How to distinguish a lymph node from a wen is a pressing issue caused by incorrect self-diagnosis of patients. Having felt a “playing” ball under the skin, a person makes a diagnosis - inflammation of the lymph node, atheroma or boil. To avoid such situations and properly treat the resulting formations, you need to understand the differences in possible diseases that lead to the appearance of external defects.
What is a wen and its differences from a lymph node
A fatty tissue (medically called lipoma) is a benign neoplasm that develops from adipose tissue cells. The reasons for the appearance are most often violations of the body's metabolic processes, in particular lipolysis, endocrine pathologies, diabetes, etc.
The lymph node, in turn, is a peripheral organ of the lymphatic system. Acts as a so-called “biofilter”. All lymph coming from human organs flows through them. Most often, lymph nodes are located in groups. Such collections of lymph nodes are called regional. By structure, lymph nodes are oval, round or bean-shaped. These structures play an important role in the functioning of the immune system. Lymph, which flows from various organs, carries with it various foreign agents. Immune reactions occur in the lymph nodes, thanks to which human health is maintained.
Treatment
When the lipoma is small, grows slowly, does not become inflamed and does not cause subjective discomfort, it can simply be observed without any treatment. In other cases, it is necessary to decide on the appropriate correction.
Surgical removal
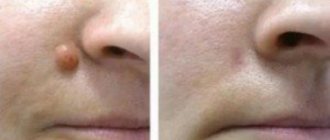
The most suitable and only correct method of treatment is to remove the wen surgically. The operation is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia (in children). The indications include the following:
- Rapid growth in education.
- Compression of surrounding tissues.
- Suspicion of malignant transformation.
- Severe aesthetic discomfort.
An incision is made directly above the tumor area, after which the lipoma is removed and the bleeding vessels are cauterized. The wound is sutured with a regular or cosmetic suture, after which the scar will become almost invisible.
What to do in case of inflammation?
If the lipoma is inflamed, then the treatment tactics change. First, it is necessary to eliminate the acute process: remove the pus (if any), apply bandages with antibacterial ointments, and treat with antiseptics. And only after this can the remaining tumor be removed in the usual way.
Is it possible to massage?
It is necessary to understand that a lipoma, although a benign tumor, is prone to enlargement and transformation into sarcoma. Therefore, you need to handle it carefully. A light massage in the form of stroking, of course, will not harm, but it is better to refrain from more intense effects. It is not recommended to intensively rub the area with the wen, subject it to strong pressure and kneading.
What should the diet be like?
There is no specific diet for lipomas. However, taking into account the risk factors for its development, it is still worth making some adjustments to the diet:
- Limit animal fats and smoked foods.
- Eat less sweet and spicy foods.
- Eliminate harmful products (with chemical additives, fast food).
- Consume enough vegetables and fruits and liquids.
Summarizing the above, we can recommend a healthy diet for lipomas, which takes into account the basic needs of the body, without excesses and frankly harmful substances.
How to get rid of it using folk methods?
Adherents of traditional methods can also find suitable remedies used for lipomas. Among such recipes are:
- Compresses from ivy tincture.
- Grind garlic in vegetable oil.
- Applications of red clay.
- Lubricating with lamb fat.
- A mask made from a mixture of herbs (aloe, golden mustache, wild rosemary, coltsfoot).
What is the difference between the symptoms of inflammation of a wen and a lymph node?
It is worth noting that inflammatory processes can occur both in the wen and in the lymph nodes. If the causes of inflammation of the wen are not reliably known, then in the second case they are well studied. Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs for a variety of reasons:
- when an infection enters the body (viruses, bacteria, fungi);
- with parasitic infestation;
- oncological diseases of the immune system;
- with metastasis of various malignant tumors
We recommend reading:
- Wen on the nose
- Atheroma of the scrotum
- Papilloma on the face
There are some features of inflammation of the lymph nodes. These include:
- increased size of lymph nodes;
- the surface may remain smooth or acquire a bumpy structure;
- the consistency of the lymph nodes can be dense or soft;
- in some pathologies, lymph nodes can adhere to surrounding tissues and become immobile;
- the skin that is located directly above the lymph nodes may become hyperemic and swollen.
In turn, the symptoms of lipoma inflammation are:
- significant increase in size;
- redness and aching pain;
- when pressing on the wen, sharp pain may appear and a sensation of the presence of fluid in the capsule of the neoplasm
What can cause a wen to form on the neck?
Despite the fact that today there are a huge number of ways to treat pathology, all the causes of its occurrence have not yet been established. Each case is individual, and there are situations when doctors have to spend a long time figuring out why a wen appeared in a particular person. As a result, it turns out that the reason is established for the first time.
In any case, before you find out how to treat a wen on the neck, you need to familiarize yourself with at least the common causes. Among the standard reasons are the following:
- Changes in hormonal levels for any reason. Wen can form during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, lactation, and so on. All of these reasons have one common factor - changes in hormonal rhythm. This affects the basic processes, as a result of which the adipose tissue becomes inflamed.
- Genetic inheritance. Wen can occur if there were people in your family affected by this pathology. This is especially true in cases where the mother or father has had lipomatosis. This is a pathology in which wen quickly spreads throughout the body.
