Features of the disease
This form of urticaria can appear in both children and adults of any age and gender. It is especially often diagnosed in children, occurring chronically with periods of exacerbation and remission. Sometimes the disease disappears by adolescence due to hormonal changes in the body and never bothers you again. In other cases, urticaria occurs throughout life, causing significant discomfort.
This pathology is especially poorly tolerated by infants who have not yet developed body thermoregulation . In children, urticaria is often combined with other forms of allergies - to food, dust, detergents. Women during menopause also often suffer from increased sensitivity to temperature. Against the background of hormonal imbalance, hot flashes are observed, which are accompanied by a sudden feeling of heat. It is because of this condition that the symptoms of urticaria develop, which manifest themselves even more intensely with additional exposure to a stress factor.
In a person of any age, excessive sensitivity to temperature effects is observed from a fever that lasts for several days. This occurs because the patient’s body is weakened by infection and medication. As a result, the immune system reacts with a rash and other unpleasant symptoms.
Varieties
Classification of urticaria into heat implies its division into two main forms:
- Generalized cholinergic. Rashes appear throughout the body.
- Local. The rash forms only on certain areas of the body that are in direct contact with the heat factor.
The local form refers to contact urticaria, which can also occur when exposed to cold, water, friction, and vibration.
The disease is classified according to the duration of clinical manifestations:
- Acute form. Over the course of one and a half months, all symptoms gradually disappear
- Chronic form. Unpleasant symptoms persist for longer than 6 weeks.
Therapeutic treatment of heat urticaria
If this type of allergic reaction is detected, immediate treatment is necessary. If you notice a local form of manifestation, then try to eliminate the factor causing the negative reaction.
If itching bothers you for a long period, a specialist will prescribe antihistamines. The doctor will consider the severity of the allergic reaction. In more severe cases, Hydroxyzine . The drug is convenient because it has two actions at once, antihistamine and anticholinergic. Moreover, the drug can be taken by children from 1 year.
Causes
The reasons for the development of the disease are not fully known. It has been established that most often it manifests itself in people with a predisposition to various allergic reactions . The appearance of rashes on the body occurs due to a combination of several factors:
- high sensitivity of cells to a special substance - acetylcholine;
- susceptibility of the centers responsible for thermoregulation of the body to substances released during temperature exposure;
- increased sensitivity of the immune system to any external irritants.
People with heat urticaria often have other autoimmune diseases: bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, sensitivity to certain foods, angioedema.
Local urticaria develops if a specific area of the body is exposed to temperatures above 40 °C.
The generalized form appears after such negative influences:
- physical activity, which is accompanied by intense sweating;
- taking a hot bath or shower;
- high air temperature;
- emotional shock;
- increased body temperature caused by infectious or any other diseases;
- eating excessively spicy foods, which leads to vasodilation;
- the presence of VSD, pathologies of the thyroid gland or gastrointestinal tract in a person.
Characteristic symptoms
The appearance of thermal urticaria depends on specific reaction to overheating. The usual localization of rashes on the body is the upper body, arms. Appears immediately after exposure to a negative factor. Girls are most often susceptible to this type of illness, although the pathology can manifest itself in absolutely anyone.
Heat urticaria in adults is almost no different from the clinical manifestations of the disease in children. The difference lies in the severity of the body's reaction to the stimulus.
Characteristic symptoms:
- the appearance of blisters on the skin with a diameter of no more than 5-10 mm;
- temperature increase;
- in rare cases, nausea, vomiting, and problems with stool are observed.
All manifestations are noticeable within a few minutes after contact with the irritant.
For convenience, doctors distinguish several forms of heat illness .
Knowing the exact diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Only then the chances of a quick recovery increase significantly:
- Cold urticaria . It is characterized by an allergic reaction to contact with cold air or even food (science knows of cases when, after drinking a glass of a cool drink, a person breaks out in a rash).
The pathology is accompanied not only by blisters and itching, the patient experiences constant nausea, chills, body aches, and headaches. - Solar urticaria . From the name it is clear what causes the disease; exacerbations are most often recorded in the spring and summer.
Blisters almost always appear on open areas of the skin and are small in size. A severe form of the pathology is fraught with loss of consciousness and serious complications. - False urticaria . This type of symptoms is similar to the manifestations of heat illness, but is caused by internal problems with the kidneys, liver, and stomach.
Almost always, the patient feels unwell, rashes appear on the body, other symptoms depend on the specific ailment.
