Papillomavirus can attack the human body at almost any time. It develops on the skin and mucous membranes, so sometimes neoplasms appear in the vagina. This should serve as a signal for the woman to immediately begin treatment, since papilloma in the vagina can lead to a number of complications, including the formation of cancerous tumors.
READERS RECOMMEND!!!
To treat papillomas, our readers actively use the remedy... Read more
In the article below you will find a lot of useful information about the causes of this disease, its symptoms, and most importantly, how to treat papillomas in the vagina and which method should be preferred.
What is HPV in gynecology
HPV in gynecology unites one of the largest families of viruses. More than 100 types of this virus have been identified, and 80 of them are dangerous. Currently, each strain was given a serial number and divided into 3 groups.
- Non-oncogenic. Viruses of genotype 1,2,4,5 cannot degenerate into malignant formations. They cause warts on the hands, feet and other parts of the body.
- Low oncogenic. In rare cases, genotypes 6,11, 43 and 44 are detected when examining patients with precancerous diseases. They form pointed papillomas in the perineum.
- Highly oncogenic. This group includes more than 13 types of viruses, but the most dangerous are 16 and 18. They were identified in women who were diagnosed with cervical cancer.
It is believed that HPV is the cause of cancer. It disrupts the normal division of cells in a certain area, which provokes their degeneration into malignant ones.
The danger of vaginal papillomas
Condylomas that form in the vagina due to exposure to the virus, when it is activated, grow to their maximum size within just a few hours. Single neoplasms in the vagina are usually painless, but multiple ones, on the contrary, are the culprits of quite severe painful sensations. But psychological and physical discomfort is not the only danger. These genital rashes, called condylomatosis, lead to serious genital cancer. The risk of this scenario developing is high.
Growths on the vaginal mucosa in women are much more dangerous than HPV in men. Vulvar papillomas in women are much more difficult to detect due to the structural features of the genital organs, so the disease can only be recognized during a preventive examination, which many ignore. The situation is aggravated by estrogen produced in the ovaries: it has been found that thanks to it, ordinary papillomatosis degenerates into a malignant neoplasm of the cervix. Most often this is squamous cell carcinoma, the leader in genital cancer.
During pregnancy, danger awaits the expectant mother from several sides at once, since weakened immunity and changes in the hormonal system lead to a sharp increase in the number of neoplasms. This is fraught with the following troubles of varying severity:
- If multiple condylomas appear in the birth canal, childbirth may be difficult, and bleeding is possible. Then the only option will be a caesarean section.
- The infection from the mother will be transmitted to the child during childbirth, and this threatens the baby with respiratory tract papillomatosis.
- A dangerous complication is the addition of secondary infections in case of bleeding in the vagina.
The reason for the appearance of the tumor
Papillomas in the vagina appear unexpectedly and are usually discovered during a gynecological examination. Papillomas on the labia can also be seen independently. Vaginal papillomas come in several types - pointed on a high stalk and flatter, merging with the mucous membranes. The latter are more dangerous - they cause dysplasia and cervical cancer.
Papillomas on the genitals appear due to HPV infection. This viral disease is easily transmitted through sexual contact. Women are more susceptible to HPV than men due to the structure of their genitals. Moreover, in women, papillomas in the vagina more often degenerate and become malignant than those located on the genitals of men.
With unprotected sexual intercourse, the risk of infection is 80%. Women who have a strong immune system that will prevent the virus from entering the body remain healthy. Papillomavirus is transmitted through any type of sex and even kissing. To do this, contact of skin or mucous membranes with infected people is sufficient. Even when using a condom, the risk of infection is 30%.
Papilloma in an intimate area can occur not only after sexual intercourse with men who are infected. The human papillomavirus in gynecology is almost as common as genital herpes, but is slightly inferior to it. The disease is transmitted through household and household contact. Using other people's towels, visiting bathhouses, shaking hands and wearing other people's clothes can provoke papillomas in the vagina.
Medicinal and traditional methods of treating papilloma on the vaginal walls
If during sex with your lover you still “caught” the papillomavirus, then treatment should begin immediately after the disease is diagnosed (this is especially important during pregnancy, so that the dangerous infection is not passed on to the child). To do this, you can use both medications that will be prescribed to you by your doctor, and folk remedies.
