Herpes is a viral disease with the main symptom being blisters on the skin. 90% of the population has the virus, but only 5% show symptoms. In other cases, the disease occurs without symptoms or clinical consequences. A virus of the Herpresviridae family provokes life-threatening diseases and infections, which are one of the causes of deformities in children.
The disease affects:
- Mucous membrane.
- Eyes (keratitis, conjunctivitis), skin.
- Nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis).
- The mucous membrane of the genital organs.
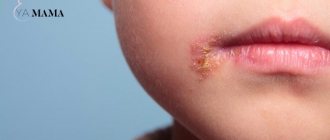
Rashes appear on the porches of the nose, borders of the lips, cheeks, eyelids, forehead, ear area, inner surface of the cheeks and lips. The most common place is the corners of the lips. There are cases when herpes on the body (photo) occurs in all places at the same time.
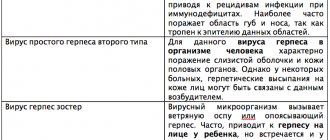
Symptoms of herpes type 1 - the virus that causes the “cold”
Herpes type 1 is the simplest and most quickly suppressed virus. Basically, the infection is stored in the nerve endings of the cervical spine in a dormant state, but with a decrease in immunity or under the influence of stress, it becomes more active and manifests itself with the following symptoms:
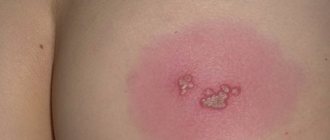
- First, the skin turns red and there is a burning sensation and itching.
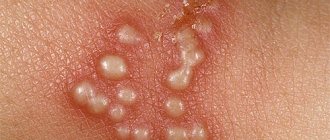
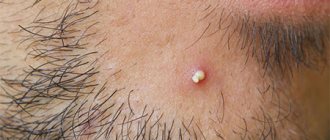
- After 6-48 hours, one or more vesicles - bubbles containing a clear liquid inside - form on the inflamed area.
- If left untreated or scratched, the vesicles burst, spreading infected fluid around and causing the affected area of skin to enlarge.
- In place of the burst bubbles, a wound appears, which over time becomes covered with a crust.
- With the support of the immune system, the disease gradually “falls asleep” again—it goes into a latent state. Without support, large areas are damaged and wounds do not heal normally.
If a person has symptoms, they can infect others through contact. Most often, herpes 1 is localized on the face and mucous membranes of the mouth. It can affect the lips, cheeks, chin, mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, mouth or larynx. Sometimes the infection gets to the skin of the torso, causing the disease to spread to the body.
How does it manifest?
Almost everyone knows what this disease looks like on the skin. Herpetic rash of all types forms similar rashes.
Bubbles form on all parts of the body, especially often their locations appear in the cheeks and lips. The viruses that cause different types of disease are so similar that the differences cannot be seen even under a powerful electron microscope.
The initial stage is small blisters filled with clear liquid, which becomes cloudy after a couple of days. They itch, gradually bursting and forming wounds on which a crust forms. These sores never heal, so the disease manifests itself painfully in humans.
With good immunity, the disease can go away without treatment within one or two weeks. If the immune system is weakened, a person suffers from allergies, then healing of wounds takes a long time, and herpes ulcers form.
With herpes, a sick person can infect people from his social circle. The infection spreads when herpetic blisters burst and sores form. If the immune system is weakened, then herpes formations quickly spread throughout the body, the skin is affected in large areas.
If a rash accompanies an acute respiratory infection, its appearance may be mistaken for a sign of recovery. This is wrong. In this case, viral herpes is a complication caused by a cold or acute respiratory infection .
Symptoms of herpes type 2 - the genital form of the virus
The symptoms of herpes type 2 are similar to type 1, but the localization of the blisters is different. In a dormant state, this virus is located in the nerve endings of the sacral clutch. Vesicles are formed mainly in the groin area, on the thighs, buttocks, anus and genitals.
