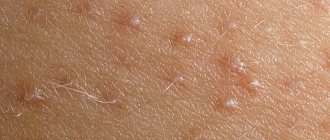
What kind of disease is this
Eczema is a common dermatological disease, which, according to statistics, affects approximately 10% of the world's population. This is a chronic disease that manifests itself in the form of skin rashes of various types, which constantly become wet during the development of eczema. In turn, such symptoms cause not only physical, but also psychological discomfort to the patient.
Causes
Doctors have not yet been able to determine the exact cause of the development of eczema, but there are certain factors that contribute to this. The most common ones include:
- food poisoning of the body;
- negative impact of airborne allergens;
- consequences of taking certain medications;
- food intolerance;
- previous infectious diseases;
- weakening of the immune system;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the nervous or endocrine system.
Causes of eczema
Note! Anyone can experience the unpleasant symptoms of eczema, regardless of gender or age. But most often the skin disease is diagnosed in young people, and with age the number of exacerbations gradually decreases.
Kinds
Doctors distinguish several types of eczema, namely:
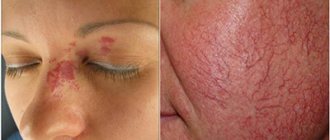
- true. It is the result of an allergic reaction to an external irritant (cosmetics, citrus fruits, animal hair, dust, etc.). Appears in the form of small blisters on the face or limbs;
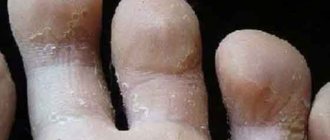
- dyshidrotic. Accompanied by severe burning and itching in the affected area. Typically, the most commonly affected areas of dyshidrotic eczema are the fingers, toes, feet, and palms;
- professional. It is diagnosed in people whose work requires regular contact with different types of allergens (chemists, miners, builders and others). The peculiarity of occupational eczema is that the disease can manifest itself on any part of the skin;
- microbial Develops against the background of infection with staphylococci and streptococci. Often, pathology occurs at the site of wounds or minor scratches;
- mycotic. The main factor that provokes the development of this type of eczema is a fungus. The disease manifests itself mainly on the toes or nails;
- seborrheic. Occurs when the sebaceous glands malfunction. Most often it affects the scalp, knees, shoulder blades or forehead. Seborrheic eczema appears in the form of yellow plaques that form various “patterns”.
Main types of eczema
Problems with the functioning of the sebaceous glands can also manifest themselves in the form of ordinary dandruff. Therefore, if you are faced with this cosmetic defect, be sure to get examined by a doctor.
Symptoms
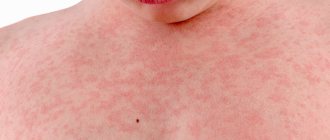
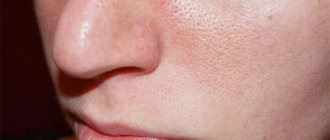
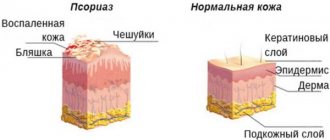
Depending on the type of pathology developing, clinical signs may vary. But there are basic symptoms that appear in all types of eczema. First of all, such symptoms include rash, itching, burning of the skin, general weakness of the body and neuroses. Many symptoms of eczema are similar to those of other diseases, such as pyoderma or psoriasis, so it is important to distinguish them when diagnosing.
Characteristic symptoms of eczema
Contraindications to the technique
A natural preparation must be approved by a doctor. Folk remedies may have contraindications for use:
- allergic reaction to a component in the composition;
- lactation (breastfeeding should be stopped);
- pregnancy - for taking medications orally.
Eczema is a capricious disease that requires complex action from the outside and inside.
Coin-shaped inflamed skin can be quickly treated. Venous blood flow accelerates and carries beneficial substances. Natural therapies do not always cure rashes. The patient needs rest and diet - important conditions for recovery and transition into remission. The article has been verified by the editors
Possible complications
Incorrect or untimely treatment can lead to the skin disease becoming chronic, which is accompanied by frequent relapses. Thickening of the epidermis may occur on the patient's skin and infiltrates may form. Often, in advanced stages of eczema, the skin pattern intensifies, but at the same time its elasticity decreases.
Kaposi's eczema is one of the possible complications of eczema
As a complication of a skin disease, there may be an inflammatory process that affects the surface of the palms or feet, a purulent infection, which causes problems with the lymph nodes. But the most dangerous complications of eczema include neurodermatitis - a chronic skin disease that is of a neuro-allergic nature. The disease is accompanied by insomnia, constant itching and disruption of the central nervous system. An incorrectly formulated therapeutic course can provoke the appearance of neurosis of the skin with frequent inflammatory processes.
