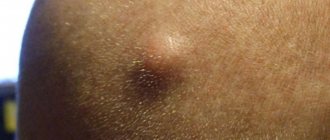
What is a wen?
A fatty tumor (fatty tumor) is a tumor that arises from connective tissue and has a benign etiology. Wen develops in the subcutaneous layer of connective fibers, but with intensive growth they can penetrate into the space between muscle fibers and reach bone structures.
In a newborn baby, wen (milia) can cover the entire face or appear in separate areas: around the eyes, on the forehead, chin and nose. Externally, they appear as white pimples, with no purulent contents. In some cases, milia can resemble acne.
Note! Wen in a newborn goes away on its own 1-1.5 months after birth. If this does not happen, it is necessary to show the child to a dermatologist or pediatrician.
Causes
The main reason for the growth of adipose tissue lies in the disturbance of lipid metabolism in the body. However, in newborns, wen can also appear due to other factors. For example, the formation of a lipoma can be caused by complications during pregnancy, such as vitamin deficiency, hormonal imbalance, or an exacerbation of an allergic reaction. A predisposition to wen can be hereditary. The reason may also have purely external influences:
- improper baby skin hygiene,
- use of synthetic diapers and clothing.
In addition, skin growths may depend on the individual characteristics of the child. For example, excessive skin sensitivity or immaturity of the skin can lead to excessive blockage of pores, and as a result, the formation of lipomas. There is an opinion that children develop wen as a reaction to changes in the environment, especially emotionally.
Types of formations and their localization
All wen are movable, closed-type pimples that are white in color. Upon palpation, the doctor can detect the lobular structure of the formation. In total, experts distinguish four groups of wen, which do not have significant differences, except for the choice of treatment tactics.
- Milia.
Small white nodules that appear most often in groups of 6-8 pieces. In children, milia are localized on the wings of the nose, frontal and temporal areas.
- Xanthomas.
Movable white wen of large size (can reach 1-1.5 cm), which appear in areas with thin skin. In children, this is the bridge of the nose, the space around the eyes, the area between the eyebrows. When palpated, xanthomas can move, as they have a movable structure.
- Lipomas.
This type of wen is formed in the deep layers of subcutaneous fat and often grows into the space between the muscle layers, reaching the bone and connective tissue. They can appear on any part of the face.
- Xanthelasmas.
Formations, most often localized in the area of the upper eyelid. They have a yellowish color and a random flat shape. The structure is soft and flexible.
Only a specialist can correctly determine the type of formation and draw a conclusion about the need for medical or surgical treatment. In most cases, lumps in children go away on their own, so therapy for this type of benign tumor is rarely prescribed.
Symptoms
There are no symptoms at an early stage. The child does not feel itching, pain, or discomfort. As they grow, the symptoms do not change, unless the tumors reach large sizes and do not contribute to compression of internal organs, tissues, nerve endings, and blood vessels.
Clinical manifestations change dramatically with inflammation of neoplasms due to the tenderness of the skin in children and the high rate of spread of infectious agents:
- Redness of the skin around the lesion;
- Increased body temperature;
- Severe swelling;
- The appearance of pus and new pathological nodes.
In case of inflammation and the addition of intoxication syndrome, a mandatory visit to a doctor is required. If the infectious process spreads quickly, urgent hospitalization may be required.
Why wen appears on a child’s face: reasons
The main reason for the appearance of wen in children is the improper functioning of the sebaceous glands, which results in blockage of the ducts. This is a physiological state of a newborn baby, which normalizes by 2-3 months, so specific treatment is not required in this situation.
Some doctors believe that lipomas can appear due to impaired metabolism - in this case, the child must be shown to a pediatric endocrinologist to rule out severe congenital diseases.
The release of female hormones in the mother's body before the onset of labor can also affect the functioning of the sweat and sebaceous glands, causing them to become blocked. If pimples do not become inflamed or fester, there is no need to worry about their occurrence.
In older children, lipomas can be caused by the following factors:
- unbalanced diet with a large number of flavors, preservatives, flavor enhancers and other chemical additives;
- excess body weight;
- diseases of the genitourinary system (for example, chronic pyelonephritis, which affects about 35% of children aged 3 to 12 years);
- physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle).
Doctors do not exclude the influence of a hereditary factor. If parents encountered milia or lipomas in childhood, the likelihood that the pathology will manifest itself in the child is more than 50%.
How to treat?
To eliminate long-lasting or subcutaneous wen in a child, you need to contact a specialist.
