The incidence of cancer in the 21st century worries doctors all over the world. One of these dangerous types of pathology is amelanotic melanoma. This cancerous tumor, which is located on the human skin and has a high degree of malignancy, is very difficult to recognize in the early stages and even more difficult to eliminate.
Leading clinics in Israel
Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv
Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv
Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
According to statistics, achromatic melanoma occurs more often in women than in men or children. Women aged 30-50 years are more often at risk.
The danger of melanoma is its rapid metastasis and high mortality rate . Pigmentless melanoma has ICD-10 code C43-C44.
Amelanotic melanoma can have different forms, the most common are:
- superficial spreading species. This form is also characteristic of colored melanomas and those that appear on the skin without strong pigmentation. This type is observed in 3 out of 4 cases of melanoma development. Externally, such a neoplasm looks like a plaque with a heterogeneous structure and color, uneven edges and relatively slow growth. It can be located in the superficial layers of the skin for about 4-5 years, and then go deeper, metastasizing to different organs. Such melanomas in men are usually localized on the arms, and in women – on the legs;
- nodal view. It is diagnosed somewhat less frequently, but is the most aggressive, as it has a tendency to grow rapidly. Often occurs in a place free of moles. Over time, this neoplasm can acquire a dark color, but it can also remain light, grows quickly (over several months), and can ulcerate and bleed. Nodular non-pigmented melanoma can occur on the neck, face, back and other parts of the body; this form is more common in men than in women.
A subtype of nodular melanoma is the desmoplastic form, which appears as a hard, irregularly shaped nodule, similar to a scar or scar. It is quite difficult to diagnose this form of neoplasm, since even a superficial biopsy (not to mention dermatoscopy) can be mistaken, mistaking melanoma for a keloid or dermatofibroma, which have nothing to do with oncology.
Reasons for appearance
The etiology of melanoma is not clear. In addition, it is not known why in some people the tumor produces pigment and in others it does not . Risk factors for developing achromatic melanoma are:
- Frequent ultraviolet irradiation;
- Congenital deficiency of melanin (albinism, fair skin, hair and eyes);
- Progressive melanosis of Pick (hereditary disease, manifests itself in childhood);
- History of sunburn;
- Heredity (presence of melanoma in blood relatives);
- Atypical nevus syndrome.
- Risk factors only mean a person’s predisposition to a tumor disease, but are not the direct cause of its development.
Pathogenesis
Melanoma, like most cancers, is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
The tumor is formed when DNA damage occurs in skin cells. Such disorders may be associated with excessive exposure to UV radiation. Albinism is also one of the basic reasons for the formation of the achromatic form of pathology.
The role of genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out. Some of these genes have been identified. They are responsible for 20% of cases of disease formation.
Cases when there are a large number of moles on the patient’s body (more than 50), as well as decreased immunity, are considered dangerous.
Video on the topic:
There is a connection between the formation of pathology and the following conditions:
- pregnancy after 30 years, lactation period;
- hyperestrogenism in women;
- work in hazardous industries (chemical, coal, pharmaceutical industries);
- influence of ionizing radiation;
- mechanical injury to moles or benign skin growths;
- scars or trophic ulcers located on the skin;
- various disruptions in the process of skin pigmentation (xeroderma pigmentosum and others);
- Paget's cancer, Bowen's disease or intraepidermal cancer;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- borderline nevi (moles with dark edging, blurred edges, irregular shape, and others). Amelanotic melanoma can form next to such moles;
- overweight, large build.
Malignancy of cells can also be promoted by poor nutrition and the use of certain medications (hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives).
Treatment of melanoma: what will happen with delayed examination and treatment?
When analyzing methods of treating melanoma, it is indicated that surgical treatment is the basis. However, you should know that only rapid diagnosis and radical action, that is, removal of the entire lesion, can determine the effectiveness of treatment. The basis for the treatment method is an excisional biopsy, which determines the malignancy of the tumor. The lesion is excised along with the edge of healthy tissue.
In special cases, re-treatment is carried out, during which the original lesion site is cut off. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is also performed to assess the severity of the disease. The selection of the sentinel node is made taking into account the location of the original lesion.
Excision of the lesion and histopathological result allow the selection of appropriate treatment. As a rule, if the lesion has been removed and the correct margin has been preserved, and lymphadenectomy has been performed, that is, removal of the lymph nodes, then there is usually no indication for further treatment, but it is necessary to be under constant medical supervision.
Metastases associated with melanoma can appear even several years after surgery to remove the primary lesion. The risk of metastases, as well as the time at which they may appear, depend on several factors, the most important of which is the thickness of the primary lesion.
