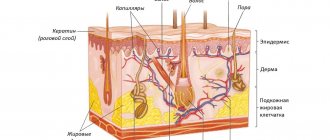
Skin hyperemia is a pathological condition manifested in abundant blood flow to a particular area of the body with severe redness of the skin. The disease is not contagious. Facial hyperemia causes a lot of inconvenience to a person, because sudden and severe redness of the skin on the face looks extremely unaesthetic.
General characteristics of the disease
Hyperemia, which occurs for natural reasons, accompanies the entire life of every person. A short-term rush of blood to the face is caused by a reaction of the nervous system to overheating or hypothermia of the body, the release of hormones during emotions, physical activity and mechanical stress on the skin.
It is important to pay closer attention to hyperemia, which manifests itself for no apparent reason. In this case, the overcrowding of tissues with blood indicates disturbances in the vascular system or a pathological process in the body.
There are two forms of hyperemia:
- arterial (active);
- venous (passive).
By origin, hyperemia is divided into:
- physical (the influence of temperature, atmospheric pressure);
- mechanical (friction, shock);
- chemical (alkalis, acids);
- biological (toxins, metabolites);
- emotional (feelings of joy, shame, anger).
Venous hyperemia can be acute or chronic. The chronic form occurs against the background of chronic heart failure, when the pumping function of the heart cannot provide adequate hemodynamics.
Pathogenesis of venous hyperemia
The main links in the development of venous hyperemia are the occurrence of an obstacle in the blood flow (thrombosis, compression) and a violation of the mechanisms of its regulation by the pumping function of the heart.
Since the venous system has well-developed connections, blockage of the veins often occurs without a change in pressure or occurs for a short time. The main reason for the increase in venous pressure is the insufficient development of collaterals - bypass routes for the outflow of blood flow when an obstacle occurs in the vessels.
As venous pressure increases, the capillaries dilate. This is facilitated by the peculiarity of the connective tissue of the capillary walls, which are highly extensible.
Due to slow blood flow in areas with venous stagnation, there is an intense release of oxygen into the tissues and a more active entry of carbon dioxide into the blood. As a result, disturbances in the composition of the blood occur with a deficiency of oxygen and an excessive content of carbon dioxide.
Externally, this is manifested by redness of the tissues with a bluish tint (cyanosis). This is explained by the predominance of reduced hemoglobin in the blood, which has a dark cherry color and, when visible through the skin, visually appears bluish.
Pathogenesis of arterial hyperemia
Arterial hyperemia develops after the expansion of arterioles and an increase in the number of active capillaries, which increases the mass of blood flowing through the tissue. Basically, the expansion of arterioles occurs due to irritation of tissue or vascular receptors.
This may occur due to increased tone of the vasodilator nerves, suppression of vasoconstrictor mechanisms, or complex transmission of reflexes from damaged tissues to the vessels.
The reason for the dilation of blood vessels may be the lack of special impulses sent by the nervous system to narrow them. This occurs due to the destruction of vasoconstrictor nerves (vasoconstrictors), due to severe injuries, severe infections or intoxications.
The expansion of arterioles can be provoked by metabolites: amines and kinins, which accumulate on the walls of arterioles. This disrupts their functionality and additionally stimulates central vasodilator mechanisms.
The constantly increasing speed of blood flow provokes the opening of previously inactive capillaries. Thus, the number of functioning capillaries increases.
With increased blood flow, the release of oxygen from the blood to the tissues is limited. As a result, oxygen and oxyhemoglobin accumulate in the venous blood, giving the blood a bright red color, which affects the color of the tissues.
Women over 40 years of age are susceptible to the appearance of hyperemia. This is explained by hormonal changes associated with a decrease in the synthesis of the hormones progesterone and estrogen. People with congenital vascular and heart diseases are at risk. Hyperemia is more noticeable in appearance in people with thin and white skin.
Causes
There are many main reasons why cheeks are red. This:
- fluctuations in the emotional state (a person does not control these reactions, their manifestation is associated with the work of the autonomic nervous system, its sympathetic department);
- hormonal changes in the body (adolescence, menopause);
- taking medications (especially hormonal ones);
- alcohol consumption;
- in rare cases - liver or stomach diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- hypersensitivity and skin diseases.
