Kinds
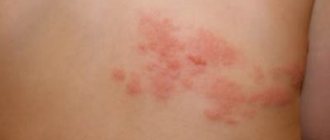
It turns out that rashes come in different natures and types. Primary and secondary rashes are distinguished. This is what a rash happens on a child’s legs and arms:
- The tubercles do not have a cavity, are located deep in the dermis, up to 1 cm in diameter. At the same time, the color and texture of the skin is different. They can leave scars and develop into ulcers.
- Blisters are without a cavity, have blurry outlines and are pink in color. Appear due to swelling of the papillary dermis. They pass without a trace, they itch.
- Papules or nodules - do not have a cavity. They may or may not be inflamed and their color has changed. They pass without leaving traces.
- Bubbles - have a bottom, a tire, a cavity. Once they are opened, erosion can occur.
- Pustules or pustules have pus inside. May be superficial or deep.
- Roseola appears as irregularly shaped pink spots. When the skin is stretched, the stain disappears.
If the rash appears again, then the following may form:
- Scarring.
- Abrasions.
- Cracks.
- Scales.
- Erosion.
- Ulcers.
Diagnostics
If a rash appears on your child’s legs and arms, you should urgently seek help from a pediatrician and dermatologist. First, the doctor should carefully examine:
- View.
- Form.
- Color.
- Quantity.
- The nature of the rash.
- The location of the rash is also important.
Next it turns out:
- Presence or absence of fever.
- What infectious diseases have you suffered?
- What hereditary diseases are there?
- Tendency to allergies.
- Photosensitivity.
As a rule, a rash is not the main disease, but is a symptom of some disease. It is a sign that a malfunction has occurred in the body. To determine the cause of this manifestation, the doctor prescribes tests. First of all, a blood and urine test. It is also possible to analyze the secretion of ulcers. After examination and analysis, the doctor prescribes treatment. What could be the reasons why a child has a rash on his legs and arms?
Prerequisites for the appearance of stains
Why baby’s skin becomes dry and spots appear:
- Hormonal imbalance in the body of a newborn. It leads to the appearance of a reddish rash and roughness of the skin ( the outer covering of the animal's body - organ
) - this is how acne appears in a baby (see also: acne on the face of a baby). As soon as the hormones return to normal, and this traditionally happens by one and a half months, the baby’s skin will again become clean and smooth. - Dry spots in a baby may appear as a result of the negative influence of external causes:
- dry air and lack of water in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- poor water quality or extremely drying bath infusions (chamomile, oak bark);
- roughness occurs under the influence of wind or frost (mainly exposed parts of the face and body suffer);
- very frequent use of shampoo: despite the highest quality of the product, more frequent washing can cause dry scalp;
- when a mother uses powder very actively, she can unnecessarily dry out the delicate, narrow skin of the baby’s bottom.
The reason may lie in genetic pathology. Such hereditary manifestations of roughness make themselves felt at 2-3 years of age, traditionally no later than 6 years:
- Ichthyosis. The cells become horny as a result of mutations at the gene level: over-dried skin eventually becomes covered with snow-white or grayish scales, as a result the whole body becomes covered with “fish scales”. In addition to skin dilemmas, internal ones are also added: malfunctions of organs, metabolic disorders. Photos of snow-white scales can be found on the Internet.
- Hyperkeratosis. The epidermis thickens extremely, the skin becomes horny. Most often, these anomalies are recorded on the hips, feet, elbows and head. What is the reason ( Reason, pretext for some action. For example: Good reason; Laugh without reason; Because..., for the reason that..., because
) given to the disease? Scientists cannot yet give a specific answer. In addition to hereditary disposition, other reasons are also important: lack of vitamins E, C and A, dry skin, the consequences of taking hormonal drugs, stressful situations, hormonal imbalance during teenage puberty, very long-term exposure to ultraviolet rays, gastrointestinal diseases, the result of the action of drugs for cleaning, washing, washing. - Helminthiases.
