They are classified depending on the pathogen, location and degree of damage to the skin. According to WHO statistics, more than 70% of children are affected by this skin disease, both in newborns and older.
The group of lichens includes:
- lichen Zhibera or pink lichen;
- ringworm (the most common form);
- shingles;
- lichen planus or Wilson's lichen;
- ringworm or eczema;
- lichen simplex of the face;
- scaly lichen or psoriasis;
- pityriasis versicolor.
The mechanism of infection has not been reliably identified, since not every child who comes into contact with a carrier of the pathology gets lichen.
There are a number of catalyst factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease, including:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- endocrinological dysfunctions;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- hyperfunction of the sweat and sebaceous glands;
- stress;
- physical stress;
- hypothermia of the body;
- taking certain medications, etc.
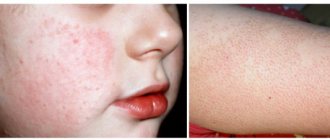
Late detection of a lichen spot often leads to an increasingly larger area of skin being affected, causing itching, peeling and discomfort. Often children scratch and injure the affected areas of the skin, which contributes to the addition of a bacterial infection to the underlying disease.
In order to identify and remove lichen from a child’s skin, you need to contact a specialist. A doctor whose competence is the diagnosis and treatment of lichen in children is a pediatric dermatologist.
In addition to treatment, prevention is important in eliminating and preventing relapse of the disease.
Preventive measures for the primary or recurrence of lichen are:
- strengthening the child’s immunity (hardening, etc.);
- compliance with hygiene standards (washing hands, cleaning premises with disinfectants, etc.);
- separate individual items (bed and personal linen, dishes, toys, etc.);
- frequent washing of the child’s clothes, especially after contact with animals or sick people;
- showering rather than bathing to avoid the spread of infection;
- replacing synthetic clothing with natural ones;
- reducing exposure to the sun (heat provokes the growth of fungal colonies), etc.
How is lichen transmitted?
The main sources of the disease are street cats and dogs, or objects containing flakes of their skin affected by the pathogen - a zoonotic form. However, lichen can be transmitted from person to person - an anthroponotic form of transmission, as well as with the help of fungi living in the soil - a geophilic transmission route. Viruses, as a cause of deprivation, can remain in the body of humans and animals for a long time, and only when the child’s immunity decreases can they provoke a disease.
Ringworm is not always contagious. Thus, children's weeping eczema occurs due to infection of microcracks in the skin, dermatoses, or the presence of allergic reactivity in the child's parents. According to the observations of experts, allergic diseases of the mother (asthma, rhinitis or neurodermatitis) increase the likelihood of eczema in the child by 40%. And Zhiber's pityriasis rosea is often a consequence of ARVI and is not transmitted to other people.
The period of high risk of contracting lichen is spring-summer, since the child spends most of his time outdoors and in contact with other children.
Contagious (infectious) types of lichen are pink, ringworm and herpes zoster. They require mandatory isolation of the child to prevent the rapid spread of the disease.
Lichen planus and pityriasis versicolor, as well as psoriasis and weeping eczema are not transmitted.
Reasons for deprivation
The main reason for the formation of lichen is associated with the penetration of a viral or fungal infection into the body.
However, the infection process itself has not been fully studied. Scientists remain unknown why not all children (even those at risk) suffer from lichen. Despite this, there are factors that increase the risk of developing the disease in a child:
- excessive emotional and physical stress;
- exposure to stress;
- decreased immunity;
- the presence of infectious inflammatory processes;
- avitaminosis;
- allergic reactions;
- increased sweating;
- hereditary predisposition.
Infection of children most often occurs in crowded places: kindergarten, school, summer camp, public swimming pool.
Also, a common cause of the development of lichen is contact with domestic or street animals, after which the rules of personal hygiene were not followed. Each form of lichen has specific causes. Thus, pityriasis rosea clearly shows an infectious-allergic nature. Shingles develops as a result of various types of viruses entering the body, ringworm and multicolored fungi.
What does ringworm look like?
The nature of the specific symptoms of lichen depends on the type of pathogen and the characteristics of the body’s response to the pathogen.
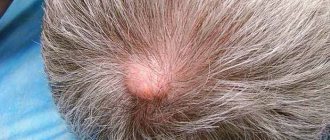
Thus, ringworm or trichophia is caused by the fungus trichophyton and mainly affects children under 14 years of age. The most common locations for ringworm are the scalp and neck, nails and armpits.
Signs of trichophia:
- a clearly defined red or pink spot on the scalp;
- high rate of increase in spot area;
- swelling and rash (blisters) on the affected area of the skin;
- the appearance of white scales on the lichen spot;
- frequent absence of itching;
- hair thinning in the area of inflamed skin, etc.
