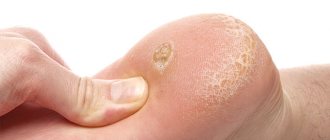
Fat deposits, more often referred to in the field of practical medicine as “lipomas,” are pathological growths of adipose tissue, characterized by a pronounced external manifestation in the form of a subcutaneous neoplasm that is soft to the touch.
A particularly common location for wen is the abdominal area. This is quite simple to explain; it is in this area that the largest number of fat cells are located.
Lipomas have the status of a benign neoplasm that has no tendency to degenerate into malignant tumors, but in fairness it should be noted that in exceptional cases this is still possible. To remove fatty deposits, invasive and conservative methods of therapy are used. The choice of treatment regimen depends on the characteristics and location of the lipoma.
General characteristics of the disease
Preperitoneal lipoma is a lump of fatty epithelium located between the wall of the abdominal cavity and the abdominal muscle fibers. A neoplasm of the anterior abdominal wall of the abdomen differs from a preperitoneal lipoma in its location between the muscle fibers of the subcutaneous layer and the absence of a direct effect on the activity of internal organs.
The retroperitoneal fatty tissue is formed from atypical adipose tissue cells with the presence of septa made of connective tissue fiber. A lipoma on the abdomen is often confused with a hernia. Unlike a lipoma, a hernia is a protrusion of an internal organ into the skin area through weak areas in the abdominal wall. Surgical manipulations on the abdomen, excessive physical activity, or congenital formation can provoke the development of a hernia. A hernia is dangerous due to pinching of nearby tissue organs, followed by necrosis of the affected tissues and the development of severe consequences in the absence of medical care - gangrene of the organ, death of the person.
Lipoma on the stomach
A lipoma on the abdomen does not threaten the patient’s life until active growth or an inflammatory process inside the capsule begins. It is impossible to determine the nature of the preperitoneal formation before histology. Therefore, if there is pathology in the abdominal muscle, you need to consult a doctor for advice.
The ICD-10 code for the disease is D17.7 “Benign formations of adipose tissue in other locations.” The neoplasm develops mainly in adults after 30 years of age. Women are more susceptible to pathology than men. In a child, a lump inside the abdomen is rarely diagnosed.
Why is it dangerous?
As a rule, wen is not dangerous to children's health. However, depending on its location, certain problems may arise.
Thus, when a formation forms in the scalp area, there is a risk of damage, against which an inflammatory process or suppuration may begin to develop.
If the abdomen becomes the localization site, then the appearance of an abscess cannot be ruled out.
Large lipomas can cause sepsis and mental disorders.
The mechanism of pathology formation
Wen on the anterior wall is common and is benign in 95% of diagnosed cases. Complex neoplasms affecting internal organs or the peritoneal area occur in 5% of patients. A lipoma inside the abdomen can transform into a malignant form - liposarcoma.
Preperitoneal formations are pathological diseases with the development of severe complications during growth. Epigastric hernia, or hernia of the white line of the abdomen, is the process of formation of gaps between the connective fibers of the central part of the abdomen, through which adipose tissue is excreted and protrusion of internal organs under the abdomen is observed. It is characterized by painful growth and requires urgent surgical excision.
Pathology is formed mainly in the umbilical cavity, which determines the following varieties:
- supra-umbilical view is located in the area above the navel;
- the peri-umbilical form is localized in the navel itself or near the ring - on the side;
- The infraumbilical view is diagnosed below the umbilical region.
It can be detected by chance during ultrasound examination of the peritoneum. Preperitoneal lipoma is considered the initial form of epigastric hernia. The soft tissue tissue of the abdomen forms a defect in the form of a gap in the wall, which leads to the removal of fat and the subsequent formation of a hernial sac. The muscles continue to stretch and cause the omentum to accumulate with areas of the small intestine. This gradually turns into the formation of a hernia.
Description
Wen is a benign tumor formation formed from connective tissue.
Lipoma in a child develops in the subcutaneous layer of fibrous structures. If their growth is noted, bone tissue may be damaged.
In a baby, they may appear around the eyes, in the area of the chin, on the forehead and cheeks.
On this topic
- General
What is a cancer examination
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
Externally, the neoplasms resemble white pimples with no purulent contents inside the cavity. Sometimes lipomas can appear as acne.