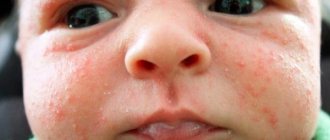
- Atopic or exudative dermatitis. It is he who, in most cases, is the culprit of bright pink and rough cheeks and butts. The appearance of rough snow-white or burgundy spots above the lip and on other parts of the body is his “hands”. The root cause of this disease is allergic reactions.
Sources of the problem
For a child’s body, a rash is a very important symptom of certain diseases, so consulting a doctor is important. The reasons for this may be the following:
- Allergic diseases.
- Infectious.
- Parasitic infections.
- Vascular and blood diseases.
- Violations of hygiene rules.
If the rash accompanies an infectious disease, the body temperature will certainly increase. There are other signs, these could be:
- Cough.
- Rhinitis.
- A sore throat.
Let's look at some diseases that are accompanied, in addition to a rash, also by fever.
Rash with fever
When an infection enters the body, its first reaction is fever. Skin rashes can appear with or without fever. There are several infectious diseases, the symptom of which is a rash.
This group includes:
- Chicken pox.
- Rubella.
- Scarlet fever.
- Measles.
- Enterovirus infection.
- Meningococcemia.
Each disease has its own characteristics of the spread of rashes.
This is especially true for childhood diseases. Let's look at which of them cause a rash on the child's legs and arms, as well as on the body and face.
Infections that cause red spots on the skin
If red spots on the skin are due to a viral, fungal or bacterial infection, then the person may pose a threat to others. This is especially true in cases where the lesions are localized in the groin area. Here it is necessary to exclude epidurmophytosis in the groin, candidiasis of large folds and rubromycosis, which are transmitted through close bodily contact and through personal hygiene items. Men aged 25-55 years are most often affected. People who are obese are at risk. The main symptoms are large spots in the groin and on the inside of the thighs, which merge into one large lesion over the course of the process. Color - red-brown, less often pink. Rashes and peeling are almost always present on the surface.
Measles
This childhood viral disease has recently become increasingly common due to neglect of vaccination. It all starts with fever, runny nose, cough, conjunctivitis and headache. After 2–3 days, pink-red spots appear behind the ears and on the head. They merge with each other and gradually descend lower along the body to the very lower extremities. Complications are especially dangerous for a child, from which 3% of patients died before the introduction of mandatory vaccinations.
Scarlet fever
The culprit is the bacterium streptococcus. A person suddenly develops a fever and a severe sore throat. Having penetrated the body, the pathogen releases a toxin, which provokes the appearance of a rash. The red skin of the entire body is covered with small red dots, and against the background of hyperemia, a white nasolabial triangle on the face is clearly visible.
Erysipelas
It also occurs due to infection with streptococci. It begins acutely with fever, headaches, nausea and vomiting. Local symptoms occur within 12–14 hours. This is itching and swelling of the skin, pain, erythema. The red spots have smooth, clear boundaries and resemble flames or geographic outlines.
Rubella
The symptoms are similar to measles, but it is much milder. Infection is dangerous for a woman in the first trimester of pregnancy, as the virus penetrates the lymphatic system and tissues of the embryo. The risk of serious intrauterine fetal damage and miscarriage is especially high before 14 weeks.
Ringworm
The fungus is transmitted not only from sick people, but also from animals. Red ring-shaped spots all over the body itch, often affecting the feet and nails, scalp and lead to baldness. It is particularly contagious, so it is treated under quarantine conditions. It is recommended to change and boil the patient's linen and belongings daily.
Shingles
The causative agent of the infection is the varicella zoster virus, which is also the culprit of chickenpox. Red, swollen spots throughout the body are localized on the torso, accompanied by itching, pain, and covered with papules and watery blisters with liquid contents. After recovery, the patient continues to feel neuralgic pain for a long time.
Pink lichen of Zhiber
Red round spots on the body are found mainly in young people aged 20–35 years. Weakness often occurs, body temperature rises slightly, and lymph nodes enlarge. Most doctors say that Zhiber's lichen does not require treatment and goes away on its own. As a preventive measure, hypothermia and a sharp drop in immunity should be avoided.