Lichen Zhibera (pink) is believed to be caused by the herpes virus and is localized primarily on the back, abdomen, face and skin folds.
Signs of pityriasis rosea:
- the presence of one large (maternal) spot, which gradually increases in size;
- a rounded spot with clear boundaries;
- dry flaky skin in the center of the spot;
- itchy skin.
Pityriasis versicolor or versicolor versicolor occurs in children due to the activity of the fungi Malassezia furfur and Pityrpsporum orbiculare, which are localized in the stratum corneum of the skin and gradually cover increasingly larger areas of the skin. This type of disease mainly affects the skin of the chest, abdomen and back, especially in children with hormonal disorders (diabetes, obesity, etc.) and hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). This form of the disease can also be provoked by: tuberculosis, leukemia or rheumatism.
Signs of pityriasis versicolor:
- at an early stage, spots are greenish in color without clear boundaries, which then transform into yellow, brown or pink;
- tendency to form a large lesion on the skin;
- peeling and itching, especially due to stress and hygiene procedures.
Shingles or herpes zoster is caused by the herpes virus, but in childhood it has the form of chickenpox or chickenpox, to which lifelong immunity is developed.
The etiology of lichen planus has not been reliably established; it is localized both on the skin of the wrists, abdomen, chest, and on the mucous membranes.
Signs of lichen planus:
- flat nodules on the skin of a red or purple color, prone to the formation of large foci of pathology;
- pale pink flat nodules on the mucous membranes;
- itching and sensitivity of the affected skin areas;
- deformation of the nail plate, followed by its destruction.
Lichen simplex of the face or streptodemia sicca occurs due to the activity of streptococcus and is localized mainly on the face, but also on the skin of the buttocks, limbs and back.
Signs of simple facial lichen:
- round pink scaly spots up to 4 cm in diameter;
- no itching;
- disappearance of stains under the influence of ultraviolet radiation;
- the presence of temporary depigmentation at the site of lichen spots.
Herbal remedies
At the first manifestations of lichen, it is necessary to begin its treatment. The initial stage of the disease can be treated using folk remedies in one to two weeks; the advanced form will require months of constant use of medications. One of the most common ways to get rid of lichen is the use of herbal and natural products.
Due to the bactericidal properties of garlic, this product has become the basis for many folk recipes for the treatment of lichen in children.
Garlic, known for its antibacterial properties, is an excellent remedy for all types of ringworm, including hard-to-treat ringworm. The easiest way to get rid of stains is to apply a cut clove of garlic to them several times a day until they are completely healed.
Garlic vinegar will not only get rid of lichen, but also scabies, warts and calluses on the feet. To do this, pour a few cloves of garlic into two glasses of natural apple cider vinegar and leave for two weeks. You can also use garlic vinegar for a compress, which is changed twice a day and remains until the stains are completely removed.
A paste is prepared using garlic and eucalyptus decoction to wipe the affected areas. To do this, combine chopped garlic and a strong broth in equal proportions. To stir thoroughly. Use for wiping once a day. This mass can also be used as a base for a compress.
An infusion of birch buds is used for lotions in the treatment of pink and multi-colored lichen. To do this, pour a glass of raw material with the same amount of boiling water and leave for two hours. Apply lotions several times a day, each time using a new cloth.
Citric acid perfectly kills fungal spores, stopping its reproduction in cases of lichen.
Citric acid, mixed in equal proportions with any vegetable oil, will help quickly reduce the manifestations of lichen in children. Mix the ingredients until a paste forms, lubricate the affected areas of the skin daily, shaking the product beforehand.
How to recognize lichen in a child?
Since there are different types of the disease, differential diagnosis is carried out, usually including:
- examination of skin scrapings under a microscope;
- luminescent tests (characteristic fluorescence of affected areas);
- serological test (blood test for the presence of antibodies to the pathogen);
- bacterial culture for microflora;
- skin biopsy;
- examination under Wood's lamp;
- study of cell morphology, etc.
Under the guidance of a doctor, recovery occurs quite quickly, and compliance with all his recommendations minimizes the likelihood of relapse of the disease.
Various forms of lichen have similar clinical signs. Usually the first symptom of the disease is the appearance of a predominantly pink spot on the child's skin. Subsequently, the next spot appears on an adjacent area of skin, which can merge. In addition to the formation of spots, the infected skin begins to peel and itch; in some cases, the child’s body temperature rises and the lymph nodes become enlarged.
Among the most likely locations of lichen spots are:
- upper limbs;
- scalp;
- stomach;
- localization of sweat glands, etc.
