Classification
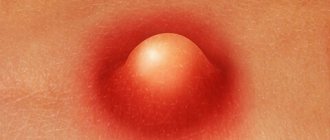
What does furunculosis look like photo
According to the course of the pathological process, acute and chronic furunculosis are distinguished. There is also a recurrent form, in which a new one quickly forms in place of a healed abscess. The course of such furunculosis is long and difficult to treat with antibiotics. Most often, this form develops in adolescents, allergy sufferers, alcoholics and people with diabetes.
According to its etiology, the disease can be primary or secondary, that is, it develops as a concomitant pathology against the background of another disease.
The clinical picture can be classic, when the body is gradually covered with numerous abscesses, or erased, in which the formation of a necrotic core does not occur.
According to their prevalence, they distinguish between localized furunculosis - damage to a separate area, and disseminated furunculosis - ulcers appear throughout the body.
What is a boil?
Furuncle (boil) is a pustular skin disease characterized by acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding connective tissue.
The main cause of a boil is a bacterial infection, mainly Staphylococcus aureus, less often white.
Furunculosis is a massive, repeated, chronic formation of boils.
The place where the boil appears can be anywhere except the soles of the feet and palms, but most often, boils form on the back of the head, forearms, lower back, buttocks, abdomen, and lower extremities. The most painful boils are in the ear, nose, face and genitals.
The prognosis for a boil is positive, but there are still complications with this disease - thrombosis, lymphadenitis, sepsis, due to which the formation of boils is considered a fairly serious disease.
Boils have a certain seasonality - most often they form in autumn and spring. In addition, doctors note that most often, boils appear in men, but in children this is generally rare.
Development of a boil
The development of a boil can occur primarily - on healthy skin and secondary, when development occurs against the background of other pathological conditions and diseases of the body, for example, staphyloderma.
The development of a boil occurs in 3 stages, the duration of which, in the absence of complications, is up to 10 days:
Furuncle stage 1 (beginning) - characterized by inflammation of the follicle, in which a solid infiltrate (compaction) of bright red color with unclear boundaries appears in a given place. At the site of the inflamed follicle, pain and tingling are felt. As the boil grows, the seal increases in size, expands, and the surrounding tissues swell.
Stage 2 boil (3-4 days) – characterized by expansion of the boil up to 3 cm in diameter, while in the center of the compaction a purulent-necrotic core with a pustule on the surface is formed. Not only the hair follicle is involved in the process of suppuration, but also the sweat gland with the surrounding connective tissue, while the vessels around it dilate and swelling of collagen is observed. The shape of the boil begins to take on a cone-shaped shape, as if it were a growing mountain. Elastic and collagen fibers inside the “mountain” are destroyed
Collagenized bundles of fibers form a thick protective ring inside the boil, preventing the infectious purulent formation from exiting into the body and its further infection, so it is very important not to squeeze out the boil without understanding the consequences of this process. The opening of the boil must be correct
Further, the skin at the site of inflammation becomes smooth, bluish in color, and the pain intensifies. In case of extensive damage to the body by infection (in the case of a large number of boils), a person may experience symptoms of intoxication, which are expressed by general malaise, weakness, nausea, lack of appetite, headaches and an increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C.
Stage 2 of boil development ends with the spontaneous or artificial opening of the pustule and the release of its contents. The contents of the pustule are a necrotic rod of yellow-green color with a purulent formation, sometimes with the addition of blood.
Stage 3 boil – characterized by the appearance of a “crater” at the site of the opening of the abscess, which is initially filled with granulations, and after 2-3 days, scarring occurs in this place. The scar at the beginning of healing is red, but as it heals it turns white and becomes almost invisible.
The entire flow cycle may be erased; for example, the entire process sometimes occurs only with the formation of infiltrate, i.e. without pus and necrosis. In other cases, the boil, against the background of weakened immunity and other diseases, acquires an abscess or phlegmonous form.
Differences in Pathogenesis
Human skin, except for the feet and palms, has a large number of hair follicles. In some parts of the body they are not activated, while in others they provide thick hair. Each such hair follicle has a sebaceous gland duct. If the sebaceous duct is affected by the inflammatory process, sebum accumulates in it, which begins to decompose, becoming an ideal breeding ground for pathogenic microflora.
Considering that the sebaceous duct itself is located close to the surface of the skin, the inflammatory process, as a rule, is extremely localized, which leads to the appearance of a small abscess. The volume of pus that accumulates under the skin when a pimple forms is no more than 2-5 ml. Such inflammatory processes, after a maximum of 2-3 days, lead to the formation of a white core, damage to which provokes the release of purulent contents.
A furuncle develops as a result of damage to a hair follicle that lies deeper in the skin. In this case, the passage to the outside is usually blocked. Against the background of a developing inflammatory process, an abscess forms inside the hair follicle, which quickly leads to the melting of the soft tissues located under the skin and an increase in the size of the boil.
Boils can reach sizes from 0.5 to 10 cm. As if floating, they increase in size until they form a rod and burst, releasing purulent contents to the surface. Boils should never be squeezed out, especially if an abscess has not yet formed. If treated incorrectly, they can cause the formation of extensive phlegmon and even sepsis, so this formation cannot be treated negligently, as is observed with the formation of usually a single pimple. It is quite simple to distinguish a boil from a pimple, because even externally both of these formations have serious differences.
