What is genital herpes?
This is a chronic viral disease, with periodic exacerbations - a characteristic vesicular (small bubble) rash appears on the skin, mucous membranes of the genitals and perineum.
The causative agent of genital herpes is the herpes simplex virus type 2, which, after infection, remains in the human body forever. Stress, hypothermia, nutritional deficiency - everything that leads to a weakened immune system - can provoke a relapse of genital herpes. In patients with HIV-positive status, relapses are especially frequent, and the risk of complications is high. People taking immunosuppressive drugs are also at greater risk.
The disease has a high prevalence: according to WHO, in the world about 3.7 billion people under the age of 50 are infected with type 1 virus and about 491 million people. under the age of 50 are infected with type 2 virus.
Treatment methods for herpes on the labia
Knowing what a herpetic rash looks like and who to contact if it is detected, you need to seriously think about the question of how to treat an unpleasant sore.
Pregnant women are strictly not recommended to treat genital herpes by taking pills for this disease! It is better to resort to using absolutely safe and very effective ointments for external use.
How to quickly cure herpes on the genitals, and how to smear the resulting vesicles? To combat the disease, there are special ointments, as well as tablet preparations, the active substances of which act directly on the herpes virus, without causing harm to beneficial bacteria in the human body. The most famous and effective medications for different types of HHV are:
- Acyclovir. Available in the form of ointments or tablets for oral administration (they should not be given to children under 3 years of age). The active ingredient is acyclovir. Analogue – Atsik. Approximate price: 20 rubles.
- Zovirax. The imported drug is a complete analogue of Acyclovir. The average cost is 190 rubles.
- Famciclovir (Famvir). The active ingredient is Famciclovir. The price of the drug varies from 900-1500 rubles.
Antiviral tablets help in the fight against genital herpes in women
Almost all of the above drugs are available in the form of ointments and tablets. The doctor will tell you which form of medication is best to choose in each specific case.
If the patient has no contraindications to taking pills (pregnancy, lactation, individual intolerance to the components included in the drug, etc.), then this form of release of the medicine for herpes will be the best option. The active substances of tablet products are quickly absorbed into the blood and begin to act, while the ointment is absorbed into the skin much longer.
Treatment with Acyclovir
For greater effectiveness, the drug is used at an early stage of the disease. During the period of antiviral therapy, you need to drink a lot of water. The course of treatment varies from 5 to 14 days.
- Pills. Take 200 mg 5 times a day with an interval of 4 hours.
- Ointment. Used in parallel. Apply a thin layer to the vesicles 4-5 times a day.
Zovirax against herpes rashes
Taking this drug is similar to Acyclovir. The dosage form for oral use is combined with ointments for external use. The course of treatment is up to 2 weeks.
- Pills. You need to drink 1 piece. (200 mg) 5 times a day, every 4 hours.
- Cream. Apply to the affected areas daily 4-5 times during the day.
Zovirax in tube 5g
Famciclovir for HSV-2
The tablets are taken orally regardless of your diet. The same as with other antiviral agents. It is necessary to maintain a drinking regime and consume as much liquid as possible.
- If the immune system is weakened. The course of treatment is up to 7 days. Take 500 mg orally three times a day.
- For kidney dysfunction. Treatment therapy lasts 5 days. Tablets are taken orally at 250 mg.
- Relapses. It is enough to take 1000 mg in the morning and evening with an interval of 12 hours.
What can be done to make the wounds left after opening the vesicles heal faster? To do this, they must be regularly lubricated with Synthomycin Liniment cream. This remedy has a wound-healing and antiseptic effect, with its help you can achieve faster results from the treatment of herpes at the last stage of its development.
Why does genital herpes appear and how is it transmitted?
The most common ways of spreading the herpes virus are sexual intercourse, contact with secretions, and saliva. There are differences in transmission routes between HSV 1 and 2. The first type of virus first affects the oral mucosa. Because of this, it is more often transmitted during oral contact (including sex) and through kissing. The second type of virus is almost always transmitted through sexual intercourse. The risk of infection increases with frequent changes of partners or unprotected sex.