Melanoma metastasis
Symptoms of non-pigmented melanoma
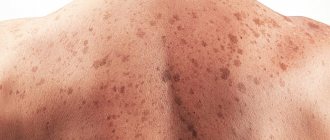
Signs of the disease appear on the body suddenly, in the area of normal skin. The focus of the disease grows slowly and is capable of changing shape. Melanoma has a rough, bumpy surface, is painless to the touch, and may peel off slightly. Externally, the neoplasm can be in the form of a small scar with uneven edges, or in the form of a nodule, a polyp, or it can be completely flat, merging with the surface of the skin. Simple flat melanomas are small in size, nodular melanomas are voluminous and large.
As amelanoma develops, it begins to itch and hurt. Redness and swelling occur at the site of the tubercle and around it. The surface of the melanoma may crack and bleed, and small ulcers may form on it. This indicates the transition of the disease to more severe stages that can be treated with great difficulty.
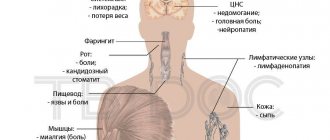
In the presence of metastases, various signs may occur depending on the affected organ:
- headache and convulsions - with metastases in the brain;
- shortness of breath, weakness - with lung damage;
- pain and pathological fractures when bones are involved in the oncological process.
A characteristic feature of non-pigmented melanoma is considered to be an uneven increase in its parts, and the asymmetry of the compaction is visible. A flat neoplasm often has uneven edges and uneven pigmentation.
Do you want to know the cost of cancer treatment abroad?
* Having received data about the patient’s disease, the clinic representative will be able to calculate the exact price for treatment.
If there were hairs on the lump, and then they began to fall out, this is considered an alarming sign that indicates the tumor has become malignant.
How to recognize colorless melanoma in the early stages?
The main signs include changes in the following parameters of the neoplasm:
- size;
- colors;
- forms.
The development of these signs can continue over a long period of time (from several weeks to several months).
Early symptoms indicating the presence of a dangerous disease are the following:
- the appearance of pain in the mole area;
- bleeding;
- the spot thickens and rises above the skin;
- the appearance of an unpleasant burning sensation;
- itching;
- the appearance of discharge;
- hyperemia and swelling of nearby tissues;
- ulceration of the neoplasm;
- the mole becomes soft.
Diagnosis of the disease
The ABCDE test is suitable for self-diagnosis of amelanoma:
A (Asymmetry) - shape - asymmetrical.
B (Border) – borders – usually they are absent.
C (Colour) – color . New growths change color over time.
D (Diameter) – diameter . They are more than 6 mm in size and can grow.
E (Evolution) – development . Over time, the size, shape, density and color of the tumor change.
To diagnose non-pigmented melanoma, dermatoscopy is used - an examination using a device that uses polarized light and magnification.
A sample is taken from suspicious areas and sent for histology.
Also usually prescribed:
- blood and urine tests;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- cytological analysis of the damaged surface (if there are ulcers);
- scintigraphy or radioisotope study.
If the diagnosis confirms the presence of cancer cells, various organs are checked for the presence of metastases:
- Ultrasound;
- CT or MRI of the brain;
- plain radiography.
It is important to determine all the ways in which cancer cells spread and accurately determine the stage of the disease. The prescribed treatment regimen depends on these points. Additional diagnostic methods are:
- urine test for Yaksha reaction;
- lymph and thermography,
- radioisotope diagnostics using radioactive phosphorus.
Differential diagnosis is usually carried out with warts and other benign neoplasms on the surface of the skin.
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy is an examination in which a dermatologist uses a dermatoscope. This is an instrument that combines a magnifying glass 10 or 20 times, magnifying the fragment under study, equipped with a standardized light source. In such conditions, the doctor may initially assess skin changes.
Dermatoscopy
Videodermatoscopy is a study that, in addition to the techniques used in dermatoscopy, uses visualization on a computer monitor. This allows the clinician to store the displayed image in the device's memory, which can be useful for comparative purposes at a later stage in treatment. In practice, several dermoscopic methods are used to diagnose melanoma.
The doctor, based on the appearance of the lesion, will evaluate whether there is a reason to remove it along with a margin of healthy skin, and send the material after the procedure for histopathological examination.
The specialist studies the characteristic features of the mole, in particular:
- Color—uneven color, darker and lighter areas, or pink and red areas are abnormal;
- Ragged edges - moles with smooth edges are less dangerous to health;
- Asymmetrical shape;
- Size greater than 5 mm - smaller lesions are usually not a cause for concern, but if they are growing dynamically or show other abnormalities, they need to be removed;
- Bleeding, ulceration, presence of discharge.
