Treatment of furunculosis with system-wide drugs is carried out as prescribed by a doctor. Only local remedies that promote the maturation of the abscess are allowed on their own: ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky’s liniment.
The goal of drug treatment of furunculosis is to suppress the activity of staphylococcus, stop the purulent process, regenerate the skin in a short time and improve the patient’s immune defense.
Causes and mechanism of development
Furunculosis is an inflammation of the hair follicle with the formation of a purulent core, accompanied by the spread of infection to the surrounding connective tissue of the middle layer of the skin. The causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus, less commonly the cause of infection is Staphylococcus epidermidis.
These microorganisms are common in the environment: street dust, industrial premises, clothing, living rooms. They quite often live on the surface of human skin and the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx without causing any diseases. According to some reports, up to 75% of people are carriers of staphylococci.
Is it possible to become infected with furunculosis from another person? Transmission of staphylococcus itself is possible, but for the development of the disease, the presence of exogenous and endogenous factors is necessary, which we will discuss below.
Staphylococci are most often found in the mouths of hair follicles, where hair exits the skin, as well as in the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands. Up to 90% of these microbes are non-pathogenic strains. Under certain conditions, non-dangerous forms of this bacterium can become pathogenic (disease-causing).
A furuncle can occur both on healthy skin and on skin affected by other forms of staphyloderma when the process spreads to the hair follicle. Like any infectious disease, furunculosis occurs as a result of the interaction of a pathogen and a macroorganism. For its development, not only a source (staphylococcus), but also internal (endogenous) predisposing factors, as well as certain environmental conditions (exogenous factors) are required.
Exogenous factors contributing to the development of furunculosis:
- minor injuries caused by solid particles of coal or metal suspended in the air in production, creating an entry gate for bacteria;
- friction of clothing on the lower back, neck, buttocks, which contributes to the transition of saprophytic (safe for humans) forms into pathogenic ones and their penetration deep into the skin;
- scratching the skin of patients with other pathologies - eczema, neurodermatitis, scabies.
Endogenous factors that increase the risk of developing furunculosis:
- exhaustion of the body and hypovitaminosis;
- diseases of the endocrine glands (diabetes mellitus, obesity), anemia, intestinal diseases, nervous system diseases;
- alcoholism;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body, especially repeated.
Endogenous factors cause a decrease in the body's reactivity, in particular, inhibition of local immune reactions. The pathogen penetrates the skin through damage caused by external factors. There it finds itself in a favorable environment and begins to actively multiply, causing inflammation.
Among the many substances secreted by this microbe, coagulase is of particular importance. Under the influence of this enzyme, coagulation (clotting) of blood plasma and blockade of surrounding lymphatic vessels occurs. This leads to the limitation of infection with the formation of infiltrates with the subsequent formation of purulent-necrotic rods. Staphylococcus aureus also secretes hyaluronidase, which dissolves the base of connective tissue and promotes the penetration of microorganisms into the deep layers of the skin. Thus, staphylococcal infection is characterized by spread not laterally, but in depth.
Furunculosis most often appears in autumn and spring. Mostly men suffer from it. The disease affects women and children less frequently. This is explained by the fact that the causes of furunculosis are much more often observed in adult men.
There is an opinion that many diseases are based on psychological causes. The psychosomatics of furunculosis is based on the assertion that emotions such as anger and constant irritation are favorable for its appearance. It can be assumed that negative emotions cause a prolonged release of stress hormones and subsequent exhaustion of the adrenal glands, which, in turn, leads to suppression of the immune system and the development of chronic furunculosis.
There are single boils, recurrent boils that appear after some time, and furunculosis, in which pustules appear continuously one after another.
Differential diagnosis
A boil is an inflamed formation in the skin filled with purulent contents. Inflammations can be of various sizes, from small painful pimples to large formations of purulent tumors. The difference between boils is that the place of their formation must necessarily have hair or areas of skin where friction is present. Most often this is the area of the lower back, chest, armpits and groin. A boil under the armpit is much more dangerous than abscesses in other parts of the body.
