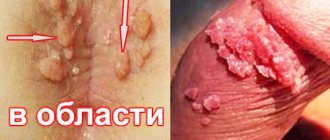
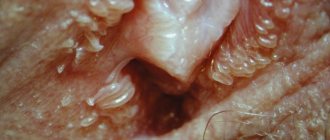
Genital warts appear in women:
- on the cervix;
- around the anus;
- in the vaginal cavity,
- in the cervical canal;
- at the entrance to the urethra;
- on the labia majora and minora.
Very rarely, genital warts appear on the nasal mucosa and in the oral cavity.
It is worth noting that the human papillomavirus affects women almost 2 times more often than men. It is also noteworthy that in 80% of cases, the virus, which manifests itself in the genital area, causes the development of cervical cancer.
Having penetrated the female body, the virus cells begin to divide at an accelerated pace. This leads to tissue growth and the formation of characteristic growths on the surface of the skin.
In 20% of cases, the virus develops within 5 years from the onset of infection and leads to cervical cancer.
Types of growths
A growth that appears inside the vagina is medically called condyloma. Appears due to invasion by the human papillomavirus. They can appear at any age and have a different nature of occurrence. The following condylomas are classified:
- by size into small, medium, large;
- according to the structure: loose, hard;
- according to form.
Condylomas on the vagina are distinguished by color and density. Such nodules can be either benign or malignant. But besides condylomas, other types of neoplasms can be observed: lipoma, cyst and others. A white growth in the vagina may indicate a genital wart. Hemorrhoids (coming out) or a polyp can also appear in the form of a nodule. If a growth appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Condylomas in the vagina grow near the perineum and on the labia.
Location of condylomas
HPV tumors are localized at the entrance to the perineum, inside or outside the labia. The vaginal mucosa is a frequent area of distribution of formations in the form of pink papillae, which can be either single or multiple. They may increase near the anus, on the thighs or pubis. The human papillomavirus is located inside the body, and when it matures, it appears outside in the form of pink or flesh-colored lumps. Depending on the strain (science knows of 100 types of HPV), the formation in the vagina has a specific localization zone. Growths such as hemorrhoids appear between the anus and the entrance to the vagina. The walls are often affected by lipomas or cystic structures. Internal growths are papillomas.
Warts in the vagina: factors contributing to their development
- frequent change/multiple sexual partners;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- decreased immunity (for example, due to hypothermia, general diseases, including ARVI, hormonal disorders, etc.);
- infection with HIV and other sexually transmitted infections;
- disruption of the normal composition of the vaginal microflora;
- pregnancy (in this situation, after childbirth, formations often disappear spontaneously);
- vitamin deficiency;
- stress, etc.
It has been established that in almost 90% of episodes, papillomavirus infection is combined with infection with other sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Most often, HPV is detected simultaneously with ureaplasma.
Chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, and candidiasis are less frequently detected (vaginal warts, when clarifying the diagnosis, necessitate additional research due to the high risk of other STIs).
Causes of formations
Depending on the state of the immune system, HPV may not appear in the form of condylomas for up to 3 months, but there are cases when a growth appears 2 weeks after infection. The main reasons for this process:
- decreased human immune system;
- promiscuous sex life;
- unprotected sex;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases (vulvovaginitis, chlamydia, gonorrhea and others).
Weak immunity, infections, poor hygiene, and unsafe sex can cause the formation of condylomas in the vagina.
The exact reason why condylomas appeared cannot be reliably established. Since the virus can stay in a woman’s body for a long time and not manifest itself, and with high immune function it may not arise at all. HPV easily penetrates the genital mucosa, so sex is a common cause of infection. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, a woman’s body is more susceptible to viral invasion, so the risk of contracting HPV is higher. Problems with the nervous system, when exposed to shock and stress, can also play a negative role in the development of condylomas, provoking the activity of the strain.
What are the dangers of lack of appropriate therapy?
The presence of genital warts in women is a serious sign to see a doctor. Lack of timely therapy increases the likelihood of a number of complications. The presence of favorable conditions for the virus can provoke the development of uterine dysplasia in women. With high oncogenic activity of condylomas, they can transform into malignant neoplasms (squamous cell carcinoma) against the background of certain factors.
The development of pointed neoplasms provokes disruption of the normal functioning of internal organs. Also, with HPV, there is a strong decrease in immunity, which increases the risk of infectious diseases. Damage to a large area of the mucous membrane of the genital organs leads to loosening of the tissues of the vagina, as a result of which a woman may experience complications during childbirth.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of the disease and the period of their occurrence depend on the functionality of the body’s defense system. The incubation period lasts from approximately 2 weeks to 3 months. In this case, the virus waits for a favorable moment to manifest itself. When a growth appears in the vagina, the patient experiences itching, burning, and pain. The mucous membrane swells and redness appears. Often the nodules have white tops and emit an unpleasant sour odor. Ignoring such manifestations leads to serious complications: cervical erosion, dysplasia, and subsequently to oncology. When bleeding appears, the gynecologist checks the surface of the condylomas for the presence of injured areas.
Preventive actions
There are no preventive measures for condylomatosis. In some cases, even high-quality treatment and removal of tumors does not guarantee relapse of the disease.
HPV vaccines have been developed for children under 13 years of age. An important criterion is that it is carried out before the onset of sexual activity. Vaccination is not included in the list of mandatory requirements.
