The article describes the causes of peeling skin on a child’s arms and legs, provides a list of diseases that are characterized by this symptom, and offers a number of recommendations for caring for dry, flaky skin.
The thickness of a child's skin is less than that of an adult. In addition, children are more active and more exposed and vulnerable to external stimuli. Often the epidermis becomes a reflection of the result of these influences, as well as internal processes occurring in the body.
Rash, redness, peeling and other forms of reaction of the stratum corneum of the skin can be a cause for concern for many parents. Visible changes on a child’s skin can be either symptoms of various diseases, or a signal of a lack of vitamins, an allergic reaction, a peculiarity of the skin of a particular child, etc.
Let us dwell in more detail on such a fairly common phenomenon as dryness, roughness and flaking of the skin on the hands and feet of a child.
The skin of a newborn is peeling between the fingers
Normally, the skin of a healthy person is characterized by integrity, uniformity, the absence of rough or discolored spots, pimples, pustules, etc. However, a newborn baby is an exception. A newborn baby first goes through a period of adaptation to new conditions: temperature conditions, humidity levels, etc. Therefore, the presence of dry patches and excessive peeling of the skin is a completely natural and temporary phenomenon.
You can notice erythema in a child within a few days after birth. Most often, post-term babies experience this. In addition to abundant peeling, usually found between the fingers, behind the ears or on the bend of the limbs, you can notice redness, as well as toxic erythema in the form of yellowish-white pimples. After a few weeks, everything goes away on its own and does not require special measures.
If after a month the skin still peels off, or new symptoms appear, it would be a good idea to seek medical advice.
Skin structure
If the baby’s skin integrity is compromised, namely peeling, then the damage concerns the very top layer of the skin - the epithelium. In general, this body consists of:
- The epidermis, which includes the same epithelium and basement membrane;
- The dermis, which is the skin, is represented by elastic fibers, skin muscles, sweat and skin glands, loops of capillaries and nerve endings;
- Subcutaneous fat, among which nerve fibers and blood vessels are dispersed.
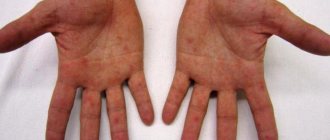
And while the skin is healthy, it is smooth, elastic, elastic. It looks aesthetically pleasing and a person feels comfortable. On the contrary, fingers look very unsightly when they peel. People around you do not always react favorably to such hands, especially since the fingers are always visible, so the defect is constantly striking. And the painful sensations that the child experiences must also be taken into account.
Signs and symptoms of what disease when the skin peels off?
Increased renewal of epidermal cells, externally manifested in the form of peeling, is a symptom of a huge number of diseases. An approximate list of the most common of them:
• Vitamin deficiency is typical for the winter and spring periods, when, due to natural reasons, a deficiency of nutrients may be observed in the child’s body. As a manifestation, the child has peeling skin on his fingers • Allergic manifestations Peeling of the skin can be a sign of atopic and contact dermatitis, chronic eczema and other allergic reactions
•
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract Problems with the pancreas, intestinal dysfunction (dysbiosis) can affect the condition of the skin and lead to excessive peeling • Fungal diseases Caused by parasitic fungi, which often affect the nails, areas between the toes and the sole of the foot. The main sign of the disease is the presence of scales, ulcers and cracks on the skin • Psoriasis A non-infectious disease that manifests itself in the form of red, scaly spots accompanied by itching. Most often, characteristic plaques are localized on the elbows, knees, and scalp
• Presence of worms Roughness and redness of the skin can be one of a number of symptoms of worm infection • Ichthyosis A genetic congenital disease, the signs of which in most cases are visible to the naked eye: excessively dry skin, visually resembling fish scales
• Scarlet fever An infectious disease caused by streptococcus. The patient has a high temperature of up to 39°C and an itchy rash all over the body. After a few days, you may notice extensive peeling, in particular the skin on your palms will peel off greatly.
• Scabies A parasitic disease caused by the scabies mite. Characterized by very severe itching, intensifying in the evening and at night, the presence of scabies, externally manifested in the form of red nodules. Signs of the disease can be found on the buttocks, abdomen, arms, etc. Fingertips may peel off
IMPORTANT: In the case of a serious illness, peeling skin is not the only symptom, so it is difficult to miss it.
Types of skin lesions
Different types of skin lesions that lead to peeling may have characteristic symptoms, among the most common types:
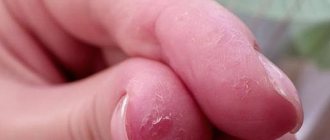
- Membrane form. It will cause problems with the skin between the 4th and 5th fingers. It differs in that peeling is combined with cracking, severe peeling, and a scaly appearance.
- Moccasin-like infection. Discomfort appears on the foot, and as it gets worse, the skin on the foot thickens and cracks.
- Vesicular infection. It will show itself as blisters, they are filled with liquid. The lesion develops on the bottom of the foot, sometimes spreading much more widely.
- Fungus. It occurs in the surface layers. Comfortable conditions for its development are warmth and humidity. Their ideal place is between the fingers. One type of athlete's foot fungus is a contagious disease that is transmitted from person to person. The risk of infection is especially high in public places such as swimming pools. This pathological condition is characterized by: skin cracks between the fingers, itching, peeling, and the development of an inflammatory process.
