Why do papillomas itch? As a rule, this is explained by the fact that another infection is added to the prevailing virus, the cause of which is pathogenic bacteria, which causes additional discomfort to the patient; in addition to the fact that the papilloma itches, the following signs are added: severe pain occurs, especially if the growth is localized in genital area. Let's try to figure out what will help get rid of itching and what other causes of inflammation of papilloma.
The mechanism of appearance of papillomas
The first stage is characterized by damage to epithelial cells by the human papillomavirus. A viral infection enters the body directly through small cracks in the skin, microtraumas and other damage. The pathology may not manifest itself for a long time, effectively making the infected person a chronic carrier.
The reproduction of HPV in the superficial layers of the skin leads to the appearance of growths that can cause visual and physical discomfort (itching).
HPV is transmitted both sexually and through household contact. Bad habits and reduced immunity are factors predisposing to infection.
Papilloma itches during pregnancy
Papillomavirus does not affect pregnancy in any way. The very state of bearing a child cannot be the cause of itching papilloma. Pregnancy is associated with a sharp decrease in immunity. Thus, the body tries to prevent rejection of the developing fetus.
Decreased immunity can trigger HPV activation, so warts can grow and multiply, and this phenomenon can cause some discomfort. That is why a pregnant woman whose body is infected with HPV should regularly visit a dermatologist and, together with him, monitor the course of the viral infection. Then, if alarming signals are detected, it will be possible to take control not only of the woman’s health, but also of her unborn child.
Causes of itching and discomfort
Papillomas can appear on any part of the body. The following areas are often affected:
- neck.
- Genital area.
- Armpits.
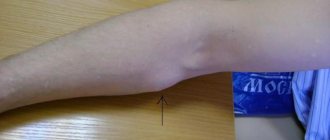
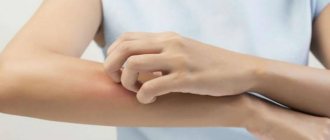
A benign neoplasm usually does not cause any discomfort and does not manifest itself in any way. If the papilloma itches and increases in size, this can be explained by many reasons.
Injury
One of the reasons why a tumor itches is because it is injured. Mechanical damage to papilloma occurs due to systematic friction of the growth on clothing, underwear or shoes. Even a scarf or headdress can contribute to injury to the tumor located in the corresponding area.
In addition, itching can be caused by unnatural fabrics from which clothing is made, or jewelry.
Occurrence of infection
Papilloma infection is a fairly common cause of itching and discomfort. Active reproduction of the virus is necessarily accompanied by swelling, slight tingling, and an increase in size of the growth. The clinical picture of the pathology suggests the appearance of new rashes.
The affected area should be kept clean. If papillomas itch, this may indicate a lack of proper care for the skin and mucous membranes. Particular attention should be paid to the groin area and anus, the appearance of growths in which is not a rare occurrence.
Excess ultraviolet radiation
Papillomas can itch from exposure to direct sunlight. Moreover, excessive passion for natural tanning can provoke not only itching, but also malignancy of papilloma.
To prevent the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation on existing growths, you should use special cosmetics before going out into the sun. It is better to choose the highest possible degree of protection.
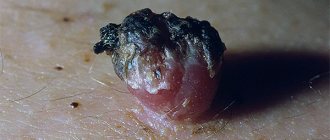
Malignant degeneration
Another name for this process is malignancy. The definition implies the transition of a growth from a benign to a malignant tumor, which explains why papilloma itches. The appearance of a tumor is necessarily accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- severe itching, pain.
- Changing the shade of papilloma.
- Inflammation of the growth and nearby tissues, redness.
- The appearance of ulcers on the papilloma, which bleed when the thin film is removed from them.
Even if the growth has dried and fallen off without using any therapy for papillomatosis, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Why do wounds itch after papilloma removal?
After removing the warts, the places where they were previously dislocated also itch. This is the natural healing process of damaged skin. Thus, the body copes with the consequences that arise after injury to the skin. Damaged tissue is rejected, the wound is cleared of them and allows the formation of new cells. During the regeneration phase, inflammatory mediators are released. Histamine is one of the causes of itching, due to which tissue renewal occurs.