Clinical picture
The development of the boil occurs sequentially and has three stages:
- development of infiltration;
- suppuration and necrosis;
- healing.
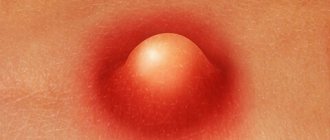
As such, the incubation period of furunculosis is difficult to determine, since in most cases the disease is caused by its own microorganisms that have long settled on the skin. Initially, a raised compaction (infiltrate) appears around the hair follicle. It is bright red in color, has unclear boundaries, is slightly painful, or is accompanied by a tingling sensation.
After one or two days, the infiltrate thickens and expands, taking on the shape of a tumor and becoming painful. Nearby tissues swell, especially if a boil develops on the face.
After three to four days, the next stage develops. The infiltrate increases to 1-3 cm, in the middle of it a core is formed, consisting of dead and disintegrated tissue. A pustule forms at the top of the boil, which looks like a white head. The formation of a purulent-necrotic core is due to the fact that active inflammation occurs in the center of the follicle, which results in massive death of immune cells recruited to fight the infection. Pus consists of remnants of leukocytes, destroyed microorganisms, and decayed tissue of the hair follicle.
Read also Psoriasis - causes, stages, treatment
At this stage, the boil resembles a cone covered with smooth, stretched skin. The formation is painful, especially when located in the external auditory canal, scalp, fingers, or shins. If there are multiple ulcers, the patient’s body temperature may rise to 37-38 degrees. Symptoms of intoxication (poisoning) appear: weakness, headache.
This stage lasts about 3 days. Then the pustule opens, pus is released through the top of the follicle, sometimes with blood, and then a yellow-green purulent “plug” comes out - a necrotic core. In place of the abscess, an ulcer forms, which has uneven edges and a “undermined” bottom. It is filled with necrotic masses.
After cleansing the follicle cavity, the patient’s condition improves, the temperature returns to normal, and the pain goes away. Within a few days, the ulcer cavity is filled with granulations, that is, it heals. A bluish-red scar forms, which then fades. The total duration of such a cycle is about 10 days. Especially large boils form in diabetes mellitus.
Recurrent furunculosis is accompanied by the formation of a new abscess after the previous one has healed. This condition most often occurs in adolescents, young men, and young adults with an allergic predisposition (sensitization) to staphylococci, as well as in patients with diabetes, alcoholism, and diseases of the stomach and intestines. Often a recurrence of the boil occurs with pediculosis (lice) and scabies.
When the course of the disease is erased, the infiltrate does not suppurate, and a necrotic core does not form.
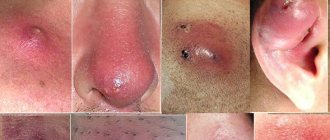
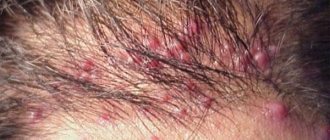
Boils can form on any part of the body, except the soles and palms, where there are no hair follicles. Favorite sites of infection are the back of the head, forearms, lower back, abdomen, buttocks and lower extremities.
Acute furunculosis lasts from several weeks to two months. It is accompanied by the appearance of numerous boils. Chronic furunculosis is characterized by a few follicles that appear constantly or with short breaks over several months.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a boil is a very complex process . During diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate it from deep trichophytosis, anthrax and hidradenitis.
- Trichophytosis granuloma - appears on the beard and head. When diagnosing this disease, anamnesis or contact with animals, which could be the cause of the infection, is of particular importance, as well as painful sensations with a purulent core.
- Anthrax - the disease begins with a papulovesicle, gradually becoming covered with a black stupor. Accompanied by infiltration of the hypodermis, severe pain and disturbances in general condition.
- Hidradenitis is a purulent formation of apocrine glands. The infection does not have a core and manifests itself in the area of the breast nipples, armpits, in the anal area and inguinal folds.
The main feature of boils under the arm is that they form only in areas of hair growth . It is difficult to identify a boil; the first sign of a boil can be confused with ordinary irritation. A clear sign is swelling, itching, swelling in the area of the hair follicle and redness. Then, at the site of redness, an inflamed node forms, which is purple or red in color and very painful. The swelling increases all the time, and after a few days, the inflamed skin becomes green, and a rod appears in this area.