Symptoms and stages of development
The boil forms gradually: first, an infiltrate (accumulation of blood and lymph impurities in the tissues) collects around the follicle. It becomes inflamed and looks like folliculitis. After a day or two, the inflammatory process engulfs the entire internal space of the hair follicle and spreads to the sebaceous gland located underneath it. The tissues around the abscess become red and swollen. A congestive-hyperemic node gradually forms inside the follicle. Gradually it begins to rise above the skin, soreness increases, which is pulsating in nature. Pus forms in the cavity of the bulb, and then a fistula.
The process of abscess formation ends with the opening of the abscess. After the upper contents pour out, the bottom of the boil becomes visible. A greenish colored rod is visible in it. Its presence is a fundamental factor for diagnosing the disease. The rod is also rejected over time, then a small portion of blood and the remains of purulent masses pour out. The inflammatory process subsides, the affected area becomes smaller, and the pain disappears.
Upon completion of the eruption of pus, a deep ulcer forms at the site of the boil, shaped like a volcanic crater. If there are remains of pus in it, after some time a boil will ripen in this place again. When the abscess ends in complete cleansing, the ulcer is gradually filled with granulation tissue, and in its place a scar is formed, pulled deep into the skin. Its width and depth depend on how deep the core of the abscess sits.
There are three forms of development of skin pathology:
- Mild - the appearance of single boils on the body is observed, along with this there is an increase in regional lymph nodes. The formation of ulcers causes moderate pain. In a chronic course, relapses occur no more than twice a year.
- Moderate – the appearance of single or multiple ulcers is noted, the formation of which is accompanied by a violent inflammatory reaction. Therefore, the body temperature rises, moderate manifestations of intoxication occur, and regional lymph nodes enlarge.
- Severe – the appearance of several small boils is diagnosed. There is no clear localization. They constantly form on the skin: some pass, new ones appear. Abscesses cause moderate inflammation, enlargement of regional lymph nodes, and the appearance of signs of severe intoxication. The patient may complain of general weakness, excessive sweating, a significant increase in body temperature, and severe headache. With such a clinical picture, it is imperative to seek medical help from a dermatologist.
The causes and treatment of furunculosis are interconnected phenomena; knowledge of how the disease is formed and how it manifests itself helps to develop the correct therapeutic tactics.
What is the core of a boil?
The core of the boil is formed at stage 2 of the disease, called purulent-necrotic. At the end of this stage, a white abscess rising above the surface of the skin, surrounded by a red inflammatory halo, is visible on the surface of the boil.
The natural process of a boil involves a gradual thickening of necrotic masses to a dense cylinder located under the covering of the abscess. The walls of the boil thicken, forming a protective membrane around the purulent infiltrate, preventing the spread of infection to the subcutaneous fat.
Under the influence of leukocytes, a dense cylinder is formed from the pus, which is pushed out, after which the healing stage begins.
Purulent exudate, located in the depths of the formation and having the appearance of a compact yellow-greenish “column”, is called the core of the boil.
The rod is a cluster of:
- Inflammatory cells.
- Secretion of the sebaceous gland.
- Epithelium destroyed during the inflammatory reaction.
- A large number of bacteria that caused the boil - staphylococci.
IMPORTANT: Trying to squeeze out a boil that does not have a white “head” on the surface, and therefore a surrounding dense capsule, is very dangerous. You can damage capillaries and lymphatic vessels, into the lumen of which purulent contents with a large number of bacteria will enter
What does it look like in the photo?
The cone can be seen after the boil opens on its own. When the abscess is opened, its cover softens and bursts, thick purulent masses leave the formed cavity, and a dense greenish-yellow column is found in the center.
And this is what the boil stem looks like in the photo.
What happens if you run it: consequences and complications
An ignored boil is dangerous because it can cause complications. In the absence of adequate treatment, the following are possible:
- carbuncle - the fusion of several boils into one large one;
- abscess (abscess boil) - spread of pus with inflammation in adjacent soft tissues;
- phlegmon - the transition of inflammation to the layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue, has no boundaries, unlike an abscess;
- lymphadenitis - the transition of inflammation to the lymph nodes;
- sepsis – infection of the bloodstream and spread of pathogenic bacteria throughout the body.
Complications arise not only when boils are ignored. They are also possible due to careless or early extrusion attempts or accidental injury.
Important Tips
When treating boils, several important rules should be followed to help speed up recovery and prevent complications:
- It is prohibited to squeeze out boils yourself - this is a huge risk of spreading infection and dangerous consequences;
- Water procedures should be excluded until complete recovery; going to the bathhouse can be forgotten until better times; even a shower is not recommended.
It is impossible to get boils wet so as not to complicate the treatment process. The only acceptable hygienic procedure is wiping healthy skin with antiseptics and baths with potassium permanganate; - to strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators are used - Interferon, Polyoxidonium, Galavit;
- The spots on the skin or bumps remaining after the boil has healed do not require special treatment; they heal over time without leaving marks.