A wart can itch for various reasons, but sometimes such a symptom becomes the beginning of malignancy. Therefore, if you experience discomfort associated with the growth of papilloma, it is important to consult a dermatologist and undergo a full diagnostic examination.
Treatment of itching and removal of growths
Visual changes and physical discomfort may well indicate negative processes occurring in the body. Since there is a risk of developing cancer, if the papilloma begins to itch, you should consult a doctor.
Therapy for itching involves an integrated approach, which is based on relief of symptoms and subsequent removal of papilloma. To stop the growth from itching, they take medication.
Please note: you cannot select medications yourself. Only a competent specialist can recommend a medicine.
Anti-itch medications
If suspicious symptoms occur, you should immediately visit a doctor. A qualified specialist will tell you what to do if papillomas itch.
Drug therapy for papillomatosis is aimed not only at relieving itching. The patient is additionally prescribed drugs that stimulate a weakened immune system. Taking them will suppress the human papilloma virus.
The following remedies will help stop itching and reduce the size of the wart:
- antihistamines. Typically, antiallergic drugs are taken orally.
- Antiviral. Reduce the rate of virus reproduction.
- Anti-inflammatory.
A specialist may recommend the following medications:
- Feresol. Disinfects the skin, relieves itching, and reduces the size of warts.
- Oxolinic ointment. Relieves pain and relieves physical discomfort. Use for 1.5 weeks freezes the tumor.
- Carbolic acid. Has a disinfecting effect.
- Etc.
If conservative therapy does not bring the desired effect, the patient will be offered other ways to relieve itching.
Folk remedies
In addition to drug treatment, it is permissible to use traditional medicine. It is believed that some of the home recipes may well help get rid of benign growths and associated discomfort.
If the papilloma grows and itches, it is recommended to use the following methods:
- Castor oil.
Apply to the affected area, cover the skin with a bandage. Do this bandage twice a day for a week.
- Celandine juice.
Steam the papilloma, apply a rich cream. Lubricate the tumor with freshly squeezed celandine juice. Please note: it is important not to affect healthy nearby tissue. Repeat the procedure every 2-3 days until the growth is completely removed.
- Calendula infusion.
Alcohol infusion of calendula can be purchased at a pharmacy or made yourself. To do this, add 10 grams. calendula flowers in a small container with alcohol (70%). The mixture must be infused for 2 weeks, then strained. It is recommended to wipe the resulting decoction on the affected areas. Use several times a day.
- Bay leaf.
Brew 3 leaves with a glass of boiling water, keep on low heat until the water partially boils away. Remove from heat, add boiled water. Treat the skin with the resulting decoction at least three times a day (more often is allowed).
- Propolis.
Soak a clean cloth with ointment or tincture and, if possible, fix it on the injured area. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, hold the compress for at least 10 minutes.
- Any medicinal plants.
To make lotions or compresses, pour boiling water (250-300 ml) into 1-2 tbsp. l. plants or flowers. The mixture is infused and cooled, after which it is used for its intended purpose. The most suitable plants are string, chamomile, mint, calendula.
The easiest way to temporarily relieve the itching is to lightly press the wart with a clean finger.
Please note: removing papilloma yourself can provoke infection and will only worsen the situation.
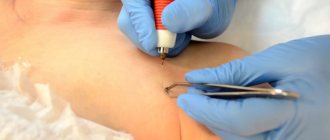
Surgical intervention
Conservative therapy can be used as an additional treatment to surgery. This applies in the following cases:
- if the papilloma itches.
- The growth has increased in size.
- A color change has occurred.
- There is severe irritation and an inflammatory process in the active stage.
The operation to remove papilloma is carried out according to the indications of the attending physician. The procedure does not take much time and significantly improves the condition of the skin affected by pathology.
There are several methods for removing papillomas, but cryodestruction is most often used. The essence of the procedure is to freeze tumors by exposing them to liquid nitrogen. The likelihood of relapse after such an operation is extremely low, and no scars or cicatrices remain in place of the previous wart.