During pregnancy, transmission of infection from mother to child is possible, and this is deadly for the baby. To eliminate the risk of infection, when planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to be examined and use preventive measures. If she is already a carrier of the virus, special therapy is used to suppress its activity. Sometimes, to avoid infection during childbirth, a caesarean section is performed.
Both adults and children can get genital herpes after contact with a carrier of the virus.
Important! It is impossible to become infected through dishes, bedding, toilet seats and other household methods.
Factors provoking the development of the disease
Almost all people on the planet are carriers of the virus, so for what reason does the disease manifest itself in only some? This is due to several factors that provoke the onset of symptoms of the disease:
- Weakened immune system. This can be caused by an unbalanced diet, stress, and overwork. Also, drinking alcohol, using certain medications, in women this can be caused by hormonal changes. In addition, chronic diseases and immunodeficiencies predispose to disease manifestation;
- Often the disease can worsen due to uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives. In addition, intrauterine device placement or abortion can be provoking factors for frequent relapses;
- Due to promiscuity, the virus can spread very quickly, different types of it combine, which strengthens its resistance to treatment;
- Close household contacts. Even in the same family, someone can be a carrier of the infection, and someone can be a healthy person. Using the same towels and dishes increases the risk of infection with HS.
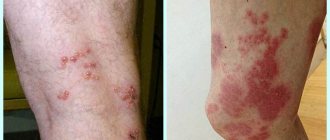
The photo shows the mucous membrane and skin affected by genital herpes. In order not to experience such symptoms on yourself, you need to follow the recommendations and monitor your lifestyle.
Symptoms
The incubation period, during which the disease has no manifestations, lasts on average up to 10 days after infection (maximum duration 26 days).
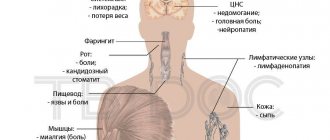
Primary symptoms are headaches, muscle pain, and fever. In the genital area, painful fluid-filled blisters form on the skin and mucous membranes, in place of which ulcers later form. There is a feeling of discomfort, burning, itching. Urinating may be difficult. Such symptoms persist for up to two weeks.
Figure 1. Stages of mucosal lesions in genital herpes. Source: CC0 Public Domain.
Periodically, with a frequency of 2-3 times a month to 1 time a year, the patient experiences relapses, which are usually associated with a decrease in immunity. Symptoms intensify gradually: the skin swells, itches, burning or soreness appears, and only then does a rash form. Against this background, body temperature may rise and general malaise may occur. The rash can spread over the mucous membranes and skin of the genitals, in the area of the inner thighs, pubis, and buttocks. Recovery occurs in about 1-2 weeks, no marks remain on the skin.
When affected by the first type of virus, the course of the disease is usually asymptomatic. It appears only occasionally as a small number of sores or painful blisters in the anus or genital area. Relapses are usually rare.
The second type provokes more pronounced symptoms: the affected area is larger, the formation of ulcers is accompanied by fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes, muscle, headaches, and joint pain. Relapses occur more frequently.
In children, genital herpes occurs almost the same as in adults, but is more difficult to tolerate. If your child scratches the sores, they will take longer to heal.
Classification
Herpes on the labia majora and labia minora is classified into:
- primary;
- recurrent;
Primary herpes is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture, which is often accompanied by general intoxication of the body. Women with primary herpes have never previously noted signs of the disease; antibodies to HSV are not detected in their blood.
At the end of the incubation period, which lasts on average 7-10 days, the woman’s labia swell and hyperemia is noted. Then abundant painful rashes of small vesicles appear, which subsequently burst, forming erosions and ulcers. During this period, the woman feels
Often the pelvic nerves are involved in the process, which leads to paresthesia of the skin of the thighs and pain in the lumbar region. Sometimes patients report headaches, weakness and fever.
The initial episode of the disease lasts 15-20 days.
