This pathology is considered to be one of the most common diseases in childhood. Statistics show that it occurs in every fourth child aged one to three years. Therefore, parents of children should familiarize themselves with the information: what can cause urticaria in children, symptoms and treatment, photos of signs of this disease will help you become familiar with the consequences of this disease for the child’s health.
In the process of diagnosing the disease urticaria in children, the causes of its appearance are quite difficult to establish . But this must be done so that the treatment of urticaria is effective. In almost all cases, the cause of pathology in a child is an allergen. And if you quickly recognize its nature and then eliminate it, then the signs of the disease will disappear in a short time.
What is histamine and how is it related to hives
The substance histamine is a biological mediator of an allergic reaction that is present in the body of every person. It is wrong to consider it an enemy to your health. It is involved in many regulatory processes, including helping to perform the functions of organs controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
As a rule, it is in a bound, that is, inactive, state and monitors the stability of the environment. Relatively speaking, this substance is a guardian of order. When situations arise that pose the slightest threat to the body, it contacts immune cells (the so-called “mast cells”) and together they trigger a defense mechanism.
loading…
In this capacity there is a special reaction to an irritant - inflammation, one of the signs of which is swelling. It occurs due to the release of fluid from the vascular bed into the surrounding tissues. At the same time, the plasma concentration decreases, which entails a decrease in the volume of circulating blood. This condition can lead to vascular collapse and shock.
It sounds scary, but if you look at the situation from the other side, you can understand that this mechanism works to eliminate serious consequences. Local edema with the release of fluid is necessary in order to limit the spread of foreign agents. The plasma in the tissues is static, foreign proteins are retained in it, while macrophages and leukocytes multiply intensely to strike and destroy enemies.
Agree, it is more convenient to fight the enemy when he is in one location than to catch him throughout the body. Therefore, histamine is an alarming substance; it must quickly give a signal and raise all the defenses before the invader spreads throughout the body.
Allergic reactions occur on the principle of inflammation, but the body can recognize any even insignificant and everyday factor as an enemy. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that the immune response manifests itself suddenly and extremely violently.
In children, allergic urticaria develops in some cases due to the immaturity of the immune system and insufficient debugging of the connections between the release of histamine and the triggering of the inflammatory response. Imagine a new work team in which relations between employees are at the level of initial acquaintance (not everyone even remembers each other’s last names) and no one has work experience.
Any difficulty or unfamiliar circumstances cause panic and lack of a clear action plan. It will take some time before the operating tempo is developed and the operating program is established. Approximately the same processes occur in the child’s immune system, which is extremely active, but does not have sufficient experience and clear instructions on how to react.
Therefore, allergic urticaria in children is a very common and widespread phenomenon; the following factors contribute to its development:
- heredity;
- excessive sterility of environmental conditions;
- immaturity of the digestive organs;
- physiological dysbacteriosis;
- hormonal instability;
- complications during childbirth: postperinatal damage to the nervous system, prematurity, surgical operations and drug treatment during the neonatal period;
- intrauterine infections;
- pathologies of pregnancy: fetal hypoxia, taking various medications by the mother and her bad habits.
It is impossible to predict whether a baby will be allergic, but knowing the reasons for the development of such a reaction in children, it should be assumed that any child may be at risk for the disease.
Pathogenesis (mechanism) of development
The mechanisms of development of the disease have not been fully identified, but the pathogenesis is based on impaired microcirculation and degranulation of mast cells, which causes rapid swelling and the release of histamine in large quantities.
Laboratory tests revealed an increased level of cryoglobulins in the blood serum. Precipitating, they increase the viscosity of the blood, which leads to a deterioration in the supply of organs and tissues with useful substances and oxygen. Such a deficiency leads to various pathologies.
Cooling the body, and therefore the blood, reduces platelet aggregation and increases platelet factor IV levels and increases antibody production. The “gluing” of the platelet mass leads to the fact that the body perceives its own cells as a threat and begins to actively fight it.
All internal processes of this kind give external unhealthy manifestations on the skin of patients.
