- painful reaction to hot and spicy foods.
In severe cases, a general deterioration in health may occur. Patients complain of loss of strength, nausea at the sight of food, a burning sensation in the mouth that worsens when eating food or liquid. The most severe symptoms are observed in patients who wear dentures. Due to constant pressure on the mucous membrane, in this case there is a pronounced pain syndrome.
Features of manifestation in children
Mouth fungus is a fairly common disease in infants. Damage to the oral cavity is characterized by the formation of a light plaque, which can be easily cleaned with a cotton swab or a piece of gauze. When scraping the tongue or the mucous membrane of the cheeks covered with this plaque, pronounced hyperemia of the mucous membrane is detected. In advanced cases, after the plaque is removed, painful erosions and ulcers appear.
Thrush fungus on the gums of children
Every second baby had the oral form of candidiasis in the first year of life. The disease occurs due to the imperfect immunity of the child, who is not yet “familiar” with many types of pathogens and bacteria. Candida fungi are transmitted from parents or other family members through kisses, care items and dishes. Most often, microflora enters the mucous membranes from the mother, who is a carrier of the infection. This occurs during childbirth or daily care.
The most problematic periods when gum fungus most often appears:
- breastfeeding by a mother who has thrush;
- teething;
- switching to artificial mixtures with added sugar;
- post-vaccination and ARVI.
In older children, signs of oral candidiasis may appear after suffering from the flu or other infectious disease. They greatly upset the balance of beneficial bacteria in the nasopharynx. Therefore, pediatricians recommend that parents be as attentive as possible during this period and strengthen their health with vitamins.
Local preparations for the treatment of fungus
The basis of treatment is local antifungal drugs
For fungus in the mouth, treatment is carried out with local remedies. The oral cavity is treated with solutions containing an antimycotic (Candide) or ointments active against yeast fungi - Nystatin, Candide, Clotrimazole. The ointment is applied using a cotton swab, stick or gauze roll directly to the affected area. Treatment is carried out 4 times a day.
Additionally, rinsing the mouth with solutions of iodine, fucorcin, and hydrogen peroxide diluted with water in a ratio of 1:4 is prescribed. For antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity, the doctor may also recommend chlorhexidine or miramistin. Rinse the mouth every two hours.
To treat the affected areas, you can use Yodicirin solution or Lugol's composition. These products are applied with a cotton swab every three hours.
Antiseptics should be used for at least 15 days. Antifungal drugs are used until symptoms disappear completely, and then for another week to avoid recurrence of the disease.
Systemic antimycotics
For mild forms of the disease, only ointments and antiseptics are used. These remedies are enough to get rid of the disease within a few weeks. In case of atrophic fungal infection of the oral cavity, it is necessary to additionally take antimycotics in tablets.
In the treatment of fungal inflammation in the mouth, the following is used:
- Fluconazole;
- Ketoconazole;
- Itraconazole;
- Diflucan;
- Nystatin.
These medications must be taken daily for two weeks. Fluconazole and Diflucan are prescribed at a dosage of 50 mg, Itraconazole is taken at 15 mg daily for 10 days. The dosage of Nystatin is selected individually for each patient due to the low bioavailability of this drug.
It is important not to skip pills and take them strictly as recommended by your doctor.
Folk remedies
For fungus in the mouth, traditional medicine is ineffective, due to the peculiarities of the localization of the fungal infection. To speed up recovery, you can use mouth rinses:
- decoction of calamus root;
- soda solution;
- iodized salt solution;
- garlic infusion;
- decoction of chamomile;
- sage decoction.
Additionally, you can lubricate the affected areas of the mucous membrane with lemon juice diluted in half with water. These remedies will not get rid of the fungus in a matter of days, but will protect against further progression of the disease.