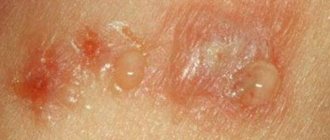
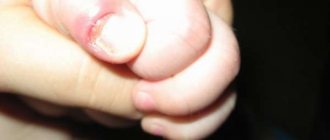
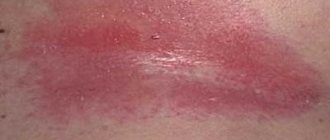
Dermatitis on the hands - what is it?
Dermatitis on the hands is an acute inflammation of the skin that occurs as a response to any irritant. Typically, acute dermatitis of the skin of the hands first appears suddenly and progresses very quickly: blisters filled with liquid appear, which soon burst and form weeping wounds. As the skin dries, it becomes crusty.
Appearance of dermatitis on the hands
If treatment is not started in time, dermatitis on the hands becomes chronic. The patient constantly feels discomfort of the epithelium: the skin is dry, thickened, peeling and cracks appear, calluses and other traces of the disease.
About 90% of clinical cases of dermatitis occur in women.
As it progresses, the skin begins to atrophy, inflammation penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin, and there is a risk of sepsis and necrosis of areas. In advanced cases, a person’s performance decreases; doing anything with his hands becomes difficult if his hands are affected. In addition, the patient begins to experience psycho-emotional discomfort, he is ashamed of his hands, closes himself off from the outside world, which causes a decrease in the quality of life.
The disease can be different: dry dermatitis on the hands, dermatitis on the fingers, dermatitis between the fingers, from fingers to elbows, dermatitis of the hands, the back of the hand, wrists, forearms and others.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of the disease are few.
Blistering dermatitis on the elbows or other areas of the skin of the hands is characterized by the following symptoms:
- skin itching;
- burning;
- swelling of the skin;
- redness;
- the appearance of bubbles filled with liquid;
- painful sensations.
Blisters on the elbows form only when the skin is severely inflamed. Over time, they open up, and erosion remains in their place. Crusts later form on the surface of the erosions. The chronic form of the disease has slightly different symptoms. It is characterized by thickening of the skin in the affected area, slight blue discoloration, and peeling. Often the skin cracks. In the absence of proper therapy, atrophy of the epidermis is possible. For some people, the inflammation looks similar to calluses. The main signs of cold skin dermatitis are itching and swelling.
The presence of dermatitis on the palms of a person with timely treatment does not pose a great danger. If treatment is not carried out, the disease can lead to complications. These include the addition of a secondary infection with the development of eczema or sepsis, and psycho-emotional disorders. Dermatitis can leave behind scars. In addition, the skin color in the affected area often changes. In advanced cases, inflammation affects the deeper layers. In this situation, there is a risk of developing tissue necrosis.
Dermatitis on the hands - photo
In order to understand what dermatitis on the hands looks like, below are photographs of this disease.
Types of dermatitis on the skin of the hands
There are several types of dermatitis on the hands. In the vast majority of cases, the clinical picture is the same, but the causes and factors in the development of the disease are different.
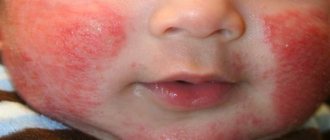
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis on a child’s hand
A chronic form of dermatitis, which manifests itself in the form of exacerbations and remissions. This is a non-contagious inflammation, which is often caused by a hereditary predisposition.
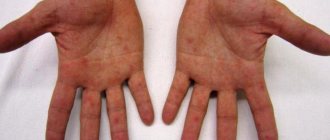
Allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis on the hand in an adult
This type of dermatitis on the hands appears when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritant (household chemicals, cosmetics, fabric, pollen, etc.) and is recognized by severe itching and redness.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis on the hands
Contact dermatitis is often used as a synonym for allergic dermatitis. However, there is one significant difference: the contact form appears immediately, upon first contact with the irritant, while the allergic form occurs with constant or prolonged exposure to a pathogenic factor. The clinical picture is the same for both diseases.
Solar dermatitis
Solar dermatitis on the hands
Solar dermatitis is photodermatitis, or simply an allergy to the sun. This is an inflammatory reaction of the skin in response to direct exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Actinic dermatitis
Actinic dermatitis on the hands
Actinic dermatitis occurs mainly due to radiation exposure, as well as under the influence of artificial or natural UV rays. The risk group includes workers in hazardous industries (X-ray rooms, workshops).
