Pimples in the vagina are a fairly common occurrence among the fair sex. A woman may experience not only discomfort on a physical level, but also suffer from an inferiority complex. Sometimes these defects on the skin and mucous membranes can be a signal of serious health problems.
Do you think skin “diseases” are primarily an aesthetic problem?
Not really
Features of female physiology determine the development of this type of neoplasm. Thanks to mucous secretions and an optimal level of acidity in the vagina, the risk of acne is reduced. But in an unfavorable environmental situation, an increasing number of women are faced with gynecological diseases.
It is important to consider why a rash occurs near the vagina and how to treat the disease. After all, refusal of competent therapy can lead to a worsening of the situation. Additionally, you should be able to distinguish the appearance of white pimples in the vagina from herpetic rashes.
Characteristics and description of the problem
Pimples on the vagina are one of the symptoms of a disorder in the functioning of a woman’s body. They can cause pain and poor health.
Pimples can have different shapes and colors, as well as localization. There are many reasons for the development of pathology. Some of them are not dangerous, others can provoke the development of serious complications, so it is very important to visit a gynecologist.
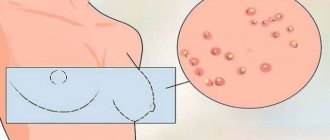
White pimples in the vagina
Small pimples may contain purulent contents. When the contents are removed, the acne goes away.
White pimples in the vagina can appear for several reasons:
- Epilation in the bikini area often leads to skin irritation. Inflammation forms at the site of hair growth, and pimples appear that are filled with a cloudy liquid.
- Synthetic underwear. This material does not allow air to pass through, the skin sweats, and irritation appears.
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body. This leads to circulatory disorders, local immunity decreases, which facilitates the penetration of bacteria that provoke the development of acne.
- STD. Typically, acne due to sexually transmitted diseases is localized near the mucous epithelium. This may be caused by papillomavirus. This phenomenon is dangerous, as in some cases it leads to the development of a cancerous tumor.
HPV manifests itself in the form of warts, papillomas and condylomas, which female representatives often confuse with acne. They are denser to the touch, have an uneven surface, and can be either white or dark in color. Such formations often grow over a short period of time.
4% of people worldwide are diagnosed with hidradenitis, which is a chronic skin condition affecting the sweat glands in the genital and breast areas. With this disease, pimples and spots appear, which over time develop into ulcers with purulent contents. They do not heal for a long time and leave scars behind.
Prevention measures
From childhood, every girl’s mother imparts important knowledge about how to care for the genitals, have a sexual life and monitor women’s health.
But the statistics are disappointing: bartholinitis is a disease of young people under the age of 30. Sexual liberation or other factors influenced this, but girls do not always follow simple rules. In order to maintain women's health, have a full sex life, and be able to give birth to children, it is important to prevent the development of bartholinitis. The following rules prevent its occurrence:
- Comfortable, natural linen, non-squeezing, soft. Thongs do not belong to this category. It is ideal when the panties are seamless;
- Refusal of panty liners. If this is not possible, then it is important to change this hygiene item every three hours. Longer wearing leads to the creation of a favorable environment for the activation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- Limiting the number of sexual partners. Ideally - up to one. If it happens that there are more of them, then it is strictly necessary to use barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse;
- Treatment of any acute and chronic diseases occurring in the body. Do not underestimate even ordinary caries, which can also provoke the development of bartholinitis and many other diseases. After all, this is a source of infection that progresses inside the body;
- Compliance with the rules of genital hygiene. Especially during menstruation and after sexual intercourse, even with a single partner. Under normal conditions, you should wash yourself in the morning, after the first urination, and in the evening, before going to bed. It is correct to wash with movements from front to back: from the urethra to the anus;
- Accurate depilation. If you prefer shaving intimate areas, then remember that a razor, like a comb and a toothbrush, is a strictly individual item. The blades must be sharp, otherwise there is a high risk of irritation. It is necessary to use foam during the procedure, and after it - a cream to disinfect and soothe the skin. Trust other types of hair removal only to qualified cosmetologists in specialized salons;
- If you find any rashes, pimples, bumps, balls or other formations on the genitals or vagina, you should not self-medicate. It is important to consult a gynecologist to solve these problems;
- Boosting immunity. The stronger it is, the more confidently the body fights pathogenic microorganisms. Hundreds of species of bacteria live on and inside our body, which form part of the natural microflora of organs and systems. But under favorable conditions they become more active, provoking diseases. Eat right, exercise, drink clean water, breathe fresh air and take vitamins during the off-season.
