Forms of the disease
Depending on the time of occurrence and duration of the disease, generalized urticaria is divided into:
- Acute - can last from several hours to several weeks, rarely exceeds the threshold of 1.5 months. When initially occurring, it can be quite severe and malignant.
- Chronic – lasts more than 1.5 months. It occurs either with frequent periods of remission and exacerbations, or is represented by a long-term, sluggish form that is difficult to treat.
On this topic
- Hives
What are the dangers of mechanical urticaria?
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2020
Depending on which link predominates in the etiopathogenesis of the disease, urticaria is usually divided into:
- immune;
- non-immune;
- idiopathic – when it is not possible to reliably establish the cause.
Among the most common forms of generalized urticaria caused by a specific allergen are:
- Contact – occurs when there is direct close contact with an allergen (household chemicals, cosmetic products, medications for topical use, etc.).
- Food – occurs after the allergen enters the body with food.
- Medicinal - clinical manifestations appear immediately after taking a particular medicinal substance to which there is an individual intolerance.
- Solar - occurs as a pathological reaction to the action of ultraviolet rays.
- Cold – periods of exacerbation of the disease are observed during the cold season (autumn, winter) – as the body’s reaction to the effect of low temperatures. It can also occur in warm weather in case of contact with low temperature water.
- Thermal - appears during a sharp transition from cold to heat.
- Aquagenic – manifested by an allergic reaction to the action of substances contained in water.
- Cholinergic – a form, the development of which is directly related to the body’s increased sensitivity to the production of acetylcholine, a substance that is an integral component in the process of transmitting nerve impulses. Occurs under stress, excessive physical activity, sudden climate change and a change in the usual habitat.
The occurrence of urticaria can be caused not only by the action of one allergen; in some cases, the development of cross-allergy is noted, in which several allergens are released at once, the action of one of which potentiates the effect on the body of the second.
When and how to reduce the fever?
Temperatures up to +38°C indicate the development of an inflammatory process. The hypothalamus specifically causes hyperthermia to facilitate the destruction of pathogens. In this case, you should not take medications. If the temperature rises to +38.5...+40°C, immediate use of antipyretics, application of cold compresses and ice baths are required.
In what cases is it necessary to reduce a child’s temperature?
When there is a fever against the background of urticaria, it is necessary to pay attention to the cause of the inadequate immune response. If hyperthermia was caused by an infectious agent, the fever should not be reduced to +38°C. When the reading is above +37°C with simple allergies, it is necessary to take antipyretic drugs.
In the latter case, indicators should not be allowed to increase above +38°C. Otherwise, interferon will begin to be produced, and the patient’s condition will worsen. The body cannot cope with the fever on its own, since the immune system is impaired.
What does official medicine offer?
If the cause of the development of high temperature was urticaria, antihistamines are prescribed:
- Zyrteca;
- Suprastina;
- Citrina;
- Erius;
- Tavegila.
If allergies occur as a result of infection, antipyretic medications such as Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are used. It is forbidden to give Aspirin to children to avoid the development of bleeding from blisters.
Traditional methods
At a temperature of +38°C, you can use traditional methods of treatment:
- Regularly ventilate the room where the patient is located to ensure access to fresh air.
- Give plenty of water. You need to drink 3-4 sips of liquid every half hour. It is not recommended to replace water with juices, compotes and tea. If desired, you can add 1 tbsp to the water. l. lemon or honey.
- A decoction of chamomile and linden helps reduce fever. 1 tsp. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over each ingredient and leave for 2 hours. Give the patient 3 times a day 150 ml.
- Do not force a person to eat.
- Avoid using warm blankets. They disrupt heat exchange.
The patient is provided with complete rest. He must remain in bed. Physical activity can lead to recurrent hyperthermia.
Causes
The main reason for the development of generalized urticaria is considered to be the introduction of an allergen into the body, which triggers a chain of allergic reactions. The most common allergens may include:
- products : meat and fish products, fruits (especially citrus fruits), dairy products, honey, berries, chocolate, food additives, flavor enhancers and flavorings;
- medications : anesthetics (often local), antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins of various groups, muscle relaxants, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, antiseptics for topical use, etc.;
- poisons of insects and snakes;
- chemicals , cosmetics and household chemicals;
- psychogenic factors that trigger the development of psychosomatic allergies;
- physical factors: cold, heat, ultraviolet radiation, water;
- parasitic infestations (roundworms, lamblia);
- periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases (especially bronchial asthma).