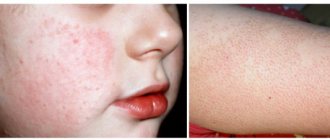
Flushing, which externally manifests itself as red cheeks, causes stretching of the capillary walls and their thinning. As a result, blood stagnates in small blood vessels and produces harmful substances. Frequent redness of the cheeks leads to serious consequences - the development of rosacea. It is easy to identify it at home, but for treatment you need to see a doctor.
The child has
The baby's rosy cheeks delight parents and are perceived as an indicator of health; the pale skin of young children is more worrying. If your child’s cheeks suddenly turn red or this phenomenon occurs frequently, it may be associated with illness or the presence of a disease. Don’t worry right away if your child’s skin turns red due to certain factors:
- after playing in the cold, walking in the cool season (the blush lasts about half an hour after returning indoors);
- psychological reaction of the child (anger, shyness) - the redness will disappear when the child calms down;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- in children 1-2 years old, redness is observed after eating (especially in those who can eat on their own, the remains of some dishes cause irritation on the baby’s delicate skin).
There are reasons that should definitely alert attentive parents:
- red spots on the cheeks when the skin of the nose and the skin around the mouth turns red and burns when teething;
- redness of the entire face and chin - indicates dryness and high temperature in the room;
- red spots on a child’s cheeks, peeling, itching – appear due to diathesis and allergies;
- redness of a point nature, followed by the appearance of tubercles - may be an indicator of the presence of parasites in the child;
- red hot cheeks with pallor of the tip of the nose and lips, lethargy, poor appetite, cough, fever - sure signs of pneumonia;
- Red cheeks during night sleep are evidence of heart disease.
In an adult
Redness on the cheeks of an adult becomes an indicator of serious diseases and allergic manifestations. This reaction occurs from several hours to several weeks. There are many reasons for redness: some are associated with genetic disorders, others are simple reactions to environmental influences. In some cases, the doctor recommends that the patient undergo blood and urine tests.
Red skin on the cheeks is due to one of the reasons:
- blood flow during exercise;
- allergic reactions;
- hormonal changes;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- reaction of sensitive skin to the sun and wind;
- infectious diseases.
Why do teenagers' cheeks turn red?
From a physiological point of view, adolescence is a difficult period. At this time, growth processes are actively launched, the sex glands begin to work, and hormonal levels change dramatically. The teenager’s body still needs to get used to the new substances that have appeared in his blood. Facial redness in adolescents may be associated with this. When hormone levels stabilize, the phenomenon disappears.
In addition, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system is observed in the body of a teenager. The heart grows faster than blood vessels, so it has to work harder. In this regard, during adolescence, changes in blood pressure are observed, which can cause red skin on the cheeks. When the processes of the final formation of the cardiovascular system are completed, such reactions stop.
Causes of hyperemia on the skin of the face and neck
Hyperemia, which occurs due to natural causes, does not require treatment and quickly disappears after eliminating the etiological factor. Prolonged and persistent hyperemia always indicates serious disorders and diseases in the body.
Main reasons:
- all allergic diseases;
- carcinoid syndrome;
- inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- blood diseases: thrombophilia, erythrocytosis;
- intoxication with chemicals, alcohol, helminth metabolites;
- disruption of hormone synthesis (menopause, menopause, hormonal diseases);
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system;
- Kawasaki syndrome;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- cardiovascular failure;
- inflammatory processes in blood vessels;
- prolonged compression of veins (tumor, ligature), space-occupying injuries;
- disorders of oxygen transport from the lungs (bronchopulmonary diseases, pneumonia, ascites, peritonitis).
In some people, excessive facial redness is associated with individual characteristics of the body. This is due to the thickness of the epidermis and blood vessels, hypersensitivity of the nervous and hormonal systems.
Assessing the redness of the cheeks
If an adult's cheeks often turn red, you should see a doctor who can help identify the cause of the problem.
It is important to understand when red cheeks first appeared. If this happened near a body of water, it is simply a reaction to weather conditions. In this case, it is enough to buy sunscreen - it will protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation and prevent redness from appearing. If the skin turns red during physical activity, this is fatigue. When spots appear and disappear spontaneously, this is a clear symptom of an allergy. It is necessary to monitor exactly when they appear: after eating food, contact with animals, or using chemicals. Symptoms of an allergic reaction are well relieved by antihistamines.