In addition to the usual symptoms, deterioration in mood and mental state, loss of appetite, and signs of intoxication are observed. Possible enlargement of the lymph nodes in the groin area. In women, vesicles can appear inside the vagina and on the cervix, in men - in the urethra.
Attention! Most often, relapses of the second herpes simplex occur in the fall or winter, when the prevalence of other viral diseases is high. On average, with the support of the immune system, symptoms disappear within 2-3 weeks.
Prevention methods
It is much easier to prevent the appearance of herpes than to try to get rid of a progressive virus.
Therefore, for prevention you should follow simple rules:
- healthy lifestyle,
- proper nutrition,
- moderate physical activity,
- maintaining personal hygiene rules,
- correct treatment of diseases.
Only your own desire and responsible attitude towards your health will protect you from the appearance of herpes and other diseases!
Symptoms of herpes type 3 - the Zoster virus, which causes chickenpox and shingles
The herpes zoster virus is usually infected in childhood, and it manifests itself in the form of ordinary chickenpox. When a child recovers, an infection remains in the endings of his trigeminal nerve forever, although it does not manifest itself under normal living conditions.
When immunity falls, a person gets sick with an acute respiratory infection or simply lives unhealthy, the symptoms of the disease appear again. Most often, the lesion occurs in people over 50 years of age, while recurrence of this type of herpes is the rarest (observed in only 5% of patients).
Repeated disease is called herpes zoster and has the following symptoms:
- the affected nerves hurt, burn, or tingle;
- when moving, heating or touching this area, the discomfort increases;
- duration of pain – 3-12 days;
- the temperature may rise to subfebrile;
- a few days after the onset of pain, redness and swelling occur on the skin and mucous membranes;
- contagious (infectious) vesicles appear on the surface of the inflamed area;
- the liquid in the bubbles gradually becomes cloudy, after which they explode;
- wounds from burst vesicles become covered with crusts.
As a rule, the disease goes away after 1-3 weeks. After the rash appears, the pain is replaced by itching. In rare cases, the pain does not go away, it subsides, but appears throughout life.
Where could it be?
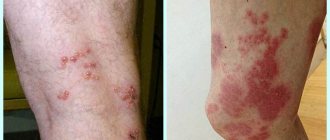
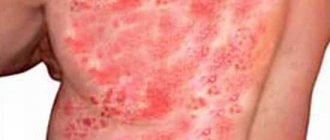
Located on the chest, abdomen, neck, under the armpit, on the surfaces of the mucous membranes. Spread to all parts of the body indicates reduced immunity and a significant titer of antibodies to the virus.
Varieties of herpes are sometimes localized to specific areas of the body. Localization is an indicator of the body’s successful fight.
There are such types:
- Labial or oral . Spreads during kissing, sharing cutlery and towels.
- Genital . It is transmitted through contact between sexual partners.
- Zoster (chickenpox). Distributed through the air by droplets.
Zoster is localized on the sternum, on the back, on the shoulder.
Related article:
How is vaginal herpes treated? What are the dangers of illness during pregnancy?
Genital herpes can be seen in the buttocks, thighs, and lower back. In women it appears on the abdomen and thighs as a relapse at the end of menstruation. A rash in the abdominal area is a sign that your period is approaching.
A rash during pregnancy is considered especially dangerous , as it can provoke neonatal herpes, which is the cause of death in 90% of those infected during pregnancy.
Herpes zoster may appear on the chest, hips, back, and spine. It is caused by the chickenpox virus. sometimes called herpes zoster . It affects not only adults, but also children. The virus attacks the fibers of the nervous system, causing severe pain and scratching.
The third type (Zoster) can form in the legs and feet, causing pain when walking.
Lichen simplex is a typical presentation caused by the herpes simplex virus . It consists of bubbles with clear liquid randomly located throughout the body. Often appears in areas that are inflamed. One of the rare forms of lichen appears on the fingers and is transmitted through injuries and skin damage. In severe forms, it provokes the development of Kaposi's eczema, covering large areas, causing an increase in body temperature.