Eczematous dermatitis
Eczematous dermatitis on the hands
Eczematous dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of eczema, and the provoking factors are the same as for other types of dermatitis.
However, the danger of the disease is that in the absence of treatment, eliminating the allergen alone is not enough, because the reaction occurs to the proteins of one’s own skin.
Allergic dermatitis causes
It is still not possible to accurately determine the main cause of allergic dermatitis; the prerequisites for the occurrence of this disease may be:
- Exposure to physical irritants: plant pollen, house dust, animal hair, solar radiation, low temperatures.
- Chemicals and their combinations: medicines, plastics, heavy metals, formaldehyde, acids, alkalis, fabric dyes.
- Household chemicals, decorative cosmetics, perfumes, creams, deodorants.
- Preparations based on medicinal herbs and natural ingredients.
- Pathologies of the nervous system, stress, psychological problems.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Ecologically unfavorable environment.
- Preservatives in products.
- Impact of essential oils or plant juice: hogweed, parsnip, tobacco, nettle, ash, buttercup.
All these allergens can act for a long time without showing themselves.
The speed of the body’s response depends on the state of immunity; a person’s hereditary predisposition accelerates the reaction.
Before you learn how to treat allergic dermatitis, it is worth getting acquainted with its manifestations.
Top
Causes of dermatitis on the hands
Depending on the type of dermatitis and the characteristics of its appearance, there are different causes of its occurrence and risk factors.
The causes of dermatitis on the hands in adults are a number of individual characteristics of all systems (especially the digestive, nervous and immune systems), which favor the development of diseases, and risk factors are a direct irritant.
However, often the causes, risk factors and triggers are used interchangeably, so we will simply give an answer to the question “what causes dermatitis on the hands?”
Exposure to physical pathogens
Pressure or friction of fabrics and materials (the strap of a backpack or bag), wearing watches or jewelry made of nickel, low or high temperatures, sunlight, radiation, polluted air.
Allergy from watches
Signs of dermatitis appear on those areas of the skin of the hands that are directly affected.
Chemical irritants
Such irritants are acids, alkalis, washing and detergents, hygiene products and cosmetics, varnishes and paints, perfumes, etc.
Biological factors
This group includes factors of living nature: pollen and plant sap, insect or animal bites.
Medicines
In some special cases, the use of medications may be the cause of dermatitis. However, it is difficult to single out specific drugs, since much depends on the person’s “allergic” immunity. In this case, consultation with an experienced allergist is necessary.
Food
As a result of exposure to food allergens, atopic dermatitis usually appears, and less often - allergic dermatitis.
Factors that increase the risk of developing dermatitis on the hands:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Frequent stress and nervous experiences;
- Work in high-risk environments (X-ray room, chemical laboratory, etc.);
- Gastrointestinal disorders;
- Weakened immunity;
- Hormonal disbalance;
- Autoimmune diseases.
Preventive measures against dermatitis
The most effective preventive measure against dermatitis is the least possible contact with irritants in everyday life.
To do this, you must follow some rules:
- Protect the skin of your hands when working with household chemicals and chemicals,
- Buy cleaning and detergents with a gentle composition, without strong reagents,
- Use products made for children - washing powders, soaps, products for sensitive skin,
- When going outside, especially in frosty weather, always wear gloves or mittens,
- To protect the skin of your hands in the summer, apply a cream with a moisturizing effect,
- Use high quality soap with a moisturizing effect,
- Apply hand cream as often as possible, but at least in the morning and before bed,
- Carry out therapy using yarrow infusion every month for three to five days.
Symptoms of hand skin dermatitis
Symptoms of dermatitis on the hands are as follows:
- Redness of the skin of the hands. In this case, small areas (the space between the fingers, elbows, individual points) or a large area of the skin of the hands may suffer;
- Severe itching, which is constant, intensifies upon contact with the allergen (if it is not identified), at certain times of the day, periodically;
- Formation of bubbles filled with liquid;
- The appearance of erosions and ulcers. They usually occur after the blisters burst;
- Weeping wounds;
- Peeling and cracking of the skin occurs when weeping wounds begin to dry out;
- Crusts on the affected areas.
Diets
After consulting a dermatologist and identifying the main allergen responsible for the onset of the disease, you must adhere to some rules. First of all, it is important to reduce contact with water to a minimum. Hands should only be washed when necessary. When at home, it is recommended to use special gloves and a special silicone-based cream. This composition protects the skin from additional infections.