Scars can be removed surgically or through therapy with special ointments and creams - Contractubex, Kelofibrase, Dermatix.
Fundamental differences between boils and acne
Pimples and boils seem so similar to each other to an unknowing person that it is impossible to figure out where what is. Only a doctor can find the differences by examining the site of inflammation. And they are significant. Let's look at each in more detail:
- First of all, this concerns the reasons that provoked the occurrence of inflammation. In the case of acne, there are many of them. Boils are caused by bacteria.
- When the skin becomes inflamed, a pimple appears. A boil is an already developed inflammation.
- Painful sensations. In the case of boils, they are always present, and a pimple may often not cause discomfort.
- The redness of the epidermis around the pimple is much weaker, it is smaller in size, matures faster and disappears without a trace. This inflammation is close to the surface of the skin and its temperature at the site of infection does not rise, unlike cases with a boil.
- Duration of treatment. A pimple goes away in a few days, but a boil can be treated for about two weeks if there are no complications.
- Means used in treatment. To get rid of acne faster, it is enough to use any folk remedy: various medicinal herbs, vegetable juices, decoctions. In the case of boils, it is necessary to use special ointments and creams to promote wound healing. If you have multiple rashes, you should immediately make an appointment with a dermatologist, as this can be dangerous to your health.
What pimples and boils have in common is that they should not be squeezed out, as the area of infection may increase. This is especially true for ulcers on the hair and face. Squeezing pimples in these areas can lead to inflammation of the brain.
Whichever of the rashes in question is found, it is better to consult a doctor to identify the cause. This is especially true for sudden multiple inflammations that are not an allergic reaction.
Treatment of ulcers continues for a long time. Even if a person takes the necessary measures to combat boils, they are not always effective.
Treatment of furunculosis on the face
First of all, if the initial symptoms of a boil appear on the face (that is, compaction under the skin, redness without a clear boundary), you should consult a doctor. There are methods of getting rid of the disease using folk remedies at home, and many patients also prefer to use some medications on their own. But the doctor will choose the right medicine for a particular patient based on his stage of the disease.
All diseases are most effectively treated with means in a complex, that is, including traditional and medicinal ones. Timely treatment promotes a speedy recovery.
You should contact the following doctors:
- Dermatologist.
- Therapist.
- Surgeon.
Often localization of a boil on the face leads to hospitalization and surgical intervention.
In order not to provoke complications, it is recommended to follow a diet excluding fatty, spicy foods, and alcoholic beverages.
It is imperative to disinfect the affected area as often as possible. Use alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and furatsilin solution for treatment. It is not recommended to use iodine under any circumstances; it only complicates the situation. It is necessary to treat not only the affected area, but also the skin around it.
Experts recommend ultraviolet light or laser therapy. This helps speed up skin recovery.
If a patient has developed chronic furunculosis, antibiotics cannot be avoided. They should be prescribed only by the attending physician in accordance with the type of bacteria that causes the disease.
In some cases, doctors resort to surgery. Thus, the surgeon removes all the pus from the boil. The patient is prescribed to use ointments such as Levomekol, Erythromycin.
Treatment of furunculosis on the face with folk remedies
There are many recipes for treating boils on the face at home. As already mentioned, the most effective treatment is carried out comprehensively using pharmaceutical and folk remedies. Many people prefer to use “grandmother’s” recipes. Before using them, you should definitely consult your doctor.
In complex therapy, it is effective to use tinctures and ointments. So, the affected area is treated with calendula tincture, then Vishnevsky or Ichthyol ointment is applied to it. This treatment promotes the maturation of the boil. Its core forms faster, and it also comes out earlier. The procedure should be carried out 2-3 times a day, applying the product to the skin.
When the rod comes out, you need to treat the skin with an antiseptic (alcohol or peroxide will do) to disinfect it and protect it from secondary infection.
If traditional methods do not help, you should contact a dermatologist, therapist or surgeon, so that the doctor independently examines the patient and prescribes appropriate treatment.
People use plantain to treat furunculosis. It is used fresh - the leaf is attached with a plaster to the affected area. The bandage should be changed as often as possible - every couple of hours.
Aloe is very effective and is also used fresh.
Ointments that are prepared independently at home are popular. The ointment ingredients are simple. For example, salt, honey, egg and flour perfectly contribute to the ripening of the boil.
Treatment of furunculosis on the face with medications
The doctor may prescribe antibiotics to the patient. They are prescribed at the second stage, when pus forms in the affected area, so that the patient’s condition does not worsen, and the lesion matures and is successfully cured. Antibiotics, when used correctly, protect the body from re-infection. It is strictly not recommended to select antibiotics for yourself. Doctors usually prescribe Amoxiclav and Cephalexin. Antibiotics are prescribed both oral and intramuscular.
For direct treatment of boils, ointments such as Tetracycline and Erythromycin are used. Compresses are made from them - applied to a cotton pad, bandage (gauze) and applied to the affected area twice a day. When the core of the abscess comes out, they should continue to be applied to the area around the lesion.
If the surgeon removes the boil surgically, the patient is given an anesthetic.