If the redness of the cheeks is associated with problems of any organs, treatment with local drugs will not help. It is important to eliminate the root cause, and redness will stop bothering you. During therapy, you should not use cosmetics; it is advisable to exclude unhealthy foods and possible allergens from the menu.
Main symptoms in women
Since venous and arterial hyperemia cause different changes in the vascular system, hemodynamics and blood composition, the clinical manifestations of the two forms differ.
With venous hyperemia, the skin becomes dark cherry in color with a bluish tint. The face is always cold to the touch and swollen. Turgor decreases. In some cases, swollen large and small vessels protrude above the skin. This form of hyperemia is characterized by numerous vascular “stars” on the wings of the nose and cheeks.
With arterial hyperemia, the face becomes bright red, hot to the touch, there is no swelling, and elasticity is normal.
Redness may appear locally or spread over the entire area of the face. With local manifestation, red spots are most often located on the back and wings of the nose, cheeks, and neck. Hyperemia does not appear on the forehead.
Consequences and complications of the disease
How venous hyperemia or arterial hyperemia will turn out in the future, if timely treatment is not carried out, depends on the causes of occurrence and the intensity with which the development and aggravation of the disease occurs.
In most cases, arterial hyperemia has negative consequences, mainly of an aesthetic and moral type, especially if redness occurs on the face. A person begins to feel embarrassed about his appearance, and complexes arise about his appearance.
The lack of proper treatment will lead to the development of accompanying symptoms - itching and burning; a person may damage the skin when scratching, which can cause a secondary infection.
The consequences of hyperemia of the venous or arterial type can be much more severe than just moral dissatisfaction with appearance. In the venous type of the disease, blood circulation is impaired due to poor blood flow through the veins due to blockage of the blood vessel.
If the disease is not treated, the gap between the walls of the veins will close even more. In the future, this will lead to the fact that blood, which cannot pass through the vessel, will begin to accumulate in the reservoirs of the veins.
The result of this process will be a decrease in blood pressure, poor blood circulation in the brain, due to which the organ will not be able to receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients and will not function fully. With arterial hyperemia, blood will overflow the blood vessel, provoking a rapid increase in pressure on a particular part of the body.
Other more dangerous consequences of skin hyperemia are rupture of blood vessels under the pressure of a large amount of accumulated blood, resulting in internal bleeding. If blood flow is slowed down for a long time, this means total dysfunction of the heart muscle with the prospect of organ failure.
Diagnostics
For prolonged manifestations of hyperemia, you should contact a dermatologist or therapist. Since hyperemia is considered as a symptom of various pathologies and disorders, a comprehensive examination of the body is prescribed.
The examination includes:
- collection of anamnesis, analysis of the clinical picture;
- general blood, urine, stool tests;
- angiography, Dopplerography of blood vessels;
- monitoring pulse, blood pressure;
- hormonal studies;
- electrocardiography;
- computed tomography;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs.
Depending on the ongoing disease, different specialists are involved in the diagnosis and determination of treatment tactics.
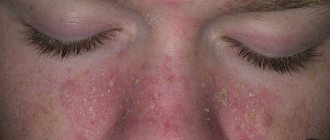
Allergy on the cheeks
There are many reasons for the appearance of allergic skin reactions that appear on the face in children and adults, these include:
- toxicosis in pregnant women;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- unformed immune system;
- pet hair and skin/immune system reaction to it;
- cosmetics of dubious quality;
- contact with household chemical cleaners and detergents;
- carcinogens in food.
Allergic manifestations are not the only reactions of the body; the disease manifests itself in redness and rashes in other parts of the internal organs, inflammatory processes on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, eyes, enlarged lymph nodes, the appearance of signs of eczema, dermatitis. You definitely shouldn’t perceive red spots on your face as a harmless reaction or an aesthetic defect.
- Ilizarov apparatus for fusion and lengthening of bones. How to install the Ilizarov apparatus in the treatment of fractures
- Brine for cucumbers per 1 liter of water
- Volumizing hair mask
Treatment of hyperemia
There is no independent treatment for hyperemia. The disease goes away only after the etiological factor is completely eliminated.
After determining the cause, the patient is prescribed treatment with drugs for a specific pathology. For general treatment, auxiliary drugs may be prescribed for specific indications.
Vasodilating agents
Drugs in this group dilate blood vessels, strengthen their walls, improve local microcirculation and rheological properties of blood (viscosity, fluidity).