An important factor is compliance with special diets. You should try to completely eliminate salty, fatty or spicy foods from your daily diet. You should also avoid products that contain preservatives and dyes. You should completely avoid nuts, citrus fruits and chocolate, as they are quite strong allergens.
Diagnosis of the disease
Skin dermatitis on the hands can appear completely unexpectedly, and a person does not understand what it is and how to deal with it. The longer he relies on his own strength and ignores going to the doctor, the sooner the disease will turn into chronic dermatitis of the skin of the hands.
In addition, cream for dermatitis on the hands and other methods of treatment that are not agreed upon with the doctor may not only be useless, but also aggravate the problem.
If signs of the disease appear, you can contact a dermatologist, allergist or therapist. First, the specialist will ask you to tell in detail how and when signs of dermatitis on your hands first appeared and will prescribe a series of examinations:
- General blood test (sometimes urine);
- Serological and immunological research;
- Biopsy of the affected areas of the skin of the hands.
In most cases, the attending physician prescribes a serological test.
If the affected area is rapidly increasing and causes a lot of inconvenience, it is recommended to take tests for allergens.
How is dermatitis diagnosed?
To identify dermatitis and make an accurate diagnosis, you should go to an allergist or dermatovenerologist.
There are cases that do not require examination to establish a diagnosis. It is enough for a professional to conduct a visual examination and ask the patient about contacts with the irritant in order to determine the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment with the exclusion of the irritating factor from everyday life.
If the presence of symptoms of dermatitis raises doubts about the diagnosis, then tests are prescribed.
What tests are prescribed to diagnose dermatitis:
- General detailed tests (blood, urine);
- Tests for the presence of antibodies and antigens (serological, immunological);
- Examination for the presence of cancer cells using histology;
- Blood testing for various manifestations of allergens.
In a child, the signs of dermatitis on the hands and fingers are exactly the same as in adults. The only difference is the reason for its appearance. The main place here is the high sensitivity of children's skin.
In second place are allergic reactions to medications, pollen, and fruit and berry juices.
The disease fades and goes away completely as soon as the child is removed from irritating factors.
Treatment of dermatitis on the hands in adults
How to treat dermatitis on the hands of an adult? Treatment methods are determined for each case separately, especially for medications. Some remedies for hand dermatitis can worsen the situation if the patient is allergic to them.
How to treat dermatitis on the hands is determined by the attending physician. For example, dry dermatitis on the fingers, which appeared just a couple of days ago, can be cured with topical products and diet, but chronic dermatitis on the hands can be treated more seriously.
In case of “dry” dermatitis of the skin of the hands, special creams and ointments are prescribed
When diagnosed with “dermatitis on the hands,” treatment should be comprehensive and include:
- Drug therapy. Preparations for external use (ointments and creams for dermatitis on the hands), anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, and antiallergic drugs are suitable for this. In particularly severe cases, glucocorticoids, antibiotics and sedatives may be prescribed;
- Diet;
- Physiotherapy;
- Folk remedies for dermatitis on the hands.
Key aspects of therapy
Treatment depends on the type, form and severity of the disease.
The first and most important stage is the identification and complete elimination of the allergen leading to the development of dermatitis on the dermis of the hands. If a hypersensitivity reaction is caused by food, specific gastronomic “provocateurs” are simply excluded from the diet.
If reactions are caused by household chemicals or cosmetics, you should also avoid them. If contact with a particular chemical cannot be avoided, maximum safety precautions should be taken. For example, wear gloves when cleaning an apartment.
The next stage of therapy is the elimination of symptoms accompanying the body’s abnormal reaction to a particular allergen.
The basis of treatment is correctly selected pharmacological products for internal and external use.
Medicines for internal use
In order to stop the progression of allergic reactions and help the body fully recover, the patient is prescribed antihistamines.
Depending on how severely developed the inflammation and damaged structures of the skin tissue are, pime products can be prescribed for several weeks, and sometimes even months.
Related article:
How to treat dermatitis on the legs? Photos, causes and symptoms
All anti-allergy drugs are divided into three generations:
Clemastine
- First generation (Clematsin, Promethazine). The drugs relieve swelling and itching well, but can cause drowsiness and significantly reduce muscle tone;
- Second generation (Terfenadine, Loratadine). They eliminate the symptoms characteristic of allergies well, but can significantly affect the functioning of the heart. These medications are not prescribed for people with cardiac problems. There is no negative effect on the tone and activity of the nervous system;
- Third generation (Cetirizine, Hifenadine). The products help eliminate the symptoms of allergic reactions without causing drowsiness or interruptions in heart function.
