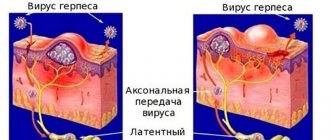
Genital herpes in children is a serious problem in pediatrics. The imperfection of the children's immune response does not allow the body to adequately fight the virus, which is fraught with frequent relapses and the formation of various consequences.
The severity of complications correlates with the age of the child who develops genital herpes: the earlier infection occurs, the more noticeable the consequences will be - from generalized infection in infants to infertility in teenage girls.
What is genital herpes?
Genital herpes is one of the serious infectious diseases. The center of this disease is in the nerve cells of almost all organs. This fairly common disease belongs to the venereological group. This pathology is not hereditary.
Genital herpes is transmitted sexually, through kissing, and through shared objects (cutlery, toys, personal hygiene items). It is important to note that most infected people do not notice any symptoms at all. They may not realize that they pose a danger to others.
The incubation period of herpes is 7 days. The infection reaches its peak in one and a half months. The disease is prone to persistent progression with relapses. Symptomatic elements of the rash can be located grouped or separately. These are small blisters that appear on the swollen and reddened base of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system, as well as on the skin of the perineum.
Here you will find a similar article on the topic of herpes on the body.
Genital herpes in children
Newborn babies have very weak immunity, so the disease can manifest itself in the first week after birth. The main signs are the appearance of hemorrhage in the form of dots on the genital mucosa, the presence of blisters, and redness of the skin. The temperature often rises, vomiting and diarrhea appear.
Such symptoms are very dangerous; they can lead to severe dehydration and negatively affect the functioning of internal organs and the brain. Genital herpes can cause many serious diseases: meningitis, atherosclerosis, urethritis, etc.
Symptoms
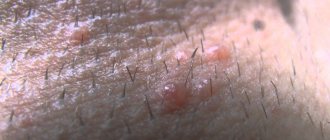
photo of genital herpes in children
Herpes in the intimate area of a child after the incubation period is manifested by the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- sleep disturbance, tearfulness, loss of appetite;
- pain along the affected nerve;
- the appearance of redness of the skin or mucous membrane;
- itching, scratching;
- the appearance of groups of bubbles filled with transparent contents;
- opening of elements with the formation of a wet surface;
- drying of the rash and formation of a crust;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The patient becomes non-infectious after the new rash stops appearing and the crusts fall off.
Recurrence of infection is described by increasing pain along the nerve followed by rashes, but there may not be any.
Locations affected: skin of the perineum, anus, labia or penis, foreskin, vulva, vagina, cervical canal.
New elements of the rash appear in an uncomplicated form within a week. If fresh blisters form for more than 7 days, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Herpes on the labia of a child is considered a milder variant of the disease, while on the mucous membranes it is less favorable.
If the blisters become covered with a yellow crust and suppurate, infectious bacterial herpes in children develops due to the addition of bacteria. Treatment in such cases is delayed.
Symptoms in children with atypical forms:
- The abortive form is characterized by the formation of weeping papules without vesicles.
- The edematous variety is described by tissue swelling and redness without the typical rash.
- The zosteriform type is characterized by massive rashes along the genital nerve.
- The necrotic form is described by deep ulcers ending in scarring. Occurs in weakened children.
- Hemorrhagic is characterized by the bloody contents of the vesicles. Described in cases of impaired coagulation processes and other blood pathologies.
If the symptoms of herpes in an infant are complemented by a deterioration in the condition, progression of rashes, the appearance of lethargy, and an increase in temperature, you should immediately go to the hospital.
How is genital herpes transmitted to children?
Ways of infection with genital herpes:
- Intrauterine. This option is possible if there is a high concentration of viral units in the mother’s body. This route of infection can cause abortion.
- Ascending infection. It represents the movement of the virus from the mother’s genitals to the amniotic fluid and directly to the fetus. What is possible in the presence of placental abruption or its defect.
- Antenatal. After the child passes through the maternal birth canal, the viral particles are localized in the child’s body. By touching the mucous membrane of the birth canal, the child comes into contact with the virus. For infection, a sluggish or latent form of the disease is sufficient.
- Infection through contact with the site of the rash. This is the most common option for children from 5 months to three years. At this age, susceptibility to herpes is very high, and those around you try to kiss the baby.
- Infection through household means through bed linen, through the mother's hands and hygiene items affected by herpetic rash.