Compliance with such rules will reduce the likelihood of not only bartholinitis, but also most diseases of the genitourinary system. Health is taken for granted until a problem arises. In order not to reproach yourself for frivolity in the future, it is easier to avoid making mistakes today.
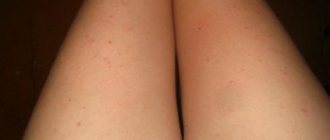
Red pimples
If there are small pimples on the vagina that do not cause pain, this may indicate acne. When pain and inflammation appear, we can talk about the following pathologies:
- disruption of the hormonal or endocrine system;
- emotional stress, lack of sleep;
- a nervous system disorder that causes red bumps to appear in the vagina.
Red formations with a white coating indicate candidiasis, which is accompanied by a viral infection. Candidiasis itself does not cause pain; with this pathology, white discharge and itching appear. The reason for this phenomenon may be prolonged stress, uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs, and a decrease in the body’s protective properties.
If red, dark, round formations appear in the vagina and anus, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is how secondary syphilis can manifest itself. In this case, there is no pain or discomfort; peeling of the skin may begin. In some cases, acne disappears on its own without forming scars.
Pimples can appear as a result of lice pubis, which is caused by pubic lice. In addition to rashes, a woman may experience itching, burning, and discomfort.
Types of lumps, symptoms and treatment
Cysts are lumpy lumps filled with air, fluid, or other substances. In most cases, cysts are neither harmful nor painful.
Cysts range in size from too small to see to the size of an orange. These lumps can appear anywhere on the body, including the vagina.
Vaginal cysts can be caused by damage to the vagina during childbirth, benign tumors in the vagina, or a buildup of fluid.
Share on Pinterest Some types of cysts are caused by trauma during childbirth, surgery, or material left behind after the baby is born.
Vaginal cysts occur in various forms. These include the following:
- Bartholin gland cysts : These are fluid-filled cysts that form on the Bartholin glands, which are found on either side of the vaginal opening. The glands produce a fluid that lubricates the outer lips of the vagina.
- Inclusion cysts : These typically form in the lower part of the back wall of the vagina. They tend to be very small and are unlikely to be noticed. They are also one of the most common forms of cysts that can develop in the vagina. They can be caused by trauma during childbirth or surgery.
- Müller's cysts : These are another common type of cyst that form as a result of material left behind as the baby develops. They grow anywhere on the walls of the vagina and often contain mucus.
- Gartner Ductal Cysts : This can happen when the ducts in a developing fetus do not disappear as well as they should after the baby is born. The remaining ducts can eventually develop into vaginal cysts.
Causes and risk factors
Vaginal cysts most often occur when a duct or gland becomes blocked, causing fluid and other materials to accumulate. The cause of a vaginal cyst usually determines the type of cyst.
For example, damage to the vaginal walls causes the inclusion of cysts.
The most likely risk factors for the inclusion of cysts are rupture or rupture during childbirth, surgery that damages the vaginal lining, or an episiotomy (a small cut between the vagina and anus) performed before childbirth to widen the vaginal opening.
Bartholin gland cysts occur when the opening in the Bartholin gland becomes blocked by a flap of skin that covers it, causing a fluid-filled growth.
Share on Pinterest A cyst often goes unnoticed until it is discovered by a gynecologist during the next examination.
Vaginal cysts are unlikely to cause any noticeable symptoms in a woman. Depending on the size and location, she may or may not be able to feel the lump from the cyst.
Often, a gynecologist discovers cysts during a routine annual examination. The cyst may remain the same size or grow over time.
Most cysts will not be painful. However, some large cysts may cause discomfort during sex, walking, exercise, or inserting a tampon.
Cysts most often cause pain if they become infected. Normal bacteria from the skin or sexually transmitted diseases can cause a vaginal cyst to become infected, which can lead to an abscess.
Complications
The most likely complication of a cyst is infection, which causes an abscess. An abscess is a large collection of pus and fluid that can cause redness, pain, and swelling. If an abscess forms, it may need to be drained to allow it to heal.
Large numbers of bacteria both on the skin and in sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause a cyst to develop into an abscess. In other cases, bacteria normally found in the intestines, such as E.coli, can lead to an abscess Bartolina.
When to see a doctor
A woman should have an annual gynecological examination as part of her usual routine care. It is also a good idea for a doctor to check any new lump in the vagina to make sure it is benign.
Women should also see a doctor if the vaginal cyst or lump becomes painful or shows signs of infection.