Lyme disease
The carriers of the bacterial disease are ticks. After a bite, fatigue, weakness, and discomfort in the neck muscles appear. At the site of suction, a red papule appears, and then a round or oval annular erythema slightly raised above the surface. In some cases, the bite size can reach the diameter of a small saucer. In some cases, the stain after a tick bite can last for several months.
Sudden exanthema
Roseola is a childhood disease that affects all children under 2 years of age. It is often ignored or confused with allergies. The main symptom is an acute increase in temperature without any other symptoms. On the third day of illness, the temperature subsides, and the child’s entire body and face becomes covered with a pink-red spotty rash. The appearance of rashes means that the child is no longer contagious. The infection is mild and requires only symptomatic treatment.
When nothing bothers a person except red spots, then it is worth checking for the presence of parasites in the body. Worm infestations and Giardia can cause a similar reaction on the skin.
Chickenpox
This disease occurs most often in children. There are no vaccinations for it. The first sign of this disease is the appearance of red spots, which very quickly turn into blisters. In addition to blisters on the face, head, and body, the child also has a rash on the legs and arms. The temperature is elevated, and the baby may experience weakness and headache for some time.
If the blister is torn off, scars remain. The main problem of this disease is that the rash on the child’s arms and legs itches, and there is a risk of infection. The doctor may prescribe medications to relieve itching.
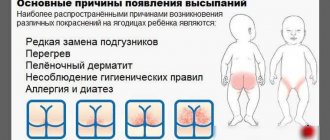
Diathesis (exudative and allergic) in a baby
In newborns and infants, flaky skin areas on the face, abdomen, butt, back, arms and legs often occur due to diathesis. Contrary to the widespread erroneous worldview, this phenomenon does not apply to diseases. This is nothing less than a constitutional anomaly. In pediatrics, this term implies the hereditary disposition of an organism (a living body that has a set of properties that distinguish it from inanimate matter, including metabolism, self-sustaining of its structure and organization, the ability to reproduce them when
) to the occurrence of certain pathological reactions or diseases. The table shows the characteristics of the types of the given phenomenon.
| Type of diathesis | Prerequisites for the appearance | Symptoms |
| Exudative |
| At first, spots appear on the head in the form of seborrheic scales - gneiss. After this, diaper rash begins to appear on the body, which is extremely difficult to heal. Then reddish spots with a rough surface form on the baby’s cheeks. |
| Allergic |
| Flaky red areas of skin appear on the baby's face (on the cheeks, above the lip, on the forehead), arms, legs, tummy, back, butt. |
Rubella
This disease occurs with elevated temperature. In older children, joint pain and general intoxication are possible. Rashes appear on the 1st day or on the second day. First - on the face, neck, torso, then a small rash spreads on the child’s arms and legs, mainly on the folds. The younger the child, the milder this disease occurs.
However, in adolescents, complications such as encephalitis and meningoencephalitis are possible. This disease is especially dangerous for pregnant women; fetal developmental defects are possible. Vaccination is also prohibited for immunocompromised patients. However, rubella is milder than scarlet fever.
Measles
A dangerous infectious disease that is easily transmitted through the air with minor contact with a carrier of the infection.
There is a vaccine against measles. This disease is accompanied by intoxication of the body. Symptoms characteristic of a cold are present - coughing, watery eyes, sneezing. The temperature rises to high values. The rash begins from the mucous membrane of the cheeks, then moves to the face, the entire torso, and limbs (in the form of papules rising above the skin). Dangerous complications on the bronchi, can cause pneumonia.
Enterovirus infection
Preschool children are susceptible to these diseases. A rash appears on the child’s legs and arms without fever. It usually doesn't itch.
