Abscessing (undermining) Hoffmann's folliculitis refers to a number of dermatological diseases of a purulent nature. It affects skin that is rich in hair follicles. The provoking factor in the formation of the disease is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin and those areas of the body that are covered with hair. It is characterized by slow development and the possibility of becoming chronic. Folliculitis is most often diagnosed in representatives of the stronger half of humanity aged 17 to 40 years. To prevent relapses, timely treatment is recommended.
Causes
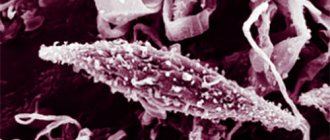
Hoffmann's folliculitis is most often caused by:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- Staphylococcus aureus.
Various factors can provoke its appearance; they are divided into endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous includes:
- undergoing a long course of antibiotic therapy;
- carbohydrate imbalance;
- cancer diseases;
- immunodeficiency;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- liver diseases;
- carrying out chemotherapy;
- anemia;
- long-term use of glucocorticoids;
- decreased protective function of the skin;
- infectious processes.
Exogenous provoking factors are:
- exposure to cold or hot air over a long period of time;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- violation of the integrity of the skin in the form of abrasions, cracks, burns and animal scratches;
- skin contamination at work;
- wearing tight clothing made from synthetic fabrics;
- incorrect or untimely application of occlusive dressings;
- non-compliance with skin care rules after laser hair removal and other cosmetic procedures.
There are also factors that indirectly contribute to the formation of the disease, these include:
- periodontal disease;
- gingivitis;
- caries;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- obesity.
These conditions deplete the immune system, resulting in the skin losing its ability to resist skin infections.
As the disease progresses, the pathological process spreads to adjacent areas of the skin, and abscess formation of the deep layers of the epidermis and hair follicles is observed. Abscesses and fistulas form and merge with each other. The disease can be transmitted at the genetic level.
Hoffmann's folliculitis (undermining)
Abscessing (undermining) Hoffmann's folliculitis refers to a number of dermatological diseases of a purulent nature. It affects skin that is rich in hair follicles.
The provoking factor in the formation of the disease is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin and those areas of the body that are covered with hair. It is characterized by slow development and the possibility of becoming chronic.
Folliculitis is most often diagnosed in representatives of the stronger half of humanity aged 17 to 40 years. To prevent relapses, timely treatment is recommended.
Causes
Hoffmann's folliculitis is most often caused by:
- staphylococci,
- streptococci,
- Staphylococcus aureus.
Various factors can provoke its appearance; they are divided into endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous includes:
- undergoing a long course of antibiotic therapy,
- carbohydrate imbalance
- cancer diseases,
- immunodeficiency,
- diabetes,
- hormonal imbalance,
- liver diseases,
- carrying out chemotherapy,
- anemia,
- long-term use of glucocorticoids,
- decreased protective function of the skin,
- infectious processes.
Exogenous provoking factors are:
- exposure to cold or hot air over a long period of time,
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules,
- violation of the integrity of the skin in the form of abrasions, cracks, burns and animal scratches,
- skin contamination at work,
- wearing tight clothing made from synthetic fabrics,
- incorrect or untimely application of occlusive dressings,
- non-compliance with skin care rules after laser hair removal and other cosmetic procedures.
There are also factors that indirectly contribute to the formation of the disease, these include:
- periodontal disease,
- gingivitis,
- caries,
- chronic tonsillitis,
- chronic pharyngitis,
- obesity.
These conditions deplete the immune system, resulting in the skin losing its ability to resist skin infections.
As the disease progresses, the pathological process spreads to adjacent areas of the skin, and abscess formation of the deep layers of the epidermis and hair follicles is observed. Abscesses and fistulas form and merge with each other. The disease can be transmitted at the genetic level.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hoffmann's folliculitis responds well to treatment, the main thing is to start it on time. If pathological symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible, namely a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist. After a thorough examination of the patient, he will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor collects the patient’s complaints and anamnestic data, specifying the time of onset of pathological symptoms, the presence of chronic diseases and similar problems in relatives. After this, a dermatoscopy (examination of the patient) is performed. Inflamed follicles are examined under multiple magnification, this allows you to determine the depth of the inflammatory process.
Also prescribed:
- Bacteriological culture of discharge from pustules. The study makes it possible to establish the type of pathogen, and in the future also determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
- PCR diagnostics. It is carried out to exclude the presence of diseases such as syphilis and gonorrhea.
- Test for the presence of fungal flora. To do this, scraping is carried out from the affected area and examined under a microscope.
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
It is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis; deep folliculitis must be differentiated:
- with a superficial form of the disease (ostiofolliculitis),
- with streptococcal impetigo,
- furunculosis,
- nodular cystic acne,
- drug toxicoderma.
If necessary, the patient is referred for examination to an immunologist and allergist.
Drug therapy
Of the medications, the following drugs are considered justified:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics, preference is given to penicillins of semi-synthetic origin: Unazine, Augmentin, Clavulin, Amoxiclav, Claventin. Cephalesporin derivatives Cefobid, Claforan, Kefzol, Cefuroxime can also be used. If such antibiotic therapy is impossible for certain reasons, then sulfonamides are used: Septrin, Groseptol, Bactrim and Biseptol.
- Immunostimulants, such as Immunoglobulin, Bacteriophage, Antifagin.
- Vitamins and restoratives; vitamins E, A, C, and group B are considered the drugs of choice.