Treatment of papillomas in the vagina involves the use of the following medications:
- Alpisarin or Lycopid. These drugs cope excellently with all kinds of viruses and help get rid of even a large number of tumors. In order to cure papillomatosis in the vagina as quickly as possible, it is recommended to take them in combination with immunostimulating agents;
- Special creams or vaginal suppositories. The most popular is Galaderm ointment, which should be applied to the affected areas 2-3 times a day for several weeks. Riodoxol also boasts high efficiency, but when using this gel it is important not to overdo it with the dosage - it can cause minor burns, which are very unpleasant;
- Solcoderm or Interferon, prescribed during pregnancy.
In order to treat papillomas in the vagina at home, without seeing a doctor, you can use:
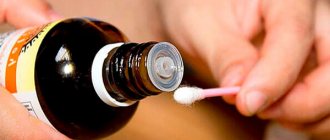
- Ammonia, which is used to treat the affected areas of the vagina several times a day;
- Sea buckthorn oil, thanks to its powerful antibacterial properties, allows you to quickly get rid of the external manifestations of papilloma;
- A solution of tar soap, which is an excellent antiseptic.
How does the virus manifest itself?
Papillomas on the labia after infection may not appear for a long time. In the latent form of the disease, the virus can be detected using laboratory tests. Treatment in this case is necessary, since the human papillomavirus in women can lead to the appearance of tumors in the future.
In the subclinical form, diagnosis is possible by colcoscopy and laboratory tests using special solutions. This form is quite dangerous and requires immediate treatment. It is necessary to remove papillomas from the vagina.
Clinical forms are diagnosed by visual examination. With the naked eye, neoplasms can be seen on the labia minora, vulva and vagina. They are a direct source of infection for sexual partners, as well as self-infection of other areas.
Micropapillomatosis of the vaginal vestibule
Sometimes the virus may not develop on the vaginal walls, but directly at the entrance to the vagina. This disease is called micropapillomatosis. According to medical professionals, it occurs in approximately every thirtieth woman.
The main culprits of infection are pathogenic viruses, which belong to one of the varieties of HPV. However, it should be said right away that they are safe for the female body and cannot cause any harm to it.
Papillomas at the entrance to the vagina are characteristic nodular neoplasms of flesh color. In most cases they are arranged symmetrically or in one row.
Symptoms of the disease
Papillomas in women are most often located on the external genitalia. When there is a large accumulation of them, they can resemble the comb of a rooster. If women have genital warts in the groin, they can be distinguished by their long stalk. Due to increased humidity and sweating, papillomas in the groin are injured and can become inflamed.
The most dangerous are flat condylomas in intimate places. They are provoked by genotypes of high oncogenic risk. Such a papilloma on the labia slightly rises above the mucous membranes and rarely merges with the rest into large formations. They are quite difficult to notice when they first appear.
Women with HPV may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain and itching in the genital area.
- Nonspecific vaginal discharge.
- The labia are slightly swollen.
- Irregularities and small compactions in the intimate area.
New growths may appear on the pubic area and other areas. Papillomas of the vulva and vagina are observed quite often. Regardless of their location, mandatory removal is required.
When condylomas form on the cervix, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain of unknown origin in the lower abdomen.
- Bloody issues.
- Weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Discomfort and pain during sex.
With these symptoms, a mandatory colcoscopy is required to rule out a precancerous condition, and if so, begin timely treatment. In this case, it is impossible to diagnose the disease yourself.
Description and varieties
Vulvar papillomatosis is characterized by severe swelling of the intimate area, inflammatory reactions with hyperemia, itching, and pain when urinating. The disease itself is of viral origin. Experts note that vulvovaginitis is one of the most common reasons for visiting a gynecologist. Genital papillomatosis develops as a result of increased HPV activity. When the clinical picture is pronounced, the patient may experience great discomfort. Against the background of secondary bacterial microflora, foul-smelling discharge may appear.
It is surprising that this disease is most often diagnosed in teenage girls, as well as in older women who are already in menopause. All local defense mechanisms of the body are suppressed, which is why the risk of developing such an insidious pathology rapidly increases. If a woman begins to notice that genital warts have appeared on the genitals, then they will certainly be followed by symptoms of an inflammatory nature, and this significantly complicates the correct diagnosis of the disease.