The child may be healthy or there may be a slight increase in temperature within one or two days. This occurs due to imperfections and sensitivity of children's skin.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis
This disease is characterized by a rash on the child’s arms and legs with fever, mainly in the area of the folds. At first, small blisters or lumps appear, then the rash turns red, acquires the color of rust, and disappears completely. It is believed that the disease can be caused by allergies, trauma, or be a consequence of acute infectious diseases such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis. Accompanied by fever and joint pain. With the lightning-fast course of this disease, death is possible. It is necessary to pay careful attention to treatment.
Non-infectious rash with itching
There are a number of diseases in which the rashes are very itchy. For example, with scabies, a rash appears on a child’s legs and arms without fever, most often on the folds between the fingers. As a rule, it itches a lot, especially at night. Also, with helminthiasis, the rashes itch.
The presence of fungus on the skin of children is one of the causes of rashes in the form of blisters, erosions, and red spots. The localization of the fungus is usually on the legs, palms, feet, and wrists. The rash spreads especially quickly on moist areas of the skin. Can be easily transmitted through contact with a contaminated object. Infections occur especially often in places where there is a damp environment (shower, bathroom). The disease is accompanied by severe itching without fever.
Methods for treating a rash on a child’s body
Without harming the baby's health, you can use the following ointments:
- Elidel - indicated for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, can be applied to any area of the skin. Price: 965 rubles (15 g).
- Bepanten - improves tissue regeneration and accelerates the healing process of wounds. Price: 750 rubles (100 g).
- Fenistil gel has an antipruritic effect and is used for urticaria and insect bites. Price: 470 rubles (50 g).
- Gistan - contains extracts of lily of the valley, violet and string, used for eczema and other skin diseases. Price: 165 rubles (30 ml).
If none of the ointments has the desired effect and the child does not feel better, you should consult a doctor - a pediatrician or dermatologist. It is possible that treatment will require hormonal medications or physical therapy. One way or another, you first need to find out the reason and only then select the appropriate means.
Small rash without itching
If a small rash appears on the child’s arms and legs and does not itch, pseudotuberculosis may be at the initial stage of development. This disease is transmitted by rodents - after contact with things to which they had access. This disease appears very rarely in children, but it still exists.
If a child was born with congenital syphilis or was infected in utero, the rash may appear from time to time without bothering him. These are papules with a pustular core. Such rashes are not accompanied by itching and fever.
Also, a small rash can be the result of a hereditary infectious disease such as psoriasis. In children under 2 years of age it is rare, but at an older age the risk of development, due to heredity, is quite possible. It begins with a small rash in the form of dry plaques of round and oval shape, red-pink in color, with noticeable peeling on top. It spreads over large areas of the skin, in the area of the knees, elbows, and head - this is a characteristic sign of psoriasis. This rash does not itch. In infants it can appear and go away, and in adulthood it can return again.
Causes of pathology
Very often, all sorts of skin problems appear on the hands in the elbow area.
It may have:
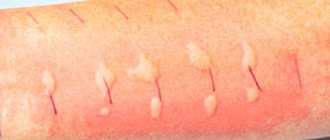
- red spots (see photo)
- peeling, cracks;
- blisters, pimples;
- sores, rashes;
- rash.
They are localized both on the inside and outside, on the bends of the elbow joint.
There are many reasons for this pathology, for example:
- heredity;
- injury, infection;
- allergies, psoriasis;
- lichen, fungus;
- avitaminosis;
- errors in hygiene.
There are a number of diseases characterized by pathology on the elbows:
- atopic dermatitis;
- granuloma annulare;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- mycosis.
Signs of these diseases will be spots of different sizes and colors or a rash on the elbows in both adults and children, causing itching of varying intensity.
Mycosis is distinguished by the presence of oval spots, first pink, then turning into scaly white ones. Appears on the inside of the elbows and knees, where sweat is produced most. A small rash covering the spots causes itching. More often it affects people suffering from diabetes and HIV-infected people.
Redness of the skin on the elbows, covered with gray scales that grow into rough, flaky crusts, is observed in psoriasis. Occurs with autoimmune disorders in the body.
Photos of various rashes on the elbows:
Eczema appears as small, fluid-filled blisters on the inside of the elbows and knees.