For topical use use:
- antibacterial ointments,
- Ichthyol,
- Fulevil,
- Levosin,
- Levomekol.
After opening abscesses and fistulas, clean them using antiseptic solutions, such as:
- Nitrofuran,
- Iodoform,
- Potassium permanganate,
- Hydrogen peroxide.
The course of treatment ranges from 7 to 12 days; to consolidate the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to repeat it after 10 days.
In advanced and complicated cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
Hardware treatment methods
A high level of effectiveness is observed when combining drug treatment of acute folliculitis with physiotherapeutic methods. The use of ultraviolet rays is considered the most effective, because ultraviolet rays penetrate into the thickness of tissues, providing an anti-inflammatory and restorative effect. Good results are also observed when using:
- carbon dioxide laser,
- low-intensity UHF therapy,
- magnetic therapy,
- dry heat.
Forecast
With timely therapy, the prognosis is favorable; foci of inflammation can be completely eliminated within 2 weeks. Patients who self-medicate most often encounter complications such as:
- furunculosis,
- carbunculosis,
- abscess,
- dermatophytosis,
- lymphadenitis.
Damage to the deeper layers of the skin leads to the formation of scars and dark spots. In severe cases, complications can threaten the patient's life.
Remember that pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the development of folliculitis can be transmitted through contact, so for the sake of the health of your family, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Preventive actions
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. To avoid skin problems, it is recommended:
- Carry out personal hygiene manipulations in areas with active hair growth with caution.
- Regularly undergo medical examination if you have a history of diabetes.
- Men should shave, and women should depilate only with the use of special products with disinfectant properties.
- Treat damaged or abraded skin with antiseptic solutions.
- Conduct timely treatment of diseases that can provoke the development of Hoffmann folliculitis.
- Carefully ensure that chemical solutions and compounds do not come into contact with your skin.
- If even minor pathological symptoms appear that resemble disruptive folliculitis, seek help from a doctor.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Enrich the body with vitamins A and E.
- Avoid excessively greasy hair.
To summarize, I would like to focus on the fact that Hoffmann’s folliculitis is a rather dangerous disease that requires timely treatment. Remember this, be attentive to your body, and it will thank you with good health.
Source: https://mfarma.ru/dermatologiya/follikulit-gofmana-opasnoe-zabolevanie-trebuyushhee-svoevremennogo-lecheniya
Clinical picture
As already noted, Hoffmann folliculitis affects men 20-35 years old; the favorite areas of localization are areas of the body with developed hair.
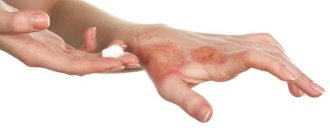
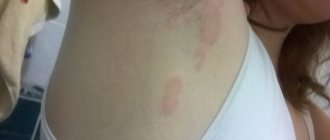
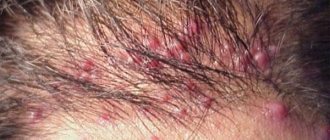
At the initial stages of the development of the disease, itching and burning appear. There are several affected areas, they become hyperemic. In rare cases, undermining folliculitis occupies most of the head, while healthy areas look like narrow stripes. As the disease progresses, the formation of oblong or hemispherical nodes is observed; they are surrounded by areas of hair loss.
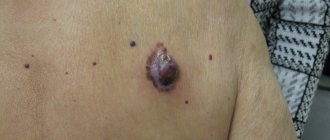
If left untreated, the nodes turn into fistulas, the size of which reaches 1-2 centimeters; when they are palpated, pus is released, sometimes mixed with blood. In complicated cases, ulcers form at the site of nodes and fistulas, the surrounding skin becomes thinner, and alopecia (areas where hair is completely absent) spreads 1-2 centimeters around.
The general condition of the patient also changes, an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes and an increase in body temperature are observed.
In the absence of adequate therapy, abscess folliculitis may persist for several weeks, after which the ulcers heal, forming scars in their place. Alopecia persists and is accompanied by the formation of new nodes and abscesses. The disease is prone to relapse and may be present for several years.
Signs of perifolliculitis
Mostly men suffer; the first signs of the disease are diagnosed at a young age (25-30 years), which is especially unpleasant for men. Since this is the age of maximum sexual activity, and external defects lead to psychological complexes and a decrease in the level of communication with the opposite sex.
The onset of the pathological process is characterized by:
- itching;
- burning;
- During examination, the doctor detects areas of redness on the skin.
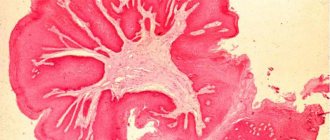
Figure No. 1. Undermining folliculitis, hair loss
The first lesions are located in the crown and on the back of the head. The lesions are multiple, but fortunately, they rarely cover most of the head. If this happens, healthy tissue appears as thin stripes between the bumps (knots) of inflamed tissue with areas of hair loss.
At the stage of disease development:
- nodules transform into pathological openings (medical term “fistulas”) with a diameter of up to 2 cm;
- from the fistula, when you press on the skin around it, pus flows out;
- nodules may become covered with ulcers;
- the skin around the inflamed area becomes thinner;
- hair also falls out in a healthy area in a strip up to 2 cm wide around the red bumpy area.
Figure No. 2. Undermining folliculitis, scalp abscesses, hair loss
Unfortunately, the lost hair is not replaced by new ones, and nodes, lumps and abscesses continue to form around the diseased area. The disease takes a long (up to several years) course with stages of relapse and remission.