Symptoms
From the heat, an adult or child develops urticaria, which is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Occurs within 5-20 minutes after exposure to the provoking factor.
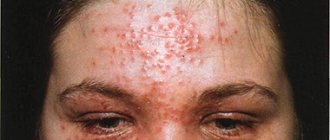
- Small whitish pimples are observed on the body. They are surrounded by bright pink swelling tissue. The pimples gradually merge, forming an area slightly raised above the skin.
- The rash is very itchy, which causes anxiety for the patient.
- Heat urticaria acne most often appears on the face or upper body.
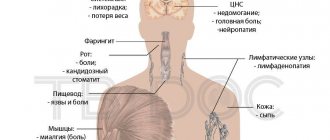
- Signs of intoxication appear - weakness, nausea, vomiting, loose stools, headaches, fever.
Features of the manifestation of thermal urticaria
The disease is characterized by the presence of certain symptoms that distinguish it from other types of disease. During the course of the pathology, the appearance of pink blisters is observed, which rise above the skin.
Quite often the disease is accompanied by swelling. Almost half of patients complain of itching during the course of thermal urticaria. This symptomatology is characteristic of a local type of urticaria.
The persistence of symptoms is observed from 30 to 90 minutes after the lesion. If a cholinergic type of urticaria is observed, then the manifestation of symptoms is observed throughout the patient’s body.
The disease may be accompanied by:
- Nausea;
- Diarrhea;
- Vomiting;
- Headaches;
- Bloating.
In some patients, when a pathological condition appears, an increase in salivation is observed. Swelling is observed on the patient's skin. All swollen areas are characterized by the development of itching.
Patients complain of discomfort in the stomach and intestines. Bubbles are observed on the patient’s body, which can have different diameters and are characterized by itching.
ATTENTION! If the patient has a slight sensitivity to the allergen, this leads to the appearance of a small rash and mild itching.
If appropriate treatment is not provided in this case, then the patient will develop a chronic form of the disease. An allergic reaction can occur anywhere.
Most often, the pathology is localized on such parts of the body as the chest, forearm, neck, and face. After exposure to provoking factors, the appearance of symptoms can be observed within half an hour.
If a person is again exposed to negative factors, this may lead to the reappearance of the disease. In this case, patients are diagnosed with an increase in body temperature.
If unpleasant symptoms appear, it is necessary to exclude the allergen. Symptoms of the disease can go away on their own within a few hours.
Heat urticaria is a rather unpleasant disease. Due to the presence of a large number of signs, a person can determine the disease independently. To determine the allergen, he is recommended to contact a medical center.
Causes
This type of disease is characterized by the absence of a specific genesis.
This disease occurs when the body reacts inadequately to heat.
If the body's sensitivity to the effects of neurotransmitters is increased, this leads to the appearance of the disease. Quite often the cause of the disease is high sensitization of the body.
The development of an allergic reaction is often diagnosed when exposed to external and internal factors. If water with a temperature of more than 40 degrees comes into contact with a person’s skin, this can lead to the appearance of a disease.
What is heat urticaria, watch in this video:
Stressful situations and strong emotions can cause illness. People who frequently visit baths and saunas are at risk. If a person eats foods that cause vasodilation, this can lead to the development of thermal urticaria.
Walking in the fresh air at high temperatures can cause the development of pathology. Quite often, heat urticaria develops against the background of infectious diseases.
This is explained by sudden changes in the patient’s body temperature. The possibility of developing thermal urticaria in the fairer sex can be observed during the period of hot flashes during menopause. The disease can occur against the background of:
- Improper functioning of the digestive system;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Neuroses.
If the patient has active muscle tension, this leads to active production of sweat by the body, which becomes the cause of thermal urticaria.
The causes of urticaria are quite varied. To avoid this disease, the patient must avoid the negative effects of external and internal factors.
Contacting the doctor
If a patient suspects the development of thermal urticaria, he should immediately consult a doctor. This will make it possible to timely relieve symptoms, as well as eliminate the allergen.
What are the symptoms of urticaria discussed in this video:
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose a pathological condition, provocative tests are used, which involve the effect of heat on the human body. In most cases, a person's hands are immersed in warm water.
After half an hour, it is possible to assess the body's reaction to the allergen. If the patient develops itching and a rash, this indicates the development of thermal urticaria.
To confirm the patient’s diagnosis, blood and urine tests, gastroscopy, immunoglobulin test, and ultrasound examination of the digestive tract.