- Nervous system disorder. All processes occurring in the skin are closely related to elements of the nervous system. Therefore, any even the slightest disorder can cause lipoma.
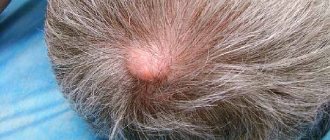
How to distinguish a lipoma from a lymph node in a child and an adult
How to distinguish a wen from an inflamed lymph node? It should be noted that both children and adults are susceptible to the formation of lipomas. By external signs, both in a child and an adult, benign tumors of adipose tissue and lymph nodes are very similar to each other and it is often difficult to determine which particular formation it is. However, both one and the other have certain characteristics that distinguish them from each other. The wen looks like an inflamed lymph node. All other signs indicate their differences:
- When pressure is applied to the lymph node, painful sensations occur. This will not happen when you press on the wen.
- The occurrence of a lipoma can go unnoticed for a long time due to the fact that it does not manifest itself in any way (there is no pain or other sensations, there is no increase in body temperature).
- Lipoma can be located on any part of the body, wherever fatty tissue is present. Lymph nodes are located regionally and in groups (for example, a group of submandibular lymph nodes, inguinal lymph nodes, etc.).
- Another difference is that the size of a lipoma can reach 10 cm or more, while the size of the lymph nodes is much smaller.
Classification of lipomas
There are several signs by which cervical wen differs from each other. These include:
- structural features of lipoma;
- location;
- involved tissues and inclusions;
- plurality.
On the contrary, the proliferation of connective tissue, causing the tumor to harden, gives rise to a dense, or fibrous lipoma. Further saturation of fat with calcium salts forms petrified (fossilized) wen.
The seizure of a blood vessel by the wen leads to the formation of cavernous angiolipoma. The involvement of nerve fibers creates a perineural formation. Muscle fibers in the tumor are a characteristic sign of myolipoma, while the presence of periosteum makes it possible to diagnose an ossified (ossified) wen.
A fatty formation located under the skin that has captured the sweat glands is called adenolipoma. Single lipomas can be located on any side of the neck: front, back, sides, directly under the jaw.
Wen can form on any part of the neck. More complex and dangerous types of cervical wen have some localization features.
Dercum's disease, or painful lipomatosis, forms multiple tumors on the neck, head and upper back. Many of them are associated with nerve endings, and therefore can cause unpleasant sensations.
Ringed lipoma of the neck (symmetrical lipomatosis, Launois-Bansaud syndrome, Madelung syndrome, Madelung fatty neck) is a rare condition that affects men 30 times more often than women. It appears as a rapidly growing “collar” of fatty tissue around the neck. The pressure from the lipoma can be so intense that breathing and speech become difficult.
A characteristic picture of Madelung syndrome developed in a patient with alcoholism. Bichat's hump, also known as the “widow's hump,” is a massive lipoma on the back of the neck, located opposite the seventh cervical vertebra (C7). With rapid growth, it can impede the flow of blood through the vertebral artery.
Consequences of inflammation of the wen and lymph node
Inflammatory processes occurring in the wen are an unpleasant complication of the disease. It is not recommended to operate on an inflamed lipoma. Not all surgeons will undertake an operation in the presence of inflammation. Before performing surgical procedures, you must first get rid of the inflammation. Treatment of this situation is not difficult. For this purpose, various ointments and preparations from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Vishnevsky ointment and Ichthyol ointment are also used. However, you should not self-medicate. The inflammatory process needs to be diagnosed by a specialist and the selection of an adequate treatment method. The outcome of this complication is most often favorable.
Doctors call this condition as inflammation of the lymph nodes lymphadenitis. As mentioned above, there are a huge number of reasons due to which inflammation of the lymph nodes develops.
There are specific and nonspecific lymphadenitis. The cause of specific inflammation is a severe infectious disease (for example, AIDS, syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.).
Secondary lymphadenitis is caused by pathological processes resulting from pathogens entering the human body. To treat lymphadenitis, it is first necessary to diagnose and identify the primary disease and separate it from cancer. Elimination of lymphadenitis is aimed at curing the primary source of infection.
Conclusion
Inflamed lymph nodes are very similar to fatty tissues.
However, it is still possible to distinguish a lipoma from an inflamed lymph node. Inflammatory processes of both lymph nodes and lipomas are painful conditions that adversely affect the human body. Inflammation of formations has both common symptomatic features and differences. This complication can be treated provided that you contact a specialist in a timely manner, determine the source of the pathology and carry out adequate treatment. The prognosis is often favorable. The article has been verified by the editors
Localization
Wen can appear in any part of the neck. It develops in areas with a lack of lipid layer.
Locations of pathology:
- Posterior – the tumor is most often detected in this part of the neck. The location of the lipoma makes it difficult to detect in the early stages of development. It is often confused with an enlarged lymph node. It is difficult to monitor its changes, but it must be done.
- In the front - lipomas in this part of the neck cause many symptoms and complications, since important vessels are located here, the esophagus passes through.
- Intermuscular - the wen may contain smooth muscle fibers. It's called myelolipoma.