Figure No. 4. Hoffmann’s perifolliculitis: alopecia, nodes, tubercles
If the disease is caused by toxigenic staphylococcus (its waste products cause acute intoxication), the patient will experience symptoms of general intoxication.
Figure No. 5. Hoffmann's perifolliculitis: nodes, bumps, scars
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor collects the patient’s complaints and anamnestic data, specifying the time of onset of pathological symptoms, the presence of chronic diseases and similar problems in relatives. After this, a dermatoscopy (examination of the patient) is performed. Inflamed follicles are examined under multiple magnification, this allows you to determine the depth of the inflammatory process.
- Bacteriological culture of discharge from pustules. The study makes it possible to establish the type of pathogen, and in the future also determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
- PCR diagnostics. It is carried out to exclude the presence of diseases such as syphilis and gonorrhea.
- Test for the presence of fungal flora. To do this, scraping is carried out from the affected area and examined under a microscope.
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
It is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis; deep folliculitis must be differentiated:
- with a superficial form of the disease (ostiofolliculitis);
- with streptococcal impetigo;
- furunculosis;
- nodular cystic acne;
- drug toxicoderma.
If necessary, the patient is referred for examination to an immunologist and allergist.
Treatment
First of all, it is necessary to direct all efforts to strengthen the body’s immune defense. You need to monitor your diet; your diet should include as many vitamins, vegetables and fruits as possible, as well as protein-rich foods. The consumption of sweets, baked goods, seasonings, spicy and salty foods should be kept to a minimum.
An important point is compliance with the drinking regime. During an exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water, because pathogenic microorganisms leave the body cavity with liquid.
Forecast
With timely therapy, the prognosis is favorable; foci of inflammation can be completely eliminated within 2 weeks. Patients who self-medicate most often encounter complications such as:
- furunculosis;
- carbunculosis;
- abscess;
- dermatophytosis;
- lymphadenitis.
Damage to the deeper layers of the skin leads to the formation of scars and dark spots. In severe cases, complications can threaten the patient's life.
Remember that pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the development of folliculitis can be transmitted through contact, so for the sake of the health of your family, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Preventive actions
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. To avoid skin problems, it is recommended:
- Carry out personal hygiene manipulations in areas with active hair growth with caution.
- Regularly undergo medical examination if you have a history of diabetes.
- Men should shave, and women should depilate only with the use of special products with disinfectant properties.
- Treat damaged or abraded skin with antiseptic solutions.
- Conduct timely treatment of diseases that can provoke the development of Hoffmann folliculitis.
- Carefully ensure that chemical solutions and compounds do not come into contact with your skin.
- If even minor pathological symptoms appear that resemble disruptive folliculitis, seek help from a doctor.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Enrich the body with vitamins A and E.
- Avoid excessively greasy hair.
To summarize, I would like to focus on the fact that Hoffmann’s folliculitis is a rather dangerous disease that requires timely treatment. Remember this, be attentive to your body, and it will thank you with good health.
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis (abscessing) is a rare dermatological disease with a purulent nature. The disease affects the hair follicles and scalp, but can also appear on other hairy parts of the body. Today, the main cause of Hoffmann's folliculitis is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin near the hairline. The disease mainly affects men aged 17-40 years. Racial predisposition to Hoffmann's folliculitis has also been proven - the disease is less common in European men than in African Americans. Undermining folliculitis most often develops slowly. It is characterized by a sluggish, chronic and long-term course, which sometimes takes several years. Only correct and timely treatment can speed up the recovery process and prevent relapse.
Hoffmann's perifolliculitis
Hoffmann's perifolliculitis (abscessing undermining folliculitis) is a rare chronic skin disease that is characterized by the formation of purulent-inflammatory foci in areas of the body with developed hair. This condition has been known for a long time, but the German dermatologist Hoffmann was the first to compile its detailed description in 1907. Hoffman defined the pathology as the result of infection of perifollicular tissues by bacteria from the staphylococcus group. Hoffmann's perifolliculitis is a rare dermatological condition, its incidence in the population is currently unknown. This disease affects men much more often; the ratio of male to female patients is 5:1. In addition to the inflammatory symptoms themselves, Hoffmann's perifolliculitis leads to persistent focal alopecia, therefore, when pathological foci are localized on the scalp, it can cause severe aesthetic discomfort. In some cases, areas of baldness bother patients more than other symptoms of the pathology.
Causes of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
The photo shows an advanced form of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Since E. Hoffman's study of abscess folliculitis, pathogenic staphylococcal flora was considered the only cause of the disease. It has now become clear that the disease develops not only due to infection by microorganisms, but also due to the physiological characteristics of the skin. Bacteria colonize around the hair roots, which provokes the development of the disease.
In almost all patients, the secretion of the sebaceous glands changes, and after a while they become clogged. Similar symptoms of Hoffmann folliculitis indicate many other dermatological diseases (acne, comedones). However, for the development of perifolliculitis, an additional pathological reaction of the skin to the components of the breakdown of clogged sebaceous glands, in particular keratin, is necessary. Studies have shown that in patients with this pathology, granulomatous inflammation is formed due to the breakdown products of keratin. This aggravates infection with staphylococcal flora. Similar processes and disturbances of microcirculation in the dermis lead to the occurrence of Hoffmann's folliculitis.
In addition, Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis can be hereditary and occur due to other factors:
Even more interesting:
Sores around the head
Mouth ulcers hiv
- Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Diabetes.
- Hypothermia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Disturbance of the hormonal system.
