Genital warts HPV in men and women. Genital warts are medically called genital warts and are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
At the initial stage of development, a papillary growth appears, soft and non-painful to the touch.
In the process of changing the composition and functioning of epithelial cells, the virus begins to divide uncontrollably, occupies large areas, resulting in the appearance of genital warts.
The growth sites are located on the mucous membranes of the genitals, around the anus, and the oral cavity.
It is transmitted through close contact with the skin of an infected person. The virus can stay in the body for a long time and not bother a person; a decrease in immunity provokes the growth of papilloma.
Some formations are benign, others mutate into malignant ones.
- Symptoms of genital warts
- Why are genital warts dangerous?
- Causes of genital warts
- Genital warts in pregnant women
- Treatment of genital warts
- Prevention of genital warts
What it is?
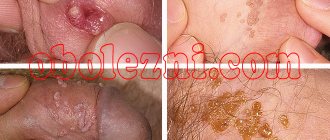
Anogenital warts are growths protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes that appear on the genitals or in the anus.
They are formed after infection with the human papillomavirus. In total, more than a hundred types of the virus are known, and it can also cause ordinary warts. They differ from anogenital ones in location and form on the skin of the palms, knees, fingers, protrude above it, feel compacted to the touch, and can grow together. The types of virus that cause anogenital warts are not associated with cervical cancer. In 70% of cases it is caused by a number of other types of pathogens. However, such neoplasms require monitoring and treatment by a dermatologist or venereologist. Read more about it in our article “Human papillomavirus”.
How is this disease treated?
Today, it is completely impossible to rid a person of the papilloma virus, and all the methods used by doctors are based on reducing its activity and stopping clinical manifestations.
Treatment involves:
- physical or chemical destruction of growths;
- taking antiviral drugs;
- taking cytostatics;
- taking immunomodulators.
In most cases, Panavir is prescribed as an antiviral agent; interferon and its inducers are prescribed to increase local and general immunity.
Cytostatics are recommended for condylomas of the external genitalia; a good drug is Podophyllin, which is used topically.
When it comes to removing growths, the following methods are most often used:
- classic removal with a scalpel;
- electrosurgical techniques;
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction.
Chemical removal is based on the effect on growths of various aggressive substances - acids, alkalis and their combinations. The following substances are used:
- Triacetic acid.
- Solcoderm.
- Podophylloctoxin.
- Epigen.
Transmission routes
Both adults and children can become infected with the human papillomavirus. In adults, the most common route of transmission is through sexual intercourse. Infection can occur through contact with an affected area of skin. The types of HPV that cause anogenital warts can also be transmitted through anal sex. Using condoms reduces the risk of infection, but does not completely eliminate it. People who frequently change sexual partners are at risk.
Important! Infection with the human papillomavirus is possible even from a person with an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Children become infected with HPV in several ways. If a pregnant woman is infected, the virus can be transmitted to the baby during childbirth. Prenatal transmission (before birth) is rare. Infection is also possible through contact with affected areas of the skin.
Types of warts
HPV can cause several types of skin lesions.
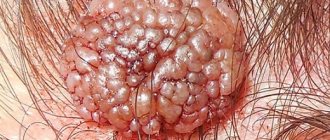
Condylomas acuminata
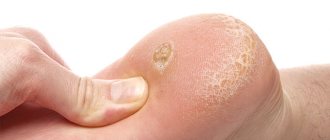
Neoplasms protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. They may consist of nodules with a loop-like structure, the surface may be variegated. Their appearance may be accompanied by discomfort and itching (not in all cases). Condylomas are localized in the groin, perineum, anus, and genitals;
Papular rash
They look like a rash, are flat, almost do not protrude above the surface of the skin, and are localized in the same way as genital warts;
Stains
Areas of discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes of the genitals (grayish-white or red spots appear);
Bowenoid papulosis
A sexually transmitted disease, which is accompanied by the formation of many nodules of discolored color (brown, gray, red) on the mucous membrane and skin of the genital organs. Later, such nodules merge into large papules;
Giant condyloma
Papillomas merging with each other (look like small warts), forming a large lesion.