Lichen blisters can be caused by genital herpes due to self-infection or from using someone else's hygiene products.
Herpes on the body - video
Symptoms of herpes type 4 - mononucleosis from the Epstein-Barr virus
Epstein-Barr virus causes a disease called infectious mononucleosis. The disease is quite dangerous and requires treatment to prevent undesirable consequences - deep genital ulcers in women, destruction of blood cells, oncological pathologies (types of lymphomas), autoimmune diseases and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Typically, when infected with herpes virus type 4, the following symptoms are observed after 7-14 days:
- weakness;
- headache;
- drowsiness;
- nausea;
- heat;
- sore throat with cough;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- itchy rash;
- white or yellowish coating on the palate;
- enlarged liver and spleen (possible jaundice);
- formation of atypical cells in the blood - mononuclear cells.
The patient is often thirsty and has a fever for about a week. Lymph nodes shrink within a month, blood changes can last up to 6 months. Correct treatment leads to recovery and lifelong immunity; its absence leads to a chronic form of the disease:
- Erased - muscle pain, aching joints, frequent low-grade fever, fatigue.
- Atypical – frequent relapses of infectious diseases (acute respiratory infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or genitourinary system).
- Active - ordinary mononucleosis symptoms are complicated by herpetic eruptions, fungal or bacterial infection. Possible damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, dyspepsia.
- Generalized – severe damage to the central nervous system, including meningitis, encephalitis, radiculoneuritis. Increased risk of myocarditis, hepatitis or pneumonitis.
Symptoms of chronic Epstein-Barr infection manifest themselves in waves - the number and intensity of symptoms gradually increase and also gradually decrease depending on the state of the immune system.
Symptoms of herpes type 5 - cytomegalovirus infection (CMV)
Cytomegalovirus does not appear immediately after infection; the carrier of the infection often does not even know about his own situation. With a strong immune system, the disease may never enter the active phase, but simply “sleep” in the body asymptomatically until the end of life (in 90% of cases this happens). However, the person will continue to transmit the virus to other people.
Patients with symptoms of CMV most often complain of signs of acute respiratory infections and mononucleosis (fever, fatigue, headaches, chills) that occur 20-60 days after infection. The duration of the disease is generally 4-6 weeks. If the activity of the virus is caused by immunodeficiency, pleurisy, pneumonia, arthritis, encephalitis or myocarditis may occur. Autonomic disorders are observed.
In its generalized form, CMV causes damage to the entire body - inflammation of the tissues of internal organs, eyes, brain, as well as paralysis. In men, there may be damage to the tissues of the testicles and urethra; in women, there may be inflammation or erosion on the cervix, uterus, vagina or ovaries, and blue-white discharge.
Symptoms of poorly studied forms of herpes virus types 6, 7 and 8
Herpes type 6 lives in microphages and lymphocytes. Among all adults, about 50% are carriers of this infection, infecting the rest through blood and saliva, as well as by airborne droplets.
Symptoms of the disease are an itchy rash on the skin and mucous membranes, fever, ulcers or spots on the skin of the back, chest or abdomen (exanthema), mononucleosis syndrome, asthenia. With immunodeficiency, encephalitis is possible.
The infection often occurs in young children (3 months - 4 years). It is manifested by sudden exanthema and fever (up to 40° C), signs of intoxication. Symptoms last up to 4 days, then they are replaced by a rash that goes away within 3 days. Sometimes after a fever there is no rash, but there may be cramps due to too high a temperature. Upon reaching 5 years of age, most children develop immunity against herpes type 6; relapse can only be caused by particularly severe immunodeficiency.
Herpes type 7 promotes the activation of type 6 virus and increases the risk of developing chronic fatigue syndrome. This syndrome is the main manifestation of a viral infection.
It manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- general loss of strength;
- constant fatigue and lack of tone;
- bad mood, anxiety and psycho-emotional overload;
- loss of ability to work and concentrate;
- lack of positive changes even after a long rest;
- memory disorders;
- headaches and tearfulness;
- sleep disturbances and lack of sleep even during prolonged sleep;
- signs of depression;
- slight increase in temperature for a long time (up to six months);
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Worth noticing! When making a diagnosis based on these symptoms, a specialist must differentiate the disease from psychiatric/nervous pathologies, HIV infection, cancer, anemia and thyroid dysfunction.
Herpes type 8 is the least studied. Its symptoms include the development of other diseases - Kaposi's sarcoma, primary lymphomas, Castleman's disease and multiple myeloma. In this case, the patient develops malignant neoplasms on the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs and lymph nodes, which look like symmetrical plaques or dark red or purple spots. There may also be a bloody cough, severe dyspepsia, and pain when eating.
Treatment tactics
If you notice the first signs of the disease, you should immediately contact a specialist. He will prescribe the correct treatment tactics and prevent the progression of the disease.
Since the main reason for the activation of herpes is a decrease in immunity, it will be necessary to undergo examination by an endocrinologist and an infectious disease specialist.
To speed up treatment, the use of ointments and other local remedies is effective. They are applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin several times a day. The use of these drugs will not only reduce the concentration of the virus in the wound, but also prevent dust and other foreign objects from entering it.
For example, Fenestil ointment will relieve swelling and eliminate itching, zinc will accelerate the process of skin regeneration, and antibacterial drugs will eliminate the possibility of infection on the skin.
Additional medications in the form of tablets for oral administration are prescribed by the doctor. You cannot undertake treatment on your own, because some of the drugs have side effects and can cause the following pathologies:
- cystitis,
- inflammatory processes,
- suppuration of vesicles,
- damage to the heart muscle.
For frequent exacerbations, suppressive therapy is prescribed, in which drugs are prescribed for a long time. Their action is aimed at destroying not the symptoms of herpes, but its foci in the nerve ganglia.
Symptoms of any type of ocular herpes
Ophthalmoherpes develops on the retina, eyelids or mucous membranes of the eyes. Relapses can occur 3-5 times a year - this is one of the most common forms of herpes infection, mainly caused by types 1 and 3 of the virus.
The symptoms of ocular herpes are similar to allergies or from a bacterial infection; herpetic vesicles appear on the eyes, and the following signs are also observed:
- the eyeballs and eyelids turn red;
- there is pain and a feeling as if there is a foreign body in the eye;
- in good lighting there is discomfort;
- visual acuity decreases and becomes “foggy”;
- sparks or flashes are visible before the eyes;
- the shape and size of objects seem incorrect or double;
- twilight vision is significantly reduced;
- blepharospasms - the eyelids contract convulsively.
Patients often complain of severe pain in the orbit and above the eyebrow. The field of view becomes narrower, and there may be a blind spot in the center. Moving your eyes is difficult and painful. All this may be accompanied by nausea, low-grade fever and headaches.
Diagnostics
To confirm the presence of the disease, a series of examinations must be carried out.
On this topic
- Herpes
All about herpes on the lower back
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 16, 2020
A presumptive diagnosis of herpetic infection can be made based on severe symptoms, since the rash has specific characteristics.
At the first visit to a specialist, an external examination of the patient and anamnesis will be taken.
If this is not enough to make a final diagnosis, the attending physician will order additional laboratory tests:
- General blood - allows you to determine the typical inflammatory process of the virus; There is an increased level of lymphocytes, ESR, and leukopenia.
- Polymerase chain reaction - helps to identify the genetic material of a viral infection in the human body and evaluates the overall infectious impact - the level of the pathogen in the blood.
- Enzyme immunoassay - helps in determining antibodies to the herpes virus. Due to the fact that the production of antibodies occurs already during the initial infection, the method is of no value.
To make a correct diagnosis, these examinations are more than enough. Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines the appropriate treatment method.