A small wen appears even on the face of a child under one year of age. It is mainly localized on the nose or eyelids and looks like a pimple with white, hard contents inside. Most often, such pimples are associated with a malfunction in the hormonal system of a recently born baby. After some time they go away on their own. What you should absolutely not do is remove them mechanically, squeezing them out with two fingers or piercing them with a needle. You need to show the child to a dermatologist, who will prescribe a treatment plan, if required.
A subcutaneous wen on the back of a child’s head, around a child’s neck, on the head can only be removed through surgery, since there are many blood vessels in this area, and the resulting formation, even of a small size, can interfere with their normal functioning. A lump on a child’s chest also requires surgical intervention, especially if it is a little girl. Education may cause deformation of the mammary glands in the future.
How to remove it using conservative therapy?
If the child is still small, and the formations have appeared recently, you can try to get rid of them with the help of conservative treatment. Education is treated with therapy and medications. It is also used if the lipoma has already been removed or to prevent its reappearance. But there is a risk of tumor recurrence. The conservative method includes:
- the use of ointment, which is used to treat the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- eating foods high in fiber and vitamins, which improves the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Removing formations
When the age of the child allows, or the formation puts pressure on important arteries or vessels, such as a wen on a child’s head, surgical removal of the tumor is performed. Radical therapy allows you to remove formations, avoiding possible complications and, in most cases, without leaving scars at the site of lipoma removal. The doctor decides which method of removing a wen in a child is based on the patient’s medical history, the size and location of the tumor.
| Wen removal method | Action |
| Mechanical | A needle is inserted into the tumor and its contents are drawn out using a syringe. This method of removing a lipoma can lead to its reappearance, since the sac in which the fat collected remains under the skin. |
| Laser | It leaves no scars and removal is less painful compared to other methods. The laser evaporates the sebum, leaving a crust at the site of formation, which disappears on its own after 10 days. This removal method is suitable if there is a wen on the child’s nipple or on the genitals. |
| Scalpel | Does not lead to re-occurrence of the formation, but leaves behind scars. |
Folk remedies
If the wen has appeared recently and is small in size, they try to remove the wen using traditional methods. You should never heat it, pierce it or massage it. At the first manifestation of pain, a change in the appearance of the formation, its redness or growth, you should stop self-medication and consult a doctor. It is recommended to treat with the following folk remedies:
- Cut the aloe, apply it to the formation and secure the bandage. Repeat until the wen opens on its own and its contents come out.
- Mix baked grated onions with grated laundry soap, wrap in a gauze bandage and apply to the formation 3 times a day.
When a lipoma is inflamed, it can come out on its own - this is not uncommon, and you should not be afraid of it. In this case, the resulting contents are sent to the laboratory for histological examination and accurate diagnosis. It is worth noting that removal of a lipoma in a child will be effective and will not recur if the tumor is exfoliated in a calm, non-inflamed state.
Diagnostics
To determine the type of formation, the child must be shown to a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist. In most cases, a visual examination and medical history is sufficient for diagnosis. In severe cases, the doctor will prescribe additional examinations and consultation with specialized specialists. This may be needed if:
- the wen is large in size;
- the lipoma is located on the neck, mucous membranes of the mouth (gum tissue) or in the ears (auditory canal);
- signs of a purulent-infectious inflammatory process appeared.
For any type of formation, the child is prescribed biochemical tests of urine and blood to exclude the possibility of renal pathologies or diseases of the endocrine system. In some cases, ultrasound diagnostics may be required.
What types are there?
There are several types of lipomas:
- Diffuse lipoma does not have a connective tissue capsule, so the boundaries of the wen are not clearly defined.
- Angiolipoma contains blood vessels and mature fatty tissue. It is yellow in color and can be painful. In rare cases, it can develop into a malignant tumor.
- Atypical lipoma is localized only in areas with brown fat: on the neck, in the axillary and interscapular areas.
- Liposarcoma is a variant of malignant lipomas. This tumor is dangerous because it can metastasize.
Surgical treatment of lipoma
The use of surgical methods is justified if the lipoma is large or growing rapidly.
The risk increases if the tumor is in the neck, as it can block important blood vessels.
The situation is the same with wen located in the ears: if the wen begins to grow, it can block part of the auditory canal and reduce hearing acuity.
In some cases, changes may be irreversible, so parents should not refuse the proposed surgical treatment if such indications exist.