It is also worth noting that the wen in a child after birth disappears on its own after a month and a half. If this does not happen, then you need to consult a pediatrician or dermatologist.
Causes and signs of pathology formation
Fibrolipoma in the abdomen or navel can provoke a dangerous process of muscle stretching, which is accompanied by the formation of gaps and a hernial sac, which, with severe physical exertion, turns into a hernia. Several factors can trigger the disease. The peritoneum is responsible for protecting the internal organs.
The causes of the pathology may be as follows:
- excess body weight;
- pathology of the endocrine system – diabetes mellitus, pancreatic tumors;
- malfunction of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of sex hormones;
- hormonal imbalance;
- hereditary predisposition;
- injury to an internal organ with the wall of the abdominal cavity;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- unhealthy diet – predominance of fats and proteins.
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by a secretive nature - no obvious signs are observed. The first symptoms appear with an active increase in the volume of pathology and the hernia sac. Compression of nearby organs, vessels and tissues leads to disruption of functional actions and malfunction of an individual organ or an entire system. The location near the intestine causes a disruption in the organ's motility and leads to the development of chronic or acute intestinal obstruction.
Localization
Lipoma can affect any part of the body. More often, wen appear where the subcutaneous fat layer predominates.
Nose
Wen are small in size, up to one millimeter. Localized on the back or nasal wings. Externally, the neoplasms look like pimples and have a white head. Can be single or multiple.
Neck
They are often located in this area, and also affect the deep layers of tissue. The child must be observed by a specialist at all times. If a lipoma growth is observed, it is recommended to remove it as soon as possible. This is explained by the risk of the tumor squeezing important vessels located in this area.
Face
Wen, which are localized on the chin or cheeks, are small in size. They do not cause any inconvenience to the child. In most cases, such lipomas disappear on their own. The main thing is not to take any independent measures to remove them.
Scalp
The wen will resemble a bump, which is quite mobile, with a soft consistency. The disease is not dangerous to children's health and does not require special therapeutic measures.
If the tumors are large, they must be removed. However, the operation is indicated only for children over two years of age.
Limbs
Single formations more often appear on the arms and legs. If the lipoma does not grow and does not change the condition of the skin, then there is no need to rush into surgery.
Eyelid
Wen that forms in the eye or eyelid area, as a rule, does not reach large sizes. However, despite this, they can negatively affect the quality of visual function. It is important that the child is under medical supervision.
Ear
If the formation is localized in the inner ear, it often leads to hearing loss or complete loss.
Shoulders, back or stomach
In these areas, wen can grow to impressive volumes. In this case, the child will experience discomfort. Such tumors must be removed.
Gum tissue
Such situations occur quite often, especially in newborns. The spontaneous disappearance of the pathological process is observed after teething.
Possible complications of the disease
In the absence of medical care and the presence of accompanying factors, a fatty tumor can degenerate into an oncological formation - liposarcoma. At the benign stage, the disease does not spread to neighboring and distant areas, remaining within its own capsule. Liposarcoma is characterized by active metastatic spread to distant areas of the body, which causes massive disruption of organic processes. The transformation of atypical cells can be triggered by mechanical damage to the diseased area, exposure to radioactive substances or aggressive ultraviolet radiation; interaction with chemical compounds.
Growth to large sizes is accompanied by the following dangerous consequences for the patient:
- A hernia on the anterior wall of the abdomen is actively developing with the process of pinching the intestinal loop, which requires urgent removal of the tumor and the affected part of the intestine.
- Pressure on internal organs is accompanied by certain disturbances in the functioning of a particular system - it depends on the location of the node.
- The effect of a large compaction on blood vessels can lead to blood stagnation and subsequent tissue necrosis.
Therefore, doctors advise that if you have suspicious symptoms or a formation in the umbilical area, do not delay your visit to the clinic. The initial stage of the disease is easy to treat and allows you to avoid the development of serious complications.
Should I delete it?
The decision to remove a lipoma must be supported not only by the desire of the patient or doctor, but also by clinical data obtained as a result of the examination.
Wen is characterized by the unpredictability of its growth: in some cases it reaches only 0.5–3 cm and does not grow any further, in others it quickly grows to 30 cm or more . With a minimal size of the wen, if over a long period of time it does not increase in volume and does not cause discomfort, then they adhere to observation tactics , leaving it untouched.