In some cases, papillomas on the vulva can be disguised as nodular neoplasms (abscesses with maceration, purulent spots) after accidental damage or scratching of the upper layer. High-quality diagnosis of vaginal papilloma cannot be done without a comprehensive examination with histological examination. Only after this can specialists develop individual therapy for the underlying disease with mandatory correction of the woman’s immune system.
If papillomas appear in the vagina, you should immediately contact a specialist, since at any moment these tumors can develop into melanoma - skin cancer. And this disease is considered the most dangerous among specialists, since in 89% of all cases the patient dies within two years. In addition, this pathology most often begins to manifest itself with papillomas and warts, which may not interfere at all with everyday life.
The more such neoplasms there are on the human body, the higher the likelihood that one of them will develop into a malignant neoplasm. Particularly dangerous are those cases when papillomas are located in the armpits and in the groin area.
Experts have found that absolutely all types of condylomas can be divided into two groups: pointed and broad. In the first case, the neoplasms are very similar in shape to a cone. Over time, numerous warts can unite with each other, merging into large growths. Experts say that such papillomas are very similar to a rooster's comb. They are soft and do not cause any discomfort or pain in the patient.
The situation is completely different with wide benign neoplasms, since they have a large diameter. Most often they are painted in a light color. They look more like dense plaques. Quite often, such papillomas appear against the background of secondary syphilis. In order not to get confused in the diagnosis, experts identify several forms of human condylomas:
- The subclinical type is characterized by latent formation of papillomas. Even with a standard gynecological examination, a specialist cannot determine them without the use of additional tests. In this case, it is best to use extended colposcopy.
- In the standard clinical form, clearly visible wide or pointed formations appear on the surface of the genitals, which rise above the surface of the body. Such condylomas are noticed by all women.
- Warts do not form in the latent form of papillomavirus. But the disease itself is in the body and continues to affect it. It is worth noting that only 6% of all people infected with HPV exhibit characteristic clinical symptoms. Most often, patients are faced with a latent form of the virus.
HPV during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of hormonal disruptions and weakened immunity. This is why papillomas in the groin area and vagina appear during this period if the virus was detected in the body. But it is worth understanding that HPV is not any contraindication for pregnancy. With it you can carry and give birth to a child.
If the appearance of papillomas on the female genital organs is accompanied by dysplastic changes, then the issue of treatment is decided on an individual basis. It is worth knowing that the disease can be transmitted to the baby. Papillomas may later appear in the baby’s larynx area. But in any case, HPV treatment cannot be carried out during this period.
Preventive measures
To protect yourself from HPV infection, which becomes the root cause of cervical cancer, preventive measures should not be forgotten for a minute. It is possible to prevent a dangerous disease, and the rules are quite simple:
- Regular intimate hygiene should become a law.
- Constant change of sexual partners is excluded. Promiscuous sex life will inevitably lead to papillomas.
- A gynecological examination and tests are required annually.
- Increasing immunity is impossible without getting rid of bad habits, changing your lifestyle and correcting your diet.
- At the slightest suspicion of illness, you should consult a doctor.
- Self-medication can make diagnosis difficult.
It will not be possible to cure HPV, but by following these recommendations, you can still achieve results - the disappearance of relapses of the disease, a happy disposal of condylomas in the vagina.
Diagnostics
In order to prescribe the correct treatment, it is not enough to conduct a visual examination, even if there are papillomas of the vulva and vagina. The HPV genotype plays a major role. It can be established using PCR diagnostics. The analysis is similar to a regular smear in women in gynecology, which is taken with a special brush. DNA testing is carried out to identify the smallest viruses that may be in latent form.
There are other tests, but PCR is the most reliable and is performed in almost all laboratories. Digene has proven itself well - a test that also detects the virus, indicates its quantity and degree of oncogenicity, but it is not performed everywhere and has a high cost.
Are papillomas dangerous?
Papillomas of any type can pose a hidden danger.
- If the growth is injured, it begins to spread to healthy areas, which leads to the growth of unpleasant formations.
- Infection can penetrate into damaged papilloma tissue, which threatens the development of inflammation of the groin area.
- There is a high tendency of papilloma to enter the oncogenic stage, especially those that affect the woman’s cervix.
Papillomas in the intimate area can develop into cancer
Treatment
Treatment of papillomas on the labia consists not only of removing tumors, but also of antiviral therapy and strengthening the immune system. Only the attending physician can prescribe effective antiviral drugs, depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
Most often used:
- Panavir.