There are several methods of radical therapy that will help remove fatty tissue in childhood.
- Laser excision.
Using a special laser knife, the lipoma and its capsule are excised from the connective tissue. The operation can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. For children under 10 years of age, use of the method is recommended only if there are serious indications. Some clinics do not perform this operation on adolescents under fourteen years of age.
- Electrothermocoagulation.
This is the cauterization of the tumor with electric current. This treatment method is considered effective only for small lipomas, since it is not always possible to control the complete removal of the tumor. If the pathological tissue is not completely excised, the chance of recurrence will be about 38-40%.
- Aspiration method.
A special needle with a thin tube is inserted into the formation, through which the doctor pumps out the contents of the capsule. The method is also not effective enough, since there remains a risk of refilling the capsule.
Important! Surgical treatment of lipoma in childhood is used only in the absence of effect from conservative therapy or in the presence of serious indications. In all other cases, experts advise fighting milia (if necessary) using medications.
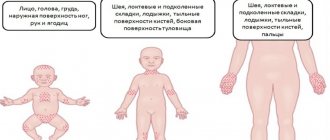
Localization location
Wen can appear on any part of a baby’s body, and you shouldn’t be afraid of them.
However, lumps in some places can cause certain inconvenience to the child, causing him anxiety and irritability. In the first days of a baby's life, lipomas can form in the head and face area. Usually, it is precisely this localization of neoplasms that causes concern among parents, and in addition, it significantly spoils the appearance of the baby. Before the age of 3 months, children often develop wen:
- on the nose (the so-called milia of the newborn);
- in the eye area;
- around the lips;
- on the cheeks.
Such lipomas do not require treatment, as they resolve on their own over time. You just need to carefully monitor the child’s condition and do not allow him to scratch the wen.
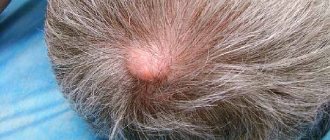
Lipomas on the forehead or scalp can be quite dense due to the deep location of the fatty tissue in these areas. But even dense wen, as a rule, is not removed until the child reaches the age of five.
Lipomas located on the baby's neck or ears require special attention. The growth of such wen can lead to serious complications: disruption of normal blood circulation due to pressure on blood vessels, hearing impairment, and so on. Therefore, you need to monitor the size of the wen in these places. The same applies to lipomas around the eyes.
Wen that appears on the baby’s body often causes discomfort, especially when it comes to the baby’s chest or back.
Wearing tight clothing aggravates the problem, so it is possible that lipomas in these areas will require removal if they continue to grow.
A wen that pops up in the genital area will cause a lot of inconvenience, but due to its delicate localization, surgical intervention is undesirable. Lipomas on the arms and legs, as a rule, do not interfere and therefore do not require treatment.
How to get rid of lipoma with medication?
For the conservative treatment of milia and lipomas, topical medications are used. Children can use “Ichthyol ointment” or “Vishnevsky Ointment”.
They prevent inflammation and infection of formations, draw out pus and promote restoration of the epithelial layer and wound healing. The drugs are used according to the following scheme:
- apply a small amount of ointment to the wen and cover with a cotton pad, leaving overnight (repeat the procedure for three days);
- two days - break;
- Repeat the procedure again for another three days.
In some cases, to get rid of the problem, the doctor may suggest injecting medicine directly into the tumor. This is done using a thin needle. This method has its pros and cons. The advantages include the absence of scars after lipoma resorption, which is especially important when treating formations that are located on the face. Among the disadvantages, experts highlight the following:
- insufficiently effective (about 25% of lipomas recur after such treatment);
- duration of therapeutic result (more than 2 months);
- impossibility of use for tumors larger than 2 cm.
Important! Treatment must be combined with diet. It is necessary to exclude spicy and fried foods, any canned food, marinades, and sauces from the child’s diet (with the exception of tomato sauces and dressings). Butter baked goods should be consumed in limited quantities no more than once a week.
Preventive actions
Experts recommend following the tips described below from birth to prevent the development of tumors in a child:
- physical activity appropriate for the child’s age (gymnastics, massage);
- a diet with plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits for the mother if the baby is breastfed;
- timely implementation of hygiene procedures.
It is strictly prohibited to get rid of benign tumors in a child without consultation. Careless manipulation can cost the newborn's health.
Skin care after wen removal
For several days after removal, the problem area must be treated with a cotton swab soaked in iodine or any alcohol tincture (you can use calendula or St. John's wort).
