Types of urticaria
The type of urticaria depends on external factors and the way the allergen affects the body. In this regard, the classification considers such types of urticaria as:
- spontaneous - occurs without a specific preliminary effect on the body;
- physical - manifests itself after certain contact or exposure to external factors.
Depending on the irritating allergen, physical urticaria can be of the following types:
- cholinergic – occurs against the background of stressful situations, increased emotional and physical stress, a sharp rise in temperature;
- dermographic - appears after a slight violation of the integrity of the dermis - scratches, squeezing, friction.
- cold - manifests itself due to the influence of negative external factors - wind, air, low temperature water;
- thermal – symptoms appear after staying in an area of increased heat exposure;
- solar – occurs against the background of exposure to ultraviolet rays on the body;
- aquagenic , which is provoked by water. When it comes into contact with the skin, it dissolves the allergen and promotes the penetration of negative substances into the dermis;
- vibration , as the body’s reaction to vibration (jackhammer, shaking in transport);
- contact , which occurs after direct contact with a strong allergen - pollen, dust, wool.
According to the nature of the disease, urticaria can be acute or chronic:
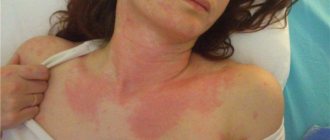
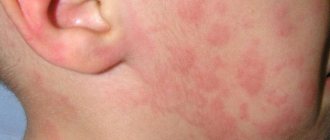
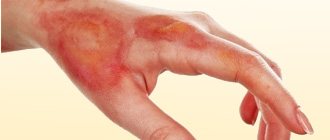
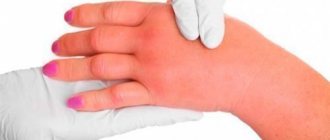
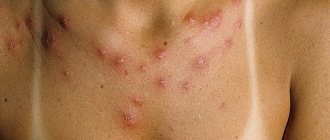
- Acute stage - symptoms appear suddenly and sharply, accompanied by intensely colored rash lesions, swelling of the subcutaneous tissues and mucous membranes (Quincke's edema) and debilitating itching. From the moment the disease is detected until the symptoms completely disappear, it can take from several hours to several days, but no more than 6.
- Chronic stage - it is characterized by relapses of the disease, which appear again after a period of recovery, caused by the patient’s high sensitivity to irritants. Periods of remission are followed by periods of exacerbation due to infectious diseases, gastrointestinal disorders, and also depending on seasonality.
Rash caused by digestive problems
The condition of the skin largely depends on the functioning of the internal organs. Using a map of rashes on the face, you can determine which organs have problems.
- pimples on the forehead indicate problems with the intestines;
- a rash along the hairline indicates problems with the gallbladder;
- pimples on the bridge of the nose - liver problems;
- ulcers on the temples - problems with the spleen;
- rashes above the lip - disruption of intestinal function;
- pimples on the nose - heart disease or endocrine disorders;
- rash on the chin - gynecological problems.
Causes
After the first signs of urticaria appear, it is necessary to analyze the possible causes of its occurrence and observe how long the symptoms will remain most pronounced. The reasons why urticaria does not go away even after the second month of treatment include:
- medicines;
- food agents;
- household irritants;
- chronic pathologies;
- physical exercise;
- prolonged depression;
- hormonal imbalance;
- unfavorable external factors.
When possible irritants are eliminated and the body is reinforced with drugs that neutralize allergens - antihistamines, the urticaria will go away.
But the cause of persistent urticaria can also be the idiopathic form of the disease.
Idiopathic urticaria is a symptomatic manifestation of a malfunction of the immune system, leading to an autoimmune disease that cannot be treated, but becomes chronic.
This is exactly the case when acute periods can last several months and be replaced by remissions lasting up to six months.
Skin rashes due to gynecological problems
The condition of a woman’s reproductive organs is closely dependent on her hormonal levels. Many diseases (uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis) are caused by hormonal imbalance, in particular, the ratio of androgens (male sex hormones) and female sex hormones, which is primarily signaled by a specific rash on the skin. Androgens, particularly testosterone and DHT (dihydrotestosterone), are produced in women by the adrenal glands and testicles. The cells lining the sebaceous glands of the skin have androgen receptors. When the amount of hormones increases, the receptors react and the skin secretes more sebum, creating a nutritional base for bacteria. Moreover, DHT begins to be produced by the adrenal glands even before the onset of puberty, so in adolescents, especially girls, rashes have been observed since the age of 10-12.
When a woman has polycystic ovary syndrome, the amount of female hormones estrogen and progesterone decreases and the level of androgens increases sharply. Along with menstrual irregularities, a woman develops severe “teenage” acne on her face and chest. Darkening of the skin is noticeable in the groin, armpits and around the neck. The woman also notes increased hairiness on her legs, arms, and above her lip. All this is due to hormonal imbalance.
An increase in the level of female hormones also affects the condition of the skin. In addition to acne on the face and body, excess estrogen makes the skin dull and dull. She seems to be losing her tone. There is also a decrease in blood sugar levels and an increase in platelet counts.