On this topic
- Hives
How to prevent an allergic reaction like hives
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
In addition to the etiological factors - those that are the direct cause of the development of the disease, it should be noted that there are predisposing ones - those that create favorable conditions for the start of the pathological process.
Factors that provoke the occurrence of generalized urticaria include the following:
- existing concomitant chronic current diseases of fungal, bacterial, viral etiology;
- frequent emotional and physical stress;
- autoimmune processes and diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine system.
How to eat when you have hives
With urticaria, considerable attention is paid to nutrition. Food allergies require following a diet. Foods that can provoke an exacerbation of the disease are excluded from the diet.
| It is forbidden | Allowed |
| Nuts | Lean meats – veal, poultry – boiled |
| Dairy | Cucumbers, zucchini, cabbage - all green vegetables |
| Fruit yoghurts | Green apples |
| Processed and hard cheeses | Kefir, low-fat yoghurts without additives |
| Tomatoes, eggplants, red peppers | Any porridge, excluding semolina |
| Preservation and smoked meats | Diet bread made from wholemeal flour |
| Citrus, red and orange fruits | Boiled lean fish |
| Products containing synthetic additives | Pasta made from durum wheat flour |
| Carbonated drinks | Green tea |
| Alcohol products | Sunflower or olive oil |
| Coffee, cocoa | |
| Eggs | |
| Seafood | |
| Sweets and honey |
It is necessary to adhere to the specified list and prevent prohibited foods from entering the diet.
If the hives are too severe, in rare cases it is recommended to abstain from eating for a while. It is necessary to maintain a drinking regime during the recovery period after illness. Preference is given to pure mineral water without carbon, green tea without sugar, juices from permitted vegetables and fruits. All food is steamed or boiled.
It is necessary to take vitamin complexes during the treatment period to restore normal functioning of the body.
Symptoms
Generalized urticaria has a clear clinical picture, which makes it possible to diagnose the disease based on medical history and the initial symptom complex. Variants of the clinical course may differ depending on the specific clinical form and the etiological factor that caused it.
The main common symptoms of all forms of generalized urticaria are:
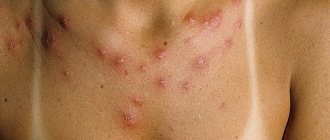
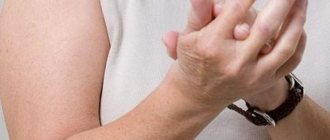
- a rash represented by blisters or papules with a bright color.
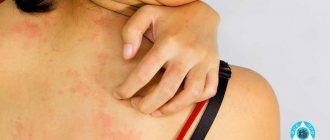
- intense itching of the skin, intensifying in the evening and at night;
- soreness, burning sensation in places where the rash is localized;
- swelling of the subcutaneous tissue and soft tissues in areas of skin lesions;
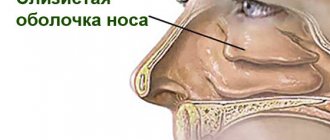
- manifestation of allergic rhinitis: copious mucous discharge from the nose;
- lacrimation;
- feeling of tightness in the chest;
- hoarseness of the voice, changes in its pitch and timbre, attacks of suffocation, which often develop into Quincke's edema;
- arterial hypotension, up to collapse;
- chills, increased body temperature to high numbers (39-400C);
- anaphylactic shock with a sharp drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness;
- arthralgia – pain that can appear in both large and small joints;
- general weakness and malaise;
- dyspeptic disorders: lack of appetite, nausea, sometimes vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
On this topic
- Hives
How to cure water urticaria permanently
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 13, 2020
Depending on the severity of the course, generalized urticaria can manifest itself with 2-3 symptoms, or it can have a developed wide symptom complex.