Child's skin - rough skin, skin rashes in children
In the absence of other symptoms, excessively dry and flaky skin in a child may indicate:
- lack of vitamins
- unfavorable climatic conditions
- allergic dermatitis
- If you begin to observe that your child’s skin becomes dry and rough in winter or early spring, most likely the body is signaling a lack of vitamins A and E. To compensate for the nutritional deficiency, add foods rich in these vitamins to your child’s diet
Products containing vitamins A:
- liver
- caviar
- fish fat
- eggs
- carrot
- apricots, peaches
- plums
- pumpkin
- red pepper
- potato
Products containing vitamins E:
- whole grain
- nuts
- seeds
- spinach
- broccoli
- olive, linseed oil
IMPORTANT: These vitamins are absorbed only with sufficient fat intake into the body. Therefore, ensure that your child consumes the required amount of oil.
- Very often, the cause of peeling skin can be very dry air and insufficient humidity. This is typical for the period when heating devices are operating in houses. If your child’s skin becomes dry and peeling during this period, you should take care to create a favorable microclimate: ventilate the room, use a humidifier, or hang wet towels/sheets in the child’s room to increase humidity.
- In addition, an external factor that can cause peeling of the skin is exposure to cold and wind. In this case, the hands or face are usually affected. To solve the problem, you should use a special baby cream before going for a walk, and also put warm mittens on your child.
- Peeling skin is often a symptom of an allergy. This can be either a food allergy or a reaction to household cosmetics, medications, etc. In this case, peeling is accompanied by such signs as rash, redness, roughness
Other reasons
You should not decide on your own why the skin on your fingers is peeling. The reasons for such symptoms may lie in diseases occurring in the child’s body.
An unpleasant defect can be caused by:
- allergic reactions caused by both external and internal provocateurs;
- fungal infections and various dermatoses;
- viral diseases;
- staphylococcal and streptococcal infection;
- irradiation of the baby;
- pancreatic diseases.
As you can see, a variety of sources can underlie an unpleasant condition. Therefore, only a doctor, having examined the baby, can reliably say what the true reason is.
Rough spots on a child's body
- The appearance of rough patches of skin is a fairly common phenomenon among children in the first three years of life. If you find rough spots with a small reddish rash on your child’s body, most likely you are dealing with atopic dermatitis
- At the same time, in the morning while sleeping, the rash may be invisible and dry, rough skin can only be detected by touch. Spots may appear on different parts of the body, most often on the cheeks, arms or legs. During exacerbations, particularly in winter, the spots become irritated, red and raised
- Atopic dermatitis may be caused by a hereditary immune system that reacts to allergens in food and the environment, as well as a genetic predisposition to dry skin
- Atopic skin needs special care and hydration. In addition, an important role is played by the need to eliminate the allergen, follow a diet and carefully select cosmetics, clothing and everything that comes into contact with the child’s skin.
More information about atopic dermatitis can be found in the article Diet for atopic dermatitis in a child. Modern and traditional treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
Rough or dry skin can also be a consequence of dry air, chlorinated water, abuse of herbal decoctions when bathing, lack of moisture in the body, etc.
Child’s body – white spots, red spots, skin rashes
Possible diseases whose symptoms are white spots:
- Pityriasis versicolor Fungal disease of the epidermis. At the first stages it appears in the form of flaky spots of a pinkish color, and when exposed to sunlight, the spots become more noticeable and acquire a white color. Usually the location is the neck, chest, shoulders, back.
Among the reasons for the occurrence of such unaesthetic spots:
- increased sweating
- hormonal changes (typical for teenagers)
- failure to comply with hygiene rules
This disease is not dangerous. The main thing is to contact a dermatologist in time, who will prescribe the appropriate antifungal ointment.
- Vitiligo is a disease associated with abnormal pigmentation of the skin, resulting in distinct white heels that may peel. Most often, this disease is hereditary. In addition, the disease can develop after an infection, due to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems, and in autoimmune diseases
Red spots appear on the body much more often and in most cases are not symptoms of serious diseases. However, the reasons for the appearance of redness may be:
- allergy
- stress
- insect bites
- infectious diseases (measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever, rubella)
Redness usually does not occur on its own without other symptoms. With the exception of cases when we are talking about temporary redness when a child cries, overheating, or nervous feelings. In other cases, red spots are accompanied by additional symptoms. Most often, this is a rash, itching, peeling, depending on the combination of which one can suspect the presence of a particular disease.
- Rashes in children , especially at an early age, are a common occurrence. For young children, redness combined with a rash may indicate the presence of heat rash, diaper rash or allergies.
- Miliaria and diaper rash are characterized by wet red spots in the folds of the skin, which arise due to excessive overheating of the child, poor hygiene
- If there is redness + rash + peeling, the vast majority are symptoms of an allergy, which the child may outgrow. In older children (after one year), rashes on the body can be the result of infectious diseases, each of which has its own symptoms and requires timely diagnosis by the attending physician
Symptoms of pathology
How to promptly identify an unpleasant condition? Parents should closely monitor the child. In most cases, the first signs of pathology are itching. At the same time, initially the baby rarely scratches his hands. Over time, the itching becomes quite annoying.
