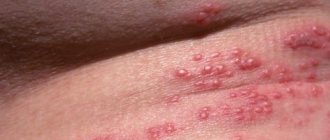
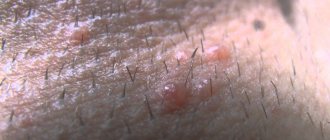
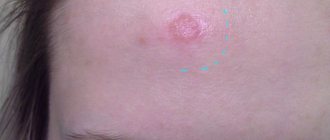
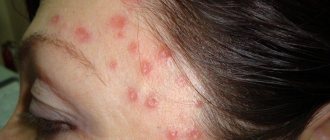
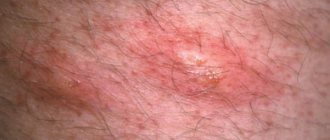
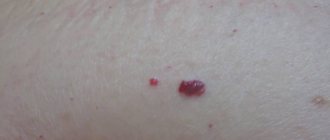
Lumps, nodules, tubercles and other lumps on a woman’s outer labia are almost always a pathological phenomenon that requires emergency medical attention. Even if the neoplasms seem benign to you, without causing acute discomfort and pain.
Most common reasons
- Such phenomena can be detected in childhood and be congenital. In this case, it is advisable for parents to check their blood for syphilis, since most often changes in the genital organs in infants indicate its presence.
- In addition, the tubercles may be a sign of abnormal development of the labia, congenital defects of the urethra and other features that do not have an infectious or viral etiology. However, this is more of a special case than a healthy phenomenon.
- We should not forget that neoplasms in the genital area can become a sign of tumor processes in the body.
- In addition, nodular fragments may indicate the development of HPV (human papillomavirus). This disease in a certain percentage of cases leads to cervical cancer.
Our doctors will help you accurately determine the etiology of your genital tubercles.
Such deviations are not a reason to be embarrassed and ignore medical help.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
Make an appointment
The doctor's consultation
1290 rub.
If the tubercles appear suddenly and can be easily felt under the skin or mucous membrane, immediately contact a specialist for advice and all necessary tests. Perhaps it is the early intervention of a specialist that will help you avoid terrible irreversible consequences.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma in the groin is a rounded compaction that occurs due to blockage of the excretory duct in women. Since the secretion is not removed, it forms a cyst or atheroma. It consists of a capsule filled with liquid contents. There may be pus or blood clots inside (if the vascular walls are damaged).
A rounded compaction that occurs due to blockage of the excretory duct.
Unlike lipoma, this neoplasm is more mobile. In women, it rolls under the skin if you touch it with your finger. The lipoma remains in place, while the atheroma on the labia moves in different directions. The lump often contains a black dot. It is a blockage of the duct, which is located in the center.
Benign tumors are often localized where the sebaceous glands pass. In the groin of women, the contents sometimes leak out of them and settle on the skin. They smell bad.
Causes
Atheroma occurs on the labia, pubic area, vulva and other groin areas. The exact reasons for its formation are unknown. Experts name the main risk factors due to which women may encounter a neoplasm:
- hormonal disorders, endocrine disruption;
- mechanical damage to the skin, increased trauma to the skin and hair follicles;
- hereditary factor;
- frequent use of underwear made of synthetic materials that restrict movement;
- excessive use of low-quality cosmetics intended for intimate care for women;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- eating large amounts of fatty, spicy foods, as well as confectionery;
- diseases associated with excess sebum production.
Frequent depilation provokes injuries to the hairline and, as a result, atheroma appears in the groin. In addition, its formation in women is facilitated by diseases of the genital area.
Prevention of labia cancer
Regular gynecological examinations help prevent the development of labia cancer, which not everyone can avoid. It is also advisable to follow the recommendations of oncologists to reduce the risk of getting sick. Increased immune status protects well from cancer, for which it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, which includes:
- • moderate physical activity, hardening;
- • absence of bad habits (alcohol consumption, smoking, drug addiction should be excluded);
- • diet and proper diet with foods rich in vitamins, microelements, and plant fiber;
- • proper sleep and rest (it is better to avoid stressful situations and overwork, which, according to psychosomatics, provoke cancer);
- • genital hygiene;
- • maintaining normal weight;
- • absence of promiscuity.
A tumor of the labia is a neoplasm that can be benign or malignant. The oncological course of the process is quite rare (no more than 3% of women) and most often affects the labia majora.