- Chemotherapy.
- Liver diseases.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Causes of pathology
Hoffmann's disease is a disease that not even doctors see every day. This form of folliculitis is diagnosed 5 times more often in men and leads to persistent alopecia and skin deformation. Considering that the process is localized on the scalp, patients experience significant psychological discomfort.
Until recently, the only cause of the disease was considered to be damage to the hair follicles by staphylococcus. But today doctors dispute this fact. Judge for yourself, pustular and purulent processes caused by this type of bacteria are found everywhere. Inflammation caused by staphylococcus is a frequent guest in the area of the nail fold, on the skin of the face and body, and on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. Why then does undermining folliculitis not occur in every 2 patients with staphylococcal infection?
The answer lies in human physiology, with the peculiarity of the functioning of its largest organ - the skin. Only 3 factors trigger the mechanism of colonization of the human scalp by cocci bacteria and the development of Hoffmann’s perifolliculitis:
- Changes in the chemical structure of sebum. The secretion of the sebaceous glands becomes viscous and clogs the sebaceous ducts, up to occlusion (complete blocking of the duct). The mechanism is familiar to us from the example of acne or acne. A nutrient medium (sebum, sebum) plus occlusion (blockage without air access) creates incubator conditions for coccal flora. This is enough for pustular skin lesions, but not enough for the development of abscess folliculitis. We need additional incentive.
- The body’s pathological reaction to its own altered secretion is this factor. For some reason, patients with this disease have developed an inflammatory granulomatous reaction to keratin breakdown products.
- Violation of skin microcirculation and slower removal of decay products from the lesion aggravates the process and makes it easier for bacteria to colonize.
These are the causes and mechanism of development of the disease, from the point of view of modern medicine.
Symptoms of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With abscess folliculitis, the hair follicles become inflamed. At the initial stages of the disease, a burning sensation, itching appears and small seals measuring 0.5 cm are formed. With the progression of undermining folliculitis, the seals soften and increase to 2 cm, oblong or hemispherical nodes are formed, which are surrounded by places of hair loss. There may be several affected areas, they become hyperemic. The general condition of the patient also changes: regional lymph nodes enlarge and body temperature rises. When complicated, Hoffmann's folliculitis often causes the formation of fistulas in the lesions. After the pus comes out, a wound forms, which heals, but a scar forms in its place. The disease is prone to relapses, can last several years and is always accompanied by:
Diagnosis of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
The photo shows a medical examination of the head of a patient with Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's folliculitis is treated by a dermatologist and an infectious disease specialist. Specialists examine the patient and carry out a number of activities as part of the study:
- Dermatological examination.
- Histological study of affected tissues.
- Microbiological examination of abscess discharge.
- The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined in order to select the optimal treatment.
- A general blood test is prescribed to determine the nonspecific features of purulent inflammation.
- The presence of similar problems in relatives and chronic diseases is clarified.
Diagnosis of Hoffmann's perifolliculitis
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
To determine Hoffmann's perifolliculitis, a dermatological examination, microbiological examination of abscess discharge and histological examination of tissue in the lesions are performed. Upon examination, foci of alopecia are revealed (usually on the head, less often in the armpits and groin area), red spots or nodes, often with ulcerations. When pressure is applied to the abscess, pus is released, often mixed with blood. There is also an increase in regional lymph nodes (cervical, occipital, inguinal, axillary) and an increase in body temperature; patients may complain of general malaise.
When bacteriologically studying purulent discharge (inoculation on nutrient media), pyogenic staphylococcal flora is usually determined. As part of this study, it is also possible to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to various antibiotics to select the optimal treatment for Hoffmann's perifolliculitis. A general blood test, as a rule, indicates the presence of nonspecific signs of purulent inflammation. Leukocytosis with a neutrophilic shift to the left and a sharp increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are detected. The histological picture of Hoffmann's perifolliculitis is a sharp swelling of the dermis and epidermis with pronounced tissue infiltration (mainly neutrophilic in nature), the presence of signs of granulomatous inflammation, partial destruction of the basement membrane.
Treatment of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
To treat Hoffmann's folliculitis, drug therapy is prescribed: antibacterial drugs internally (Clindamycin, Tetracycline, Rifampicin) and externally (Clindamycin). For local use use: Levosin, Levomekol, Ichthyol, Fulevil, antibacterial ointments.
According to some doctors, the effect of antibacterial drugs is short-term; it is more effective to simultaneously combine antibiotics with injections of corticosteroids in the affected areas. Of the antibiotics, broad-spectrum penicillin drugs of semi-synthetic origin are considered justified: Augmentin, Clavulin, Unazin, Amoxiclav, Claventin. Sometimes the cephalosporin series is used: Kefzol, Cefobid, Cefuroxime, Claforan. If antibiotic therapy is not possible, then sulfonamides are prescribed: Biseptol, Septrin, Groseptol, Bactrim.
High effectiveness is observed when drug treatment is combined with physiotherapeutic methods. UV therapy is effective because ultraviolet rays penetrate the tissue, providing a general strengthening and anti-inflammatory effect. Good results are observed when using: magnetic therapy, low-intensity UHF therapy, dry heat and carbon dioxide laser.
In case of complications and in advanced cases of Hoffmann's folliculitis, surgical intervention is resorted to. Surgical treatment is carried out against the background of antibacterial therapy with resection of the affected tissues of the head and subsequent reconstruction of the skin.