- Vikferon.
- Reaferon.
- Gropronosin.
It is necessary to treat HPV with antiviral drugs for a long time. The course of treatment may take several months. In order to evaluate the success of therapy, a study is carried out to quantify the virus. Finding an effective drug is quite difficult, since the virus is too stable.
Removal of genital warts on the perineum is possible using the following methods:
- Electrocoagulation. Removal occurs through electric current. Papillomas on small or other areas of the body receive an electrical burn, after which a crust forms, which heals in about 2 weeks. A rather painful method that can lead to burns of healthy tissue.
- Surgical removal. It is performed very rarely in the case of malignant neoplasms of the vagina. May cause scarring and bleeding.
- Cryodestruction. It is the removal of papillomas on the vulva with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperatures, the neoplasm is destroyed. The procedure is painless, but if the doctor is inexperienced, it can cause frostbite to adjacent tissues.
- Radiocoagulation. High frequency affects tumors and destroys them painlessly. One of the best ways to remove vaginal papillomas, as it does not lead to scarring or bleeding.
- Laser removal. Allows you to remove papillomas from almost any part of the body. After the procedures, minor discomfort is possible.
Before removing tumors, it is worth eliminating the causes that caused the activation of the virus. It is important to know what papilloma is, since it is simply an accumulation of viral cells on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. If antiviral therapy is not carried out and the immune system is not strengthened, neoplasms may arise again.
Removal is possible using special alkali solutions. Regardless of the method chosen, viral pathology must be removed by the treating specialist. When independently using chemicals with active chemicals, many people received severe chemical burns.
Products for external use:
- Solcoderm.
- Condilin.
- Verrucacid.
The most effective remedy for removing genital warts is Solcoderm. In most cases, one use of this remedy is enough to get rid of tumors. However, this drug should be applied by a doctor who can avoid affecting healthy areas of the skin.
There are also more aggressive agents, the removal of which is undesirable on mucous membranes. For example, super celandine can be applied to the pubis and other areas of the body. This remedy is a solution of alkalis and acids, and papillomas are removed by cauterizing them. If the chemical is applied to the genitals, you can get burned.
If there is at least one sign of the appearance of HPV in the body, you should immediately contact a specialist. Papilloma in gynecology is not just a cosmetic defect, but a high risk of developing oncogenic neoplasms. Treatment at an early stage reduces the risk of malignant degeneration and helps drive the virus into a dormant state.
Removal of papillomas in the vagina using a hardware technique
If it is not possible to get rid of tumors using traditional treatment or folk methods, then it is recommended to use the so-called “hardware method”. How to get rid of all kinds of papillomas in this way? What procedures do qualified doctors recommend to use? You can find out about this by studying the table below.
| Laser therapy | Involves the use of a laser beam. After treatment with the last papilloma inside the vagina, it almost instantly loses moisture and dries out. It can then be quickly and painlessly removed. In most cases, one session is enough to get rid of tumors. |
| Radio wave surgery | Perhaps the most effective and painless way. The neoplasm is treated with radio waves, which disrupt the DNA structure of the virus and prevent it from multiplying. After removal of papillomas, no scars or scars remain. The only disadvantage of the procedure is its high cost, so not everyone can afford it. |
| Electrocoagulation | Vaginal papillomas are exposed to directed electric current. As a result, HPV reproduction stops and after a couple of hours the neoplasm dies. |
| Cryodestruction | It involves treating the neoplasm with liquid nitrogen. Low temperature prevents further division of pathogenic cells and localizes the affected area, which makes further spread of the virus impossible. |
Reviews
“I didn’t pay any attention when I discovered a small lump in my vagina that looked like a wart. A few months later, several more growths appeared. I don't understand where they come from. After the examination, I was prescribed injections and Panavir ointment. Education is gradually decreasing.”
“Warts suddenly began to appear in my pubic area, and later near my anus. I underwent an examination, after which the doctors prescribed laser removal. I was worried, but everything went painlessly. I took Acyclovir tablets for some time to consolidate the effect, as the doctor said.”
“I treated papillomas in the groin (in the crease between the legs) with celandine for a long time, but they did not disappear. After consulting with a doctor, it turned out that complex therapy was needed. They cut off the growths and sent me for analysis. Thank God, the formations turned out to be benign. I continue treatment with immunomodulators.”
Rate this article (No ratings yet)