Symptoms of atheroma
When atheroma appears in the groin in women, signs may not appear for a long time. In most cases, this tumor slowly increases in size, so it does not bother the woman. It is often not noticed until a mechanical injury occurs that damages the capsule.
The body temperature rises, the thickening hurts even when it is not touched.
In this case, an inflammatory process develops. The body temperature rises, the thickening hurts even when it is not touched. The affected area swells.
In women, the appearance of atheroma on the labia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the tumor is mobile, moves under the fingers and is not tied to a specific place in the groin;
- Abscessation of the labia majora contains a dark dot in the center - a blocked duct;
- When inflamed, the skin in the localized area in women turns red and becomes hot to the touch.
Since perineal atheroma is located in a sensitive area, underwear or clothing often puts pressure on the capsule, causing constant friction. Because of this, a tumor in women can spontaneously open. In this case, the unpleasantly smelling light-colored contents will end up on the skin and underwear. After this, the capsule will begin to fill again and the thickening will form again.
Danger of complications
In most cases, in women, atheroma in the groin does not pose a threat to life or health. However, this statement is valid only until the neoplasm reaches a large size and there is a risk of its suppuration. The contents can penetrate the internal tissues, and sepsis will develop.
If the thickening is not removed in time, the woman risks encountering the following complications:
- an infection will penetrate into the wound, which will provoke increased growth of a benign tumor;
- the process of suppuration leads to spontaneous rupture of the capsule and the entry of purulent contents into the body;
- benign atheroma in some cases can transform into cancer;
- if the membrane opens spontaneously, long-term non-healing wounds often form in its place.
Therefore, if a suspicious lump appears in the groin area, a woman should definitely visit her doctor.
Prevention and treatment
Treatment at home is allowed only if you are sure that the cause lies in folliculitis or a regular purulent pimple. And even here there is a risk of infection, which can lead to an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. As for seals in the groin, which can be lipomas or atheromas, the need for their removal is determined by the doctor. Inflammatory processes are treated with medication.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to avoid casual sexual contact, hypothermia and injury to the groin area. If you find hard or soft lumps, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Timely treatment can help avoid surgery.
Diagnosis of pathology
To accurately determine atheroma on the labia, a woman will need to make an appointment with a gynecologist. The doctor may prescribe an additional consultation with a surgeon. The diagnosis is made based on examination of the groin area, as well as by palpating the lump. Usually this is enough to diagnose the pathology.
An ultrasound is performed before the operation.
Additionally, the doctor takes a smear, prescribes an ultrasound, as well as a biopsy. Using a puncture, the contents of the capsule are pumped out and then sent for histological examination. This will exclude the malignant nature of the tumor.
Treatment of sebaceous cysts in the groin
For atheroma, the same treatment methods are used as for other cystic formations. Since they are not amenable to drug therapy, the woman is recommended to have the capsule removed surgically.
However, if there is suppuration, the procedure is not carried out. In this situation, drugs are first used to eliminate the inflammatory process, and then surgery is prescribed.
Removal methods
To eliminate atheroma, doctors use one of the following intervention methods:
- classic surgical operation. This is the most common way to remove benign tumors in women. With this type of intervention, the skin is excised, as well as the capsule is opened. It is removed along with the contents, then stitches are applied. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is most often prescribed if the lump has reached a large size. In this case, traces of the stitches remain, and they are removed after a couple of weeks, after the excised tissue has healed. The possibility of re-development of atheroma with the classical procedure is minimized;
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is most often prescribed if the lump has reached a large size.
- Radio wave radiation involves the destruction of the structure of neoplasm cells using radio waves. During the operation, the woman experiences virtually no discomfort; moreover, it does not last long (a few minutes). There are no scars left at the site of exposure, but only a small depression appears, which will disappear in the future;
- The laser procedure is used for different types of cystic lesions. Using a laser, the atheroma is opened using a bloodless method. The skin is instantly cauterized, so the risk of tissue infection is minimized. Using a small incision made with a laser scalpel, the neoplasm is opened and the capsule is cauterized, simultaneously removing its contents. After the operation, the sebaceous masses are evaporated and the membrane is destroyed. Relapse is excluded.