Share on PinterestSitz Baths can be used to treat a cyst that may burst and drain on its own.
In most cases of vaginal cysts, treatment is not required. Treatment is usually given if a person experiences any discomfort or pain, due to the size of the cyst, or if there is an infection.
If treatment is necessary, one of the following options may be used:
- Antibiotics are usually prescribed if a vaginal cyst is infected or in cases where testing reveals the presence of a sexually transmitted infection. If an abscess has formed and is draining properly, antibiotics may not be needed.
- Calico baths , which involve a woman soaking in a tub filled with several inches of warm water several times a day for 3-4 days. This absorption may help a small infected cyst to burst and drain without further intervention.
- Marsupialization , for frequently recurring or bothersome cysts. The doctor places stitches on each side of the drainage incision to create a permanent opening. A rubber tube may be inserted to provide drainage for several days after the procedure and prevent recurrence.
- Removal of the gland is performed in rare cases of Bartholin cysts. However, this is usually not the case.
Surgical drainage may be required for infected or large cysts to remove their contents. This is often done using local anesthesia or sedation and can be done in a doctor's office.
The doctor makes a small incision in the cyst, which is then drained. After draining the cyst, the doctor inserts a small rubber tube into the incision. This allows the cyst to remain open for several weeks to drain completely.
Prevention
The growth of vaginal cysts is difficult to prevent. Prevention should be aimed not so much at stopping the formation of a cyst, but at maintaining the cleanliness of the vagina. Practicing safe sex can help prevent contracting sexually transmitted diseases.
Watery formations
If there is the appearance of acne with a dense structure that looks like watery formations, this may indicate the development of papillomas. In this case, a person may be infected with HPV or have reduced protective properties of the body, lacking vitamins and minerals in the body.
When pimples with watery contents form, which often burst, they speak of the development of a herpes infection. During this period, the woman is a source of infection, which can easily be transmitted to her sexual partner.
Subcutaneous formations
Pimples inside the vagina, which look like tubercles, do not cause discomfort and are easily palpable, can develop for the following reasons:
- The development of wen as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands. This phenomenon is not dangerous to health; in severe cases, surgery may be required.
- Disorder of the functionality of the sebaceous glands. In this case, the formations may change in size, but do not cause discomfort. They do not pose a threat to health and are an individual feature of a woman’s body.
- Immune system disorders, autoimmune diseases. This pathology requires treatment. With such disorders, the pimples on the vaginal lips will hurt.
Molluscum contagiosum appears in the form of a dense small nodule. This pathology develops with weakened immunity, the presence of arthritis, and also in those who are prone to allergic reactions. The formation disappears spontaneously, but can be observed within two years.
Cysts of the Bartholin glands, which are located in the vagina, may also be observed. When the glands become blocked, benign growths develop that do not cause pain. They usually do not require therapy. But when infected, they become inflamed and filled with purulent contents, and therefore require treatment with antibacterial drugs.
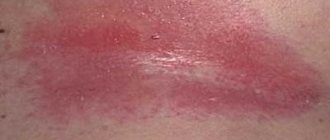
Symptoms of the disease
The first sign of possible bartholinitis is the appearance of a deep subcutaneous pimple, which looks like a boil and can be felt in the vestibule of the vagina. It is painful and the area around it is swollen. The size at the onset of the disease does not exceed a pea, but without treatment the area of inflammation reaches a diameter of up to seven centimeters.
A boil near the vestibule of the vagina, similar to a ball under the skin, is not the only symptom of bartholinitis in the early stages.
Besides him, the woman is worried about:
- discomfort during sexual intercourse, movement, sitting, defecation;
- low temperature (up to 37.5 °C and above).
The described symptoms are characteristic of the early stage of the disease, when the excretory duct becomes inflamed. This condition is called canaliculitis, which, without treatment, is complicated by inflammation of the gland itself (abscess) or leads to the formation of a cyst.
A lump, similar to a pimple or boil ball, can be felt inside the vagina, where the duct exits. The duct itself is also easily detected by palpation, gives off pain and, when pressed, releases pus.
It's time to sound the alarm!
Even a small pimple in the vagina can indicate the development of serious pathologies in the body. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner for examination. It is recommended to pay special attention to the following situations:
If such signs appear, you should immediately visit a gynecologist, as serious complications may develop.
When should you visit a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if the causes of acne on the vagina cannot be determined, if they appear constantly or if the skin condition worsens. Your doctor may drain pimples that are particularly painful, large, or filled with significant amounts of pus.