With a deficiency of vitamins, especially groups B, A and E, skin redness appears on the elbows, flaking and turning into dark spots.
A characteristic rash appears on the elbows with granuloma annulare.
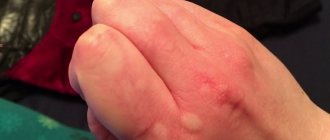
Atopic dermatitis causes a particular nuisance, accompanied by severe itching (see photo). It begins with hives as a reaction of the body to an allergen. The rash is most often localized on the outside of the elbows or knees in both adults and children.
They are pimples filled with fluid. They may bleed when scratched.
The delicate, thin skin of the elbows is more susceptible to allergic rashes. Allergies are caused by both direct contact with the allergen and the body’s general reaction to it.
Direct contacts include exposure to any chemicals:
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Sustalife to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- oils, gasoline;
- detergents;
- household chemicals;
- dyes;
- cosmetics.
The general reaction of the body is caused by certain allergens contained:
- in food products;
- clothes;
- dust;
- medicines;
- toxins from insect bites.
Allergic reaction
With allergic dermatitis, in addition to rashes on the face and torso, the child may have a rash on the legs and arms. The photos clearly demonstrate the manifestation of an allergic reaction. Rashes can be present either on a small area of skin or on a large one. As a rule, accompanying symptoms are peeling and severe itching. The body temperature remains within normal limits, and no intoxication of the body occurs. This reaction is possible to food, household chemicals, and medications.
If a child has allergies, you need to be extremely careful with allergens and exclude them from the diet if possible, as there is a risk of angioedema. Possible respiratory arrest and laryngeal swelling.
Hives - a small rash - can be a reaction to temperature factors, cold, or sun.
Prerequisites for the appearance of stains
Why baby’s skin becomes dry and spots appear:
- Hormonal imbalance in the body of a newborn. It leads to a reddish rash and rough skin - this is how acne appears in a baby (see also: acne on the face of a baby). As soon as the hormones return to normal, and this traditionally happens by one and a half months, the baby’s skin will again become clean and smooth.
- Dry spots in a baby may appear as a result of the negative influence of external causes: dry air and lack of water in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- poor water quality or extremely drying bath infusions (chamomile, oak bark);
- roughness occurs under the influence of wind or frost (mainly exposed parts of the face and body suffer);
- very frequent use of shampoo: despite the highest quality of the product, more frequent washing can cause dry scalp;
- when a mother uses powder very actively, she can unnecessarily dry out the delicate, narrow skin of the baby’s bottom.
).
The reason may lie in genetic pathology. Such hereditary manifestations of roughness make themselves felt at 2-3 years of age, traditionally no later than 6 years:
- Ichthyosis. The cells become horny as a result of mutations at the gene level: over-dried skin eventually becomes covered with snow-white or grayish scales, as a result the whole body becomes covered with “fish scales”. In addition to skin dilemmas, internal ones are also added: malfunctions of organs, metabolic disorders. Photos of snow-white scales can be found on the Internet.
- Hyperkeratosis. The epidermis thickens extremely, the skin becomes horny. Most often, these anomalies are recorded on the hips, feet, elbows and head. What is the reason for the illness? Scientists cannot yet give a specific answer. In addition to hereditary disposition, other reasons are also important: lack of vitamins E, C and A, dry skin, the consequences of taking hormonal drugs, stressful situations, hormonal imbalance during teenage puberty, a very long-term action (an act of activity, an ambiguous word that can mean : Group action (in mathematics) Action (physics) Actions (acts) - parts into which the drama is divided
) of ultraviolet rays, gastrointestinal diseases, the result of the action of cleaning products, washing, washing. - Helminthiases.
- Atopic or exudative dermatitis. It is he who, in most cases, is the culprit of bright pink and rough cheeks and butts. The appearance of rough snow-white or burgundy spots above the lip and on other parts of the body ( a polysemantic word that can mean
) is his “handiwork.” The root cause of this disease is allergic reactions.