The increase in progesterone also does not go away without leaving a trace. The skin has progesterone receptors, which respond to the growth of the hormone by increasing the production of sebum until the appearance of oily seborrhea. The scalp becomes covered with crusts, pink spots appear on the face and body, the skin on which flakes and flakes off. In adolescents, the face becomes covered with bumps, which, when pressed, release a liquid sebaceous secretion.
Babies also experience hormonal rashes, which can be very frightening for a new mother. This is the so-called neonatal cephalic pustulosis. It arises because the baby begins to live separately from the mother’s body, and for him this is a serious hormonal shock. The secretion of the sebaceous glands increases, the ducts become clogged, which creates favorable conditions for the activity of microbes.
Diagnosis and identification of the cause
Diagnosing urticaria, as a rule, does not cause difficulties for a therapist or allergist-immunologist. However, in cases where the disease does not go away for more than 2 months, and traditional antihistamines for this treatment do not help, a more in-depth and thorough examination of the patient is required. It includes:
- collecting a general medical history;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- liver tests;
- test analysis to determine the allergen irritant;
- examination for the presence of parasites in the body.
After studying all the data, you may need the help of specialists such as a urologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist to identify concomitant pathologies that provoke urticaria. If specialists in their field do not find any abnormalities, the patient is diagnosed with idiopathic urticaria and taken under control.
Rashes due to liver diseases
In the early stages of liver disease, they practically do not manifest themselves at all. The earliest symptom is specific skin rashes. They are caused by an increase in the amount of bile acid in the blood, which causes general intoxication of the body. The skin takes on a yellowish tint.
With cholestasis (blockage of the bile ducts), the rash is localized on the feet and palms, looking like marks from a burn. With cirrhosis, liver cells die and the whole body becomes covered with spots. Parasitic liver diseases cause rashes resembling hives. They are localized in the lumbar region and abdomen.
Also characteristic is a combination of rash and spider veins, which cause severe itching, which intensifies at night. Taking antihistamines (allergy medications) does not provide relief. Increased bilirubin gives the skin a yellowish tint.
Treatment
For urticaria, treatment is prescribed by a specialist in the field that relates to the causes of the disease. In the chronic form, treatment can be outpatient, while in acute urticaria it is necessary to be treated only in a hospital setting.
Therapeutic tactics consist of the following stages:
- elimination of all provoking pathogenetic factors;
- identification and treatment of foci of chronic infections in the body;
- exclusion of possible irritants;
- consultation of specialists;
- normalization of the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system.
Drug therapy for urticaria includes antihistamines, sorbents, laxatives, medications that support the gastrointestinal tract, calcium-containing medications, and iron supplements. In severe cases of the disease, glucocorticoids - steroid hormones and histaglobin - are prescribed.
Treatment involves the use of external agents - ointments, compresses, baths, as well as cleansing enemas.
Polina Vasilyeva
dermatologist
| If you or your baby are experiencing urticaria in one form or another, it is important to know a few first aid rules. They consist of applying a cold compress in combination with taking 2nd generation antihistamines. If urticaria is accompanied by suffocation, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing and breathing, blueness of the face, as well as symptoms of anaphylaxis (drop in blood pressure, dizziness, loss of consciousness), you must immediately call an ambulance! The doctor will give an injection of adrenaline, which acts on anaphylaxis with lightning speed (unlike antihistamines and hormonal drugs). Also, if possible, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen as quickly as possible and provide the patient with plenty of fluids. |
Recommendations to speed up the healing process
For urticaria that does not go away for more than two months and causes physical and mental discomfort, the following rules must be followed on the path to recovery:
- take the medicine strictly as prescribed;
- exclude foods with a high allergenicity index from the diet;
- keep daily entries in a diary listing all foods eaten;
- clothes, bed linen, towels should be made only from natural fabric;
- do not use scented personal care products, avoid cosmetics with fragrances and dyes;
- try to avoid aggressive effects on the skin from external factors;
- wear shoes and clothes that fit;
- after an insect bite, wounds should be treated without delay;
- avoid strenuous physical activity;
- strengthen immunity.
We must not forget about the psychological aspect of urticaria - we must try to receive only positive emotions (they will replace pills) and not subject the sensitive mental organization to stress.
If urticaria is treated, adheres to an appropriate lifestyle, monitors changes in symptoms and takes control of the disease in time, then the quality of life will not be affected, even if the disease has not gone away.
Author: Natalya Kuznetsova, doctor, especially for Dermatologiya.pro
Rashes due to intestinal diseases
If the contents of the intestines are poorly removed from the body, then some of the toxins will begin to penetrate into the blood. The body begins to get rid of poisons itself through the excretory system. Because of this, the condition of the skin worsens, and it becomes characteristic of:
- increased fat content
- dull complexion
- acne, not only on the face, but also on the back, stomach, chest
- noticeable “black dots” similar to volcanic craters
- skin becomes dry and dehydrated
- After acne heals, scars remain.
After the New Year holidays, many people note a deterioration in their skin condition and notice minor rashes that go away on their own. They are associated with contamination of the body with toxins caused by eating large amounts of heavy food.