In addition to the above therapy, it is necessary to strengthen the body’s immune system and monitor the diet. The menu should contain vitamins, vegetables, fruits and protein-rich foods. It is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets, baked goods, spicy and salty foods. It is important to maintain a drinking regime, because pathogenic microorganisms leave the body with liquid. During an exacerbation, it is recommended to drink 2 liters of water.
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis: causes, symptoms and treatment
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis (abscessing) is a rare dermatological disease with a purulent nature. The disease affects the hair follicles and scalp, but can also appear on other hairy parts of the body.
Today, the main cause of Hoffmann's folliculitis is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin near the hairline. The disease mainly affects men aged 17-40 years.
Racial predisposition to Hoffmann's folliculitis has also been proven - the disease is less common in European men than in African Americans. Undermining folliculitis most often develops slowly.
It is characterized by a sluggish, chronic and long-term course, which sometimes takes several years. Only correct and timely treatment can speed up the recovery process and prevent relapse.
- Read what folliculitis is
Causes of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
The photo shows an advanced form of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Since E. Hoffman's study of abscess folliculitis, pathogenic staphylococcal flora was considered the only cause of the disease. It has now become clear that the disease develops not only due to infection by microorganisms, but also due to the physiological characteristics of the skin. Bacteria colonize around the hair roots, which provokes the development of the disease.
In almost all patients, the secretion of the sebaceous glands changes, and after a while they become clogged. Similar symptoms of Hoffmann folliculitis indicate many other dermatological diseases (acne, comedones).
However, for the development of perifolliculitis, an additional pathological reaction of the skin to the components of the breakdown of clogged sebaceous glands, in particular keratin, is necessary. Studies have shown that in patients with this pathology, granulomatous inflammation is formed due to the breakdown products of keratin.
This aggravates infection with staphylococcal flora. Similar processes and disturbances of microcirculation in the dermis lead to the occurrence of Hoffmann's folliculitis.
In addition, Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis can be hereditary and occur due to other factors:
- Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Diabetes.
- Hypothermia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Disturbance of the hormonal system.
- Chemotherapy.
- Liver diseases.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Symptoms of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With abscess folliculitis, the hair follicles become inflamed. In the initial stages of the disease, burning, itching appears and small lumps measuring 0.5 cm in size form.
With the progression of undermining folliculitis, the seals soften and increase to 2 cm, oblong or hemispherical nodes are formed, which are surrounded by places of hair loss. There may be several affected areas, they become hyperemic.
The general condition of the patient also changes: regional lymph nodes enlarge and body temperature rises. When complicated, Hoffmann's folliculitis often causes the formation of fistulas in the lesions.
After the pus comes out, a wound forms, which heals, but a scar forms in its place. The disease is prone to relapses, can last several years and is always accompanied by:
- redness of the skin over the formation;
- hair loss;
- discharge of pus with blood when pressing on the affected areas;
- abscess formation.
Diagnosis of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
The photo shows a medical examination of the head of a patient with Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's folliculitis is treated by a dermatologist and an infectious disease specialist. Specialists examine the patient and carry out a number of activities as part of the study:
- Dermatological examination.
- Histological study of affected tissues.
- Microbiological examination of abscess discharge.
- The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined in order to select the optimal treatment.
- A general blood test is prescribed to determine the nonspecific features of purulent inflammation.
- The presence of similar problems in relatives and chronic diseases is clarified.
Treatment of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
To treat Hoffmann's folliculitis, drug therapy is prescribed: antibacterial drugs internally (Clindamycin, Tetracycline, Rifampicin) and externally (Clindamycin). For local use use: Levosin, Levomekol, Ichthyol, Fulevil, antibacterial ointments.
According to some doctors, the effect of antibacterial drugs is short-term; it is more effective to simultaneously combine antibiotics with injections of corticosteroids in the affected areas.
Of the antibiotics, broad-spectrum penicillin drugs of semi-synthetic origin are considered justified: Augmentin, Clavulin, Unazin, Amoxiclav, Claventin. Sometimes the cephalosporin series is used: Kefzol, Cefobid, Cefuroxime, Claforan.
If antibiotic therapy is not possible, then sulfonamides are prescribed: Biseptol, Septrin, Groseptol, Bactrim.
High effectiveness is observed when drug treatment is combined with physiotherapeutic methods. UV therapy is effective because ultraviolet rays penetrate the tissue, providing a general strengthening and anti-inflammatory effect. Good results are observed when using: magnetic therapy, low-intensity UHF therapy, dry heat and carbon dioxide laser.
In case of complications and in advanced cases of Hoffmann's folliculitis, surgical intervention is resorted to. Surgical treatment is carried out against the background of antibacterial therapy with resection of the affected tissues of the head and subsequent reconstruction of the skin.
In addition to the above therapy, it is necessary to strengthen the body’s immune system and monitor the diet. The menu should contain vitamins, vegetables, fruits and protein-rich foods.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets, baked goods, spicy and salty foods. It is important to maintain a drinking regime, because pathogenic microorganisms leave the body with liquid. During an exacerbation, it is recommended to drink 2 liters of water.
- Read about treating folliculitis with folk remedies at home
Prognosis and prevention of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With proper treatment, the prognosis for abscessing undermining folliculitis is favorable. However, treatment is long and relapses are possible, since the disease is mainly caused by certain physiological characteristics of the skin.
After the ulcers heal, noticeable scars remain, which are an aesthetic defect. This can be corrected with plastic surgery. Conservative and cosmetic treatment does not restore hair growth.