Diagnostics
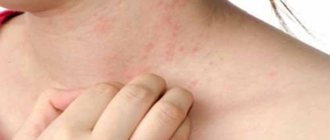
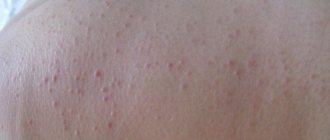
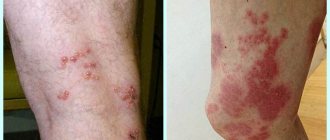
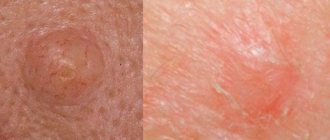
The photo shows the rash that occurs with heat urticaria.
It differs significantly from rashes associated with various dermatological diseases of an inflammatory nature - dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema.
Determining the form of the disease is also not difficult. For this purpose, the simplest diagnostic tests are used. A glass of hot liquid is applied to any part of the patient’s body for several minutes or the limb is lowered into a basin of heated water. If a rash appears on the skin within half an hour, we can say that the patient has thermal urticaria.
Sometimes, to make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is injected intradermally with carbacholine, a medicinal analogue of acetylcholine.
Why does heat urticaria occur?
For the development of any form of illness, an allergic predisposition of the body is necessary. Some patients are diagnosed with other allergic diseases: food intolerance, atopic dermatitis, other types of urticaria.
In localized heat urticaria, histamine is directly released from mast cells upon local exposure to temperatures greater than 40ºC.
The cholinergic type is characterized by a general increase in body temperature after the action of provoking factors (physical activity, hot bath, stress, high air temperature). The thermoregulation center responds by releasing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This in turn stimulates the release of histamine from mast cells.
Therapy
Treatment of heat urticaria is aimed at eliminating symptoms and preventing life-threatening complications.
It is almost impossible to get rid of the disease forever. To combat the manifestations of the disease, various external and systemic agents are prescribed, which are usually used in combination.
External preparations
You can treat urticaria using the following topical remedies:
- Medicines containing atropine or belladonna extract. These substances block the production and negative effects of acetylcholine on the patient’s body. The most popular ointments and creams from this group are Fenistil, La Cree, Advantan.
- Preparations containing diphenhydramine relieve itching and rash well. The most famous remedy is Psilo-balm.
- In case of severe development of the disease, hormonal ointments are prescribed - Hydrocortisone, Celestoderm, Bufexamak.
Drug therapy
To relieve symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition, a number of drugs are prescribed:
- antihistamines (Zyrtec, Erius, Cetirizine);
- sedatives (valerian extract, Novopassit);
- hormones intravenously in the most severe cases.
Alternative medicine
Folk remedies for the manifestations of urticaria turn out to be quite effective. The following recipes are popular:
- Taking celery juice internally. Every day you need to drink up to 300 ml of a freshly prepared drink, dividing it into several servings. Treatment is continued for one week.
- Lotions with dill juice. Help relieve itching and skin irritation. Moisten a cotton or gauze swab with the juice and apply for a few minutes until relief appears.
- Using chamomile infusion. It is recommended to add it to the bath in an amount of 1 liter to prevent rashes during the thermal procedure. To prepare the infusion, pour 3 tablespoons of chamomile into a liter of boiling water and leave for half an hour.
Therapeutic diet
There is no need to follow a special diet if you develop heat urticaria, because it does not arise from any food. It is only recommended to follow the principles of rational nutrition, excluding fatty foods, large amounts of sweets, fast food and alcohol from the menu.
Treatment
Therapeutic
Therapy for cholinergic and local forms of heat allergy is in many ways similar, but there are clear differences due to the severity of the process and the time it takes to eliminate the cause of the pathology. The effect of heat on a certain area of the skin in a local form can be easily eliminated by simply isolating the patient from the irritant, thus stopping further influence of heat. The cholinergic form affects a large surface area of the skin and more often causes accompanying signs of irritation of the nervous system by acetylcholine, including general malaise, fever, and vomiting.
The patient’s condition is improved by a shower and bath with cool water, immediate rest during muscle activity, sedatives if the patient is experiencing a stressful situation (Valoserdin, Motherwort forte, Novopassit, Milgamma, vitamins B1, B6, B12, Neuromultivitis).