Recurrent herpes usually appears 2-3 months after the initial episode. The course of the disease can be either asymptomatic or pronounced. Provoking factors for relapse of HSV include:
- stress;
- fatigue;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- decreased protective functions of the body.
The duration of a relapse of herpes is usually less than the duration of the initial episode and is about 7-10 days. The pathology may be accompanied by inflammation of regional lymph nodes. The frequency of relapses of the disease is the same in both men and women, but in men the course of the disease is longer, and in women it is more acute.
The course of recurrent herpes on the labia is divided into:
- mild, exacerbation of which is recorded no more often than every 4 months:
- moderate, in which symptoms of the disease appear every 2-3 months;
- severe with exacerbations every month.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis is difficult due to the fact that the disease is often asymptomatic, unnoticeable even to the carrier of the virus. You should pay attention to your well-being, the condition of your skin and mucous membranes. If inflammation, ulcers, and blisters appear on the lips during colds, after hypothermia, or overwork, this may indicate infection with the HSV 1 virus. If rashes appear in the genital area, this may be associated with the HSV 2 virus.
Important! There may be an atypical course of genital herpes, in which there are no rashes on the skin, but it turns red, discharge appears from the genitals, and there is a feeling of discomfort.
Diagnosis is usually carried out by a dermatologist-venereologist; you can also contact a gynecologist or urologist. The doctor interviews and examines the patient, makes a scraping or smear for laboratory testing. To make a diagnosis, the following tests can be performed: PCR (search for traces of DNA and RNA of the virus), blood tests for HSV-1 and HSV-2 antibodies, an HIV test and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
The course of treatment is prescribed taking into account the general state of health and diagnostic results. After it, you need to be examined regularly, even if stable remission remains. This will help reduce the risk of relapses and complications.
Causes and predisposing factors
The only reason for the development of the disease is infection with a virus. Once it enters the body, the virus remains in it for life, being in a “dormant” state. Activation of the virus occurs under the influence of certain factors, such as:
- stress;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- hypothermia;
- unbalanced diet;
- decreased immunity;
- vitamin deficiency;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Often, herpes in women on the labia appears during the period before and after menstrual bleeding. This is explained by a decrease in local immunity, which creates favorable conditions for the activation of the microorganism.
Treatment
The course of genital herpes can be asymptomatic, and even with repeated manifestations, the symptoms can be mild and pass quickly. In this case, specific therapy is not required. It is necessary only in severe cases of the disease - frequent long-term relapses and in the presence of concomitant diseases.
Once infected, it is impossible to get rid of the herpes virus; a person remains a carrier for life. Treatment helps control the disease, suppress the pathogen, reducing the frequency and severity of relapses, the risk of complications and infection for surrounding people.
Antiviral therapy
Antiviral therapy is used most often. Patients are prescribed the following medications:
- Acyclovir. Quickly suppresses the activity of the herpes virus and slows down its reproduction. It acts only on affected cells and is safe. Possible use in children;
- Famciclovir. It is used only for adult patients, has a long period of action and high bioavailability. The spectrum of action is narrow (targeted at the herpes virus);
- Valaciclovir. Suitable for patients over 12 years of age. Compared to acyclovir, it has a longer period of action and higher bioavailability.
Important! It is more effective to use oral medications. Local medications do not have such a pronounced effect. The specific medicine, dosage, and duration of treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the general state of health, the characteristics of the clinical picture, and other factors.
Immunotherapy
If relapses of genital herpes are associated with manifestations of immune deficiency, immunotherapy is used for treatment. It can be specific and non-specific. For specific purposes, herpetic vaccines are used. The immune response is enhanced, and the activity of the herpes virus is suppressed more quickly. Nonspecific uses antigenic drugs that increase the reactivity of the immune system in general. Usually these are interferon preparations in combination with antiviral agents.
Folk remedies
There are many folk remedies for herpes, but none of them have proven effectiveness. When trying to be treated with traditional recipes, the patient wastes time, provokes an even stronger exacerbation and does nothing to improve his health.
Possible complications
They can develop after an exacerbation of the disease. Their risk is increased for patients with reduced immunity and poor health.