In most cases, vaginal acne goes away on its own or with a little self-treatment. Change your living habits or adjust your daily hygiene. This way you can prevent new pimples from appearing on your skin.
If you are not confident in your abilities, then visit a doctor who will advise you and point you in the right direction in treating acne.
Diagnostic measures
To know how to cure a pimple on the vaginal mucosa, you need to find out the reason for its appearance. To do this, you need to contact a gynecologist and undergo an examination. First, the doctor examines the medical history, listens to complaints, studies the symptoms of the pathology, and then conducts a gynecological examination.
Laboratory tests of blood and urine, allergy tests, PCR are often prescribed, a smear is taken for analysis, and scraping. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs may also be prescribed. If a wen is suspected, an ultrasound is prescribed, since in some cases it can transform into a malignant neoplasm. When purulent acne appears, a woman’s hormonal system and the condition of her internal organs are examined using highly targeted techniques.
If a woman experiences pain and discomfort in the genital area, the doctor may prescribe her a painkiller during the examination.
After a full examination and identification of the cause of the pathology, the doctor prescribes therapy, which is aimed not only at eliminating the symptoms, but also at eliminating the cause that caused it.
What can cause vaginal acne? (with pictures)
Molluscum contagiosum, sexually transmitted diseases, ingrown hairs, or cysts in the sebaceous glands can cause vaginal acne. These pimples can appear on the inner or outer lips of the vagina, as well as on the vulva; occasionally they may appear on the clitoris or under its hood. Some vaginal pimples may be filled with pus and pus into an open, oozing sore.
Vaginal acne can be a result of shaving.
Genital human papillomavirus (HPV) and herpes are the two main sexually transmitted diseases that cause reddish, itchy vaginal pimples. Herpes pimples can be painful and often develop into sores. The pimple-like eruptions caused by HPV are actually warts and can grow into a flower if several warts grow in close proximity and swell. HPV pimples usually cause bad breath and may need to be removed surgically.
An STD can cause pimples in the vagina.
Caused by the smallpox virus, molluscum contagiosum causes a rash of tiny pimples on the genitals. Unlike HPV-related genital warts, which they are often mistaken for, these bumps are not itchy and remain the same size throughout the outbreak. Clam pimples do not turn red, but instead remain the color of the flesh; their texture is generally smooth and soft. Contagious and likely to spread, these pimples can break out beyond the genital area, infecting the anus and stomach. When spread by hand contact, clam pimples may appear on the face or lips.
Gynecologists can give advice on how to treat vaginal acne.
Sebaceous pimples or cysts, which form when oil clogs the sebaceous gland, can form in the vulva area. These pimples are harmless and may go away without treatment. Applying a warm towel to pimples to open the pores can cause inflammation. However, irritating the cyst by scratching can worsen the condition and cause bacteria to become infected in the pimple.
An allergic reaction to a latex condom can cause vaginal acne.
Shaving the vulva can cause pimples to appear in the vagina, either from ingrown hairs or bacteria introduced into the area by the razor. Ingrown hairs are often caused by shaving too closely and in the opposite direction of hair growth. Acne associated with bacterial infection can occur from bacteria on the blade itself or from the vaginal area when shaving causes abrasions or cuts, allowing any bacteria present to enter.
To diagnose vaginal acne to determine the cause and the need for immediate treatment for bumps, a woman can usually see her primary care physician or gynecologist. Many clinics also offer free and reduced-cost screenings for sexual anomalies. Keeping a log of changes in the size, shape, and location of vaginal pimples can help with proper diagnosis.
Some vaginal acne is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted disease (STD).
Therapy
Some representatives of the fairer sex try to treat vaginal pimples on their own. But self-medication can be dangerous, since treatment methods directly depend on the individual characteristics of each woman’s body and the causes of the pathology. Only an experienced specialist will select effective drugs after diagnosis.
Typically, acne treatment is complex. It is necessary to take medications to stop the inflammatory process, increase the body's defenses, and eliminate viruses and infections.
Often, the doctor prescribes antihistamines and antibacterial drugs, as well as NSAIDs, antifungals, vitamin complexes and immunomodulators. Sedatives such as valerian or motherwort are often used.
The main method of therapy is considered to be local treatment using ointments, creams, and special solutions. When the formations are located internally, suppositories and douching solutions are used. If the pimple is located at the entrance to the vagina, you can use hormonal ointments based on hydrocortisone. You can wash the formations with a solution of Miramistin or Chlorhexidine. Purulent formations are eliminated with Vishnevsky ointment or antibiotics. Regular brilliant green has a good effect. For herpes infections, it is recommended to use Acyclovir.