Symptoms of urticaria in children
In some cases, recognizing any form of urticaria is not difficult; it has pronounced clinical signs:
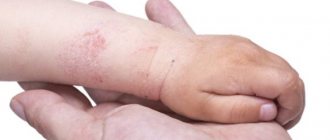
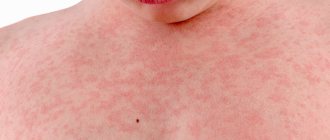
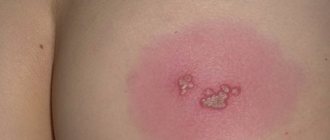
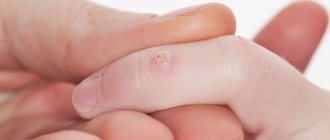
- After contact with an allergen, blisters appear . They can be of different sizes: with a transient reaction, they are large, dense, surrounded by a red border, marbled or pink in the middle. If you press lightly on the papule with your finger, it will definitely turn pale (this helps differentiate urticaria from other types of rash, such as meningeal petechiae).
- Itching. The skin of children is very delicate, with developed innervation, the itching with urticaria is therefore very peculiar, mixed with severe pain and a special burning sensation.
- The area of distribution can be varied . But more often the rash appears on the stomach, buttocks, chest, cheeks, and thighs. Often the mucous membranes are involved in the process: lips, oral cavity, genitals.
- Speed of reaction. Those who have ever observed classic urticaria on a child’s skin will forever remember this moment. Rash nodules appear instantly, swell, can disappear and appear just as quickly and powerfully in another place. Literally after the child scratches, a lump grows at the site of the scratch. This phenomenon is quite difficult to observe with indifference and it causes panic among parents. Although most often the reaction goes away quickly within a few hours, provided that contact with the allergen has been stopped and measures have been taken.
- Edema. In young children, the subcutaneous fat is well expressed, so swelling grows quickly and strongly. Usually the ankle joints, face area, hands, and neck are involved in the process. The spread of the reaction to the larynx - Quincke's edema, can cause asphyxia and be fatal. In children, this condition develops at lightning speed.
- Increase in body temperature . It may precede the appearance of urticaria, occur simultaneously with urticaria, or appear after the rash has formed. Thermometric values range from moderate fever to high values, at which seizures and confusion may occur. Fever is also one of the protective mechanisms of the immune system, and therefore often accompanies allergic reactions.
- Digestive disorders: vomiting, nausea, diarrhea. Hidden food allergies manifest themselves not as a rash, but as abdominal pain, constipation, and refusal to eat.
In addition to pronounced symptoms, urticaria is also characterized by symptoms of general intoxication:
- fatigue;
- headache;
- chills;
- irritability;
- sleep disorders;
- gastrointestinal disorders.
Timely identification of signs of allergies and measures to combat them can reduce the severity of the consequences.
Other signs
In addition to the main symptom - skin rashes - cold urticaria can be accompanied by fever, general weakness of the body, and joint pain. In severe (usually acute) cases, shortness of breath, tachycardia may appear, a decrease in blood pressure is observed, and Quincke's edema is possible (an instant reaction of the body, characterized by swelling of the lips and larynx). It should be noted that in such extreme cases it is not recommended to practice self-medication - call a doctor immediately. It is extremely rare, but death from this disease still happens - so you should not joke with this type of allergy.
Causes of urticaria in children
Urticarial rash can appear for various reasons, since in medicine the disease has the status of a polyetiological disease. Based on the frequency of occurrence, the following trends in the development of the disease can be identified in connection with a specific trigger (aggression factor of the histamine response):
- In children under 2 years of age, the main trigger is food allergens. Hives can be caused by:
- milk formulas;
- cow's milk proteins;
- eggs;
- chocolate;
- nuts;
- red fish and caviar;
- berries, some vegetables and fruits;
- sweets;
- herbal teas;
- products containing flavoring additives: chips, crackers;
- canned food
- Also, the following medications can contribute to the development of allergies in a child of any age:
- beta-lactam antibiotics;
- vitamins;
- antipyretics from the NSAID group: nimesulide, ibuprofen and others;
- neurological drugs: glycine, pantogam, vinpocetine, encephabol;
- sweet syrups: licorice root, Ascoril, and any with the addition of fruit flavor substitutes.
- During breastfeeding, the baby may develop allergies to foods consumed by the mother. Therefore, it is important for a nursing woman to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet.
- In children from 4 years of age, the list of urticaria triggers expands significantly:
- household objects: dust, pet hair, indoor plants;
- pollen;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hereditary chronic diseases: diabetes, autoimmune disorders.
- Regardless of age, hives can be provoked by any household chemicals, washing powders, cosmetics (creams, lotions), shampoos and bathing products, as well as viral and bacterial infections.