Shearer
Ringworm
The risk group mainly includes children of preschool age and sometimes children of primary school. Therefore, parents should be on both sides and listen to the child’s complaints every time and examine his body for the presence of red spots.
Pathogen and route of infection
Infection with this type of lichen occurs through direct contact with a carrier (animal or human). The disease is caused by zooanthropophilic fungi. Infection often occurs through contact with the patient's personal belongings. Depending on the type of fungal spore, trichophytosis and microsporia are distinguished. At the same time, a specialist can accurately determine the type of ringworm with further confirmation of the diagnosis based on the results of a cultural study.
Causative agents of ringworm
Where is it located?
Basically, the main affected area in children is the head. Sometimes it can spread to the face. It is extremely rare that other parts of the body are affected.
Characteristics of the disease
Initially, swelling of the skin begins at the site of the lesion. After this, a stain forms, which over time acquires a red tint. The edges of the lesion are clearly defined. The hair at the site of the lichen falls out, and white scales appear on the surface. The affected area can vary from one to ten centimeters.
Is there any itching?
The first stages after infection are practically not distinguished by alarming symptoms, so the lesion can be detected when the hair is combed. Then the child begins to be bothered by constant itching. What is characteristic is that lichen on the scalp practically does not itch; on the contrary, open areas are accompanied by severe itching.
Localization of ringworm
Provoking factors
- Weakened protective functions of the immune system.
- Constant nervous tension.
- Presence of injuries on the skin.
- Frequent contact with water, which leads to softening of the skin.
The diagnosis can be accurately confirmed by bacteriological culture. Depending on the method of infection, the incubation period can range from seven days to six weeks.
Interesting recommendations can be found in the video.
Video - Ringworm in children
Forms of ringworm
| Form | Symptoms | Location of the lesion |
| Surface | The defeat occurs without accompanied by an inflammatory process. In the absence of effective treatment, spots can quickly increase | Mainly localized on the head, but less commonly can affect the face and neck area |
| Chronic | Spots up to one centimeter in diameter are formed and are characterized by the appearance of black dots inside. The shade of the affected area may change throughout the course of the disease from pink to bluish. The skin takes on an unaesthetic appearance. Severe itching appears | In children, this subtype of lichen affects the temporal zone, sometimes the back of the head. Body parts: buttocks, palms. In medical practice, there are frequent cases of damage to marigolds. |
| Deep | Infection occurs exclusively through contact with a sick animal. The disease begins to manifest itself with an increase in body temperature, then the child develops skin rashes. On palpation, you can feel enlarged lymph nodes. The lesion appears in the form of large red spots with purulent inflammation. Treatment and wound healing may take several months | Mainly the head (especially in the hair area) |
Effective treatment
Therapy should be prescribed to the child by a dermatologist after a detailed examination. Treatment will consist of antifungal medications.
- Ointments. Antifungal agents such as Tolnaftat, Mycoseptin.
Antifungal agent Mikoseptin
- Antiseptic solution. Alternatively, you can use salicylic acid with a five percent iodine solution.
- Tablet medications. This type of treatment is prescribed for chronic forms of the disease or extensive damage. Tablets are considered the most effective Griseofulvin. The treatment regimen is determined strictly by the doctor.
The drug Griseofulvin
- Immunomodulators. It is very important to take during the chronic form, as well as during acute damage (Likopid, Radiola Extract, Imunofan).
- Folk remedies. Can be used as local therapy or as an auxiliary treatment. Must be agreed with a dermatologist.
Why is lichen dangerous in children?
The greatest danger for children are the following consequences of deprivation:
- addition of a bacterial infection;
- spread of pathology to internal organs (bones, brain, etc.);
- development of immunodeficiency.
However, the degree and nature of complications after the disease depend on the type of lichen. Thus, pityriasis rosea occurs without side effects and does not cause deterioration in the child’s health. Trichophytosis leads to the formation of bald patches, and pityriasis versicolor, ringworm and red lichen cause a secondary infection, which significantly complicates treatment.
Herpes zoster can cause postherpetic neuralgia, as well as:
- impaired motor activity of the arms and legs;
- reduction and partial loss of sensitivity of the limbs;
- inflammatory process in the structures of the eye (eyeball, cornea, etc.);
- inflammation of the tissues of internal organs (liver, membranes of the spinal cord and brain, etc.).
Features of treatment
Treatment of lichen in children includes the use of special medications. In addition, a number of rules must be followed to ensure that the treatment is quick and successful. How to apply lichen depends on the form of the disease, this is determined by the doctor after diagnosis.
Ringworm is highly contagious. Therefore, treatment of this disease includes a number of measures to help prevent infection of others. Also, these rules must be followed so that after treatment the patient does not become infected again.