After completing the course of therapy, it is necessary to take repeated tests in order to fully confirm the cure. It is also recommended to undergo therapy together with your sexual partner to eliminate the risk of re-infection.
What can cause pain in the perineum in women?
The perineum is the area between the anus and the vagina. Pain in this place, like in any other place, indicates that something is wrong in the body. This phenomenon does not always threaten health problems, however, there is reason to be wary.
Natural causes of discomfort in the perineum
Pain in the perineum in women is rarely the result of normal physiological processes. They should not cause concern unless they are unbearable and pass quickly.
Pain in the perineum as a sign of pathology
Most often, discomfort in the groin area is a sign that all is not well with your health. Usually the matter is not limited to pain; there are other unpleasant symptoms.
- Bartholinitis. Inflammation of the gland, which is located at the base of the labia. The affected area noticeably thickens and increases in size, it can even completely block the entrance to the vagina. Of course, such a neoplasm does not go unnoticed. It interferes with walking and rubs against underwear. The most accurate description of the symptoms is that a dense ball can be felt on the labia.
- Inguinal athlete's foot. A fungal disease that affects the skin in large folds. It occupies large areas, causing constant discomfort. Itchy and flaky spots appear on the epidermis, which merge with each other, forming rings with healthy skin inside and a red border outside.
- Ectopic pregnancy. With this pathology, the fertilized egg is attached not to the wall of the uterus, but inside the appendage. The growth of the fertilized egg provokes tissue stretching and severe pain. Brown discharge is observed. If medical attention is not provided in a timely manner, the pipe ruptures, accompanied by significant bleeding.
- Diseases of the urinary system. The urethra is located above the perineum, and pathological processes in it are reflected by pain in this area. Unpleasant sensations can also be a sign of cystitis or pyelonephritis. Women with such problems experience pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, a frequent urge to urinate, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. There may be a discharge streaked with blood.
- Intestinal pathologies. Some disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract are associated with constipation. Fullness of the intestines causes a feeling of constriction, and difficult passage of hard feces provokes pain in the anus and perineum.
- Diseases of the reproductive system. Discomfort in the groin area in women often occurs as a result of pathological processes in the uterus and fallopian tubes. The growth of the endometrium, neoplasms on the walls and cervix lead to heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding against the background of severe pain.
- Pinched nerve. Pain in the perineum when sitting in women may indicate a pinched sciatic nerve. In this case, the groin area becomes numb, and there is a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum and vagina. Sitting and lying down provide relief.
- Varicose veins Veins can also expand in the pelvic area. This problem most often affects pregnant women and overweight women. The pathology leads to disruption of the blood supply to the reproductive organs, which is manifested by the following symptoms: acute PMS; perineal sensitivity; cycle disruption; copious discharge; urinary disturbance; feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area.
If women have pain in the perineum, do not put off visiting a gynecologist. Unpleasant sensations in this place are often a signal of the development of a pathological process. The source of the problem can be in any organ of the pelvic floor, so it is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms for a correct diagnosis.
Loading…
Source: https://uginekologa.com/boli-v-promezhnosti-u-zhenshhin.html
Forecast
The prognosis is usually good. The appearance of pimples on the vagina does not always indicate the presence of serious pathologies that can harm health. Sometimes maintaining hygiene, eating right and wearing suitable underwear will be enough. But there are some pathologies, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in the form of acne. They require timely treatment, as they can provoke the development of negative consequences. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and develop effective treatment tactics.
Rash and pimples on a girl's pussy
Girls at any age can develop pimples and rashes on the genitals, which are formed due to the influence of various factors, including the development of:
- diaper dermatitis - is a diaper rash that appears due to prolonged interaction with the surface of the diaper, the baby's feces and the lack of circulation of moisture and air. It looks like purulent rashes, swelling of the skin, spots, bumps and redness in the groin;
- allergy – caused by food intake, manifested by redness and erythema of the skin;
- overheating - has the appearance of red spots (prickly heat), which form in the inguinal folds of girls and do not cause discomfort, characterized by the appearance of a red rash, spots and watery pimples on the genitals of girls;
- candidiasis - caused by a fungus of the genus Candida affects the genital area in girls, characterized by a red rash.
Treatment of rashes and pimples on the labia in girls requires medical supervision.
Disinfectants and drying agents are prescribed for affected areas of the skin. These can be ointments, creams, pastes and powders. In addition, you can use herbal decoctions of nettle, chamomile, string and other herbs.