- The cause of non-allergic urticaria, that is, not associated with the formation of specific antigen-antibody complexes, can be stressful situations, physical overload, and temperature changes.
Urticaria can develop completely spontaneously and it is not always possible to establish its cause. Often, the investigation of what happened is helped by a detailed study of the circumstances in which the rash was first discovered and the events preceding the incident.
Frequent severe colds, respiratory infections, and long-term illnesses make the child’s immunity more aggressive and create favorable conditions for an atypical response to an irritant.
How many days does the allergy last?
The duration of the disease depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the functioning of the immune system, as well as the sensitivity of the child’s histamine receptors.
- Mild acute urticaria occurs within a few minutes after contact with the allergen. It is characterized by intense rashes that merge, but do not pose a threat to life, since the deep layers of the dermis are little involved in this process. If contact with the pathogen is eliminated in a timely manner, the reaction can go away within a few hours, leaving no traces. On average, a mild form when taking antihistamines can disappear within 6-24 hours.
- Acute moderate to severe urticaria. May be accompanied by rhinotracheal symptoms, sneezing, mucous secretion from the nasal passages, difficulty breathing, swelling of the limbs and throat. The rash may appear after the catarrhal crisis has passed. In this case, provided that the intake of the allergen stops, the duration of the skin pathology will depend on how quickly the antigen is removed from the body. On average, this can take from 1 to 7 days. If the allergen has not been identified and there is no way to stop contact with it, the acute form of the disease is considered to be persistence of symptoms for no longer than 6 weeks.
- Chronic urticaria exhibits a less violent immune response, but can persist for a long period of time, systematically intensifying and not completely disappearing for more than 1.5 - 2 months. With chronic urticaria in children, it is difficult to establish the cause of its appearance; there may be several allergens from different groups. This often threatens the sudden development of a severe attack in the form of angioedema against the background of the relative stability of the child’s health and the well-being of the environment.
Therefore, to answer the question of how many days does urticaria last on the skin, the following points should be taken into account:
- whether a reaction trigger is set;
- how quickly first aid was provided (link to article 2);
- whether there was a positive response to taking antihistamines;
- how deep the process has spread;
- how the contact with the allergen occurred (ingestion, inhalation, through the skin, due to an insect bite, injection);
- severity of condition;
- type of urticaria.
We talked in more detail about the various forms of the disease and their relationship with the allergen in the article “Skin allergies: urticaria.”
But the duration will still be determined by the individual characteristics of immunity. So, for example, if an allergy occurs against the background of a decrease in natural defenses during illness, then the reaction is more severe and longer.
What can trigger
The reasons for this may be various factors. However, the main provoking source is the effect of low temperature on unprotected areas of the skin.
- Cold weather and wind. Typically, this allergy in children is detected in winter, when there is a sharp change in temperature in the room and in the open space.
- Contact with cold water. Signs may become apparent after washing your hands in such water or after swimming in cold water in water sources in the summer.
- Cold food and drinks. This is one of the rare reasons. Burning sensation and hives may occur after drinking cold drinks or ice cream. In addition, a more serious symptom may appear, such as swelling of the throat and tongue, and this can lead to a bad result - difficulty breathing. Children who are susceptible to cold urticaria should be taught from childhood to drink drinks only at room temperature.
- Hereditary factor. There are two types of urticaria: acquired and hereditary. Nowadays there is more and more talk about hereditary urticaria. If one of the parents had or has this disease, then there is a high chance that the baby will inherit it.
- Due to other diseases, viruses of different origins. Cold allergies occur very often if a child suffers from giardiasis, infestations, tuberculosis, pneumonia, thyroid disorders, metabolism, and cancer. If a child has suffered from volatile infections (for example, rubella, measles) or has chronic sinusitis, dysbacteriosis, then this can also provoke urticaria.
- Treatment with antibiotics. They can also indirectly affect the occurrence of this allergy. Antibiotics reduce immunity because children’s bodies become vulnerable and their skin becomes very sensitive.
- Reduced immunity. After recovery or illness associated with impaired immune function, urticaria may occur. In children with strong immune systems, such allergies are quite rare.
- Other skin diseases. If a child has symptoms of food, contact or drug allergies, then cold urticaria is, in principle, possible. In addition, it can also appear in the presence of psoriasis and dermatitis.