It should be noted that the tumor can cause discomfort, weakness and headaches. After a few more days, the infection core is rejected and a bleeding wound appears in its area. Remember that boils should not be squeezed, massaged or even touched.
One boil is not dangerous to humans , but several already indicate serious health problems. New growths on the face and neck can cause fever and chills. If neoplasms appear frequently and several at a time, then this disease is called furunculosis, it can only be cured with medications. If treatment is not done in a timely manner, complications can even lead to fatal consequences, most often blood poisoning.
Complications
The consequences of furunculosis are a cosmetic defect caused by scarring. In some people prone to the formation of keloid scars, traces of furunculosis may be significant, with tightening of the surrounding tissue. The formation of boils is especially dangerous in exhausted, weakened patients. In such patients, the disease is often complicated by an abscess or phlegmon (purulent melting) of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The appearance of boils on the upper lip is very dangerous. From here, infection through the venous and lymphatic vessels can easily spread to the vessels of the brain and even cause sepsis - a general blood infection.
Infection of the veins with a facial boil causes progressive inflammation, that is, thrombophlebitis. From there, the pathogens enter the sinuses (extensions) of the dura mater, causing a serious complication - purulent basal meningitis. It is accompanied by the rapid development of facial edema. Condensed veins are palpable and may be painful. Body temperature rises sharply to 40 degrees and above. Rigidity of the neck muscles is observed (the patient cannot tilt his head forward), headache, blurred vision and consciousness.
If the formation occurs on the neck, thigh, shoulder, it can be complicated by lymphadenitis - inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
If staphylococcus gets into the blood, purulent foci may form in the internal organs - liver, kidneys and others.
Factors contributing to the development of complications:
- attempted squeezing, piercing or other impact;
- injury while shaving;
- irrational treatment with only ointments and other topical agents;
- location of the boil in the nasolabial triangle, on the nose.
Is it possible to smear a boil with iodine?
Antiseptics, including cauterization with iodine, can stop the process of inflammation and boil formation. In order to stop the sensation of itching and burning, you should cauterize the site of inflammation with iodine. So:
- Soak a cotton swab in an iodine solution.
- Press directly onto the inflamed area for 20 seconds.
It is necessary to treat the boil before it breaks through. And supplement the process of iodine treatment with ointments and antibacterial gels.
It is important to remember that long-term use of iodine can lead to a similar allergy. Therefore, iodine should be used only during the acute period and not treat the wound for longer than 20 seconds. Otherwise, you may get a skin burn.
TREATMENT OF FURUNCULOSIS
A dermatologist treats furunculosis. But if an abscess or phlegmon has formed, they must be opened. In such cases, the patient is sent to a surgeon. If complications develop, the patient is hospitalized.
In severe cases, detoxification measures, massive antibiotic therapy, blood transfusions (blood transfusion according to a stepwise or classical scheme) and UFOB - ultraviolet irradiation of blood are carried out.
Rules of conduct for a patient with furunculosis
All rules are aimed at preserving the shell of immature abscesses.
- Limit the duration of showers and baths, and the water should be warm, but in no case hot;
- refuse scrubs, peelings, rubbing the body with a washcloth and other cosmetics and procedures that can damage the skin, and with it the integrity of the boil shell;
- It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out boils, apply warm compresses, lotions, or massage the skin around them.
Failure to comply with these rules can accelerate the maturation of boils or further aggravate the pathological process. And if the integrity of the membrane is violated, it can provoke the entry of purulent contents into the surrounding tissues, and from there into the blood and lymph.
The skin around the pustules can be wiped with antiseptic agents. This will prevent further spread of the infection.
Diet
Diet plays an important role in furunculosis. Sweets and fatty foods should be excluded from the menu. You should avoid spices and reduce your salt intake. Food should contain as much protein as possible, including animal protein, as well as plant fiber.