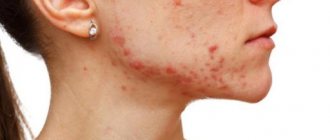
The edges of the blisters are scalloped and rise above the surface of healthy skin. Their borders are clearly defined, the elements themselves are brightly hyperemic, slightly pale in the center. The rash is localized everywhere, however, there are also favorite areas with the greatest accumulation and fusion of elements: the scalp, neck, forearms and hands, feet and thighs.
Blisters can be single, or they can be confluent, forming an extensive lesion. Externally, blisters and papules resemble nettle burns. In more severe malignant and complicated cases, in addition to blisters, bullae and areas of hemorrhage may appear.
Cold urticaria can manifest itself as a polymorphic rash, in which painful erythematous elements predominate, occurring at sites of contact with cold. The most common areas of the rash are the face, neck and arms.
Symptoms and manifestations
Symptoms of generalized urticaria are similar to those of any other form of urticaria, but are characterized by increased severity and the presence of general malaise in the patient:
- A rash in the form of blisters (swellings) on the skin of pink or red (usually burgundy) color, surrounded by an inflamed, reddened area. The rashes are usually round or oval in shape, can reach up to 15 centimeters in length, are often itchy, vary in size, they can merge into larger areas, thus spreading urticaria throughout the body in an adult or child;
- Tissue swelling or acute Quincke's edema in the mucous membranes (throat, tongue, lips), in the stomach, in the brain;
- Dizziness;
- Burning and pain of the skin in the area of edema;
- Feeling of tightness in the chest;
- Anaphylactic shock, fainting or fainting are symptoms of acute generalized urticaria;
- Decrease in systolic pressure;
- Difficulty breathing.
Severe manifestations of generalized urticaria last about 2-3 days, in the absence of treatment - up to a week, then the disease goes into remission.
learn about all the stages and symptoms of urticaria in the video:
Diagnostics
Generalized urticaria can be diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints, medical history, and clinical symptoms. However, in order to reliably identify the cause of this disease, the range of studies should be expanded.
On this topic
- Hives
All about chronic urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 12, 2020
For the purpose of differential diagnosis and establishing the root cause of the disease, laboratory and instrumental research methods are prescribed, such as:
- general blood - identifying signs of inflammation and allergies;
- biochemical blood test - search for an allergic component;
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- stool examination for dysbacteriosis;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- rheumatological tests;
- skin and contact tests for allergens;
- test with an exercise bike to exclude the cholinergic form of urticaria;
- ice test to exclude the cold form.
Allergic urticaria in children
Children are very susceptible to skin rashes, and this is the most common reaction in the case of allergies. Children under 3 years of age most often suffer from manifestations of nettle fever. But older children can also experience trouble in the form of itchy rashes.
The location of blisters is similar to adults - on the extremities (most often in folds and places of close contact with clothing), around the mouth or eyes.
The mechanism of manifestation of the rash is the formation of a large amount of histamine due to the penetration of an allergen substance into the body. The surface of the skin becomes swollen and blisters form. The skin lesion disappears quite quickly and without a trace if the child does not scratch the sore spot. But then it can appear again, in another part of the body.
The doctor can quickly diagnose the cause that provoked the hives if the parents determine the time and place of the first appearance of the spots. Accurate diagnosis involves taking the following samples: skin scraping and blood test.
Treatment
The basis of treatment for the generalized form of urticaria is not only the elimination of the etiological factor and symptoms of the disease, but also the prevention of possible complications, as well as reducing the likelihood of relapses.
To relieve an acute condition, stabilize the patient and subsequently eliminate symptoms, the following groups of medications and methods of influence are used:
- antihistamines - Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Clemastine, Chloropyramine;
- glucocorticosteroids - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Betamethasone for systemic use (administered intravenously or intramuscularly), as well as forms of the same drugs for topical use (ointments, gels, creams);
- bronchodilators, including phosphodiesterase inhibitors - Eufillin for severe bronchospasm, asthma attacks, angioedema;
- β-2-agonists - Salbutamol, Fenoterol - are administered through a nebulizer for bronchial obstruction;
- Muscle relaxants – Diazepam, Relanium – for the development of seizures;
- Adrenaline together with intravenous infusion of crystalloids and colloids (Sodium chloride, Polyglucin, Reopoliglucin) for anaphylactic shock in order to raise blood pressure and suppress the degranulation of mast cells and basophils;
- Enterosorbents – activated carbon, Polyphepan;
- Diuretics – Furosemide – for the rapid removal of the allergen and its metabolic products from the body;
- Administration of autoserum and histaglobulin.