Preparations for external use
Dermatitis is always accompanied by swelling, redness, and symptoms of general skin irritation. As a rule, discomfort intensifies in the evening, and reaches its peak at night.
This is why patients are prescribed various ointments and creams:
- Weak hormonal agents will help eliminate itching and reduce the intensity of inflammatory reactions (Prednisolone, Fluocortolone, Fluorocort);
- Moisturizers help restore the optimal level of moisture and elasticity of the dermis (Exomega, Hydrolipidic, Elidel);
- Drying agents help eliminate erosive defects and get rid of exudate (Zinc ointment, creams with added zinc);
- Products for nutrition and additional hydration on a plant basis will help at the final stage to retain moisture in the skin and nourish the structures with useful components (almond, nut, apricot, coconut, olive oil, as well as oil extract of jojoba, shea, cocoa).
Treatment of dermatitis on the hands of children
Dermatitis is quite common in childhood, even in newborns and infants, so you need to know how to treat dermatitis on a child’s hands, because it can quickly become chronic.
Dermatitis on a child’s hands causes him great discomfort, so you need to immediately take him to a pediatrician.
If a child has dermatitis of the skin of the hands, then it is necessary to contact a pediatrician to prescribe treatment.
Most often, treatment is carried out in several directions:
- Drug therapy: immunomodulators, softening and moisturizing creams and ointments;
- Phototherapy;
- A diet excluding allergens and highly allergenic foods.
Formula-fed babies are transferred to hypoallergenic formulas. When breastfeeding, the mother's diet is adjusted.
In some cases, dermatitis on a child’s hands appears only once, and after a while the reaction to the irritant will no longer appear. But sometimes, especially with a hereditary predisposition, dermatitis will appear from time to time, i.e. will become chronic.
Clinical picture of contact dermatitis
Allergic reactions, regardless of what provokes the disease, are characterized by a sudden appearance and rapid development.
The basis of dermatitis on the dermal tissue of the hands is a strong inflammatory process.
Main clinical manifestations:
The skin is very itchy and itchy. The affected area is extremely painful. A constant burning sensation may be felt;- Areas with dermatitis are hyperemic - colored deep scarlet or pink;
- Edema of a stagnant nature gradually forms;
- In severe cases, bubbles with serous contents will begin to form at the sites of redness over time. They can significantly increase in size and merge with neighboring pathological formations. When opened, the delicate irritated dermis is exposed. Weeping and extremely painful areas of skin can merge, forming necrotic lesions. Over time, weeping erosion becomes covered with scales and crusts.
If hand skin dermatitis transforms from an acute stage to a chronic form, then the symptoms of the disease partially change. The swelling is still stable and stagnant.
Related article:
Acrodermatitis: types of disease, symptoms and treatment
The upper layer of skin (in particular, all the balls of the epidermis) thickens, the surface of the skin of the hands acquires a painful bluish tint.
Weeping surfaces are replaced by abnormal dryness of the dermis. The skin is constantly peeling and cracking. Secondary foci of allergic irritation may be observed.
It is important to know! In especially severe advanced cases, the epidermis can completely atrophy in those areas where the allergic process was most intense.
Symptoms of mechanical dermatitis
Mechanical dermatitis
The clinical picture of mechanical dermatitis will be somewhat different from “classical” allergic reactions on the skin. The dermis is edematous and hyperemic.
Blisters with serous filling or specific compactions resembling a callus may appear.
Over time, hyperkeratosis gives way to the formation of a plaque colored yellow-brown or deep brown. These areas are characterized by increased sensitivity, but there are no characteristic pain reactions.
Creams for dermatitis on hands
Dry dermatitis on the hands is treated using moisturizing creams. There are products that cannot be used for weeping dermatitis, and vice versa. External remedies for the treatment of dermatitis on the hands have an anti-inflammatory, soothing, softening, healing effect, accelerate tissue regeneration and relieve itching. Cream for dermatitis on the hands can be non-hormonal and hormonal. The second type is more often used in severe cases of the disease.
Below is the TOP of common creams for dermatitis on the hands.
Cream “Zorka” or its analogue “Forest Power”
Cream “Forest Power” with Floralizin
An inexpensive but very effective product that promotes tissue restoration, nourishes, moisturizes and improves skin metabolism. The active ingredient is Floralizin.