For prevention purposes, you should avoid getting your hair dirty and maintain personal hygiene.
Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is not life-threatening.
The disease must be treated because it causes aesthetic discomfort and sometimes pain to the patient.
If you neglect the disease and do not adhere to hygiene standards, folliculitis will spread to other parts of the skin with hair. Abscess folliculitis can lead to the following complications:
- Scarring of the affected skin.
- Carbuncles.
- Boils.
- Abscesses.
In advanced and severe cases, the patient’s life is at risk, since with reduced immunity, pneumonia, meningitis and other disorders develop.
- Read - how to treat oil folliculitis
Source: https://dermatologys.ru/lechenie-vzroslyh/101-podryvayuschiy-follikulit-gofmana-prichiny-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Prognosis and prevention of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With proper treatment, the prognosis for abscessing undermining folliculitis is favorable. However, treatment is long and relapses are possible, since the disease is mainly caused by certain physiological characteristics of the skin. After the ulcers heal, noticeable scars remain, which are an aesthetic defect. This can be corrected with plastic surgery. Conservative and cosmetic treatment does not restore hair growth. For prevention purposes, you should avoid getting your hair dirty and maintain personal hygiene.
Treatment of Hoffmann's perifolliculitis
The main principles of therapy for Hoffmann's perifolliculitis are the fight against staphylococcal infection, normalization of metabolic processes in the skin and correction of the secretory function of the sebaceous glands. To eliminate a bacterial infection, antibiotics are used - either broad-spectrum or those to which the microorganism is most sensitive (this is determined by bacteriological studies). In addition to antibiotics, in some cases chemotherapeutic antibacterial agents, for example, sulfonamides, are used. When toxigenic strains of staphylococcus are detected (this form of perifolliculitis is manifested by severe general disorders), immune preparations are prescribed - serums and staphylococcal toxoid. Locally, for Hoffmann's perifolliculitis, a variety of antiseptic ointments and solutions are used - aniline dyes and chlorhexidine, which accelerate healing and prevent the formation of new foci of the disease.
In some cases of Hoffmann's perifolliculitis, abscesses are located in sufficiently deep layers of the skin, which requires their surgical opening, drainage and further washing with antiseptics. To normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands, retinoids, vitamin E and other agents are used. Mineral-vitamin complexes and iron preparations are also necessary to increase the body's defenses and neutralize the side effects of antibiotic therapy. Some physiotherapeutic procedures - ultraviolet irradiation, UHF and others - also have a positive effect on Hoffmann's perifolliculitis.
Forecast and prevention of Hoffmann's perifolliculitis
With proper treatment and compliance with all specialist recommendations, the prognosis for Hoffmann perifolliculitis is relatively favorable. Relapses of the disease are possible, since it is caused not so much by the infection as by the patient’s own physiological characteristics of the skin. After healing of pathological foci of Hoffmann's perifolliculitis, areas of scarring focal alopecia remain on the hairline, which are a noticeable aesthetic defect. This can only be corrected using plastic surgery methods; no conservative or cosmetic measures can restore hair growth on scar tissue. To prevent Hoffmann's perifolliculitis, it is necessary to provide the body with the necessary vitamins (especially A and E), avoid significant hair greasy, and adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is not life-threatening. The disease must be treated because it causes aesthetic discomfort and sometimes pain to the patient. If you neglect the disease and do not adhere to hygiene standards, folliculitis will spread to other parts of the skin with hair. Abscess folliculitis can lead to the following complications:
- Scarring of the affected skin.
- Carbuncles.
- Boils.
- Abscesses.
In advanced and severe cases, the patient’s life is at risk, since with reduced immunity, pneumonia, meningitis and other disorders develop.
City Dermatovenerologic Dispensary of St. Petersburg
Folliculitis is a dermatological infectious disease of the upper layers of hair follicles (follicles). If left untreated, it penetrates into the deep layers of the hair root, which most often leads to baldness.
It occurs mainly in men, rarely in women or children. In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) - 10 is designated by code L73.9.
Reasons for development
Most often, the causative agent of the disease penetrates through damage to the scalp, which often occurs due to trauma, dissection of the epidermis during itching, depilation, as well as during hair perm and other manipulations near the scalp.
The disease can occur for a number of other reasons :
- Wearing synthetic items
- Long-term use of adhesive plaster
- Exposure to hot and humid environments
- Weak immunity
- Diabetes
- Excessive sweating
- Incorrect use of potent medications
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
Symptoms
With superficial folliculitis, pustules form on the hairline, which, as a rule, do not cause discomfort to the patient.
This type of disease develops within 3-4 days, after which the pustular formations dry out and are torn away from the surface of the skin, causing itching.
The deep form manifests itself by the appearance of nodular, painful formations filled with yellowish-green pus. When pressed, pus with an unpleasant odor is released.
After a few days, the blisters dry out, turn into a crust and fall off, and the nodules gradually resolve. But often the pustules turn into boils, covering most of the head. This type of disease is dangerous for newborns.
- Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is the name of a form of folliculitis in which not only the hair follicle becomes inflamed, but also nearby tissues, thereby forming a large affected area. After healing of the places where there were abscesses, deep scars remain, and the follicles die completely, thereby leading the patient to hair loss and baldness. This pathology is quite rare, and its causes are still not fully known. It proceeds sluggishly and for a long time. More common in middle-aged men of African races.