- Sexual intercourse is the cause of genital herpes in adolescence.
Human papillomavirus infection
Papillomatosis is characterized by the appearance of “warts” in the genital area, respiratory system, and oral cavity. This infection is characterized by a chronic course, relapses, a high degree of infection, and 100% susceptibility. Anogenital types of the virus are characterized by the appearance of characteristic genital warts on the labia and genital mucosa.
Often, primary infection occurs after the age of 14, when a girl begins to become sexually active. Starting sexual activity too early is one of the most important risk factors. A girl who leads a promiscuous sex life is no less at risk of becoming infected. The source of infection is the virus carrier. Microtraumas and dry mucous membranes, characteristic of adolescence, contribute to the penetration of the infectious agent. It is possible for a child to become infected through contact and household contact - through hands and household objects, in addition, due to such a bad habit as biting nails. Vitamin deficiency contributes to infection, one of the manifestations of which is dryness and fragility of the mucous membranes, and a decrease in local immunity.
There is a high risk of infection in people with various pathologies of the immune system. Infection is promoted by dysbiosis of both the gastrointestinal tract and genital organs, diabetes mellitus, due to which the reaction of the environment on the surface of the mucous membranes changes.
As for adolescents over 14 years of age, endometriosis, hormonal fluctuations, menstrual irregularities, hormonal contraception and genetic predisposition contribute to infection. The quality of mucous membranes is detrimentally affected by bad habits, hypothermia, stress, and chronic fatigue. These factors help increase the permeability of the mucous membrane to the virus. A girl who has experienced an abortion or miscarriage is also at risk of contracting genital papillomatosis.
Newborns can become infected in utero and when passing through the birth canal from a sick mother. The virus penetrates epithelial cells, in the nucleus of which it can reside for a long time without causing clinical symptoms. The virus replicates and accumulates in cells, preventing their normal division and growth. Pathological reproduction and growth of epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes leads to the formation of pathological condylomatous growths.
When the immune system is effective in young people, papillomatous formations regress on their own within 2 years.
Most often, the disease first manifests itself at the age of 2-5 years. Genital types of papillomatosis in children most often cause the appearance of papillomas in the larynx.
Currently, the only effective means of prevention is HPV vaccination, which provides protection for 5 years.
Girls begin to be vaccinated in different countries in different ways: from 9 to 14 years old, and finish by 17 years old. The main condition is that three-time vaccination is carried out before the first sexual contact. Revaccination is carried out at 18-26 years of age. This protects not only from the development of respiratory papillomatosis in future children, but also from possible cervical cancer. To prevent the transmission of the virus to possible sexual partners, men are vaccinated before the age of 18. The advisability of vaccinating newborn children whose mothers are infected with the virus is still under debate.
What does genital herpes look like in children?
External symptomatic signs of herpes in a child cannot go unnoticed.
They are expressed:
- small collections of blood;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin;
- redness in the affected area;
- blisters on the genitals.
There are several forms of the disease.
As the disease progresses to a severe form, the symptoms intensify and the following are added:
- the virus causes pain when urinating;
- belching milk can turn into vomiting;
- the temperature rises;
- loose stools;
- painful paroxysmal contractions of the child’s muscles.
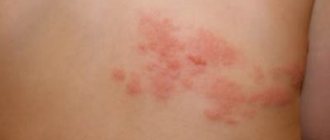
Photo
Rash is not uncommon in children. Here you will find a photo of a rash on a child’s neck with explanations.
Causes of the defect
Often the problem arises under the influence of external factors. The reasons are hygienic aspects and allergic reactions.
- Hygiene. Insufficient hygiene leads to the accumulation of dirt and active reproduction of pathogenic microflora. As a result, unpleasant symptoms appear. Excessive enthusiasm for cleanliness is also not always useful. Under the influence of detergents and chlorinated water, delicate skin dries and cracks, and various new growths appear on it.
- Allergy. Red bumps in the genital area sometimes appear due to contact with allergens. Hygiene and detergents, vaginal suppositories, condoms, toilet paper, and pads with fragrances provoke a reaction. The process is accompanied by itching, the scratched areas become inflamed. In addition, local immunity decreases and pathogenic microorganisms become more active.
- Underwear. Synthetic fabrics prevent the skin from breathing and create excess moisture under the underwear. A similar effect is achieved by rarely changing sanitary pads. May cause a small rash on the labia.
