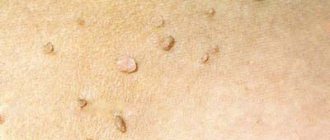
Papilloma is a benign tumor-like growth; such formations can grow on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. The nature of origin is viral. The virus enters the body and causes disruption in the functioning of cells. Depending on the location of the warts, it is decided which doctor will help the patient with papillomas.
When should you go to a specialist?
If growths appear on the skin, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor, even if the growths are small and do not cause any discomfort.
You should sign up for a consultation if:
- papillomas on the body;
- warts of various sizes;
- condylomas - growths on the external genitalia or in the anal area.
First, the patient must contact a therapist, who will determine the presence of a problem and refer to a specialist to prescribe adequate treatment.
Prevention of papilloma
Preventive measures in the described case are not much different from the measures taken to avoid any other disease.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, work and rest regime.
- Proper, balanced nutrition.
- Regular physical activity.
- Compliance with the rules of conduct in public places.
- Having a permanent healthy partner or using personal protective equipment during sexual intercourse.
- Vaccination against certain strains.
REFERENCE! Two types of vaccines are becoming increasingly popular: Gardasil and Cervarix. They contain capsid proteins that take the form of virus-like particles. These particles do not contain viral genetic materials. The effect of the vaccines is aimed at several viral strains that are more common than others: 6, 11, 16 and 18. The drug must be used as early as possible, since the vaccine does not work on already infected adults. Acceptable age is 9 years.
Why shouldn't you postpone your visit?
It is necessary to obtain qualified assistance; independent removal of skin growths using folk or traditional medicine can aggravate the condition.
Most strains of papillomavirus are harmless; they provoke the appearance of benign growths, however, if the formation is injured, certain risks arise:
- Papilloma is a source of viruses. If its integrity is violated, viruses are released into the environment in large quantities. This way, you can infect people around you, as well as spread the virus across your skin.
- If the papilloma is torn off or damaged, there is a possibility of secondary infection, which can lead to suppuration and even sepsis.
But that's not the worst thing. The main danger of having papilloma lies in the fact that not all strains of the virus have a low oncogenic status. There are viruses that provoke the appearance of malignant neoplasms, such strains include 31, 33, 35, 39, 16, 18, 45, , 52, 59, 58, , 68.
There is no way to determine the strain yourself; for this you need to undergo special studies. For this reason, if any growths occur on the skin, you must immediately contact a specialist, undergo an examination and begin proper treatment of the pathology.
Description of HPV
Human papillomavirus, abbreviated as HPV, belongs to a family of viruses that can cause warts and warts in skin cells. Today, 100 species of this microorganism have been discovered. Some of them can be dangerous. According to WHO, 70% of the world's population suffers from this insidious microorganism. It may not manifest itself in any way at first, but will make itself felt years later. At first, growths appear in various parts of the body.
Infection is possible even in childhood. The virus prefers areas with microdamages. Children have to deal with them regularly due to their increased activity. Kids love outdoor games. They often receive cuts, bruises and other types of injuries. On the surface of their skin, the infection manifests itself in the form of warts. Adults may encounter genital warts. They are transmitted sexually.
The virus penetrates the mucosa through microcracks from the partner. If the immune system is strong enough, then when microorganisms enter, they can be easily defeated. But when it fails, the disease manifests itself in the form of condylomas and warts. HPV invades the cell's DNA and affects its function, causing increased epithelial growth. Growths form on the epidermis. Any contact with a carrier of the virus can result in infection. Light contact with the mucous membrane or skin, for example, when shaking hands, can contribute to this. There are factors in which the development of the disease is observed especially quickly :
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
Which specialist should I go to, who deals with HPV removal, a surgeon or a dermatologist?
As mentioned above, you should initially consult a therapist or dermatologist. Further, you may need to consult with specialized specialists, depending on the location of the formation.
Most often, papillomas appear in places of constant moisture - in the inguinal folds, in the axillary region, on the genitals, and even on the mucous membrane of the growth cavity.
Growth on the neck, on the skin
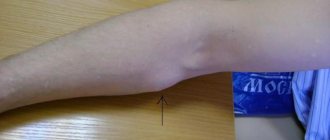
On the neck, papillomas look like papillary growths that look like cauliflower leaves. The neck is a favorite place for papillomas, and they are injured in this area quite often (friction of a collar, scarf, and so on).
At the initial stage, the growth on the neck may not differ in color from the general color of the skin, but later it may acquire a pink or brown tint.
Papillomas on the neck are treated by a dermatologist; if he determines that the pathology is caused by an oncogenic strain, he will refer the patient to an oncologist; if it is necessary to remove the tumor, the help of a surgeon will be required.
Papilloma on the face
Papillomas on the face can appear in various places. If the tumor is located on the eyelid, you need to contact an ophthalmologist, who, after all the necessary tests, will excise the tumor. Growths located in close proximity to the organs of vision are removed using a laser, liquid nitrogen or a scalpel.
HPV in intimate places on the body in an adult
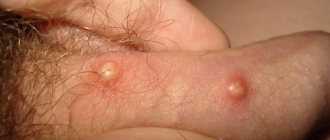
When the papilloma virus affects the male genital organs, formations can be located on the penis, around the head and on the scrotum.
In women, papillomas are localized on the labia majora and minora, on the vaginal mucosa, on the clitoris and on the cervix. In addition, in people of any sex, papillomas can appear in the anus, urethra and groin area.