- Staphylococcal folliculitis occurs when Staphylococcus bacteria attack the hair follicle. It can be superficial - it affects only the funnels of the follicle and deep - the inflammation penetrates inside the funnel. The deep form is often complicated by the formation of an abscess - a furuncle or carbuncle is formed. Often appears in places where shaving. Staphylococcal folliculitis is better known as common sycosis and passes without leaving any traces. In severe cases, the hair follicles die and are replaced by connective tissue—a scar is formed.
- Decalcative folliculitis - refers to staphylococcal folliculitis and is a chronic disease. Leads to permanent alopecia of the affected areas of the scalp. It occurs on the scalp, face in men, temples, and rarely on the armpits and pubic area.
- Candidiasis - caused by fungi of the Cand species >Photo
Hoffmann's perifolliculitis: features of the disease, its causes, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment
Undermining folliculitis (also called abscess folliculitis or Hoffmann's perifolliculitis) is a skin disease. It occurs chronically with the formation of abscesses (close to the surface of the skin and deep).
The favorite place to localize the pathological process is the scalp, since folliculitis affects the scalp. It is extremely rare that foci of perifolliculitis are found in the pubic area or armpits.
Causes of pathology
Hoffmann's disease is a disease that not even doctors see every day. This form of folliculitis is diagnosed 5 times more often in men and leads to persistent alopecia and skin deformation. Considering that the process is localized on the scalp, patients experience significant psychological discomfort.
Until recently, the only cause of the disease was considered to be damage to the hair follicles by staphylococcus. But today doctors dispute this fact.
Judge for yourself, pustular and purulent processes caused by this type of bacteria are found everywhere. Inflammation caused by staphylococcus is a frequent guest in the area of the nail fold, on the skin of the face and body, and on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx.
Why then does undermining folliculitis not occur in every 2 patients with staphylococcal infection?
The answer lies in human physiology, with the peculiarity of the functioning of its largest organ - the skin. Only 3 factors trigger the mechanism of colonization of the human scalp by cocci bacteria and the development of Hoffmann’s perifolliculitis:
- Changes in the chemical structure of sebum. The secretion of the sebaceous glands becomes viscous and clogs the sebaceous ducts, up to occlusion (complete blocking of the duct). The mechanism is familiar to us from the example of acne or acne. A nutrient medium (sebum, sebum) plus occlusion (blockage without air access) creates incubator conditions for coccal flora. This is enough for pustular skin lesions, but not enough for the development of abscess folliculitis. We need additional incentive.
- The body’s pathological reaction to its own altered secretion is this factor. For some reason, patients with this disease have developed an inflammatory granulomatous reaction to keratin breakdown products.
- Violation of skin microcirculation and slower removal of decay products from the lesion aggravates the process and makes it easier for bacteria to colonize.
These are the causes and mechanism of development of the disease, from the point of view of modern medicine.
Signs of perifolliculitis
Mostly men suffer; the first signs of the disease are diagnosed at a young age (25-30 years), which is especially unpleasant for men. Since this is the age of maximum sexual activity, and external defects lead to psychological complexes and a decrease in the level of communication with the opposite sex.
The onset of the pathological process is characterized by:
- itching;
- burning;
- During examination, the doctor detects areas of redness on the skin.
Figure No. 1. Undermining folliculitis, hair loss
The first lesions are located in the crown and on the back of the head. The lesions are multiple, but fortunately, they rarely cover most of the head. If this happens, healthy tissue appears as thin stripes between the bumps (knots) of inflamed tissue with areas of hair loss.
At the stage of disease development:
- nodules transform into pathological openings (medical term “fistulas”) with a diameter of up to 2 cm;
- from the fistula, when you press on the skin around it, pus flows out;
- nodules may become covered with ulcers;
- the skin around the inflamed area becomes thinner;
- hair also falls out in a healthy area in a strip up to 2 cm wide around the red bumpy area.
Figure No. 2. Undermining folliculitis, scalp abscesses, hair loss
Unfortunately, the lost hair is not replaced by new ones, and nodes, lumps and abscesses continue to form around the diseased area. The disease takes a long (up to several years) course with stages of relapse and remission.
Figure No. 4. Hoffmann’s perifolliculitis: alopecia, nodes, tubercles
If the disease is caused by toxigenic staphylococcus (its waste products cause acute intoxication), the patient will experience symptoms of general intoxication.
Figure No. 5. Hoffmann's perifolliculitis: nodes, bumps, scars
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the doctor needs:
- examine the patient;
- interview him (collect anamnesis);
- refer the patient for a microbiological examination (material is collected from the abscess area);
- send tissue samples for histological examination.
During the examination, the doctor notes the presence of foci of hyperemia (redness) and alopecia on the scalp, less often in the armpit or groin. If the disease has developed, lumps and nodes are noticeable. If folliculitis has abscessed, symptoms associated with purulent processes in the tissues may occur:
- fever;
- swelling of regional lymph nodes;
- discharge from fistulas of purulent contents with a bloody admixture;
- violation of the general condition (weakness, lethargy, lack of appetite, etc.).
When examining the contents protruding from the fistula, material from the abscess area is inoculated on a special nutrient medium.
Usually, every other day, experts see staphylococcus growing rapidly on it.
As part of inoculating purulent contents onto a nutrient substrate, it is additionally possible to determine the sensitivity of microbes to antibacterial drugs and select the most effective drug.
A clinical blood test demonstrates changes in the blood picture characteristic of purulent processes: an increase in ESR by an order of magnitude and leukocytosis.