How to treat at home
Eczema is one of the types of allergic inflammations of the skin. There are two types of this rash:
- Dry eczema is a red or pink patch with a scaly surface.
- Weeping eczema is an itchy, sometimes blistering inflammation that becomes covered with a crust that peels off and often sticks to clothing. Ichure flows from the resulting wound.
This inflammation occurs for various reasons:
- Allergy.
- Chemical burn.
- Infection.
- Worms.
For any of the reasons, treatment is required, otherwise the inflammation can become infected with various fungi, and then blood poisoning is not far away.
Features of eczema treatment
Drug therapy for eczema involves the use of local medications and medications taken orally. Local or external preparations are ointments or creams that have antibacterial, antipruritic and regenerating properties. If the disease is accompanied by a fungal infection, doctors may prescribe additional antifungal drugs. The most common ointments prescribed for eczema include Hydrocortisone ointment, Soderm, Salicylic ointment, Eplan and others.
Non-hormonal ointments and creams for eczema
Medicines for internal use include antihistamines (Zodak, Cetriliv, Loratadine and Suprastin), vitamin complexes and destabilizing agents. Throughout the entire treatment course, the patient must follow a special diet, which consists of avoiding the use of extractive products and limiting the amount of fried and fatty foods.
Folk remedies for the treatment of eczema
Not all people trust traditional methods of treatment, so traditional medicine is often used for eczema, which is in no way inferior in effectiveness to synthetic drugs. Some people use folk remedies only as a complement to drug treatment, while others, on the contrary, instead of traditional therapy. In any case, before using this or that product, even if it consists exclusively of natural ingredients, you must consult with your doctor.
Diet for eczema
Completely excluded:
- spicy dishes;
- smoked dishes;
- alcohol;
- canned foods, pickles;
- coffee;
- corn;
The use is limited as much as possible:
- table salt;
- citrus fruits;
- sweets and bakery products;
- tea;
For eczema, a predominantly dairy-vegetable diet is prescribed. It is best to steam or boil food.
During exacerbations, it is best to use:
- porridge (buckwheat, oatmeal with water);
- fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk);
- non-spicy vegetable soups, soups with weak meat broth;
Universal traditional medicine
Depending on the type of eczema, the products used may vary. But there are universal recipes that are equally effective for all types of skin diseases. Below are the main ones.
Table. Traditional medicine recipes for eczema.
| Product name | Application |
| Cucumber pickle | Soak a cotton swab or gauze bandage in natural cucumber brine and make lotions. Apply this compress to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day. |
| Grape | Pass 100 g of grapes through a meat grinder (use only dark varieties) and, placing the resulting pulp in gauze, apply it to the sore spot for 1 hour. Perform the procedure every day for 3 weeks. |
| Birch tar | It has excellent wound-healing properties, due to which tar eliminates itching and flaking of the skin. For eczema, it is necessary to regularly treat the affected areas of the skin with birch tar. 10-15 minutes after application, the product should be washed off with warm water. |
| Potato | You can also cope with skin damage using regular potatoes, or rather, applications made from them. To do this, soak a gauze pad in grated potatoes and apply to the affected area. The procedure must be performed daily for 10 days. |
| Saline solution | Pour 2 liters of warm water 3 tbsp. l. salt and mix the ingredients thoroughly. Then place the area of the body with the affected skin in the prepared solution for 15 minutes. In the first minutes there may be a slight tingling sensation, but it will soon go away. |
On a note! You can also cope with the signs of the disease using herbal infusions or decoctions. Chamomile and calendula are considered the most effective medicinal plants - they have an antimicrobial and antiseptic effect on the body. You can use decoctions as lotions or medicinal baths every day without fear of negative consequences.
Essential oils
Treatment of eczema with oils has long been used in folk medicine.
- Sea buckthorn oil has antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effects. It is often used for allergic eczema in young children.
- Flaxseed oil - moisturizes the skin well and eliminates irritation. It is very effective for dry eczema.
- Chamomile oil has an antibacterial effect and is used for infectious rashes.
- Lavender oil – used for dry eczema. It moisturizes the skin, relieves itching and inflammation.
But not only external influences will help cope with the disease. When the cause is inside, you should pay attention to immunity.
Treatment of eczema depending on the type
As noted earlier, there are several types of eczema, which differ from each other in clinical signs and treatment features. Therefore, when diagnosing a particular type of disease, the traditional medicine used may differ.
Dyshidrotic eczema
With the development of dyshidrosis, serous blisters appear on the affected areas of the skin, which eventually turn into erosions. Throughout the entire period, the patient experiences severe itching, and the skin thickens and begins to peel off.