The skin becomes hyperemic and inflamed. Small blisters form on the pads. They begin to increase in size. A similar phenomenon is observed on the palms.
As a result of mechanical damage, the epithelium ruptures. The skin on the fingertips peels off in large layers. The reasons for this condition must be identified. After all, only by identifying the source can a treatment plan be outlined.
Sometimes there may be no itching at all. In this case, it is much more difficult to detect pathology in a timely manner. After all, the baby, by and large, is not bothered by anything.
Child’s feet – the skin on the child’s foot is peeling, what should I do?
If you notice that the skin on or between your child's toes is peeling and peeling, the likely causes may be:
- fungus
- allergy
- avitaminosis
- poor quality shoes
For initial diagnosis, you can take the following actions:
- Pay attention to the presence of other symptoms: dryness on other parts of the body, itching, etc.
- check to see if your child's feet are wearing shoes
- ensure proper skin hydration
- adjust your diet
If peeling does not cause discomfort in the child, and there are no other signs indicating a possible disease, then following the above recommendations will help restore the integrity of the skin.
If the problem cannot be solved, you need to contact your pediatrician to find out the cause.
Useful tips
- Watch your baby closely. At the first signs of peeling skin from your child’s fingers, pay attention to the events that led to these changes.
- Remove all household chemicals as far as possible so that your child does not accidentally get their hands dirty.
- Carry out a visual inspection. As a rule, diseases are manifested by several symptoms and complaints of the child. Note the locality of the process on each hand separately and together. Infectious lesions have a generalized distribution on both hands. The effects of temperatures are often reflected on the back of the hands. Contact with a chemical substance manifests itself locally at the points of interaction. Also examine the hands of the rest of the household.
- Apply moisturizer before going outside in winter weather.
- Do not allow your child to scratch the itchy skin, because the child may introduce additional infection into the wound.
- Trim your baby's nails short to prevent them from getting an infection when scratching their skin.
- To prevent your child from scratching the peeling skin, wrap your fingers in bandages.
The skin on the child’s fingers is peeling - drugs, medicine
If a child has dry, flaky skin, increased attention should be paid to its care. An important principle should be moisturizing and nourishing dry areas of the skin, as well as comprehensive treatment of the body from the inside. Among the medications for local treatment, ointments are used:
- Radevit
- bepanten
- diaderm
Apply the ointment 2-3 times a day to dry areas of the skin.
IMPORTANT: Do not use hormonal ointments to treat flaky skin unless prescribed by a doctor.
- For the treatment of atopic dermatitis, various emollients are used (La Roche Posé Lipikar, Avene Trixera, Topicrem, Mustela Stelatopia, Bioderma Atoderm, etc.)
- When diagnosing the allergic nature of skin peeling, antihistamines (fenistil, suprastin, zyrtec) are also used.
- For additional nutrition of the skin, vitamin complexes are prescribed (Aevit, Multitabs)
IMPORTANT: Before using medications, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. In particular, if symptoms other than peeling and dry skin occur, you should definitely contact a pediatrician, who, in turn, after an examination and based on test results, will refer the child to a dermatologist, allergist or other specialist for appropriate treatment.
From the inside, the body should be enriched with food containing omega-3 fatty acids (fatty fish), vitamins A and E, as well as additional fluid.
Feet and toes are peeling, hands are peeling - tips and reviews
- Find out the cause and, if necessary, undergo treatment
- Don't bathe your baby in hot water
- Avoid frequent water treatments (chlorinated water dries out the skin)
- Do not use soap, even baby soap. There are special moisturizing bath products for dry, flaky skin.
- Maintain a sufficient level of humidity in the room (40-60%)
- Do not allow your child to come into contact with wool, synthetics and other non-natural fabrics
- Rinse your baby's clothes and bedding twice
- Moisturize your skin with hypoallergenic creams or lotions (based on coconut oil, sea buckthorn, jojoba oil, etc.)
- Keep your child's diet varied
- Offer your child more fluids
You should not be afraid that the skin may peel and peel. Epithelial cells are renewed every day. In the absence of other symptoms, this does not indicate serious problems, but only requires dietary adjustments and additional care.
ethnoscience
You can resort to old recipes. However, remember that all these measures will eliminate unpleasant symptoms caused by fairly harmless reasons. If the problem lies in illnesses, then only a doctor should prescribe treatment. No home recipes or local treatments can eliminate peeling.
The following folk remedies are very popular:
- Oatmeal decoction. It perfectly eliminates peeling. It is necessary to take daily baths with a decoction of flakes. Such procedures are repeated until the skin is completely healed.
- Linseed oil. This component is an excellent medicine for flaky skin. It is recommended to lubricate damaged areas with oil after hygiene measures.
- Wheat germ extract. Another excellent component that provides skin restoration. They should lubricate the baby's hands daily.
Finally, I would like to remind you once again: if you find a problem on children’s fingers, be sure to start with a visit to the doctor.