The method of removing papillomas with a laser can be used, regardless of the size of the growth and its location. After such exposure, no traces remain, and the risk of re-infection is also minimized.
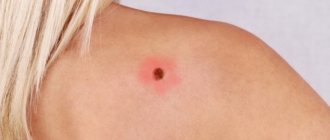
Papilloma itches - a sign of degeneration
The appearance of itching on a wart may indicate the initial stages of malignancy. The wart gradually begins to darken, its edges become inflamed, and the formation becomes covered with crusts. The process of degeneration always begins from the center of the wart, then spreads to the periphery.
But this does not happen with all papillomas, but only with those whose growth was provoked by infection with strains that have high oncogenic risks. Just being infected with them does not mean that cancer will necessarily develop. This will happen if the virus, entering the donor cell, is able to integrate its DNA into its nucleus.
The life of a human cell is programmed: it is born, divides a certain number of times during its life, then dies and becomes a breeding ground for other cells. When a virus inserts its DNA into the cell nucleus, it disables the restriction of cell division. The cell becomes immortal. Its endless division leads to the appearance of atypical cells. It is they who can be degenerated under the influence of certain factors.
Any inflammatory processes can provoke malignancy - a large dose of ultraviolet radiation, a sharp decrease in immunity. Therefore, the appearance of signs of the initial stage of degeneration should force everyone to seek medical help. Skin cancer is extremely difficult to treat, the prognosis is not always favorable, and the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of a possible recovery.
What could be the consequences?
Doctors always give an affirmative answer to questions about whether papillomas itch. Many doctors immediately warn patients about this phenomenon so that they do not worry about this in the future.
If the papilloma itches severely for a long time, it definitely needs to be checked. It is strictly forbidden to scratch the problem area on the skin, as this will lead to damage and infection. If a person decides to independently remove a problematic tumor using hands or special instruments, he risks facing the degeneration of a benign growth into a malignant one. Therefore, such manipulations must be trusted exclusively to competent specialists.
Infection of papilloma and its transformation into cancer are the most important consequences of careless handling of a growth that has begun to itch. If it itches, you need to take measures to eliminate the itching. At least thanks to this, the person will be left with an obsession to scratch the papilloma, and she will avoid serious injury.
When is a visit to the doctor necessary?
Not all viral skin neoplasms are capable of malignancy. However, you should never lose vigilance, even if the growths have been formed for a long time and the only thing that worries you is why papillomas sometimes itch. Inspect these areas of skin every time you use the toilet and notice any changes. Do not neglect consulting an oncologist if:
- inflammation appeared, micro-wounds opened, the surface began to peel off;
- color has changed;
- the edges of the skin formation have become uneven;
- there are compacted areas;
- intensive growth has been recorded.
Author of the article: Shibanov Timur Aleksandrovich
Practitioner Specialization: Infectious diseases
Publications on the site: 31 (All publications by the author)
Should I delete
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Removal of papilloma is the main component of complex treatment of viral infection, which includes taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs. The growths contain the highest concentration of pathogen cells. If you leave a papilloma on the body, the risk of spreading foci of infection increases; the person will always be potentially infectious. Permanent damage to growths due to their inconvenient location is a direct indication for disposal.
In modern medicine, papillomas are removed using hardware techniques. They allow you to achieve effective results in a short period of time, without special training or long rehabilitation.
Laser excision allows you to get rid of growths on the body. The formations are burned out under the influence of the high temperature of the laser beam. This type of treatment is quite painful and requires the use of local anesthesia. The risk of reappearance of papillomas is practically absent.
Cryodestruction or removal with liquid nitrogen. The scope of application of this technique is quite wide. Under the influence of low nitrogen temperatures, neoplasm tissues are destroyed and die. This treatment method is not recommended if the growths are located on the face, as there is a risk of residual scarring.
Diathermoelectrocoagulation allows you to get rid of warts without bleeding and the spread of viral cells. An electric current burns out the papilloma and coagulates small vessels.
Radio wave excision is considered gentle. The method is distinguished by its accuracy, bloodlessness, and painlessness. Scars and cicatrices do not remain after this procedure.
If further histological examination is necessary, the formations are removed in the usual surgical way.