Eplan
Eplan cream
An antiseptic that promotes wound healing, relieves pain and reduces symptoms, accelerates tissue regeneration.
De-panthenol and its analogues (“Bepanten”, “Panthenol”)
Creams “Bepanten” and “Panthenol”
These drugs are the most popular drugs for the treatment of dry dermatitis on the hands. Used for cracks, peeling, dry skin, promote tissue regeneration.
Fenistil gel
Fenistil Gel
is used for skin lesions as an analgesic and antipruritic drug.
La-cree cream
Restoring cream La-Cri A
cream based on natural extracts and components that soothes, moisturizes, has a regenerating effect, relieves allergy symptoms (itching, peeling, redness).
Regular fatty baby cream cannot be used for dermatitis: it forms a film on the skin and slows down healing.
When treated with external agents, healing occurs within 10-14 days.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the result of internal self-sustaining inflammatory processes triggered by an allergen. Its symptoms of skin damage are typical for dermatitis: itching, redness, swelling, rashes, weeping period, crusts and peeling, and frequent infection is characteristic.
The difference from other dermatitis is in its genetic nature. A peculiarity of the body of people who develop atopic dermatitis: even removing the irritant that triggered the chain of allergic inflammatory reactions in the body does not stop them.
Diagnostics
A dermatologist or allergist can identify dermatitis on the hands, its causes and treatment. In the case of contact dermatitis, an examination and conversation may be sufficient. In other cases, consultations with a therapist, gastroenterologist, neurologist and endocrinologist may be necessary.
When making a diagnosis, it is determined:
- degree of severity: severe or moderate;
- phase: acute (period of rashes, blisters), subacute (crusts, scales) or chronic;
- the etiology of the manifestations is clarified: the nature of the factor that is the allergen: pollen, food, mite, fungal;
- presence (absence) of secondary infections.
To identify the allergen, skin tests are performed, general and biochemical blood tests, stool tests for helminthiasis, and examination of scrapings from the affected skin.
Dermatitis is usually differentiated from eczema and fungal infection.
After the diagnosis has been established, the attending physician will prescribe a course of therapy, which will include regimens during the treatment period and medications to treat dermatitis on the hands.
Treatment
First of all, the causes and factors that provoke the disease should be minimized.
Limit contact with the allergen, water, adjust the diet, excluding chocolate, citrus fruits, etc. The treatment is complex and consists of a combination of anti-allergenic, anti-inflammatory, sedative, immunorestorative medications and local therapy - ointments, creams, gels, aerosols.
The goal of therapy is complete or partial remission, namely:
- Elimination or reduction of rashes and itching;
- Normalization of the appearance and functions of the skin in affected areas, restoration of its metabolism;
- Preventing the development of complications of the disease, improving the quality of life;
- Treatment of associated infections.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines, which relieve or reduce swelling, itching and rashes (for adult patients), are taken in courses:
- First generation : suprastin, fenistil, tavegil, taken at night. They have a sedative effect - hypnotic, calming and depressing consciousness, and lasts 5-8 hours, which allows them to be used before bedtime. Recommended for atopic dermatitis, urticaria, eczema in acute and subacute phases.
- Second generation: Loratadine, Rupafin, Kestin (effect 48 hours) non-sedative, non-addictive. Recommended for atopic dermatitis, urticaria, eczema in acute and chronic phases. Antihistamine effect 24 hours. Not recommended for use for heart disease and elderly people.
- Third and fourth (metabolites): Telfast, Citirizine, Xyzal, Desloratadine. Non-sedative, used for seasonal and year-round allergies, urticaria for prevention and during periods of remission of chronic forms of diseases. Duration of action: 24 hours, no effect on the cardiovascular system. They are addictive.
For pregnant women, lactating women and children, there are restrictions, special dosages and acceptable and recommended remedies. Some of them are listed below.
External therapy
- To avoid infection, it is recommended to treat scratches on the skin with mild antiseptic agents or herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula).
- Used at the wet stage: Lotions: rivanol solution (ethacridine lactate) 1:1000, tannin solution 1%, oak bark tincture.
- Dyes: 1% solution of methylene blue, fucorcin (Castellani liquid).
- In the case of a secondary infection: bacterial, antibacterial therapy is carried out: levomikol, miramistin, chlorhexidine;
- fungal – antimycotics: clotrimazole, fluconazole, lamisil;
- herpes - acyclovir;
- broad-spectrum corticosteroids - with antibacterial and antifungal effects: diprosalic, triderm.