Fixed assets:
- Trental;
- Vazonite;
- Rhodamine;
- Pentoxifylline.
The duration of treatment and dosage of drugs are determined by the attending physician.
Sedatives
Medicines in this group are prescribed to relieve psychomotor agitation. They help cope with the manifestations of hyperemia of emotional etiology.
These are herbal preparations:
- valerian;
- motherwort;
- mint;
- oregano.
A continuous course of treatment of at least 3 weeks is recommended.
Electrocoagulation procedure
The electrocoagulation procedure is indicated after completion of the treatment complex. It is used to eliminate dilated vessels and capillaries. This allows you to even out the skin and remove defects that give it an unaesthetic appearance.
The basis of the method is the effect on hyperemic vessels of a high-frequency current, which is performed with a needle electrode or a directed beam of light. This is the cauterization of blood vessels, in place of which crusts form and fall off over time.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Session duration is 5-10 minutes, recovery period is up to 10 days. Depending on the area of the lesion, several procedures may be needed.
Folk remedies
Herbal remedies are used to protect the skin, reduce itching, lower local temperature, alleviate burning sensation and regulate local metabolism.
Recipes
- Elimination of rosacea.
Aloe juice diluted with warm water (1:1) is used to treat rosacea, one of the complications of hyperemia. Wipe the skin of the face and neck with the product 3–4 times a day.
- Strengthening blood vessels.
Cucumber (1/2 pcs.) and aloe leaf (1/3 pcs.) are grated on a fine grater. Add 1-2 drops of a 5% vitamin C solution to the mixture. Apply the mixed mixture to the face and neck, leave for 20 minutes and rinse with warm water.
At least 20 procedures are recommended with a frequency of 2 times a week.
- Healing ointment.
This remedy is used for skin redness caused by exposure to cold and wind. To prepare the ointment, mix Vaseline (20 g), zinc ointment (10 g) and salol (3 g). Apply the product to problem skin 3-4 times a day.
- Compresses.
To normalize blood circulation and relieve redness, decoctions of herbs are used: string, raspberry leaves, coltsfoot, thyme, clover. For the procedure, a gauze napkin with slits for the eyes and nose is used, which is soaked in a cold broth and applied to the face. When the napkin becomes warm, it is re-dipped in the broth and applied again. The procedure is repeated up to 7-10 times. It is useful to take decoctions orally, 100 ml 3 times a day.
- Lotion.
To prepare the product, you need to mix Hoffmann drops (40 ml) and a 2% solution of boric acid (40 ml). The lotion is used to wipe the skin in the morning and evening to relieve irritation and redness.
When treating an underlying disease, all folk remedies are used only after the doctor’s approval.
Nutrition and hygiene for redness
There is no specially designed diet for facial hyperemia. It is recommended to improve the functioning of the digestive system. Exclude from the diet:
- hot, spicy and fatty foods;
- strong tea, coffee;
- alcoholic drinks.
Eating too hot food and drinks will cause additional vasodilation. Therefore, they are consumed only warm. Products containing vitamins A, E, K, P, C are introduced into the diet.
In case of tissue congestion, wash with exclusively warm water, using special products with moisturizing and soothing ingredients. Despite the fact that cold water constricts blood vessels, this phenomenon is temporary. After the temperature normalizes, hyperemia will manifest itself even more strongly.
To dry your face, use a soft towel made of natural fabrics, which you blot your skin with. After each water procedure, protective agents are applied to the skin depending on the weather (sun, cold). Apply the products with light movements without pressing on the skin.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS: SYMPTOMS OF DISEASES ON THE FACE
How can you learn from your tongue about malfunctions in the spine, stomach, and liver and prevent them? CURVATION OF THE FOLD AT THE TIP OF THE TONGUE signals cervical osteochondrosis. Most likely, this is the result of a sedentary lifestyle, long work with a computer or at a desk. BENDING THE FOLD IN THE MIDDLE OF THE TONGUE is lumbar osteochondrosis, it usually affects professional drivers and people who spend a lot of time behind the wheel.
To avoid osteochondrosis, you need to regularly do a warm-up: several squats, turning your head - simple but very useful exercises. REDdening of the tip of the tongue is a sign of weak cardiac activity, beginning of coronary artery disease. Diseases of the pulmonary system can be judged by changes at the edges of the tongue, closer to the tip.