- Poor stress tolerance. Cold urticaria is much more common in children who are overly excitable and vulnerable.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is not particularly difficult for a doctor to determine that a rash on a child’s skin is urticaria. To do this, it is enough to conduct an examination and collect a detailed history of life and the development of the disease.
Without special medical skills, the visual symptoms of urticaria can be confused with the following infections:
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- rubella;
- meningitis.
These are life-threatening, highly contagious diseases, so if in doubt, or even worse, the rash has appeared in several family members, you should immediately seek medical help. Do not forget that urticaria is an individual reaction of the body; it cannot be contagious.
A detailed medical history plays a huge role, taking into account all previous diseases; for young children, information about the course of pregnancy and complications during childbirth is important. As well as information about the situation and surroundings.
Additional examination methods:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- feces to detect parasite activity;
- immunoglobulin E test.
The protocol for the management of children with urticaria does not require special tests using a panel of potential allergens unless necessary.
Up to 5 years, such tests do not provide reliable information about the cause of the disease, since there are false positive reactions to many types of antigens. If such tests are prescribed (for example, in the absence of positive dynamics in treatment), then they are carried out strictly under the supervision of an immunologist, because there is a possibility of developing an acute reaction.
Determining the cause of urticaria is not always easy, especially if the chronic, severe form occurs. The fact is that excessive sensitization during prolonged contact with an allergen leads the immune response to a state of increased aggression and a reaction can occur to factors that were previously perceived neutrally by the body.
Treatment of urticaria
Mild forms of the disease, which manifest themselves exclusively as a rash and mild itching, can be treated at home as prescribed by a doctor.
This is usually a simple therapy that includes the following principles:
- Topical preparations to relieve symptoms: soothing creams and gels. For children, products containing panthenol are considered absolutely safe: Dexapanthenol, Bepanthen and zinc. And also creams Desitin, Calendula, Gistan.
- Antihistamines. Fenistil is allowed almost from birth, Zodak and Zyrtec - from six months of age. If there is no positive effect, suprastin and diazolin are used as prescribed by the doctor. The dosage is determined strictly by the pediatrician, taking into account the weight and age of the child. For children under 6 years of age, it is preferable to use the dosage form in the form of drops, at a later age - tablets.
- At the same time, it is necessary to cleanse the body of toxins and allergens, so enterosorbents are prescribed. The drugs of choice, as a rule, are Polysorb or Smecta; they bind harmful substances and remove them naturally. Enterosgel is rarely prescribed to young children, since in this age group it causes a side effect in the form of uncontrollable vomiting.
If the allergy worsens over time, despite the measures taken, the allergen is not identified, and episodes of deterioration, angioedema, chronic cough, persistent rash appear, then treatment is adjusted, or the child is admitted to a hospital for observation.
More serious therapeutic agents to combat the disease are prescribed for moderate and severe forms of chronic and acute urticaria:
- Prednisolone . Ointments and creams with this hormone help in a short time eliminate persistent skin forms of urticaria and soothe inflamed skin. The drug taken orally in the form of deep injections into the gluteal muscle is prescribed for severe lesions of the mucous membrane, the threat of shock, and Quincke's edema. Treatment with steroids gives good and quick results, but this method must be justified. Artificial interference with the body’s hormonal balance has many consequences, the most dangerous of which is adrenal atrophy. Therefore, the dosage, duration of the course and withdrawal of the drug should be monitored by a specialist. It must be remembered that glucocorticosteroids are not one-time use drugs; even if an ointment with this component is prescribed, you need to completely complete the course, which, on average, does not exceed 5-7 days. In this case, it is necessary to stop using the drug only by gradually reducing the dosage or reducing the number of applications per day.
- Immunosuppressants . They are used extremely rarely in children and only in cases of persistent lack of response to hormonal therapy. The drug of choice is Cyclosporine A. Such violent interference with the immune system is fraught with complications, since the drug significantly reduces the body’s natural defenses and there is a risk of serious complications due to damage by any infectious agents.
Occurrence on the skin
- Dermatitis. With such a reaction to cold, if it is a mild form, then after or during a walk (due to a rapid change in temperature), unprotected areas of the skin turn red or swell. The child sometimes suffers from itching all over the body, but everything stops after some time at home.
In severe situations, cold dermatitis begins to develop - red spots appear that peel off from the hands, neck and face. They reach 3-6 cm in size and are very itchy. Sometimes the rash appears on the inner thighs and knees.