Symptoms of herpetic sore throat
Adults and children who have the herpes virus in their bodies often experience a sore throat caused by this infection. Its onset is usually abrupt and extremely acute:
- The temperature rises to 40-41° C, as with pneumonia.
- Severe pain occurs in the throat, it is very difficult to swallow, the discomfort lasts for at least 3 days.
- The mucous membrane of the pharynx becomes swollen, and a herpetic rash with white blisters is visible on the tonsils and palate.
- Over time, the vesicles merge with each other, forming a dense white “patina” covered with a film and surrounded by redness.
- Suppuration of the rash lasts up to 3 weeks, during which herpes can spread to the skin of the face.
The incubation period of herpetic sore throat lasts 1-2 weeks. Sometimes the patient recovers easily - intoxication goes away before the vesicles appear by 6 days, treatment is greatly simplified. Sometimes complications arise - herpetic rhinitis, chronic tonsillitis, otitis media, myocarditis, encephalitis, etc.
Routes of infection
You can become infected with the herpes simplex virus through contact transmission. In this case, antibodies enter the body of a healthy person through interaction with a source of infection, which can be infected people or objects. The contact-household method involves infection during normal everyday activities: the direct route is handshakes, kisses, hugs, and the indirect route is through personal hygiene items, cutlery and other environmental objects.
Symptoms of herpes on internal organs
Internal herpes manifests itself with the usual symptoms of other diseases, since it causes them. No visible signs of the herpes virus are usually observed; the type of infection can only be determined by clinical studies and laboratory tests.
As a rule, with ulcers in the esophagus due to herpes rashes, a person suffers from pain behind the sternum and when swallowing. A doctor can detect ulcers through an endoscopic examination. Pneumonia, bronchitis and tracheitis with characteristic symptoms (fever, cough, shortness of breath) are detected through special tests for type 1 herpes; often these diseases are accompanied by a fungal or bacterial infection.
If the patient has herpetic hepatitis, the symptoms will be similar to those usual for hepatitis B or C - jaundice, change in the color of urine and stool, fever. To identify the cause of the disease, the patient is prescribed a test for herpes viruses. And so with any other damage to internal organs, this virus does not have any specific symptoms.
Complications
In the absence or late treatment, herpes on the abdomen can provoke the development of serious complications. Among such pathologies are:
- cystitis;
- myocarditis;
- pyoderma;
- inflammatory processes occurring in internal organs.
In order not to start the disease, it is important not to ignore the first manifestations of the rash and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Particular attention should be paid to the first signs of infection during pregnancy. Herpes can not only complicate pregnancy, but also lead to infection of the fetus during intrauterine development.
Symptoms of postherpetic neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is an echo of the disease after recovery from type 3 herpes. After a relapse of the Zoster virus, the patient remains with a feeling of discomfort and symptoms of infection, although the disease has already “subsided.” Acute symptoms also disappear completely. So, with such neuralgia there are:
- residual drying and flaking crusts in places where there was shingles;
- throbbing pain or tingling in this area, sometimes extremely strong;
- itching between painful attacks, causing irritation, which only intensifies subsequent pain;
- numbness of the skin areas at the site of the former lichen or an extremely strong reaction to external irritants;
- muscle weakness and paralytic conditions (more often in old age).
Typically, postherpetic neuralgia lasts 2-3 weeks, but sometimes it remains for 2 months or even a year. Some symptoms last even longer, such as muscle weakness or extreme skin reactions. All this interferes with the normal lifestyle of people who have experienced reactivation of the chickenpox virus.
The causative agent of infection
The causative agent is a virus called Varicella-Zoster. This microorganism belongs to the group of herpes viruses, and along with shingles, it causes chickenpox. The herpes virus is unstable in the external environment and quickly dies when exposed to disinfectants or boiling. It is resistant to low temperatures.
Transmission of the causative agent of chickenpox and shingles from person to person is carried out by contact and airborne droplets. Infection most often occurs in spring and autumn.