What not to do if a rash is detected in a child
First of all, it is strictly prohibited in situations where you see rashes on your baby’s body:
- Squeeze out pustules.
- Pop bubbles.
- Treat with brilliant green or other means until examined by a doctor.
- Self-medicate.
If the rash on your child's arms and legs itches, do not let him scratch it.
If a rash is detected, you should limit contact with others, as the disease may be contagious.
As we saw earlier, a rash can be an important symptom or result of a disease. An examination by a doctor is required to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment to eliminate possible complications.
How to help with food allergies
The most difficult ones to identify are rashes caused by an allergic reaction. Depending on the type of irritant (food, contact, medication, household, etc.), marks on the baby’s skin can take on all sorts of forms and change location. How to identify the disease?
Allergies are one of the most common reasons why a 1-year-old or younger child may develop a rash. That is why, when it comes to a newborn, this diagnosis should be suspected first. To confirm or refute their fears about the baby’s possible allergies, his parents will have to answer the following questions:
- Does your child have other symptoms of intolerance (swelling, difficulty breathing and itchy skin)? The last sign is the most important. Regardless of the type, allergy rashes usually itch.
- Can the possibility of infection be ruled out? Most of these diseases also have other characteristic symptoms (fever, loss of appetite, fatigue, apathy). If a child does not have any of the listed signs of infection, the likelihood that he is faced with an allergy increases.
- What risk factors has your baby encountered recently? Have new foods been introduced into his diet? Were any unusual medications prescribed? Has the usual environment changed? Could a new, previously unknown stimulus appear in the child’s life?
It will make it easier to diagnose the problem and know exactly what forms the disease can take in a child. As a rule, childhood allergies occur in one of 2 scenarios:
- Hives. The rash takes the form of blisters, the color of which can vary from pale pink to bright red. The visual effect is similar to what happens after a nettle burn, hence the name of the disease. Among the characteristic symptoms of the disease are swelling and severe itching of the skin. The rash with hives goes away suddenly, just as it appears.
- Atopic dermatitis. Alternative names: childhood eczema, diathesis, neurodermatitis. With this type of allergy, the rash on the child’s body is clearly localized. Most often, marks appear on the elbows, neck and head (both on the face and under the hair), a little less often - on the legs, under the knees. Side symptoms are redness and peeling of the skin. Sometimes characteristic weeping crusts form on top of the rash.
If this is an acute situation and the child suddenly breaks out, then contacting a doctor is mandatory. It is unknown how the situation will develop further and urgent measures are needed. At the appointment, the pediatrician or allergist will be interested in what the child eats and how he sleeps. The next stage is analyzes and samples. Diagnosis sometimes takes several weeks. And only after that the doctor will make a diagnosis: allergies or food poisoning.
Most often, food allergies in children are caused by an allergen contained in cow's milk. Cow's milk should not be given to children under one year of age. Only breast milk or formula. If the diagnosis is made immediately, proper nutrition is prescribed, and allergens are removed, then the consequences of the rash do not remain. Unlike contact dermatitis, it is not recommended to treat food allergies with antihistamines alone. The first thing you need to do is do an elimination diet.
To prevent allergies in a child, you need to establish proper nutrition from a very early age:
- limit sugar, chocolate;
- Give tangerines and oranges a few slices each;
- instead of sweet juices, dried fruit compote.
Treatment for elbow rash depends on the cause of its occurrence. After consultation and diagnosis, you need to start treatment. If an allergic rash on the elbows does not further spread to other areas of the skin, it most likely does not pose a big threat. But you must always approach its treatment carefully, in the part when antihistamines and lotions are used.
Therapy
Treatment of rashes is, first of all, elimination of the disease that caused them. For infectious diseases, it is recommended to adhere to bed rest, take antipyretics, antihistamines, and treat rashes. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed (to avoid the development of side effects).
Allergy sufferers should definitely see an allergist. It is necessary to exclude allergens from your diet. You should also follow your doctor’s instructions and take antihistamines or glucocorticosteroids. In case of fungal diseases or scabies, observation by a dermatologist is necessary.