This is necessary to disinfect the skin and prevent re-infection. For this purpose, medicinal antiseptic solutions, for example, Miramistin or Chlorhexidine, work well.
After removing the wen, it is important to maintain facial skin hygiene. While the baby is small, instead of washing, you need to wipe the skin with a cotton swab dipped in boiled water. The procedure must be repeated 2 times a day (further - as necessary, for example, if the child spits up or gets dirty).
Varieties of tubercles
The type of pimple can be determined independently by its appearance and effect on the child’s well-being.
Even if, after conducting a self-diagnosis, you come to the conclusion that your children are affected by wen, you still take your child to the doctor next weekend.
Do not panic if you discover that a wen is not a wen at all, but a dangerous purulent pimple on the gum. Gather the necessary things, call the doctor and go to see him and your child in the next few days. In the early stages, treating teeth and gums is easier for both the doctor and the patient, and the effectiveness of treatment doubles.
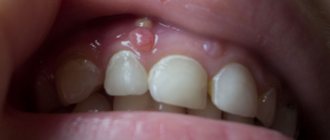
Wen on a child's gum
Wen is formed from adipose tissue. It does not cause pain or discomfort, often goes unnoticed and is usually discovered by chance. There are cases when several wen grow next to each other. Wen is considered a common occurrence on the skin of an infant. At your appointment, the doctor will recommend doing nothing with the wen - if it is located on the face, as it will go away on its own. If necessary, lipomas can be easily removed - but not with your own hands.
- When trying to remove a pimple on your own, you can accidentally cause an infection, and a scar will remain in place of the pimple.
- The symptom of herpes appears as a small blister or pimple. Newborns and older children experience a sharp loss of strength and pain in the affected areas of the gums.
- Stomatitis occurs in several forms. The mucous membrane of the mouth and sometimes the skin of the hands are affected. Stomatitis is accompanied by headaches and loss of strength. With the herpetic form, purulent pimples appear on the body, which quickly burst, leaving behind ulcers. With candidal and catarrhal forms, a white coating appears on the mucous membrane.
- Cyst - looks like an inconspicuous white pimple on the gum. The appearance of a purulent pimple is associated with improper treatment, filling and perforation of teeth. Advanced disease leads to destruction of bone tissue.
- The listed bumps are most often white, but a pimple can be not only white. Red pimples are evidence of severe inflammation caused by poor treatment and gingivitis.
Prevention measures
Experts still cannot say exactly what exactly provokes the formation of milia and lipomas, but it has been proven that following certain recommendations significantly reduces the risk of their occurrence. These include:
- correspondence of physical activity to the age of the child;
- maintaining a balanced diet, which includes all vital food groups (meat and fish, cottage cheese and dairy products, fruits, herbs, berries, nuts, vegetables, cereals, etc.);
- proper care of the child’s skin and compliance with hygiene standards.
Wen in children is an unpleasant cosmetic defect that most often goes away on its own and does not require specialized treatment. In no case should you press or pierce the milia yourself, as this can cause inflammation and infection of the tumor.
Any treatment should be prescribed only by a specialist after examining the child and studying the test results.
How to remove a wen from a child?
Further tactics depend on the localization of tumors in the child.
There are several features of lipomatous nodes depending on their location:
- A lump in the neck area requires dynamic monitoring, since its growth can provoke compression of the lymph nodes and regional vessels;
- When a lipoma appears on the head, temples, forehead, it is necessary to observe, and with growth and development, removal is carried out in early preschool age;
- Wen on the back does not pose a particular threat; wait-and-see tactics are acceptable;
- If lipomatous nodes are localized on the abdomen, near the navel , the risk of the formation of a hernial sac and dysfunction of the intestinal tract increases;
- Growing and persistent axillary lipomas require removal, as they tend to spread rapidly and compress the lymphatic and glandular ducts;
- Wen on the legs also require observation; removal is carried out at a later age, especially when lipomas are localized in the popliteal region, on the heel and pads of the toes.
Lipomas on the face are also observed, since small pimples go away on their own without complications. New growths on the eyelids and eyebrows are removed. Lipomas may appear on the gums, but this is usually associated with teething.
Treatment tactics are chosen in each individual case.
In no case should parents solve the problem of a wen on their own by piercing or cauterizing:
- Firstly, all this is unlikely to bring the expected therapeutic result.
- Secondly, self-medication often leads to even greater complications, including sepsis, severe burns, and extensive damage to the skin.