Read also Trichomoniasis - symptoms, treatment, diagnosis
If patients are weakened, their diet should consist of the following foods:
- porridge with butter;
- chicken bouillon;
- steamed minced fish cutlets;
- boiled or baked meat;
- dairy products;
- berries, vegetables and fruits, both fresh and baked.
Products that can cause allergies and containing fast carbohydrates should be completely excluded from the menu.
Treatment with antibiotics
In case of furunculosis, antibacterial therapy is mandatory. Drugs are selected individually, and the sensitivity of the microorganism is always taken into account. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets; less often, in severe cases of the pathological process, they are administered parenterally (intramuscular or intravenous). Usually the choice is made on broad-spectrum drugs:
- from the penicillin series - Amosklav or Flemoxin;
- from cephalosporins - Ceftriaxone or Cephalexin;
- from macrolides – Clarithromycin or Sumamed;
- from lincosamides – Lincomycin.
Antibiotics are taken for about 5-7 days, sometimes the course of treatment is extended for 10 days. It directly depends on the severity of the pathological process.
With massive antibiotic therapy, antifungal drugs can be prescribed in parallel, as well as agents that maintain the normal composition of the intestinal microflora.
Immunotherapy and vitamins
Since furunculosis occurs against a background of reduced immunity, along with antibiotics, the doctor usually prescribes drugs that help strengthen it:
- vitamin and mineral complexes, which include zinc, magnesium, cobalt and selenium;
- products with vitamins A and C;
- complexes containing B vitamins (for example, brewer's yeast);
- autohemotherapy according to a special scheme (intramuscular injection of the patient’s own blood);
- staphylococcal vaccine;
- gamma globulin;
- immunomodulators and immunostimulants (Polyoxidonium, Lykopid, etc.).
Additionally, medications may be prescribed to normalize the intestinal microflora, since it indirectly affects the state of the immune system.
In case of allergies or in cases of severe detoxification, antihistamines are prescribed.
Local treatment
In the presence of numerous abscesses, treating the skin with topical medications is difficult. In particular, the patient cannot always easily reach them. However, all lesions should be lubricated with a disinfectant, such as salicylic alcohol or calendula tincture. After which an antibiotic ointment is applied - gentamicin, tetracycline, Levomekol. After opening the abscesses on your own, use ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky balm. They will clean the wound and speed up healing.
For therapeutic and preventive purposes, the patient is prescribed sessions of UHF and UV irradiation - ultraviolet irradiation, which has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms.
Surgical assistance
The help of a surgeon is needed in case of abscessing furunculosis, when the surrounding tissue is involved in the pathological process. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The abscess is opened, removing the rod and necrotic tissue, after which a sterile bandage is applied. It is changed daily, treating the wound with antiseptics, followed by lubrication with syntomycin or erythromycin ointment. Healing can take up to a month, depending on the size of the abscess and the state of the immune system. As soon as the granulation stage begins, the ointments are replaced with Vishnevsky's liniment.
If there is a large accumulation of pus, the wound is drained, leaving it open for the outflow of exudate. This measure prevents further progression of inflammation and its transition to a chronic form.
Nowadays, lasers are increasingly being used. The procedure for removing an abscess is practically painless and very effective. And most importantly, there are practically no traces left at the site of the inflammatory process.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies cope well with single boils. With furunculosis, of course, you can try to treat areas of skin with ulcers, but if the lesion is too extensive, this will be problematic. What can help with furunculosis:
- a paste of aloe leaves is applied to the ulcers;
- 4 times a day, make applications from a mixture of grated laundry soap and water;
- Place cakes made from a mixture of egg yolk, honey, flour and water on the boils;
- Lubricate the fires with decoctions of oak bark or horsetail.
You cannot treat abscesses on the head, neck and chest with folk remedies, since they most often can provoke serious complications.
Any traditional medicine recipes are used only as additional treatment at home. Without antibiotics and concomitant therapy for furunculosis, they will be ineffective.
Which specialist should I contact for furunculosis? A dermatologist will help you choose the right therapy and help get rid of risk factors. If necessary, he refers the patient to a surgeon to open the abscess. The dermatologist prescribes routine tests to show the general condition of the body. In case of recurrent and chronic course of the disease, it is useful to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics, as well as to assess the person’s immune status (immunogram, diagnosis of HIV infection).