After opening, the skin should be disinfected and the prescribed ointment should be applied. Absorbable ointments accelerate the regeneration of the integument. These include Heparin, Contractubex.
Home medicine becomes auxiliary, it accelerates the maturation of the boil and increases the effectiveness of drugs.
How to distinguish a growth from internal inflammation
A boil differs from an abscess, pimple and manifestations of other diseases. The differences are not difficult to find if you know the symptoms and signs that indicate the disease. To treat boils, it is necessary to be examined by a doctor to determine the cause of the pathology. Self-treatment is fraught with complications.
From an inflamed lymph node
When the lymph nodes are in their natural state, they act as a barrier to bacteria and viruses.
Causes of inflammation:
- colds;
- cancer formation;
- the presence of infection in the body;
- malfunction of the mammary glands.
In the normal state of the lymphatic system, the patient does not feel the presence of internal nodes; they cannot be palpated. If pathology is present, the nodes become large in size, they are painful to touch, and movement often brings discomfort.
Inflammation of the axillary zones is often caused by boils, blood clots, and ulcers. Dangerous diseases of the oral cavity: caries, stomatitis, sore throat, acute respiratory infections. In such situations, treatment of the disease is required, then the nodes will return to their natural position.
When the hair follicles become inflamed, the following is reflected in the lymph nodes:
The danger lies in formations in the chest. Their appearance should be distinguished and urgently consult a doctor for examination.
At the stage of pus formation, the symptoms are determined:
- chills;
- temperature increase;
- throbbing pain in the area of the nodes.
It is important to understand the symptoms, they indicate the stage of the process.
In the early stages of the process, the patient is prescribed the following treatment:
- Application of electrophoresis procedures.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments, compresses.
- Chlorethyl aerosol is used.
- “Heparin ointment” is applied.
If there is an infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. The course of treatment ranges from 7 to 14 days, depending on the course of the disease.
For paraproctitis and mastoiditis
Paraproctitis differs from a boil in the acute or chronic inflammatory process of the pelvic fatty tissue that surrounds the rectum.
Causes: penetration of pathogenic microorganisms to the rectum by contact, hematogenous or lymphogenous route.
Provoke the pathology of the disease:
- hemorrhoids;
- anal fissures;
- eczema;
- contact through the anus;
- diseases of the intestines and genitourinary systems.
Subcutaneous paraproctitis can be determined by inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue of the perianal zone.
Signs of paraproctitis:
- pain during bowel movements and urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- lethargy;
- temperature 37.5 C or higher;
- painful sensations in the anus.
Treatment involves taking antibiotics on the recommendation of a proctologist, depending on the type of pathology: Cefotaxime, Gentamicin and performing an operation to remove pus.
Mastoiditis is directly related to inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone as a result of infection. Acute otitis media is a common cause of inflammation.
Signs:
- temperature;
- intoxication of the body;
- pulsation;
- redness of the area;
- edematous condition;
- pain in the ear.
Treatment of pathology with antibiotics: Cefaclor, Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime. Surgery on the middle ear will help get rid of the endogenous nature of the pathology.
Both boils and pimples are a problem that causes physical and psychological discomfort. Despite the external similarity, these are formations of varying degrees of severity and etiology. Therefore, before treatment, it is important to understand the difference between them.
Treatment of a boil on the body
A separate isolated boil in less dangerous areas (back, limbs) can go away without medical intervention. It is enough to cover the area with a gauze cloth, and when the abscess is opened, wipe the area with a disinfectant solution on a sterile cloth and apply an aseptic bandage, which should be changed daily until the wound heals.
The surgeon decides how to treat boils on the body in more dangerous locations or when complications develop.
The doctor chooses treatment tactics individually for each patient. This can be:
- prescription of antibiotics;
- local treatment;
- opening the abscess and draining the purulent cavity;
- physical therapy;
- strengthening the immune system;
- treatment of concomitant pathology.
A prerequisite for successful therapy is the exclusion of a number of foods from the daily diet. Do not use:
- smoked meats;
- hot, salty and spicy;
- fried and fatty;
- sweets and fresh sweet pastries;
- strong tea and coffee.
On the advice of a doctor, you can use folk remedies.
Treatment of a boil on the chest with folk remedies
Much experience has been accumulated in the treatment of boils on the body with folk remedies due to the popularity of the disease long before our era.
- Onions - an onion cut in half is baked in the oven. The cut is applied to the abscess.
- Aloe - apply the pulp of a leaf cut lengthwise.
- Potatoes are a paste of grated potatoes.
- Honey-rye flatbread.
- Calendula flowers are infused in oil and used as a compress.
- Burdock leaf - 5 tablespoons per glass of milk, boil, use as lotions.
- St. John's wort oil in the form of a compress.
- Plantain - 1 tablespoon of chopped leaves is poured with oil, used to lubricate the boil.
Many people consider a propolis-based compress to be the best folk remedy for boils on the body:
- 50 grams of propolis;
- 100 grams of beeswax;
- 50 grams of castor oil.
The mixture is simmered over low heat, cooled and applied to the boil 2 times a day for 20 minutes.
It is recommended to take decoctions of herbs and burdock seeds, kombucha, brewer's dry yeast, and beet juice internally.