What does dyshidrotic eczema look like?
The most effective traditional medicine recipes used for dyshidrotic eczema include:
- compress of grated potatoes. Grate several fresh potatoes on a fine grater and apply the resulting pulp to the sore spot for 10 minutes;
- cabbage leaf Apply a cool cabbage leaf to the affected skin and secure it with a gauze bandage;
- sea buckthorn oil. Apply the oil to the skin in a thin layer, and after 15-20 minutes, rinse with warm water. It is recommended to repeat the procedure 3 times a day.
On a note! When diagnosing dyshidrosis, doctors often prescribe sanatorium treatment by the sea. This is due to the beneficial effects of salty sea water and the sun on eczematous wounds. In such conditions, the skin heals much faster.
Microbial eczema
Local treatment of the microbial form consists of relieving the inflammatory process and healing erosive areas of the skin. For this purpose, the following means are used:
- honey with garlic. Boil a few cloves of garlic and, after mashing it until mushy, mix with 1 tbsp. l. honey Apply the finished product to the affected areas of the skin and cover with plastic wrap. It is advisable to carry out the procedure at night;
- tar ointment. Mix 3 tbsp in one bowl. l. fish oil, 2 tbsp. l. birch tar and 1 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar. Soak gauze in the prepared solution and apply it to the affected skin;
- aloe pulp. Cut an aloe leaf in half and apply the inside of it to the inflamed skin for 10 minutes. Secure the plant with a bandage or gauze bandage.
Microbial eczema
To achieve maximum therapeutic effect, experts recommend alternating medications. For example, for the first few days you can use tar ointment, and then garlic paste with honey.
Weeping eczema
Therapy for weeping eczema should be aimed at drying the skin, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and healing wounds. The following recipes are used for this:
- Kalanchoe. Peel the leaves of the plant from the film and pass them through a juicer. Soak a piece of gauze in the resulting juice and apply it to the inflamed skin;
- liquorice root. Grind 50 g of plant root and mix with the same amount of sea salt. Sprinkle the prepared powder onto the affected skin and rinse off after 30 minutes with warm water;
- medicinal baths. Place hands or feet affected by skin disease in warm water with added salt. As soon as the water has cooled, the procedure can be completed.
Folk remedies for weeping eczema
In most cases, positive changes will be noticeable after the first session. Of course, this is only possible if the technology for preparing folk remedies is followed.
Dry eczema
Traditional therapy for this type of eczema is based on moisturizing the skin and improving its nutrition with useful components. For this purpose, the following means are used:
- sea buckthorn oil. Mix freshly squeezed sea buckthorn juice with the same amount of olive oil and leave the product for 7 days in a cool place. Then treat the affected areas of the body with the prepared oil daily;
- carrot ointment. Grate 1-2 large carrots on a fine grater and mix it all with 50 ml of cream. Gently apply the prepared ointment to the affected skin 2-3 times a day. The duration of the therapeutic course is 20 days.
Treatment of dry eczema
You can also cope with the signs of the dry form with the help of aloe leaves. To do this, the plant is cut and applied to the sore spot. Alternatively, aloe can be crushed and mixed with a little honey.
What medications are used to treat eczema?
With pronounced secretion of ichor:
- boric acid solution,
- amidopyrine solution,
- silver nitrate solution,
- polcortolon,
- oxycort.
In subacute cases, glucocorticosteroid ointments:
- diprosalik,
- celestoderm,
- ultralan,
- flucinar,
- dermovate,
- sinaflan,
- fluorocort.
For microbial, paratraumatic eczema:
- fucorcin.
For local chronic lichenified eczema:
- corticosteroid ointments diprosalik,
- lorinden-A,
- sinalar,
For disseminated eczema, general therapy is indicated:
- antihistamines (astemizole, fenkarol, fenistil, terfenadine, diprazine, tavegil, peritol),
- sedatives (diazepam, gidazepam, relanium, teralen, elenium),
In particularly resistant and common cases:
- diprospan, flosteron, kenalog-40, depomedrol - tablet forms with a dose of prednisolone (30-60 mg per day) with a gradual dose reduction
Treatment of eczema in children
Many factors can trigger the appearance of eczema in children, for example, an allergic reaction of the body or genetic predisposition. A weakened immune system is also unable to resist pathology, which is why skin rashes become chronic.
According to statistics, children most often encounter the disease in the first few years of their life. This is due to the weak resistance of children's skin to various allergens contained in personal care products or creams. The use of traditional methods of treating eczema in children has a positive effect on the condition of the skin.