On this topic
- Hives
How to avoid cold urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 12, 2020
Uncomplicated urticaria can be treated at home; in the presence of life-threatening conditions, the patient is hospitalized in the allergy department and treated in a hospital setting.
In addition to the etiopathogenetic effects, for the treatment and prevention of relapses of urticaria, it is important to treat the concomitant pathology of other organs and systems.
How to treat
Treatment in adults and children begins with identifying and eliminating the allergen; for this, a number of different tests are performed.
The basis of therapy is antihistamines:
- Suprastin, Diazolin are first generation drugs that act quickly, but have a short-lived effect, no more than 8 hours. They are prohibited from being taken by people whose work requires increased concentration, since they act as a sedative and hypnotic. There is an addictive effect - if you take the pills for more than 3 weeks, their activity decreases.
- Claritin, Lomilan are second generation drugs that do not affect mental and physical activity. It should not be taken by elderly people or those with cardiovascular pathologies.
- Telfast, Zyrtec - new generation antiallergic drugs. Medicines with minimal side effects, do not have a sedative effect, can be taken by older people.
In severe forms of the disease, injections of Dexamethasone and Prednisolone are prescribed. Preparations for external use - Fenistil-gel, prednisolone ointment - help get rid of itching.
Urticaria in children does not differ in clinical picture and causes from adults. For treatment, antihistamines are used - Hydroxyzine, Cyproheptadine, Claritin. If the cause of the disease is stress, then Cimetidine is prescribed.
To treat children, you can use folk remedies after prior consultation with a doctor. It is best to use herbs for baths - mix string and chamomile in equal proportions, pour 140 g of the mixture into a bag made of thin natural fabric, and pour 3 liters of boiling water. After 6 hours, the infusion will be ready; it should be poured into the bath. The duration of the procedure is 15–20 minutes.
Is it possible to wash yourself if you have allergic urticaria? Bathing is not only possible, but also necessary, since all bacteria and microbes multiply faster on dirty skin. Do not use hot water for water procedures or vigorously rub damaged areas.
Dietary nutrition is an integral part of the treatment of allergic urticaria. In a hospital setting, therapeutic fasting may be prescribed for 3–5 days. The optimal menu is drawn up by the doctor on an individual basis.
How to create a menu correctly:
- exclude dairy products, but you can consume fermented milk products;
- do not eat exotic fruits, especially brightly colored ones, seafood;
- nuts, bee products, dried fruits can cause allergies;
- vegetables and fish should be low-fat, they can be boiled, stewed, baked;
- keep the amount of spices to a minimum.
What can you eat if you have hives? Seasonal vegetables, raw, boiled, stewed, rice and buckwheat porridge, hard, mild cheese. Fruits: green or yellow apples, pears, gooseberries, white currants. Instead of wheat bread, it is better to eat grain bread, crispbread, and homemade crackers.
Allergic urticaria is not fatal, but a very unpleasant disease, it can cause Quincke's edema, and often becomes chronic. For prevention, it is necessary to strengthen the body’s protective functions, exclude allergenic foods from the diet, promptly eliminate foci of infection, and avoid stressful situations.
The information is provided for informational purposes.
Post Views: 498
How to recognize the disease and identify its causes?
Urticaria on the body of an adult has characteristic signs:
- The rash appears immediately after exposure to the allergen, within a few minutes, and goes away just as quickly, often within a day.
- The rashes are most often localized on the arms, legs, and body, but can occur on any part of the body.
- The rash is characterized by the appearance of blisters that rise above the surface of the skin, pale pink or reddish in color, with clear contours. Blisters can merge into large spots.
- The rash is accompanied by severe itching3.
You can identify the cause of the rash yourself if you track the factor that causes specific symptoms to appear. However, the connection is not always obvious, so laboratory tests have to be carried out to accurately determine the allergen. They are called provocative tests. Investigations should not be performed during an exacerbation4.