Diagnosis that confirms or excludes a skin neoplasm, which is melanoma, is possible on the basis of a histopathological examination, which is carried out after removal of the entire lesion.
Stages of the disease
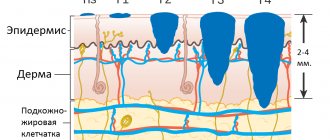
- Stage 0 - formations are located within the boundaries of the epidermis and do not extend deep into the basement membrane. At this stage, the melanoma is excised to include 1 cm of intact skin. Mohs surgery is performed - layer-by-layer excision of the lesion using a scalpel or laser with constant microscopic control for less trauma to healthy tissue.
- Stage 1 - melanoma is within 1 mm thick and does not metastasize. In this case, surgical excision is required with a margin of 2 cm of intact tissue. When the tumor has been ulcerated or the cells have begun to divide rapidly, stage IB can be determined.
- Stage 2 - tumors 1-2 mm thick, capable of ulceration, but without signs of spread beyond the boundaries of the primary focus.
- Stage 3 - a tumor of any thickness, spreading to adjacent areas of the skin or nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 4 - the pathological process spreads to distant areas of the body. At this stage, up to 20% of cases of the disease are diagnosed.
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor
Melanoma is one of the types of malignant skin tumors. The test that confirms or excludes the diagnosis is a biopsy, which confirms the diagnosis based on microscopic examination. The results of the performed biopsy provide information about factors that have a significant impact on the prognosis of the patient's treatment. This information allows you to determine the further course of the treatment process.
Melanoma biopsy
Examination of removed tumors for malignancy is carried out on the basis of macro- and microscopic examination. Among the factors that play a significant role in assessing the patient's health prognosis, primary outbreaks are of great importance. If there are no metastases in the progression of the disease, the change in thickness (Breslow scale) and the presence of ulcers observed in the primary lesion are assessed.
Due to the fact that melanoma is classified as a malignant neoplasm, some patients experience metastases to other organs. Therefore, during diagnosis and treatment, the surrounding lymph nodes are also checked.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment for this disease usually involves surgery. The doctor excises the affected area and some normal skin around it. But such an operation is possible only in the absence of metastases to distant organs and lymph nodes.
Further monitoring of the patient should be careful not to miss recurrence. The patient should be examined regularly by a doctor.
When the diagnosis does not find malignant cells in the compaction on the skin, but the neoplasm seems dangerous to the doctor in terms of degeneration, removal is prescribed using one of the following methods:
- electrical and thermocoagulation (cauterization with electric current or a heated metal loop);
- chemical or laser destruction (getting rid of skin defects with chemicals or laser);
- cryodestruction (freezing of formations with liquid nitrogen);
- radiosurgical method - non-invasive removal of tumors using waves of 10 Hz and higher.
The same methods are used to treat melanoma at an early stage. Removal using a scalpel or electric knife can be used at stages 1 and 2 of the pathology.
Pigmentless melanoma of the last stage is accompanied by the occurrence of distant metastases in the spine, bones, brain, and lungs. Palliative (auxiliary) operations, chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be used. Chemotherapy drugs are given intravenously or taken in pill form.
An additional method of treatment, biotherapy, can be used in addition to the main method of treatment. In this method, the drugs used help activate the body's internal immune system to get rid of cancer cells.
Radiation therapy alone is not used for melanoma due to its low effectiveness.
Chemotherapy is used in patients with localized types of melanoma, with recurrent cancer in the extremity area, and with the spread of metastases to the brain and bones.
Drug treatment for amelanoma is considered an additional, but not very effective, treatment option. But in combination with surgery, chemotherapy and immunotherapy can reduce the frequency of relapses and prolong the life of patients.
Imidazole-carboxamide is widely used in the chemotherapy of melanoma; Vinblastine, Temozolomide, Vindesine, Decarbazine, Lomustine, Procarbazine, Vincristine and others have less effect.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine methods are often used to treat non-pigmented melanoma, which are used in addition to the basic methods of classical cancer treatment:
- plantain. The juice is squeezed out of its fresh leaves, and the pulp is applied as a compress to the melanoma area;
- Golden mustache. Pre-crushed stems and leaves of the plant can be applied in the form of applications to the affected area;
- Birch bark is considered useful; birch bark contains a strong antitumor substance - betulinol;
- hemlock. The tincture is made by mixing 1 part of the plant and 2 parts of alcohol, after 3 weeks the drug is ready. For use, mix the tincture with water. Start using according to the following scheme: with one drop, increasing to 40, and back, decreasing to 1 drop;
- wrestler (wolf root, aconite) - used in the form of a tincture: 200 g of aconite roots are infused in 0.5 liters of vodka, taken as well as hemlock tincture.