Figure 1. Condylomas and warts. Source: CC0 Public Domain
The appearance of warts and other growths due to HPV may be accompanied by discomfort and itching. In rare cases, the affected areas of the skin may crack, bleed, and become painful.
Possible complications
Complications of the pathology can be:
- bleeding from a neoplasm (usually develops due to mechanical damage to growths, including shaving, during sexual intercourse);
- the addition of a bacterial infection with the development of a purulent process;
- papillomatosis (multiple papillomas);
- malignant degeneration.
There are types of papillomavirus with high and low degrees of oncogenicity. Common strains cause the development of warts and papillomas. Highly oncogenic strains are detected in 50–80% of cases of moderate and severe dysplasia, which are precancerous conditions, as well as in 90% of cases of invasive cancer.
With malignancy, the neoplasm grows, ulcerates, and bleeds.
Concomitant sexually transmitted diseases contribute to the progression of pathology. In this case, persistent inflammatory changes in the organs of the genitourinary system may occur. Also, a combination of infections can complicate the treatment of pathologies, increase the duration of therapy, and increase the risk of relapses.
Risks during pregnancy
In women infected with the human papillomavirus, pregnancy can provoke the appearance of anogenital warts and their growth. The virus can cause abortion. The mother can transmit the virus to the child during pregnancy (rarely), during childbirth (more often), and during subsequent contacts. For a newborn, HPV is dangerous due to damage to the respiratory tract (development of respiratory papillomatosis, breathing problems, voice formation).
To reduce the risks associated with HPV when planning pregnancy, it is advisable to undergo preventive examination and treatment when the virus is detected. If pregnancy has already occurred, treatment is performed before 36 weeks, using laser or cryodestruction, electrocoagulation to remove tumors. If there are extensive lesions, operative delivery is recommended to reduce the risk of infection to the baby.
Establishing diagnosis
How can you tell if you have these warts? Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves in different ways, but most often it is pain during lovemaking, a burning sensation, itching, and there is also discharge mixed with blood. If you have genital warts, you can see or feel them.
But the final diagnosis is made by the doctor after examination. He is required to carry out a number of procedures:
- Examine the anogynetic area. When examining women, Cusco speculums are used to see if the vagina or cervix is affected. If necessary, other procedures are prescribed: meatoscopy, urethroscopy, anoscopy.
- Make a test with acetic acid (a 3% solution is used). After treating anogenital warts with it, they turn grayish-white for a couple of minutes. But this method also gives a false positive result. But it is necessary to establish the boundaries of the tumor if surgical treatment is prescribed.
- Carry out a histological examination if there is a suspicion that these neoplasms may be malignant. Often performed on people over forty years of age.
The patient will not be able to make a diagnosis on his own, if only because there are similar diseases.
Acetic acid will help determine the boundaries of the wart
Diagnostics
You should consult a doctor if neoplasms, nodules, compactions, or areas of discoloration appear on the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs or anus.
During the examination, the doctor will evaluate the clinical manifestations and examine the affected areas.
To confirm and clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests may be performed:
- PCR diagnostics with determination of the genotype of the virus; it is additionally possible to determine the degree of viral load. Biomaterial – vaginal smear, scraping from the urethra, cervical canal.
- Morphological, cytological examination to assess the risk of oncological pathology.
The severity of the condition is assessed by the number of tumors, the volume of affected tissue during examination and laboratory testing (the number of copies of HPV DNA in the test samples is determined).
Important ! Anogenital warts are treated using destructive methods (cryodestruction, laser destruction, electrocoagulation). In this regard, before treatment, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis are required.
Diagnosis is carried out by specialists from dermatovenerology departments. Additionally, consultations with specialized doctors may be required:
- a urologist if the tumors are localized inside the urethra;
- a proctologist if warts grow extensively in the anal area;
- obstetrician-gynecologist when planning and managing pregnancy;
- immunologist (for relapses of the disease or immunodeficiency states).
Symptoms
The pathological process can occur without any symptoms; pain occurs only during sexual intercourse. But there are manifestations of more obvious symptoms.
There are 3 known forms of the disease:
- carriage of the pathogen;
- subclinical manifestations;
- clinical manifestations.