As a rule, such neoplasms can remain the same size throughout life.
The indications for mandatory removal of a tumor are:
- the location of the tumor leads to compression of organs or blood vessels, as a result of which their functioning is disrupted;
- superficial type of lipoma that has a stalk. When it twists, the tissue of the wen begins to die, provoking inflammation in the soft tissues of the abdomen;
- tumor pain;
- lipoma of any size, acting as a cosmetic defect;
- an increase in the size of the wen up to 10 cm or more. Its large size will cause disruption of metabolic processes in surrounding tissues.
Photo: a giant wen removed from the patient’s abdomen. The operation process is filmed in the video posted below.
Surgical removal
The main treatment for lipoma is its surgical removal.
Depending on the type of pathology and the volume of growth, one of several methods can be chosen:
- Standard removal of the wen along with the capsule by cutting the skin of the affected area.
- Removal is minimally invasive, which is carried out using a miniature endoscope. The operation is performed through small punctures, in which only the fatty tissue is removed, while the capsule itself remains in place. This procedure does not guarantee complete removal of the pathological tissue, which may result in the formation of secondary lipoma growth.
Dietary recommendations during chemotherapy for lung cancer. A list of foods that will help the body recover. Myoma disease: here are reviews of herbal herbal treatment.
Follow the link https://stoprak.info/vidy/nexodzhkinskie-limfomy/diffuznaya-v-krupnokletochnaya.html clinical picture of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma stage 2.
The most preferable option is complete removal of the wen using the standard method, as it allows the pathological tissue to be completely removed and reduces the risk of relapse.
The removal procedure lasts from 15 to 40 minutes , depending on the volume of the tumor. The operation is carried out in several steps:
- Anesthesia . The operation is performed under local anesthesia, which is achieved by injecting a solution of novocaine or lidocaine into the soft tissues.
- Treatment of the pathological area with aseptic preparations.
- incision . For small tumors, an incision is made along the central line of the lipoma. If the tumor is large, then an incision is made at its base, retreating from the border towards healthy skin by no more than 1 cm.
- The skin is pulled as far away from the center of the lipoma as possible, exposing it, and then fixed.
- A scalpel is used to circle the wen from all sides in order to completely destroy the ligaments connecting it to healthy tissues.
- Subsequently, the tip of the lipoma is grabbed with a clamp and pulled up, removing it along with the capsule. If a large formation is being removed, it is first divided into several parts, which are then removed in turn.
- After removing the capsule, the resulting cavity is washed with an antiseptic and sutured, after applying drainage. It will ensure the outflow of fluid that may accumulate in the cavity. The drainage is left in place for no more than 3 days, then it is removed.
Self-absorbable threads are used to suture the wound. To prevent divergence of the edges of the operated area, both external and internal sutures are applied.
When removing a voluminous lipoma, a nurse must be present in the office during the operation with equipment and facilities to provide resuscitation care.
The operation does not require further hospital stay, as it is low-traumatic. During the period of tissue healing, the patient must regularly visit the clinic for dressings for 10 days. In the first few days, this procedure is carried out daily, and as the wound heals, their frequency is reduced.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient must completely abstain from physical activity and visiting a bathhouse or sauna.
In this video, doctors filmed a unique case - the removal of a huge wen from the abdominal cavity, which weighs several kilograms:
Laser removal
Removing a lipoma with a laser is essentially the same surgical method, only in this case, instead of a scalpel, a less traumatic laser is used. It reduces the likelihood of infection and eliminates blood loss.
In addition, rehabilitation after laser use lasts no more than 7 days. When using this technology, scars and pigmentation of the skin are practically not formed. The removal procedure is carried out in the same order as during a standard operation.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence of a suspicious lump in the navel or side of the abdomen against the background of accompanying symptoms requires urgent treatment. To decide on the choice of removal method, the doctor must accurately establish the diagnosis. The patient is prescribed procedures to examine the entire body to identify pathologies:
- The doctor performs a physical examination and collects an extensive medical history.
- The peritoneal area is examined by palpation, which makes it possible to determine the location of the node with approximate boundaries.