Treatment of boils on the body with medications
Depending on the location of the boil on the body, as well as the prevalence of the process, antibiotics are prescribed.
Preference is given to semi-synthetics that belong to the penicillin series (Ampiox, Ampicillin, Amoxiclav). From other groups, cephalosporins are used (Cephalexin, Cefaclor, Cefixime), Tetracycline. They are prescribed orally or intramuscularly. The course of oral administration reaches 14 days. It is prohibited to prescribe or stop taking antibiotics on your own.
Effective pain relief is achieved by taking NSAIDs, which also have an anti-inflammatory effect. From this pharmacological group, Paracetamol, Voltaren, Diclofenac are used.
Treatment of furunculosis on the body, which has arisen due to a weakening of the body's defense reactions, requires the appointment of immunocorrectors. Herbal preparations that increase the activity of the immune system include Immunal, ginseng, and Eleutherococcus schisandra in the form of tinctures. Bacterial immunostimulants - Imudon, Ribomunil, Likopid. Drugs that affect the thymus gland are especially relevant in the treatment of boils on the body in children (Timozin, Vilozen, Timoptin). Nonspecific stimulants include Prodigiosan and Levamisole.
Complex treatment requires vitamin therapy, especially group B and antioxidants A, E, C and folic acid.
Prescribing glandular preparations turned out to be relevant. For oral use, the drugs of choice are Sorbifer, Ferroplex, Tardiferon, Novaferrum.
For hyperthermia, antipyretics (Paracetamol) are indicated.
Local treatment is carried out using antiseptic solutions (hydrogen peroxide, aqueous solution of furatsilin, chlorhexidine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate, iodine). At the infiltration stage, antibiotic ointments (Levomekol, Tetracycline, Oflocaine) are effective. The purulent core is pulled out with Ichthyol ointment, Syntomycin ointment. They are good at any stage. Heparin ointment is used as an antiseptic, antimicrobial and analgesic. At the healing stage, Vishnevsky ointment and Zinc ointment help.
Basic information about boils
Boils are purulent inflammations of the hair follicle and connective tissue with signs of necrosis (death of nearby tissues) and suppuration.
The appearance of boils is caused by Staphylococcus aureus and white staphylococci. It's not difficult to pick them up. They are found everywhere: on household items, unwashed food, handrails of public transport, entrance handles, elevators.
There is a known disease called furunculosis, when the rashes are not isolated. This phenomenon is dangerous to ignore. The consequences can be disastrous and lead to sepsis, and in advanced cases, to purulent meningitis. Self-medication of inflammation is undesirable. It is recommended to immediately contact your doctor for advice to identify a possible infection.
A boil can develop in those areas of the skin where there are hair follicles. First of all, on the face, neck, back of the hands and lower back. Infection begins with the appearance of deep red lumps that rise like a cone above the level of the skin. It is not difficult to recognize a boil by its appearance. The skin became inflamed and swollen. It looks like a nodule ranging in size from a few millimeters to a centimeter, depending on the stage of the process. A white rod is clearly visible inside the seal. There is an ulceration in the center.
Recommendations
It is quite easy to lay a floor screed with expanded clay yourself, but it is important to listen to the recommendations of specialists:
- the wires passing under the screed must be wrapped in polyethylene and secured with adhesive tape;
- It is more convenient to use metal profiles or slats as beacons;
- the final version of the screed on expanded clay should be left to dry for a month;
- systematically moisten the finished surface with water to avoid the formation of cracks;
- a plasticizer can be added to the final solution to prevent the formation of concrete cracks. It is better to clarify the proportions of expanded clay concrete for the screed with a specialist;
- You can walk on the finished surface already on the 8th day, but the screed will gain the desired strength after 1 month;
- Filling the floor with expanded clay should begin before installing any plasterboard structures, ceilings, or any materials that actively absorb moisture.
After studying the recommendations, the task will no longer seem difficult. Without professional skills in laying expanded clay screed, you can handle the job yourself by first watching training videos on the Internet.
Skin boil
Skin is the body's protective layer. She sweats and is exposed to microtrauma or damage as a result of everyday life. Many bacteria constantly live on human skin.
Photo 8 - Structure of a boil
Multiple boils are caused by staphylococcal or streptococcal bacteria. A healthy body successfully fights these bacteria, but in a weakened body, the protective barriers of the skin are disrupted, and bacteria develop more freely, stimulating the development of inflammatory processes.
Photo 9 - Furuncle behind the ear
Such a focus of inflammation in the hair follicle becomes the cause of boils on the skin.
Why do boils appear on the skin - from infection:
- due to friction from clothing, squeezing;
- scratches, wounds;
- scratched insect bite.
Boils on the body - causes and treatment
The causes of boils on the body - streptococcal or staphylococcal infection - can remain in the human body for years. Their development is suppressed by healthy immunity.
Photo 11 - Streptococcus bacteria are constantly present in the human body
But with trauma to the skin, illness, excessive sweating, and irritation, bacteria are activated, which causes inflammation to appear. The hair follicle is physiologically more “open” to dirt, sweat, and fat, which is why boils appear in areas covered with hair.