During carriage of the virus, it can only be detected through clinical diagnostics. There are no obvious symptoms at this stage.
The subclinical manifestation of such neoplasms is detected during the necessary diagnostics and tests. When laboratory signs appear, the examination will no longer be a difficult task.
Genital warts are made of soft tissue. At the initial stage of the disease, a slight red rash appears on the skin near the intimate organs.
On this topic
- Warts
All about removing warts with nitrogen
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
The rash does not go away for about 2 weeks. Then it transforms into colonies that resemble flat or irregularly shaped cauliflower inflorescences. It can be multiple or single.
In females, neoplasms are often located near the vagina, anus, and labia. In certain situations, such growths form on the cervix. In males, warts form on the scrotum, near the anus and on the head of the penis.
Children can become infected from a carrier mother through the transplacental route. These warts can form in the throat or other parts of the body.
Their appearance is associated with intense itching, redness and inflammation of the skin. In certain situations, bloody or white discharge from the intimate organs is observed. Painful discomfort occurs during sexual intercourse, and the process of urination is disrupted.
If warts are detected in the groin, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo a full examination.
Treatment
The main direction of treatment is the destruction of anogenital warts. In 70-80% of cases, after removal of tumors they do not reappear. Several methods are used for destruction.
Electrocoagulation
Destruction of neoplasm tissue under the influence of high frequency current. Around the area of the neoplasm, extensive thermal damage to tissue occurs (formation of a dry crust). After it heals, there are no traces of exposure left on the skin.
Laser destruction
Laser exposure at a controlled depth to remove tumors within clear boundaries. Once the wart tissue is destroyed, there is no bleeding and there is no need to close the wound.
Cryodestruction
Destruction and removal of tumors using liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of ultra-low temperature, instant tissue necrosis occurs, followed by rejection and wound healing.
Radiosurgery
It involves the generation of a high-power radio wave that passes through the tumor tissue, destroying it.
If the area of damage to the mucous membranes or skin is extensive, it is possible to remove the tumors surgically. With any method of destruction, the affected area is disinfected and anesthetized before the procedure.
It is also possible to use chemical and cytotoxic methods for the destruction of anogenital warts. For this purpose, local drugs are used that gradually destroy the tumor tissue. Such treatment requires caution and can only be carried out as prescribed by the attending physician.
Important! Attempts to remove anogenital warts on your own can be dangerous: you can injure healthy tissue, cause infection, and provoke the growth of tumors. If the wart was torn off by accident, you need to treat the affected area with an antiseptic, stop the bleeding, and consult a doctor.
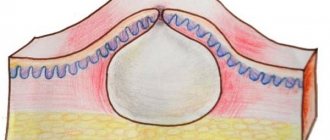
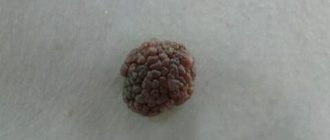
Figure 2. Structure of a wart. Source: CC0 Public Domain
In addition to methods of destruction of anogenital warts, local immunomodulators and nonspecific antiviral drugs can be used.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of anogenital warts, you need to reduce the risk of HPV infection. To do this, they exclude casual sexual intercourse and use barrier methods of protection.
An obligatory part of prevention is vaccination:
- for women, a two-, four- or nine-valent vaccine is used with a single or double revaccination;
- For men, a quadrivalent or ninevalent vaccine is used.
Vaccination to protect against HPV infection is recommended to begin in childhood. Immunization for girls can be performed from 7 years of age, for boys - from 9 years of age. For girls, HPV vaccinations are especially important because of the risk of cervical cancer associated with the virus.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies for anogenital warts can only be used with the permission of a doctor; most often, experts do not object to these remedies, but it is believed that folk treatment can only be used as an additional therapy.
Benign neoplasms are lubricated by:
- celandine juice;
- juice of sour apples;
- castor oil;
- a mixture of olive and tea tree oils.
Decoctions, infusions and tinctures of medicinal plants are also used, which enhance immune defense. In most cases, a tincture of Echinacea purpurea or Eleutherococcus is recommended.