Diseases of the heart and lungs most often affect smokers, so such changes in the tongue are a serious reason to quit smoking. YELLOWSHIP ON THE TONGUE AND PALATE indicates liver disease, chronic cholecystitis. BY THE PLAQUE AT THE BASE OF THE TONGUE one can judge about disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. TEETH PRINTS ON THE TONGUE are a sign of dysbacteriosis, slagging in the body.
In this case, it is worth changing your diet, eating less fatty and fried foods. To bring order to the body, you can take different herbal infusions. For example, brew 1 tablespoon of St. John's wort with 1 cup of boiling water and leave in a warm place for 30 minutes. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day before meals for 2-3 weeks.
TRIMING OF THE TONGUE is a manifestation of neurasthenic syndrome. Here the advice is this: try to improve the psychological situation at home, at work, change your lifestyle. CRACKS IN THE TONGUE can indicate various diseases of the blood, endocrine system, and kidney pathology. This is where we need to check most seriously.
A bluish shadow in the inner corner of the eyes: the weak point of the body is the kidneys. “Bags” under the eyes: the urinary system may be out of order. The lower part of the face (with lips) signals the state of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. The way the cheekbones look and nose, depends on the gastrointestinal tract.
The area around the eyes signals diseases of the genitourinary system. Dark circles under the eyes: it is quite possible that the liver is overloaded. But sometimes this can be a consequence of very thin skin through which the capillaries are visible. Peeling, especially around the nose, can have several causes1. The tan is fading.2. In summer, skin type often changes and normal skin becomes dry and flaky.3.
there is a possibility of problems with the gallbladder. Brown spots. Pigmentation is often caused by ultraviolet radiation and will not go away on its own. Stains can only be removed by a dermatologist. In men, they can also indicate the presence of hormonal problems. Small white dots. Metabolic disorders are possible, but more often they arise from poor skin cleansing and blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Red shapeless spots. Allergic reaction to food, cosmetics or clothing; sometimes occur against the background of prolonged stress or after prolonged colds. Yellowing. Almost always speaks of problems with the liver and gall bladder - you need to urgently consult a doctor. Red vascular network. Most often this is a consequence of a sharp temperature change, but sometimes it indicates the poor condition of blood vessels throughout the body;
watch your blood pressure!Acne. At a young age, acne occurs due to the immaturity of the endocrine system, and at a more mature age (after 25 - 28 years) - due to poor skin cleansing. Men can get infections when shaving. White spots. They usually appear not on the face, but on the neck, chest, and shoulders and are called vitiligo. Doctors do not yet know exactly where this disease comes from and how it is treated, but most doctors consider vitiligo to be a manifestation of nervous strain.
Contraindications
For people prone to congestion of facial tissues, it is important to give up some habits.
If you have hyperemia, you should not:
- use paraffin masks, scrubs, peelings;
- carry out steam bath procedures, visit the bathhouse;
- do facial skin massage;
- use skin-drying products (alcohol-based cosmetics, regular soap);
- use hard sponges or cloths to wipe the skin.
It is important to avoid prolonged sun exposure, overheating and hypothermia, intense physical activity and psycho-emotional stress.
Prevention
The reappearance of hyperemia can only be prevented if all recommended rules of hygiene, nutrition and lifestyle are fully observed.
In addition, following the rules will help:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- use of protective equipment when working with aggressive chemicals;
- optimal physical activity;
- rational sleep and rest regime;
- timely and correct treatment of pathologies, the symptom of which is hyperemia.
It is important to monitor the condition of the body and undergo regular preventive examinations.
Hyperemia is a vivid example of the interconnection of all human organs and systems. Being a symptom and complication of many diseases, in advanced cases it can lead to serious consequences. As a result of disturbances in the blood vessels, cerebral edema or hydrocephalus may occur. Therefore, it is important to treat prolonged facial redness with due attention.
Why should you see a doctor?
If hyperemia is the result of a serious illness that is accompanied by headache, difficulty breathing, chest pain, dizziness, muscle cramps, and sometimes even loss of consciousness, it is vitally important to consult a doctor immediately.
First you need to call an ambulance team. Where competent specialists will take emergency measures and take care of preserving human life. In the future, you need to visit a dermatologist who will conduct a diagnosis, identify the cause of hyperemia and take measures to eliminate it.