Treatment of furunculosis should be comprehensive. It includes:
- proper nutrition;
- systemic antimicrobial therapy;
- local impact;
- surgical methods;
- immunotherapy.
Nutrition
Nutrition for long-term furunculosis should be rich in proteins, including those of animal origin, as well as plant fiber. Fats and refined carbohydrates (sweets) should be limited. Depleted patients should be fed sufficiently high-calorie, but easily digestible food (porridge with butter, chicken broth, steamed fish cutlets, baked dishes from vegetables and lean meat, fermented milk products). It is useful to eat more fruits, berries, and vegetables. You need to give up allergenic foods (citrus fruits, chocolate, seafood, eggs and others), as well as salt and spices.
Read also Red papilloma - treatment, removal
Local therapy
With furunculosis, it is undesirable to take a bath or go to the sauna.
A single boil without recurrence can be treated using only local remedies. Treatment is carried out at home: the hair around the lesion is carefully cut off (do not shave!), the surface of the infiltrate is treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, ichthyol is applied to the skin in the form of cakes, covering it with cotton wool. Ichthyol is applied in the morning and evening, removing its remains with warm water. Then the surface is treated with an alcohol solution of boric or salicylic acid from the edges of the lesion to the center.
Sometimes it is possible to interrupt the development of the process at a very early stage by lubricating the resulting seal with iodine, brilliant green.
When a purulent core begins to form, this process can be accelerated by applying salicylic acid to the top of the boil.
After the boil has opened, use lotions with a hypertonic solution of Furacilin, and wash the wound cavity with Chlorhexidine. These procedures are carried out twice a day. When the ulcer is completely cleared, Vishnevsky ointment, Levomekol and other antimicrobial drugs are used. Dressings are carried out every other day; circular dressings cannot be used. The edges of napkins impregnated with medicines only need to be attached to healthy skin with an adhesive plaster.
If the boil is located on the face, the patient is recommended to undergo mandatory bed rest and hospitalization is often necessary. He is prohibited from talking or otherwise straining his facial muscles. He should eat exclusively liquid food. You should remember the danger of severe complications of this localization!
Treatment with antibiotics
How to treat furunculosis, that is, multiple recurrent ulcers? In this case, treatment with antibiotics is indicated.
The doctor decides which antibiotics to take for furunculosis, taking into account data on the sensitivity of staphylococci to them in a given region, as well as a sensitivity test for a given patient. Usually tablets are used, less often intramuscular or intravenous injections.
Antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action are used:
- penicillins (Flemoxin, Amoxiclav);
- cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cephalexin);
- macrolides (Sumamed, Clarithromycin);
- lincosamides (Lincomycin) and others.
The duration of antibiotic use in most cases is 10 days. Self-cessation of treatment can provoke a relapse of the disease, as well as the formation of antibiotic-resistant staphylococci. In this case, a medicine that is effective when first used will not help the patient in the future.
Immunotherapy and vitamin use
For chronic furunculosis, specific immunotherapy is prescribed, aimed at producing antibodies against staphylococci in the body, for example, staphylococcal vaccine and toxoid, anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin.
Vitamins for furunculosis should be taken constantly, and modern multivitamin complexes containing useful minerals, for example, Centrum, are recommended. It is especially important to saturate the body with vitamins C, A, E, PP.
After analyzing the immunogram, nonspecific immunostimulants, for example, Lykopid, can be prescribed. In order to “clean the blood” and increase the body’s resistance, ultraviolet irradiation (UVR) of the blood is used. Autohemotherapy has hardly been used lately.
Surgical intervention
Often, a patient with a single boil is referred to a surgeon, who opens and cleans the abscess. This happens especially often when it transforms into an abscess or a boil is located on the face.
If complications develop, for example, sepsis, a complex of treatment is carried out, including highly effective antibiotics (carbapenems), detoxification therapy, and, if indicated, blood transfusions.