- celandine. Vaseline (4 parts) is added to the fresh juice of the plant and the tumor is lubricated with this ointment;
- ginseng - improves immunity. Drink 25 drops of ginseng root tincture daily for 8 or more days;
- beet juice It is recommended to consume 600 grams of juice, which is left to stand for an hour in advance.
Homeopathic remedies are also used in the treatment of non-pigmented melanoma:
- thuja tincture. 2 times a day it is used to cover the tumor and 2 times a day the tincture is taken orally 20 minutes before meals (10 drops). Contraindications – pregnancy, epilepsy, kidney disease;
- "Radium bromatum" - a radium-based product;
- silica (homeopathic medicine);
- arsenic bromide;
- arsenous potassium. It comes in the form of homeopathic tablets;
- Calendula preparations as an adjuvant.
Don't waste your time searching for inaccurate cancer treatment prices
*Only upon receipt of information about the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate the exact price for treatment.
Principles of therapy
Treatment for amelanoma of the skin is usually done with surgery. The doctor removes the affected area and some healthy skin around it. This intervention is performed quickly and does not require long-term hospitalization. However, such an operation is possible only in the absence of metastases to the lymph nodes and distant organs.
The tumor may spread to nearby lymph nodes. In this case, their surgical removal or radiation therapy is required. Radiation is also used for metastasis to the brain or bones.
Metastasized amelanoma may require treatment with chemotherapy. Drugs in this treatment method are administered intravenously or in tablet form.
Finally, a modern method of additional tumor treatment is biotherapy. These medications activate the body's own immune system to destroy cancer cells. Pembrolizumab, ipilimumab, and drugs that help weaken the cancer cells themselves, such as Trametinib or Vemurafenib, may be used.
Stage 4 non-pigmented melanoma is accompanied by the appearance of distant metastases in the bones, spine, brain, and lungs. For its treatment, palliative (auxiliary) operations, massive chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used.
Disease prevention
There are several recommendations for the prevention of non-pigmented melanoma:
- use sunscreen;
- refuse to visit solariums;
- Wear clothing that covers your arms and legs.
It is recommended to regularly check your body to identify new moles or spots, at least once a month. You should pay attention to the signs when comparing them using the ABCDE test.
What is it and features
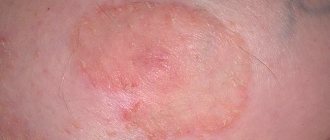
Colorless melanoma develops from melanocytes of the skin and looks like an insect bite, as can be seen in the photo on the Internet. It has a flesh-colored, pink or white color, practically not rising above the surface of the dermis. In some cases, it may have the appearance of a dome-shaped light growth.
A common cause of formation is genetic predisposition and lack of ability to synthesize melanin.
Appears due to solar or ultraviolet radiation. Their excess provokes the active proliferation of pigment cells, which can degenerate into malignant ones. One of the common forms of the disease is apigmentless nevus, which is considered a congenital pathology. This form of melanoma is hidden under it.
There are a number of cases where the source of pathology was hidden under malignant, colorless moles. It is not brightly colored or has clear boundaries, making it difficult to detect. The pathology is diagnosed with a higher frequency in women compared to children and men.
Prognosis of amelanotic melanoma
The prognosis depends on the stage of the disease. At 1, treatment is more often successful, but even here a relapse or the appearance of new lesions in another area of the skin cannot be ruled out. The greater the thickness of the tumor and its depth into the surface of the skin, the worse the prognosis. 5-year survival rate for tumor thickness up to 0.75 mm is close to 100%. If the tumor has a thickness of 0.75 mm - 1.6 mm, survival rate decreases to 85%. With greater thickness, survival rate decreases to 50%.
Neoplasms on the extremities respond better to treatment than those localized on the body, especially in the neck and back of the head, and upper back. The form of education also plays an important role. Nodular amelanotic melanoma carries the worst prognosis.
Danger and possible complications
Melanoma is considered one of the most dangerous neoplasms . It is rarely diagnosed in the early stages. The tumor metastasizes very quickly through the lymphogenous route. Screening lesions can be found in any organ.
The presence of distant metastases means that the disease has entered the fourth stage. The five-year survival rate in this case, even with treatment, according to statistics, does not exceed 20% .
The tumor itself quite treatable . Provided there are no screening lesions , a complete cure can be achieved.
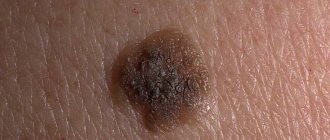
Photo 2. Amelanoma is the most insidious type of skin cancer. It is extremely rare to recognize it in the early stages. Source: Flickr (Stephanie Young Merzel)