Doctors advise adult patients to avoid unprotected sex with casual partners and to follow basic hygiene rules.
There is no need to search the Internet for what condylomas look like and how to treat them yourself.
Papillomatosis on the reproductive organs may be a precursor to cervical carcinoma. Contact a gynecologist and undergo a course of treatment! And forget about genital growths once and for all! The article has been verified by the editors
Treatment of vaginal growths and diagnosis
It is impossible to delay the treatment of formations in the vagina. The earlier removal techniques are applied, the greater the likelihood of avoiding developmental pathologies. Fixing the problem yourself is fraught with negative consequences. The method of curing the disease is prescribed only by a gynecologist who has a clear clinical picture. To establish it, diagnostics are prescribed. The table describes the main methods for diagnosing the disease.
| Method | Description |
| Visual inspection | Conducted by a gynecologist along with an oral survey of the patient for symptomatic manifestations. The walls of the vagina and uterus (colposcopy) and the anus area (anoscopy) are examined. |
| PCR diagnostics | The type of HPV, quantity and effect on the body is determined, which can be done by scraping from the affected area of skin |
| ELISA | The presence and reaction of antibodies to the virus are checked |
| Cytological and histological | Cells and tissues of nodular formations are examined using a microscope |
| Oncocytology | The presence of cancer cells is determined using a smear from the cervical area and the cervical canal area |
Having complete information about the type and type of growth around the vagina or on its walls, the treatment method is determined.
To treat condylomas, you cannot do without antiviral tablets.
Drug treatment
To get rid of condylomas using a conservative method, antiviral drugs are used. Popular medications among consumers are Alpizarin, Lykopid or Podophyllotoxin. When prescribing such medications, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, health status and individual sensitivity to the components. In combination with antiviral drugs, drugs to stimulate the immune system are prescribed: Cycloferon, Galavit, Immunofan. "Galaderm" is an ointment with restorative and healing properties that is applied directly to the growth.
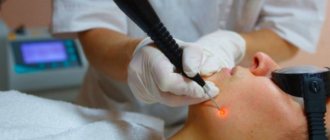
Hardware treatment
Gynecologists recommend using hardware methods for getting rid of vaginal condylomas. Such treatment is not as long as medication, not as traumatic as a conventional operation, which is performed by a surgeon with complete excision of the condyloma, and, if necessary, with nearby tissues. Hardware techniques reduce the risk of relapse and leave no scars. It is carried out in combination with immune therapy under the supervision of a physician. The table provides descriptions of hardware methods.
| Hardware treatment method | Description |
| Laser therapy | Drying and removing the growth using a laser. Used for large diameter build-up |
| Cryodestruction | Freezing with liquid nitrogen. The procedure takes place in several stages |
| Radio wave destruction | Removes using radio waves, leaves no scars |
| Electrocoagulation | Getting rid of condylomas using elevated temperature. Skin restoration course - 14 days |
It is rational to treat extensive or aggressive neoplasms in the vagina using hardware methods.
The choice of hardware treatment technique is based on the wishes of the patient and the doctor’s recommendations. Only specialized clinics perform such procedures. You should not go to a cosmetology salon because of the risk of encountering unprofessionals. The rehabilitation course does not last long; during this period you should abstain from sexual activity. Recurrence of condylomas in the vagina means that HPV remains in the woman’s body and repeated intervention is required.
Folk remedies
Small warts on the genitals can be treated using alternative medicine. Traditional healers advise women to use the following therapy methods:
- Pass 3-4 cloves of garlic through a press and squeeze out a little juice from the pulp. Apply the resulting liquid to anogenital warts three times a day.
- Wash the lemon thoroughly and grate it together with the peel on a fine grater. Add to the puree 100 ml of dry red wine, 60 ml of apple juice, preheated to a temperature of 60 degrees Celsius, and 2 cloves of garlic, passed through a press. Mix the mixture well and leave it for 3 hours in a warm place. Take the finished medicine orally, 6 sips per day.
- Pass 300 g of fresh celandine herb through a meat grinder and squeeze the juice out of the resulting mass. Use the product to treat problem areas twice a day.
- Grate 3 large potato tubers on a fine grater. Squeeze the juice out of the puree using gauze folded in 2 layers. Take the medicine throughout the day, dividing it into several small portions.
- Break a chicken egg, separate the white and beat it into foam using a mixer. Treat genital warts with the resulting product. Avoid water procedures for 6-7 hours.
- Grate a small onion on a fine grater and add 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar to the vegetable mixture. Infuse the mixture in a warm place for 4 hours, place it on a gauze napkin and press it onto the anogenital warts for 20 minutes. Repeat the described manipulations twice a day.
- Prepare a thick dough from flour and vinegar (2:1). Make small cakes out of it and press them onto problem areas for 2 hours. Repeat the procedure three times with an interval of 1 day.
- Pour a glass of chopped thyme herb into a liter of boiling water and leave in a warm place for 4 hours. Prepare a local (sitz) bath based on herbal infusion. The duration of the procedure should not exceed 30 minutes. The described steps should be repeated daily.
- Steam the anogenital warts, put a piece of propolis soaked in saliva on each of them and fix it with a plaster. Leave the bandage on for 3-4 days.
It is important to remember that all folk remedies have side effects and contraindications. Therefore, they can only be used after receiving detailed consultation from your doctor.