The following possible complications exist:
- addition of infection. Erosions, ulcers, injuries to the mucous membrane and skin in the genital area increase vulnerability to pathogens. The risk of contracting HIV and other dangerous diseases increases;
- during pregnancy there is a danger of infecting the child;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes of the urethra and bladder lead to difficulty urinating;
- meningitis;
- inflammation of the rectal mucosa;
- transfer of infection to other areas of the body;
- risk of malignant tumors.
Stages of pathology development
Harbingers
At this stage, the woman feels a slight burning and itching in the labia area. The duration of this stage varies from several hours to 1 day.
Hyperemia
When you touch the affected area, you feel a difference in skin temperature - in the area of the future rash, the skin is much hotter. The duration of the period of hyperemia is usually 24-48 hours. It is during this period that experts advise starting symptomatic and antiviral therapy.
Bubbles
At this stage, bubbles filled with a clear liquid form. The formations are covered with a thin film and are easily opened when pressed. Further, the liquid in the bubbles becomes cloudy, the formations grow, involving healthy tissues in the process. During this period, severe pain appears, which intensifies upon contact with the affected area. This stage of the disease lasts 2-3 days.
Formation of ulcers and erosions
At this stage, a person is considered to be most contagious. The resulting blisters open, and herpes now looks like ulcers and erosions of a gray hue with bright red borders. The liquid that is released contains the maximum concentration of the virus. This period of illness lasts from 4 to 9 days.
Crust formation
The surface of the ulcers dries out, forming a crust. The pain syndrome decreases, but the itching increases. The affected area may bleed. The healing process begins.
Healing
At this stage, the crusty ulcers disappear, and the wounds on their surface heal. The virus returns to “sleep mode.”
What happens if genital herpes is not treated?
Without adequate therapy, the risk of exacerbations increases, relapses can occur more often and become more severe. The infection spreads to the entire genitourinary system, and difficulties with urination appear. Immunity decreases, the risk of infection with other diseases increases (including through erosions and ulcers on the mucous membranes and skin). Without treatment, the virus becomes more active: the risk of transmitting it to other people increases.
Although genital herpes cannot be completely cured, the disease can be controlled. This will help maintain normal health and reduce the risk of infection for those who are constantly in contact with a carrier of the virus.
How dangerous is herpes?
Herpes in the genital area is dangerous due to the development of complications, both local, which affect only the genital area, and systemic, which affect the body as a whole.
Local complications include:
- increased dryness of the labia mucosa (both minor and major);
- formation of painful cracks on the mucous membranes of the external genitalia;
- involvement of nearby tissues in the process.
Local complications of the disease lead to disruption of women’s social adaptation, development of psychoneurological disorders, and depression.
Systemic complications include damage to the nervous system by herpes. Women note pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, inner thighs, and rectum.
If left unattended by a specialist, frequent relapses can become one of the reasons for a woman to develop endometriosis, infection of the pelvic organs and organs of the urinary system, cervical dysplasia, the development of infertility and oncological pathologies.
Prevention
There are several preventive measures, the main ones being reducing the number of sexual partners, using a condom, and treating the skin with an antiseptic. Emergency prevention after potentially dangerous contacts is carried out using antiviral agents. Any medications can be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
During pregnancy, screening for herpes is mandatory. It is possible to use a course of antiviral therapy if a natural birth is planned.
In prevention, careful hygiene, monitoring the state of health and the immune system, and timely treatment of sexually transmitted infections are also important.
What to read on the topic?
In order to better understand sexually transmitted infections and be able to protect yourself from them, studying basic physiology will help. It is unlikely that you will be able to enroll in medicine or biology to update your knowledge, but you can engage in self-education. To better understand female physiology (and at the same time learn about hormones, contraception and what vulvodynia is), we recommend the book Viva la Vagina. And in order to get a more complete picture, we’ll immediately point you to a male research center – Bravo Penis. In both books you can get more complete information regarding the genitals and related problems and diseases. And knowledge of physiological mechanisms and your own body will make you an even more educated interlocutor.