First of all, parents should explain to their child the dangers of scratching the affected area. When scratching, the fungus can spread to other parts of the body, which will lead to the appearance of another lesion.
The optimal environment for fungal growth is damp, hot skin. To avoid an increase in ringworm, it is important to choose the right clothing. Preference should be given to clothing made from natural fabrics and a loose fit. This will avoid excessive sweating, which can cause shingles to increase. To prevent the fungus from spreading further, it is important to cover the affected epidermis when going outside. The sun's rays provoke the growth of the lesion.
Ringworm is characterized by severe peeling, which is accompanied by the separation of large flakes of skin. These scales can become deposited on bedding, carpets and stuffed animals, leading to re-infection of the skin over time. To avoid this, it is recommended to remove from the child’s bedroom all objects on which dust may accumulate. Every day it is necessary to do wet cleaning and thoroughly ventilate the room.
For the duration of treatment, it is necessary to provide the child with two sets of bed linen and two sets of clothes. Items in contact with skin should be changed daily. Thus, every day you need to wash bedding and clothes that the baby’s skin has been in contact with over the past 24 hours. Washing should be done at high temperatures, and after drying, items should be thoroughly ironed with a hot iron.
Which doctor should I go to if my child has shingles?
As we have already mentioned, a doctor who diagnoses and treats dermatological diseases is a dermatologist. Since the structure and functioning of the skin of a small child is significantly different from the skin of an adult, it is the pediatric dermatologist who should make the diagnosis.
Features of children's skin that determine high sensitivity to external irritants and pathogens are:
- skin thickness (in an adult it is three times thicker);
- loose epidermis;
- lack of elastic fibers;
- weak ability to form skin pigments (low protective function);
- low degree of thermoregulation, etc.
Diseases of the skin and its appendages (hair and nails) can be a consequence of various pathological processes in the child’s body (systemic or autoimmune diseases, etc.), so additional consultation with a pediatric neurologist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist or other specialists may often be necessary.
Diagnosis of lichen
Medical dermatologists have many years of experience in diagnosing and treating children infected with lichen.
Modern examination methods and high-tech equipment allow specialists to identify the form and characteristics of the course of the disease even during the first visit to the clinic. At the initial appointment, the doctor talks with the child and his parents, listens to complaints, tries to determine the factors that contributed to the occurrence of skin pathology (contact with street animals, infected people, etc.). Then the specialist proceeds to a visual inspection, during which he evaluates the size of the formations, their color, shape and location. After a preliminary diagnosis has been established, the child is sent for additional studies to confirm it:
- microscopic examination of scraping of rashes;
- Balzer iodine test;
- Wood fluorescence microscopy;
- Beignet symptom test.
In addition, a general blood and urine test will help determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
girdling
Herpetic infection leads to the activation of herpes zoster in children. Children after ten years of age are at risk. In general, it occurs due to constant overwork, frequent acute respiratory viral infections, and also with a decrease in the protective functions of the immune system.
Where is it located?
Lichen rashes appear in the area of large nerve trunks. The name of the disease comes from the fact that the lesion begins to creep from place to place, as if encircling the body. There have been cases where shingles appeared before the eyes.
Shingles
Characteristics of the lesion
The disease begins with the appearance of red spots, which soon become covered with blisters. These symptoms are very similar to smallpox. The duration of the disease is several weeks. After two weeks, the lesion becomes covered with a crust. As a consequence there may be pigmentation.
Unlike other types of lichen, it has a pronounced pain syndrome and severe itching. The herpes virus even penetrates nerve fibers. Shingles can occur in several forms. The mild form is characterized by the appearance of a small number of blisters and neuralgic pain. A more severe form of the disease is expressed in purulent formations, sometimes containing blood.
What is shingles
How is the treatment carried out?
A mild form of lichen, not complicated by rashes, can go away on its own after two weeks. For moderate severity, the following course of treatment is recommended:
- Taking antiviral drugs. The drugs must be based on the active substance - glycyrrhizic acid . The duration of treatment is ten days. The dosage is determined only by the doctor. The most popular drugs (Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir).
- Painkillers may be needed to relieve pain. You can take medications based on ibuprofen . Analgin, Indomethacin, Butadione are recommended
- In the case of a purulent inflammatory process, antibiotics are taken (Gentamicin, Erythromycin, Rifampicin) .
- Vitamin therapy and immunomodulators (Interferon alpha, Interferon gamma, Inosine pranobex) are used as additional therapy.
Causes of herpes zoster
Attention! You cannot use hormonal drugs for local treatment to eliminate herpes zoster - this aggravates the clinical picture of the lesion.