Photo 12 - Boils appear on the hairy areas of the skin
Climate change, hypothermia, stress or chronic fatigue weaken the body no less than diseases. This is why boils appear on vacation, after swimming in the sea, after a nervous shock or passing difficult exams.
Photo 13 - Boils may pop up due to stress or fatigue
Advice on how to treat boils is based on removing the immediate source of inflammation and subsequent disinfection of the wound opening. The next stage of treatment is to combat the cause of the abscess.
Photo 14 - For the boil to disappear, the pus must be removedTraditional medicine offers many ways to deal with boils, how to treat an abscess at the initial stage - compresses from baked onions, rye bread, raw potatoes, iodine, sauerkraut juice with sour cream and others. All these measures are designed to speed up the maturation of the abscess and the release of the contents of the pustule.
Photo 15 - At the initial stage, the boil can be treated with folk remedies
One of the proven ways to get rid of furunculosis and restore the body is to take brewer's yeast for at least 2-3 months. Yeast can be tableted or diluted in water.
Photo 16 - Brewer's yeast - a folk remedy for treating furunculosis
A proven remedy for treating purulent slings or boils is aloe. It is applied to the abscess overnight, secured with a bandage. These measures are quite effective for small, undeveloped boils.
Photo 17 - Aloe juice can help at the initial stage of furunculosis
Photo 18 - The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment to get rid of boils
By taking blood and/or the contents of the boil for analysis, the doctor will determine the source of the infection, which will help make the correct diagnosis of the root cause of the abscess. Based on the diagnosis of the underlying disease, medications will be prescribed, and at the same time, external abscesses will be treated. Most likely, antibiotics or sulfa drugs will be prescribed.
Photo 19 - Blood test will determine the source of infection
Measures aimed at preventing boils
If a person has already become familiar with boils, he will do everything in his power to avoid encountering them. Some suffer from these inflammations throughout their lives. This is truly a problem that cannot be ignored. To determine the cause of skin infection, consult a doctor.
Prevention has been developed to prevent boils. It includes:
- Balanced diet. If a person has skin problems, it is important for him to understand what foods he eats. You should not overuse fatty, salty, spicy, sweet dishes, and baked goods. It is important to exclude smoked foods, coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks. If a number of conditions are met, the skin will become noticeably healthy. A nice bonus is losing a few kilograms.
- Taking care of skin cleanliness. Clean the skin as it becomes dirty with napkins. Wash with gel or soap. It is a good idea to use alcohol-containing wipes. Women with problem skin should avoid foundation and powder, which clog pores. We must not forget that hygiene is important for maintaining health.
- Skin treatment after hair removal. To avoid infection, wash your skin thoroughly with soap and water before the procedure. And then wipe with alcohol. This measure helps to avoid serious troubles.
- Boosting immunity. It is recommended to maintain a healthy daily routine. Go to bed early, rest more and breathe fresh air, spend less time on the computer and other electronic gadgets. After going to the doctor, take the vitamin complex he prescribed. Add hardening and water procedures to your daily life.
These rules will help not only avoid skin problems, but will improve the health of the entire body, which will thank the owner for his responsible attitude and self-care.
Video about boils:
Carbuncle
When several hair follicles are involved in the inflammatory process and inflammation spreads into the subcutaneous fatty tissue, a carbuncle develops. The name carbuncle comes from the Latin carbo - coal. In Rus', the disease was called ognevik or uglevik.
The localization of the process and the stages of development of the carbuncle are similar to those of a boil. Golden and white staphylococci are the main culprits of the disease. Failures in the functioning of the immune system contribute to the development of carbuncles, which occurs in patients with severe somatic pathology, diabetes mellitus, obesity, hypovitaminosis and hypothermia.
Rice. 17. With a boil (photo on the left), one pustule forms on the surface of the infiltrate, with a carbuncle - several (photo on the right).
Rice. 18. The photo shows carbuncles on the chin and neck in the collar area.
Signs and symptoms of carbuncle
The disease occurs with severe symptoms of intoxication: chills, elevated body temperature, weakness, loss of appetite and headaches; vomiting and loss of consciousness are less common.
Local symptoms:
- Initially, the skin over the affected surface becomes purplish-red. There is severe pain.
- After a few days, several pustules appear on the surface of the skin.
- The thinned skin breaks out in several places and resembles a “sieve.” Thick pus oozes from the holes.
- When the carbuncle is opened, an ulcerative surface with purulent discharge and several necrotic rods is exposed.
- After the rods are rejected, a deep wound (ulcer) with a dirty gray bottom is exposed. The edges of the wound are undermined. Ulcer healing is slow. In its place, a deep star-shaped retracted scar forms.
Smear microscopy confirms the diagnosis. Culture of pus allows you to identify the pathogen and determine its resistance to antibiotics. The disease lasts from 2 to 4 weeks or more.
Rice. 19. The photo shows a carbuncle. Superficial pustules and multi-chamber abscesses are visible, on the surface of which there are numerous holes resembling a “sieve” through which pus is released.
The main causes of a boil on the back
Common causes of boils are the presence of wounds, abrasions or burns on the back. Pathogenic bacteria quickly penetrate the follicles located in damaged areas of the skin.