Papillomas on the genitals can be:
- thread-like;
- flat - small bumps that can cause an unpleasant itching sensation.
Reference! Most often, genital warts are diagnosed, which are also called genital warts.
Genital warts should be treated by a gynecologist or urologist, depending on your gender.
In the oral cavity, papilloma can be recognized by the following signs:
- the size of the neoplasm is approximately 1 cm;
- the surface of the growth is rough;
- papilloma is attached to the mucous membrane with a thin stalk or wide bottom;
- the color of the neoplasm is light or pinkish;
- the growth does not cause pain when pressed.
In the mouth, on the tongue
If papilloma is detected in the oral cavity, it is necessary to make an appointment with a dentist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to an oncologist or surgeon.
So, the area of responsibility of a dermatologist includes skin diseases. You should contact this specialist if you have papilloma on the face, neck, armpits, palms, feet, stomach or back. If papillomas are located in the oral cavity and on the genitals, this doctor does not prescribe treatment, but only conducts a superficial examination.
A gynecologist treats genital warts on the intimate organs of women; growths on the genital organs in men are treated by a urologist or andrologist.
If you have papillomas in the anal area, you need to contact a proctologist; in addition to a visual examination of the anus, he will conduct a colposcopy to get more information about the prevalence of the virus.
If the growths are localized on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue or under it, you need to go to the dentist; if there are papillomas on the uvula and larynx, you need to consult an otolaryngologist.
An ophthalmologist can prescribe the correct therapy for papillomas located on the eyelids. The patient is referred to a surgeon after determining the benign quality of the tumors for their removal.
The help of an oncologist is required if a highly oncogenic papillomavirus is detected in the patient’s body.
Hardware procedures for removing papillomas
The doctor can write out a referral for hardware procedures to remove papillomas. There is no need to be afraid, because such techniques are famous for their quick results.
- Cryodestruction - the device works using the ultra-low temperature freezing method. The specialist uses liquid nitrogen to influence the formation, resulting in a bubble that will resolve within a week. An inconvenient method for plantar warts, since walking becomes limited due to the blister.
- Electrocoagulation – helps with body warts and papillomas. Removal is possible even in open areas - décolleté, arms. Using a device with high frequency, the growths are affected.
- Laser excision - a laser system can get rid of growths even on the face, since the possibility of scars is minimized. the laser accurately calculates the depth of the papilloma, so one session is enough to remove it.
- Radio wave method - papillomas are cut off with a special knife, leaving no traces. A very expensive method, but the most effective. Eliminates the possibility of relapse of the disease.
- Surgical excision - using anesthesia, the surgeon cuts out the growth and sutures the affected area. There will probably be scars. Used for large formations.
Who treats warts in children?
Papillomas can appear not only in adults, but also in children. Most often, the reasons lie in the child becoming infected with molluscum contagiosum. Children with weak immune systems are at risk. The following types of papilloma can be observed in children:
- vulgar;
- threadlike;
- flat;
- plantar;
- laryngeal papillomatosis;
- warty dysplasia;
- epithelial hyperplasia.
Of course, with any neoplasm on the skin or mucous membrane, it is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician, and, if necessary, to a narrow socialist, but an immediate visit to the doctor requires the following changes:
- the papilloma has become dark red or black;
- education is actively growing;
- the growth has acquired an unusual, non-rounded shape;
- When pressing on the formation, the child feels pain.
The pediatrician may refer the child to a surgeon or dermatologist to remove the papilloma from an open area of skin; see a proctologist or gynecologist if the papilloma is localized in the anus or perineum; with papillomas in the oral cavity, a child is referred to a dentist or otolaryngologist.
Diagnostic Basics
HPV on the skin provokes the appearance of neoplasms in the form of growths. Epithelial cells rapidly divide, which leads to an increase in growths. Depending on the state of immunity, one or another number of papillomas appear on the epidermis.
Initially, there is no discomfort from the presence of neoplasms. But despite this, you should not delay visiting a doctor. Sometimes warts and papillomas grow quickly and reach impressive sizes in 5-7 days. If you miss the initial stage of the disease, there is a risk that you will have to undergo treatment by an oncologist instead of a dermatologist.
How is human papillomavirus diagnosed in men and women?
Diagnostic activities begin in the specialist’s office. He asks in detail about the patient's condition:
- how long ago did education appear;
- whether its color or shape changes;
- what additional symptoms are there?
- what assumptions are there about the route of infection;
- Do your relatives and friends have papillomas?
After the history is collected, the doctor visually examines the growths, paying attention to their number, color, structure, size and location. If the doctor has doubts about the benignity of the neoplasm, he will refer the patient for histological analysis.
To determine the nature of the infection, PCR is prescribed. To determine the strain of the virus and the degree of its oncogenicity, a Digene test is prescribed.
If the papilloma is located on the intimate organs or in the anal area, both men and women must undergo a series of additional examinations that will exclude or confirm the presence of tumors on the internal organs. Only after a thorough diagnosis does the doctor decide on the need to remove the papilloma and further treatment.
Preventive recommendations
In order to prevent the reactivation of the papillomavirus, men and women need to follow the rules of personal hygiene, regularly take vitamin complexes, monitor the cleanliness of bed linen, clothes, shoes, streamline their sex life and avoid frequent changes of sexual partners. Such measures help curb the pathological effect of the virus and protect the body from the manifestations of HPV.