This type of dermatitis is often accompanied by a runny nose and watery eyes—short-term “companions” of this cold allergy reaction.
- Hives. If the rash on the baby’s skin, when responding to cold, turns into one whole and forms blisters, then this indicates CC.
Diet and its importance for the treatment of urticaria
Why is it so important to observe certain dietary restrictions when treating allergies of any type in children, not necessarily food allergies?
Children's immunity has one interesting feature - a significant delay in reaction.
That is, the obvious symptoms of urticaria to an irritant may not be detected for a long time, and the presence of a reaction can be guessed by indirect signs that are common to any disorder: for example, abdominal pain, bowel movements and mild malaise.
At the same time, the allergen continues to enter the body in one form or another. At some point, the patience and loyalty of the immune system runs out, and it produces such a powerful reaction that treatment with antihistamines gives a weak result.
Imagine a very irritated person, in such an extreme state of tension that any minor event or phrase can cause an emotional storm. The immune system in children behaves the same way. He begins to react to any factors that seem even remotely hostile to him, and most often food plays this role. Therefore, before the onset of stable remission of a severe form of urticaria, it is necessary to eliminate all potential threats, even if the body has never reacted negatively to them before.
In the midst of an illness, the following are allowed for use by a child:
- dried white bread;
- unsweetened tea;
- dairy-free porridges from low-gluten cereals: buckwheat, rice;
- hypoallergenic vegetables and fruits: broccoli, boiled zucchini, potatoes, cucumbers;
- greens: dill, fennel, parsley;
- soups with cereals in vegetable or beef broth.
As the body detoxifies, new foods are gradually introduced in small quantities.
Normalization of digestive function is an important step towards recovery; a properly formulated and followed diet helps to achieve this.
Prevention
Do not forget about preventive measures, which often help prevent the occurrence of allergies. Try to eliminate all factors that could cause an exacerbation of the disease.
So, a child prone to this type of allergy should not be hardened by bathing in cool water - it is harmful for him. You can try this type of hardening: wipe or pour over the baby, gradually lowering the water temperature, starting with a temperature of 30-32 degrees. Or try a contrast shower. But if you see any signs of cold urticaria, then stop hardening immediately.
Complications of urticaria in children
As in adults, childhood urticaria is always a risk of developing threatening conditions: Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock. Due to the fact that the body is still immature, the following complications may develop due to urticaria:
- Skin infections. The inflamed epidermis is the entry point for infection. Streptoderma is the most common companion to allergic urticaria. Often it develops into a more complex form - pyoderma, which literally means “suppuration of the skin.” And this, in turn, is a threat of sepsis.
- Frequent attacks of the disease over time provoke high sensitization of the body to various factors, which complicates treatment.
- Decreased immunity, susceptibility to colds.
- Transition from acute to chronic form.
- Allergic urticaria provokes the development of bronchial asthma.
- Due to improper treatment or non-compliance with the diet, gastroenterological disorders can develop: gastritis, ulcers, colitis.
- Recurrent swelling of the mucous membranes is the main factor in the loosening and persistent enlargement of the adenoids, and they also contribute to the growth of polyps in the nasopharynx and larynx.
There is a certain relationship in a child with a tendency to develop stenosis and false croup due to upper respiratory tract infections and an allergic reaction in the form of urticaria. The anatomical structure of the trachea in children under 5 years of age has its own characteristics: unlike the organ of an adult, the child’s trachea is not a straight tube, but a funnel narrowed downward. Therefore, with swelling of the larynx, respiratory failure in children develops extremely quickly.
It is important to remember that if a child has had laryngeal stenosis at least once, then the likelihood that it will develop with the next laryngitis is quite high. Always warn your doctor about this possibility when prescribing medications.
An effective prevention of the development of an attack (and parents who have had to deal with this certainly know that this almost always happens at 4-5 o’clock in the morning) is considered to be:
- taking an antihistamine before bed in the dose recommended by your doctor;
- instillation of vasoconstrictor drugs into the nasal passage, one drop per nostril;
- humidification of the respiratory tract through a nebulizer with saline solution. If attacks occur frequently, the doctor may recommend doing this with the drugs Berodual or Pulmicort in specially selected doses and concentrations.
In most cases, such measures help prevent the development of laryngeal stenosis during ARVI in children prone to stenosis and allergies.