Local
Since heat urticaria causes an acute reaction due to excess acetylcholine produced by the patient's body, gels, creams and ointments containing atropine and belladonna extract are used to relieve irritation and blisters on the skin. These products, when used two to three times a day, show a good effect: Fenistil-gel, La-Cri, Gistan-N, Advantan. Recently, pharmacological external agents with the substance diphenhydramine, which is part of Psilo-balm, have been successfully used. It is also possible to prepare 3 - 10% ointment with diphenhydramine in a pharmacy for application on rashes (several times a day). For acute manifestations, local therapy involves the use of hormonal external ointments: Sinaf-ointment, Akriderm GK, Hydrocortisone, Elokom, Celestoderm, Bufexamak.
Read below about what medications should be taken for urticaria when treating it in adults and children.
Medication
The complex of medicinal blocks provides for the introduction of the following pharmaceuticals into therapy.
Antihistamines
In the acute form of the disease, it is better to choose first-generation drugs, since the effect of second-generation drugs, as a rule, becomes noticeable at a later stage.
For severe itching, Erius (desloratadine) is prescribed: patients over 12 years old - 5 mg once, children 1 - 5 years old 1.25 mg (in syrup 2.5 ml), 6 - 11 2.5 mg each (in syrup 5 ml) once. Diphenhydramine (1st generation antihistamine with sedative and antiemetic effects). Orally from 12 years old, 30 - 50 mg up to 3 times a day, for infants for 1 dose - 2 - 5 mg, from 2 to 5 years a single dose will be 5 - 15 mg, and 15 - 30 mg is given to children 6 - 12 years old. Hydroxyzine, an antiallergic drug with a mild sedative effect in the development of a generalized form of thermal urticaria. Allowed for children over one year old. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
In cases that are difficult to treat, antihistamines are used intramuscularly (Suprastin, Tavegil, Pipolfen).
For chronic urticaria:
Ketotifen for adults 0.001 g twice, for children 6 months - 3 years - 0.0005 mg (long course 2 - 3 months). Ebastine: for patients over 12 years of age, 10–20 mg once, for younger children in the form of syrup. Cyproheptadine 3 - 4 times 4 - 8 mg (for children - based on a daily dose of 0.25 - 0.5 mg per kilogram of baby's weight, divided by 3 - 4 times) In addition to these drugs, they are used in age-specific doses: Cetrin, Alerzina, Kestin, Elertu.
Histamine H2 receptor blockers
Prescribed for weak effects of antihistamines: Cimetidine - orally 300 mg 3 - 4 times a day (from 12 months of life the daily dose is calculated according to the formula - 25 - 30 mg / kg of body weight, for infants - at the rate of 20 mg / kg of body weight), Ranitidine , Famotidine.
For severe persistent itching, a disorder of the nervous system, which is more often observed against the background of cholinergic thermal urticaria, the following are indicated:
glucocorticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone; choline blockers with a sedative effect: Bellaspon, Bellantaminal, Belloid; tranquilizers: Phenobarbital, Atarax.
This video will tell you about traditional methods of treating urticaria in adults:
Prevention
It is quite easy to prevent the development of heat urticaria if you adhere to the following recommendations:
- try to eliminate as much as possible the impact of the thermal factor on the body;
- when taking a bath or shower, there is no need to increase the water temperature excessively (optimally 36-37 °C);
- it is necessary to refuse baths and saunas;
- prevent the development of stressful situations;
- reduce the intensity of physical activity that causes excessive sweating;
- it is necessary to prevent and effectively treat any diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- You should avoid eating hot and too spicy foods.
Urticaria is most often not dangerous, but its appearance should alert you. Only an integrated approach to the problem and compliance with all doctors’ recommendations will help cope with the disease.
Reasons for appearance
To date, the etiology of thermal urticaria has not been clarified. According to dermatologists, the trigger of the disease is the organic substance acetylcholine, released in large quantities by the body when exposed to high temperatures.
Under the influence of acetylcholine, the so-called mast cells located in the subcutaneous layer release histamine into the blood, which is a mediator of allergic reactions. As a result, the permeability of the capillary walls increases, through which liquid leaks and blisters appear on the body.
Factors that can trigger heat urticaria include:
- the presence of autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, systemic lupus and others);
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- excessive wrapping in cold weather, leading to increased sweating;
- insufficient development of the immune system;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- nervous and emotional instability.
In most cases, heat urticaria occurs against the background of other allergic diseases. At the same time, the risk group includes people with a hereditary predisposition to allergies.