Doctors explain why boils appear on the shoulder blade or in another area of the back.
The list of predisposing factors included:
- intense sports activities;
- improper hygiene - overdrying and traumatizing the skin with a washcloth and detergents;
- living in an area with a hot, humid climate;
- puberty;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- menstruation period;
- diabetes;
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- incorrectly composed diet - excess of sweets, fast food.
Psychological reasons are also possible. Psychosomatics is a complex of factors, including self-doubt, frequent conflicts, and isolation. This can equally trigger the formation of boils in men or women.
There is a version that a boil on the back is formed after the evil eye. In this case, it is recommended to remove the damage with spells and rituals. Such methods have nothing to do with traditional medicine.
Pharmacy products for getting rid of boils
Often, conservative treatments alone are not enough for effective treatment. Pharmaceutical drugs in various forms are widely used for the treatment of furunculosis. The most popular include ointments, antiseptic solutions and broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Ointments
Ointments belong to the products used externally.
When treating furunculosis, the following are common:
- Ichthyol ointment. The active substance is ichthyol. It must be used when the abscess is already ripe. It has an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, healing and analgesic effect. Apply a thin layer with light movements to the affected area. It is strictly forbidden to aggressively rub the ointment in order to avoid complications. Cover the top with a gauze bandage or a wide bandage and leave for 5-6 hours.
- Levomekol ointment. The product contains two active components: chloramphenicol (has an antibacterial effect) and methyluracil (a powerful wound healing agent). Can be used in children of all ages and pregnant women, since the active ingredients are not absorbed into the systemic circulation. When the abscess matures, it is applied in a thick layer over the skin. The dressings are applied for constant wear and changed two to three times a day. When the abscess breaks through, it is necessary to fill the entire cavity from which the pus will come out with ointment. An excellent combination remedy for treating boils at home.
- Vishnevsky ointment. In addition to the bactericidal effect, it has a strong pulling property. Recommended for use during the abscess, before it has broken through. After the pus comes out, it is advisable to change it to any antibacterial ointment, for example, erythromycin.
- Erythromycin ointment. Contains the antibacterial agent erythromycin, which has a powerful effect against staphylococcus - the main causative agent of the infectious process in furunculosis. It is advisable not to use it in children under three years of age and pregnant women due to the possible development of side effects.
Antiseptic solutions
They are designed to disinfect damaged surfaces from pathogenic microorganisms. The most commonly used:
- chlorhexidine bigluconate;
- furatsilin;
- oil solution of chlorophyllipt;
- dimexide solution.
Antibacterial therapy
To cure uncomplicated furunculosis, systemic antibiotics are not used. However, in severe cases of the disease, extensive skin damage or the development of complications, general antibiotic therapy is used.
To carry it out, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are often chosen:
- Penicillins. These include drugs such as Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Ampicillin. These substances have been used for a very long time, proving their effectiveness. They actively influence the causative agent of the disease - staphylococcus and have bactericidal properties. The most commonly used drug from this group is Amoxiclav, which contains amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. The combination of active ingredients helps to cope with the resistance of some forms of the pathogen. Can be used in tablet form.
- Cephalosporins of all four generations. The most common drugs include Ceftriaxone and Cefatoxime. These are strong broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. They are used only intravenously, so they are more often used in hospital treatment.
- Lincomycin. Antibiotic of the lincosamide group. It differs from previous groups in its narrow spectrum of action on the pathogen. At the same time, it is highly effective in the treatment of boils caused by staphylococci and streptococci. It has bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties. The effect of the treatment occurs quickly.
- Fusidine sodium. The active ingredient is fusidic acid. It has a bacteriostatic effect and exhibits high activity against the causative agent of the disease. There is practically no resistance to this drug. Rarely causes adverse reactions in the form of dyspeptic disorders.
The prescription of an antibacterial agent, regimen of use and dosage should be carried out only by the attending physician. This is necessary to carry out the most effective therapy and to avoid the development of adverse reactions.
Conservative treatment methods
Conservative methods of treating furunculosis can be used in mild to moderate severity of the condition, as well as in the absence of complications. If a boil occurs, it is advisable to consult a surgeon for consultation and provision of qualified medical care.
If the condition does not pose a risk, your doctor may recommend the following treatments:
- physiotherapeutic effects on the lesion site;
- application of compresses;
- carrying out medicinal baths.
Treatment of boils with physiotherapeutic methods
To influence the affected area, the following are used:
- Dry heat. It can be used only at the healing stage, when the abscess has already broken through. For heat, you can take available means (bags of salt, water-salt heating pads).
- Ultraviolet irradiation. Used at all stages of abscess development. It has a pronounced bactericidal effect and reduces the risk of complications. In addition, it actively promotes the regeneration of damaged tissues during the healing stage.
- Laser therapy. Helps destroy pathogenic microorganisms on the surface of the affected area, improves the condition of the skin after an abscess breaks out. Has an analgesic effect.
- Ozone therapy. It is possible to use ozonated antiseptics to wipe inflamed tissues.