- It is recommended to do a general blood and urine test to identify deviations in the indicators of the main elements.
- Additionally, the patient can be sent to donate blood for tumor markers - this makes it possible to confirm or refute the malignancy of the disease.
- Ultrasound examination reveals the location of the node, shape, size and degree of organ damage.
- An X-ray of the stomach is prescribed to detect ulcerative pathologies and tumors.
- Gastroduodenoscopy is required if intestinal disorders are suspected.
- Ultrasonography examines the deep layers of the lipoma.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography provide detailed information about the disease with the ability to obtain images in 3D projection.
After a complete diagnosis of the patient and receipt of all test results, the doctor can accurately diagnose and choose a method for excision of the pathology.
Symptoms of lipoma on the abdomen
Signs of the condition at an early stage of development:
- the structure of the tumor is soft;
- has clear boundaries, the shape can be round or oval;
- there is no pain when pressing;
- color yellowish or white;
- growths can be multiple or single.
Age does not affect the occurrence of wen. The growth of the compaction is slow, which reduces the likelihood of timely detection of a lipoma.
Treatment of the disease
Lipoma of the preperitoneal zone is treated only with surgery. Drug therapy or traditional medicine are not able to cope with the tumor. The wen must be removed at any stage of formation. Timely and correct diagnosis and subsequent treatment can prevent relapse of the pathology. Removal is recommended to be carried out at the initial stages of tumor formation - this will eliminate the presence of possible consequences for deterioration of health.
Abdominal surgery to remove a wen is prescribed when a large node is detected affecting a large area of the peritoneum with complications. The procedure is quite painful and traumatic. After excision of the lipoma, the patient remains in the hospital for 5 to 10 days under medical supervision. Tissue restoration lasts up to 1.5 months.
The endoscopic method of cutting out a tumor involves introducing a special instrument with a built-in camera into the peritoneal cavity through small incisions. The surgeon performs manipulations to excise atypical tissue, monitoring the process on a special monitor. The patient goes home after the operation on the 3rd day. The body's recovery is faster.
Can it be cured with folk remedies?
A small wen in the preperitoneal cavity will help to remove folk remedies. You should not try to treat an inflamed, painful, or rapidly growing tumor on your own. Be prepared for relapses. The capsule of the cone remains under the skin, this causes the growth of new, often multiple cones larger in diameter than the first.
At home, compresses and masks made from food products, herbs, vodka, and spices are used. Pharmacy products: iodine, hydrogen peroxide, antiseptic ointments, absorbable balms. Home therapy usually lasts several months. No one guarantees a good result or excludes harm.
Folk remedies will only help in the treatment of subcutaneous preperitoneal lipoma. It will not be possible to cure retroperitoneal disease on your own.
Prevention of pathology
To prevent the development of preperitoneal lipoma, doctors advise adhering to a number of rules:
- Balance your diet - increase plant fiber, vitamins and microelements, fermented milk products and water.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks and nicotine.
- Take daily walks in the fresh air.
- Don't give up physical activity.
- Avoid injury.
- Undergo routine medical examinations and medical examinations.
Taking simple measures and monitoring your own health will help you avoid many dangers and death. At the first suspicion of illness, you should go to the clinic and do not self-medicate - this can lead to adverse consequences!
In what cases are pharmaceutical drugs used, and in what cases is surgery performed?
The use of a special substance (micropreparation) for introduction into the lipoma capsule is most suitable in cases where the growth is small in size. This allows you to guarantee complete resorption of the formation. When the lipoma is large, there is a possibility that the reaction will not occur completely, and the cells will soon grow again.
Also, surgery is a more effective method in cases where dynamic growth of the lipoma head is noticed. Firstly, resorption from the drug occurs over several months. And under these circumstances, such a phenomenon is not acceptable for the patient. Secondly, a rapid increase in growth may indicate the beginning of degeneration into a malignant tumor. In this case, immediate intervention is necessary.
Another indication for surgery is lipomatosis. When the digestive organ is sufficiently damaged by the growth of fatty tissue, conservative treatment is out of the question. Urgent surgery is needed to clear out the stomach tissue. Moreover, the procedure is quite painstaking and requires a lot of experience and precision from the surgeon.
The use of drugs is also unacceptable in the presence of allergic reactions to substances of a similar spectrum.