If a woman has inflammation of the atheroma or its spontaneous opening, treatment with antibiotics and treatment with antiseptic drugs is prescribed. After removal of the purulent contents, 2 to 3 months must pass before the surgical procedure can be performed.
Treatment of lumps on the labia
Many people are concerned about the question: is it possible to get rid of a lump? Bartholinitis therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. Only a doctor can prescribe medications that will help get rid of the disease as quickly as possible. Therapy consists of the following stages:
- if pus collects in a lump on the lip, it must be opened to allow excess liquid to come out and treated with an antiseptic;
- antibiotics are prescribed to get rid of the infection and prevent the development of complications;
- Along with the use of medications, doctors recommend taking antibacterial baths;
- compliance with hygiene rules (wash thoroughly using intimate hygiene products and dry only with a clean towel).
Rehabilitation after surgery
The intervention itself takes little time, but after it the woman requires care and medical supervision for several months. In most cases, sutures are used that dissolve on their own 1 to 2 weeks after the operation.
The site where the atheroma is removed is treated daily with an antiseptic.
During the recovery period, you will need to take medications prescribed by the doctor, as well as daily treat the area where the atheroma was excised with antiseptic solutions. This procedure must be performed several times a day to prevent the wound from becoming infected.
For 2–3 days after surgery, water should not come into contact with the seam. You can swim only after this. On average, healing takes about 2 weeks. If classic atheroma removal was used, a small scar will remain on the skin. However, after a few months it will be practically invisible.
If there is a benign tumor in the groin area, mandatory monitoring by the attending physician is required. Atheroma does not heal on its own, so it must be removed. The operation is performed using the classical surgical method or using a laser or radio waves. The recovery period lasts on average 2 weeks.
First steps to recovery
If you have a tumor of the labia, the first step to recovery is to visit a doctor and undergo all prescribed tests. After receiving the test results, only the attending oncologist can prescribe the appropriate treatment regimen. The prognosis for recovery largely depends on the stage of the disease and the severity of damage to the body by cancer cells. An important aspect is strict compliance with all instructions of the attending physician.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the nature of the origin of a tumor of the labia is based on the following studies:
- interviewing the sick patient regarding the time of appearance of the formation, the nature of the sensations experienced, assessment of the general condition;
- collecting anamnesis for the possible presence of sexually transmitted and gynecological diseases, the number of pregnancies, abortions, duration and cyclicity of menstruation;
- conducting a gynecological examination (palpation of the tumor, examination of the uterus, ovaries, vagina);
- cytology of a smear taken from the surface of the lesion; histology (determining the nature of the origin of the tumor) when studying the puncture of the formation;
- lymphography (x-ray of all lymph nodes to identify possible metastases in them);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis to determine the presence of metastases;
- CT, MRI to completely exclude or accurately detect metastases;
- X-ray of the chest organs also allows you to determine the presence of metastases;
- laparoscopy for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of neoplasms in the intimate area involves using the following techniques:
Removal of a tumor surgically using enucleation (isolation of a tumor node from healthy tissue). The wound is sutured for benign organ damage.
Vulvectomy (surgical removal of the external genitalia with lymph nodes). This operation is performed during the oncological course of the process. To restore the skin at the site of removal, a flap of healthy tissue is transplanted. radiation therapy (ion radiation), which destroys the further development of malignant cells.
Chemotherapy (prescribing cytostatic drugs to destroy cancer cells). This treatment is used in conjunction with radiation therapy.
Additional treatment includes measures aimed at strengthening the immune system, since during this period it is significantly weakened due to the use of aggressive chemotherapy drugs.
Prevention measures
Prevention of tumor development consists of following simple recommendations:
- elimination of bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes);
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, proper rest, moderate physical activity);
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- timely treatment of provoking diseases of the vulva (leukoplakia, genital warts, kraurosis).
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis for cancer of the labia depends on the diagnosed stage of the current process and the degree of spread of malignant cells. The disease responds well to initial treatment with surgery and intensive chemotherapy in combination with radiation.
The last stages have a very unfavorable prognosis, since metastases can spread throughout the body and affect all vital systems.
- pain in the perineum;
- discomfort when walking;
- difficulty performing full sexual intercourse;
- presence of a cosmetic defect;
- death in the absence of correct and timely treatment.
A tumor of the labia is a number of neoplasms that require mandatory examination, diagnosis and proper treatment. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, you can achieve stable and long-term remission.