Drug support
- To remove intoxication products and allergens from the body, sorbents are used - activated carbon, enterosgel.
- To preserve and rehabilitate the intestinal microflora, probiotics are prescribed: bifidumbacterin, bifilis, bificol.
- Sedative therapy for hand dermatitis - valerian, motherwort. When using herbal medicine, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of an allergic reaction to natural drugs and discuss the use of infusions, decoctions, and lotions with your doctor.
- For atopic dermatitis (and diathesis) during the chronic course and for prevention, polyunsaturated fatty acids and group vitamins, vitamins A, E and group B are recommended. They help restore immunity, the collagen base of damaged skin and relieve chronic inflammation.
- If therapy is ineffective or with chronic dermatitis on the hands, a course of systemic glucocorticosteroids may be prescribed.
Treatment of dermatitis on the hands should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor; if atypical symptoms appear, he will adjust the course.
Ointments for dermatitis on hands
Ointments also cope well with the symptoms of dermatitis and prevent the spread of inflammation and infection. The most commonly used drugs have proven to be effective:
- Zinc ointment;
- “Fluorocort” - relieves symptoms of dermatitis, relieves itching;
- “Flucinar” is an anti-inflammatory drug, relieves itching and signs of allergies, and has an anti-exudative effect;
- “Levomekol” promotes tissue regeneration, prevents the spread of infection, has an antimicrobial effect, and alleviates the symptoms of dermatitis;
- “Bactroban” is an antibacterial ointment.
Traditional methods of treating dermatitis on the hands
By themselves, folk remedies for dermatitis on the hands are not able to completely relieve the symptoms of the disease, but in combination with drug therapy they have a positive effect.
The use of folk remedies should be agreed with a doctor.
What folk remedies are most often used to treat dermatitis at home?
- Chamomile decoction (4 tbsp per 1 tbsp boiling water). Used in the form of baths;
- Pumpkin, potato or cucumber juice. Strained fresh juice of one of the vegetables is used in the form of lotions: dip a clean cloth or gauze and apply to the affected areas;
- A mixture of propolis and olive oil (ratio 1:4). Make lotions from the solution 1-2 times a day;
- Herbal mixture of chamomile, calendula and plantain (4 tablespoons of herbs per 300 ml of boiling water). Let the solution sit, treat the wounds throughout the day and do not rinse off;
- Vaseline with cranberry juice (200 g and 50 ml). Combine the two substances and use as a cream several times a day.
Disease prevention
Skin dermatitis on the hands will not appear if you follow simple preventive measures:
- Monitor the state of the immune system. If signs of illness appear, even the simplest ones (for example, a runny nose), you need to go to the doctor;
- Follow a diet. People who have family members who suffer from any type of dermatitis are recommended to follow a diet excluding highly allergenic foods;
- Do not self-medicate;
- To avoid dermatitis in a small child, the diet of the nursing mother needs to be adjusted, and the introduction of complementary foods should be gradual;
- Follow the rules of hygiene: use only high-quality cosmetics, hygiene products, choose underwear and bed linen and clothes from natural fabrics;
- Lead an active lifestyle: play sports and give up bad habits;
- Avoid hypothermia, prolonged exposure to the sun and severe stress.
Diet for hand skin dermatitis
Without following a diet, treatment for dermatitis on the hands may be in vain, especially if any food product has become a provoking factor. A diet for hand skin dermatitis should include a balanced, low-calorie diet high in nutrients and vitamins.
If you have dermatitis, you should follow a low-calorie diet
Basic principles of nutrition for dermatitis on the hands:
- Eat small meals 4-6 times a day;
- Exclude highly allergenic foods from the diet: chocolate, nuts, honey, mushrooms, seafood, coffee, cocoa, red and orange vegetables, berries and fruits, sweets and baked goods, alcohol and sweet soda, whole milk;
- Reduce sugar and salt intake;
- Reduce the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates and fats;
- The basis of the diet should be green vegetables and fruits, low-fat vegetable soups, cereals (except semolina and rice), fermented milk products;
- Preferred types of food processing: boiling, steaming, baking in the oven, stewing;
- Introduce drinks into your diet: herbal tea, rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote, cranberry juice and natural juices.
You need to follow a diet for dermatitis for at least 2-3 weeks, i.e. until signs of skin dermatitis of the hands completely disappear.