Histology informs the doctor about swelling of the skin down to the hypodermis and tissue infiltration. The infiltrate contains mainly neutrophils. Signs of inflammation with the formation of granulomas (granulomatous) and partial destruction of the thin acellular layer separating the connective tissue from the epidermis (basal membrane) are noticeable.
Granulomatous inflammation is called because as a result of the inflammatory process, granulomas are formed in tissues (they are considered the main element in the structure of tissues during research).
Granuloma is an accumulation of specific cells that eat foreign proteins and bacteria (macrophages and monocytes). That is, pathogens (staphylococcus) accumulate in the outbreak, and the body sends eater cells there.
There are so many of both cells that nodules are formed.
Treatment
For successful treatment of disruptive folliculitis, it is necessary to influence the 3 links mentioned above in the mechanism of development of the pathological process:
- Suppress the growth of staphylococcus.
- Normalize the chemical composition of sebum.
- Restore microcirculation.
To achieve the first point, antibiotics are prescribed (ideally those to which the microflora is sensitive, in practice - a wide spectrum of action). To achieve a lasting effect, in addition to traditional antibiotics, chemotherapeutic antibacterial drugs from the sulfonamide group may be prescribed. If toxigenic strains of cocci are identified, it makes sense to prescribe staphylococcal serum.
When bumps and ulcers appear on the skin, use local antiseptics miramistin, chlorhexidine or aniline dyes. These drugs disinfect the skin and accelerate tissue regeneration. They also help to avoid the spread of the process to healthy skin islands.
If lesions (abscesses, capsules with purulent contents) are found in the deep layers of the skin, surgical intervention is required. The purulent focus will not go anywhere, until it breaks through, but the abscess breaks not only outward, but also into the deeper layers of tissue, affecting the bones. Therefore, such an abscess is opened, drained and washed with local antiseptics.
To support the body and accelerate healing, the patient may be prescribed vitamins (especially useful for the skin A and E), retinoids, and microelements as part of complex preparations. This group of drugs not only supports the body's strength, helps it fight germs, but also reduces the harm caused by antibiotics.
At the recovery stage, physiotherapy procedures are indicated: UHF, UV irradiation and some others at the discretion of the physiotherapist.
Risk group
This group includes patients with disorders of sebum production, working in polluted industries, neglecting personal hygiene and weakened.
Prognosis and prevention
If you treat the disease consistently, strictly following the doctor's instructions, the prognosis is quite favorable. The risk of relapse remains because the trigger for the development of this disease is not infection, but physiological features. And it’s difficult to influence them.
To the dissatisfaction of patients, when deep foci of perifolliculitis heal, scars and baldness remain. The situation can only be corrected by skin plastic surgery. Conservative methods, including folk ones, will not solve the problem.
The disease is prevented with the help of vitamins required to maintain the normal condition of the skin (A and E), suppression of the growth of staphylococcus (propolis has shown itself well) and with the help of personal hygiene rules. Don't let your hair get greasy, and the risk of relapse will be minimal.
‹›
Source: https://MyKozha.ru/bolezni/perifollikulit_gofmana.html
Treatment
How to cure folliculitis with:
- Superficial form . Treatment of this form of pathology is carried out by opening the pustules and removing the pus with a sterile cotton swab. Then lubricate with an antiseptic (diamond green, levomycin alcohol, Bactroban, methylene blue or fucorcin). Repeat disinfection 2-3 times a day until complete healing.
- Deep form . In this case, antibacterial therapy is not used - antibiotics should be discontinued, as they weaken the immune system. Treatment should consist of medications prescribed by a doctor, in particular, they will help: drugs to strengthen the immune system (netifagin), physiotherapeutic procedures (UV or UHF) and taking a complex of vitamins A and C. Unlike the superficial form, ulcers are not opened! You can use ichthyol or ichthyol ointment for folliculitis, applying 2-3 times a day to the inflamed part. The skin around the ulcers is treated with camphor alcohol or 2% salicylic acid. Do not wet with water until complete healing.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis (at home).
Application of traditional medicine
Treatment with unconventional methods has long established itself among the people. These are truly effective remedies against many diseases, including folliculitis.
But you need to be careful when using traditional recipes - they can cause allergic reactions. Before use, it is better to consult a doctor. Let's look at some of them:
- Tea tree oil is one of the most popular and effective remedies against this disease. Has an antiseptic and healing effect. Apply 3-4 times a day, smearing onto affected areas.
- Calendula decoction has an anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect and accelerates healing. To prepare such a decoction, you will need to pour 5 grams of calendula into 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 20-30 minutes, then strain. Apply 3-4 times a day, moistening the affected areas.
- Chamomile decoction can be prepared by pouring 20 grams of dry chamomile with a glass of boiling water, letting it brew for about half an hour and straining. Moisten the inflammation every 3-4 hours a day.
- Thistle , which contains many useful active substances, copes well with wound healing. For folliculitis, crushed fresh thistle is applied to the inflamed areas and covered with a sterile gauze bandage.
- A multi-component product made from viburnum berries (200g), rose hips (200g), dried nettles (10g) and crushed walnut shells (10g). You will need 3 tbsp. Pour 300 ml of boiling water over the resulting dry mixture and cook over low heat for about 10 minutes. Then pour into a container, close the lid and leave for 24 hours, then strain. Mix 50 grams of the resulting infusion with 1 tbsp. honey and 50 grams of cottage cheese. Apply the mixture to the ulcers, leaving for 20 minutes. This remedy is used only for superficial folliculitis.