Application of compresses
In the traditional treatment of furunculosis at home, compresses are used based on two principles:
- Warming. It is made on an alcohol basis. Effective in relieving inflammation, accelerates the process of boil maturation. To carry it out, you need to moisten a cotton swab in a heated alcohol solution (no more than 40% alcohol to prevent burns to the surface). Place the moistened swab on the affected area and secure tightly with a gauze bandage. After 20-30 minutes it can be removed. It is advisable to use it already at the initial manifestations and repeat 2-3 times a day.
- Saline. Recommended for use from initial manifestations until the abscess breaks out. Designed to pull the purulent head out. To prepare a concentrated saline solution, add salt to a glass of warm water until it stops dissolving in it. Then moisten a cotton swab and apply it to the boil, securing it with a bandage. Application time up to three hours, can be applied two to three times a day. After the compress, ichthyol ointment can be applied to the affected area.
Carrying out therapeutic baths
Therapeutic baths can be used both locally (only on the affected area) and for the whole body. The second method is preferable, since it affects not only the affected area, but also helps fight the spread of infection to healthy tissue.
To carry them out the following can be used:
- Sea salt. We recommend 50 grams of sea salt per 10 liters of water. Temperature is approximately 37-38 degrees. Application time: 15-20 minutes.
- Coniferous solution. Pine needles have a pronounced antiseptic and bactericidal effect on the skin.
- Burdock decoction. The leaves of the plant are poured with boiling water and infused for about 30-40 minutes, after which the infusion is added to the bath.
How to eliminate boils?
Since it is quite simple to distinguish a pimple from a boil by the extent of the process, anyone can determine the degree of danger of an abscess developing under the skin. When examining the affected area of the skin, the presence of severe redness and swelling is immediately revealed. The skin where the boil forms becomes very thick to the touch after a few days. When such a formation appears, it is best to immediately consult a doctor, since in some cases the purulent contents will not be able to find a way out, and the necessary measure is prompt opening of the abscess. To prevent the development of various complications and restore the health of the skin, the following drugs are prescribed;
- antibiotics;
- multivitamin complexes;
- immunomodulators.
After opening a large boil, compresses are also required to help heal the existing wound. In cases where the cavity of the boil and the volume of purulent contents is small, in order to eliminate the formation, the affected area is first treated with an antiseptic, for example salicylic alcohol or furacilin. Next, apply a compress with Ichthyol ointment. This ointment promotes the formation and breakthrough of the boil shaft.
After the boil breaks out, the danger remains.
In order to remove all the pus from the existing cavity, compresses are applied with Vishnevsky ointment, which helps draw out the pus from the wound. Bandages need to be changed at least 2 times a day. Throughout the entire period of treatment, a person suffering from furunculosis must take broad-spectrum antibiotics. The course of antibiotic treatment is prescribed by a doctor individually and can last from 7 to 14 days. The most commonly used antibiotics include the following:
Before applying a new compress, it is necessary to thoroughly wash off the remaining ointment and purulent contents with a soap solution and treat with antiseptic agents. It is necessary to apply compresses with Vishnevsky ointment until the color of the skin is normalized and the healing of the existing wound begins. After the boil begins to heal, it is necessary to continue treating the skin with antiseptics and undergo a course of antibiotic treatment.
You can distinguish a boil - an abscess resulting from an infection in the hair follicle - on your own. At an early stage of development it is easy to eliminate. When the condition is neglected, furunculosis appears. The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the hair follicles with the presence of pus, provoked by Staphylococcus aureus. Once in the fatty layer under the skin, inflammation of the follicle occurs. Boils continue to spread to areas of the skin, and a chronic form occurs.
Symptoms of chronic furunculosis
Most often, the disease occurs in a relapsing form - when, after a period of imaginary well-being (remission), signs of the disease reappear.
The course and manifestations of the disease are determined by the degrees of severity:
- Mild degree - single boils occur that do not cause a violent local inflammatory reaction, and the general condition is moderately disturbed. Exacerbations occur once or twice a year, during which regional lymph nodes, that is, those located next to the boils, can become inflamed.
- Moderate severity - single or multiple boils appear. A pronounced inflammatory reaction develops locally, which is accompanied by severe pain. Exacerbations occur one to three times a year. As a rule, they are accompanied by enlargement of regional lymph nodes, a moderate increase in body temperature and minor signs of disturbance in the general condition of the patient (headache, weakness, malaise).
- Severe degree - multiple small boils appear on the skin, which appear one after another. At the same time, they do not cause a pronounced local inflammatory reaction (the rod may not form), and the nearby lymph nodes slightly enlarge or remain unchanged. However, the disease is severe, and the condition of patients is sharply disturbed: severe weakness, sweating and headache occur, body temperature rises to high levels, and performance decreases.
Causes of boils
Regardless of where the boil appears, its cause may be:
- decreased immunity;
- previous skin viral infection;
- minor skin trauma that can occur when scratching, due to uncomfortable clothing, industrial factors or chemicals;
- avitaminosis;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body;
- high blood sugar levels;
- obesity;
- high activity of the sebaceous glands;
- anemia;
- diseases of the nervous, endocrine and vascular systems;
- problems in the functioning of the stomach, intestines and liver.