Treatment of furunculosis with folk remedies can be used in addition to the main therapy, and after consultation with a doctor. Recipes such as compresses with crushed aloe leaf, raw grated potatoes, and baked onions are used. It is recommended to use brewer's yeast internally - a source of B vitamins.
Is it possible to squeeze a boil?
It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out boils , as this can lead to infection and worsen the situation. An inflamed boil can become large and cause severe pain. The infection zone may increase every day.
Therefore, it is important not to introduce an infection, but to quickly and professionally get rid of the disease. To do this, you should visit a doctor and consult about treatment. Only competent treatment can lead to a rapid breakthrough of the boil and scarless healing of the wound.
Prevention
Prevention of furunculosis consists of action on exogenous and endogenous factors of its occurrence:
- use personal protective equipment at production;
- do not wear clothes that rub the skin;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- treat any skin diseases in a timely manner;
- keep chronic diseases, such as diabetes, under control;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- Avoid frequent hypothermia or overheating.
To avoid the appearance of furunculosis, you should not only strengthen your immune system, but also adhere to the banal rules of prevention, which involve eliminating all provoking factors:
- maintain personal hygiene and keep your skin clean;
- treat any microtraumas and damage to the skin with antiseptics;
- do not squeeze pimples;
- adhere to a balanced diet and do not overindulge in sweets;
- engage in sports or vigorous physical activity;
- wear comfortable clothes that will not chafe your skin;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia.
In addition, in case of chronic pathologies, especially diabetes mellitus, one should keep the disease under control and try to prevent possible relapses of the pathology.
Symptoms of an abscess in the armpit
A boil that forms in the armpit makes itself felt with characteristic symptoms, which must be treated with due attention in order to begin treatment on time.
The development of a boil can often be stopped at the initial stage if you follow your doctor's recommendations.
What signs indicate that a purulent formation appears in the armpit:
- a compaction forms in the armpit, around which hyperemia is observed - redness of the skin;
- tingling, itching, burning sensation is felt at the site of the lesion, especially when rubbing against clothing;
- the patient feels throbbing pain, tightness of the skin, which becomes hot - this symptom is called hyperthermia, when the temperature in the affected area rises, usually by 2 - 3 degrees;
- freedom of movement is sharply limited, as it causes discomfort and pain;
- boils lead to inflammation of the lymph nodes, which become painful when touched. It also impairs shoulder and arm mobility;
- the swelling turns into a cone-shaped lump, in the center of which a necrotic rod appears with a black dot at the end.
The development of a boil in the armpit area is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication - weakness, fatigue, high fever, headache, aching joints.
The symptoms of chiryak change as it develops. When it matures and the purulent contents begin to emerge, the swelling gradually decreases and the pain subsides.
Not all parents know whether it is possible to swim with chickenpox. Opinions for and against water procedures are discussed in this article.
Symptoms, treatment and photos of toxicoderma are presented in this publication.
You can find a photo of herpes on the fingers here: https://udermatologa.com/zabol/gerp/gerpes-na-rukah-foto-lechenie-na-paltsah-i-ladonyah/
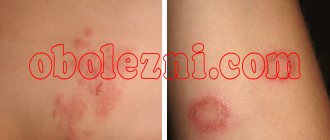
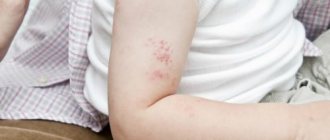
What it looks like: photo
You can understand what a boil looks like from the photo.
A boil on the skin of the back develops in three stages.
- Infiltration. At the beginning, a small red spherical lump is visualized. The place where the boil popped up is itchy and itchy.
- Purulent-necrotic stage. At the top of the compaction, a purulent mass accumulates - a mixture of dead and living leukocytes, rushing to the source of inflammation. The area around the boil thickens, body temperature rises to subfebrile levels. The patient complains of chills and malaise.
- Opening and healing. As a rule, a small boil matures and opens on its own. The pus comes out, and the wound heals completely after 5-7 days.
A large boil will not go away without intervention. Don't wait for it to pass. It is necessary to assess the extent of inflammation and decide whether home treatment methods will be effective. If necessary, consult a dermatologist.