Herbal baths for eczema
Therapeutic ointments or baths with herbal decoctions will help eliminate itching and flaking, returning the child to a full life without discomfort. The peculiarity of traditional therapy is that it is highly effective and rarely causes an allergic reaction. But before using folk remedies, regardless of their composition, you should definitely consult with your pediatrician.
Eczema during pregnancy
During pregnancy, eczema increases the risk that your baby will have similar problems. Therefore, the disease cannot be neglected, and it is better to undergo treatment under medical supervision. You can use hormonal ointments, which are safe during pregnancy, and other medications prescribed by the doctor. Thymogen cream is very effective and absolutely safe during pregnancy, which gives excellent results. Walking, lack of stress, good nutrition - all this helps to heal the pregnant woman and reduce the risk to the fetus.
Additional recommendations
Many doctors argue that when treating eczema, it is necessary not to eliminate eczematous foci, but to treat the entire body completely. Since the disease can be triggered by a large number of factors, for example, internal diseases, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, before starting treatment it is necessary to identify the main cause of development. Only after this the patient is prescribed an appropriate course of therapy, which is aimed at a specific cause.
How to cure eczema with folk remedies
On a note! For eczema, complex therapy should always be used, consisting not only of traditional medicine, but also traditional medicines. This is the only way to get rid of this unpleasant disease forever.
Diagnosis of the disease
A professional examination is necessary to prescribe the correct treatment for eczema. When diagnosing, doctors at the Paramita clinic use the following methods:
- patient interview and visual examination;
- histological studies - studying a sample of inflamed tissue;
- blood analysis.
Our doctor’s task is not only to make a diagnosis, but also to determine the factors that caused the disease. This may require additional tests, the effectiveness of which has been verified in practice.
Prevention measures
In order not to encounter eczema and other skin diseases in the future, experts recommend giving up bad habits, in particular smoking, not abusing alcohol, regularly strengthening your body and playing sports. When using cosmetics, preference should be given to products that contain a minimum amount of chemical elements and preservatives.
Try to avoid contact with household chemicals. To do this, be sure to use personal protective equipment when washing your car or cleaning your home. Such equipment includes a protective mask and rubber gloves.
Prevention of eczema
Eczema is an unpleasant pathology that can significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life, so it is important to follow medical recommendations to prevent this disease. A timely visit to a specialist when the first suspicious symptoms appear is also important.
Risk factors for eczema, causes and symptoms
In fact, there is a wide range of causes and risk factors associated with eczema. And eczema symptoms can be widespread. While a single cause of eczema has not been identified, there are certain common causes that lead to occurrences and outbreaks. In addition, a wide range of risk factors have been identified.
Risk factors for eczema
- Genetic predisposition or family history of eczema, hay fever or asthma
- Young age
- Working in a medical facility
- Children who attend kindergarten
- ADHD
- Life in a dry climate
- Nutritional deficiency
- Teenage obesity, for later onset of eczema cases
- Low vitamin D levels during pregnancy may increase the risk of developing eczema in the first year of life.
Causes of eczema
The medical community has yet to determine the definitive cause of eczema. For some, this may occur due to a nutritional deficiency, while for others, it may occur primarily due to an allergen or other irritant. Here are the common causes of eczema:
- Dry and sensitive skin
- Immune system dysfunction
- Environmental conditions
- Genetic abnormalities
- Allergies to food, cosmetics, laundry detergents, or other chemical allergies
- Chronic stress
- Temperature changes
Symptoms of eczema
While many will experience a decrease in symptoms and fewer outbreaks as they get older, some will experience eczema symptoms throughout their adult lives. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may vary from one outbreak to the next. Common symptoms include:
- The appearance of small raised areas of skin that may ooze fluid and form a crust
- Thick, dry, scaly skin with cracks
- Red, brown, or grayish patches of skin on the arms, legs, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, skin folds, and on the face and scalp of children
- Sensitive skin, swollen and raw from scratches
- A recurring rash that causes severe itching and often disrupts sleep
- Rash due to atopic eczema
Home treatments for eczema are sometimes more effective than pharmaceutical medications
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - e
| Treatment of pleural empyema |
| Treatment of emphysema |
| Treatment of endocarditis |
| Treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy |
| Treatment of endometriosis |
| Treatment of endometritis |
| Treatment of enteritis |
| Treatment of enuresis |
| Treatment of epididymitis |
| Treatment of epilepsy |
| Treatment of erectile dysfunction |
| Treatment of erythremia |
| Treatment of cervical erosion |
| Treatment of pulmonary echinococcosis |
| Treatment of liver echinococcosis |
| Treatment of echinococcosis of the spleen |
| Treatment of escherichiosis |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.