Tight panties rub sensitive areas, resulting in something like calluses.
Treatment of genital herpes in children
Treatment of infection must be carried out taking into account data on the severity of the disease. The most effective is local and internal use of antiviral drugs, for example, Zovirax (acyclovir) . Course duration is up to 10 days.
For the treatment of older children (from 12 years old), acyclovir, valacyclovir, ribavirin, and famciclovir are used. But it is necessary to take into account that the listed drugs have only a virusostatic effect.
The same antiviral drugs are used to treat lichen. Here you can find detailed information about the symptoms and treatment of shingles in adults.
Local treatment
Genital herpes is treated with local remedies. They bring relief by reducing the intensity of symptoms.
It is important to know that any independent exposure can cause harm, so you must consult a specialist. Only a doctor can create the right treatment plan based on the intensity of your symptoms.
Local exposure is the use of appropriate ointments, creams and sprays that relieve irritation, promoting tissue regeneration. Anti-virus ointments are applied by lightly rubbing into the skin. Carrying out the procedure about 6 times a day.
In this case, it is necessary to follow certain application rules:
- wash the affected area with warm water and soap;
- lubricate the bubbles with a cotton swab, after putting gloves on your hands;
- Wash your hands well after handling.
You might be interested! What is herpes zoster in children and is it contagious?
But medication alone will not get rid of herpetic disease. The main goal is to restore the protective properties of the immune system. Any therapy without the implementation of this direction is ineffective.
Systemic drugs
In the fight against herpes, antiviral drugs are used, as well as interferons and immunostimulants. It is necessary to begin treating the infection when the first signs are detected. Antiviral drugs relieve pain and burning.
Acyclovir is a medicine that is given as intravenous injections or tablets. The method of its administration is chosen depending on the form of viral manifestation and the severity of the disease. Acyclovir is administered intravenously at a dosage of 30-60 mg/kg body weight. Taking the medication should be divided into 3-4 parts.
The drug is also used externally. They lubricate the affected areas 5 times a day. Interferon is used to destroy viruses and prevent their uncontrolled reproduction .
In children, treatment of a viral disease must be monitored by an immunologist who can correctly determine the dosage that is as safe as possible for the child.
Traditional methods
There are many home remedies for treating genital herpes. In this case, you can get good results. It is important to start fighting the infection when it first appears.
Folk remedies include:
- Fir oil, which is used to treat affected areas of the skin. The procedure is repeated every three hours. A slight burning sensation is felt during treatment. On the 3rd day of treatment, positive dynamics are observed.
- Honey with celandine . Grind 50 grams of herbs in a meat grinder and mix with honey in the same amount. The resulting mixture is used to treat the affected areas.
- Herbal infusion of lemon balm, chamomile, raspberry leaves, juniper fruits, thyme, motherwort. All herbs should be taken in three spoons. Add St. John's wort, wormwood and adonis (1 tablespoon). To stir thoroughly. For infusion, you will need to mix 2 tablespoons of the mixture with two glasses of boiled water and leave for 1 hour. Then strain and take half a glass four times a day for two weeks.
- Kalanchoe juice is used as a medicine . They moisten a cotton swab and apply it to the rash.
- You can use a bag of black tea , pour boiling water over it and infuse it. Tea is applied to the affected areas.
- Healing baths are effective for treatment. To do this, add antiseptic essential oils, such as: tea tree, geranium, lemon, eucalyptus (7 drops each). The bath takes fifteen minutes. Water should be consistent with body temperature.
Recurrences of genital herpes in children
Recurrence of genital herpes begins with the appearance of precursor symptoms, expressed by burning, pain, swelling in the genital area. Later, a rash appears on the mucous membranes and skin. The vesicles contain a clear liquid that begins to become cloudy. The blisters burst, forming ulcers. After 7-9 days, the ulcers heal spontaneously, leaving no marks.
Provoking factors for relapse are:
- direct contact with a carrier of the herpes virus;
- poor genital hygiene;
- decreased immunity;
- stress.
Classification of genital rash
Acute form of allergic contact dermatitis
This is the type of allergy that is most pronounced. In addition, it extends to the perianal area and perineum. Clinical manifestations of dermatitis include unbearable itching, swelling of the mucous membranes, and a burning sensation in the area of the allergic lesion.
Dermatitis (diaper)
This allergy is a type of dermatitis that occurs in a child when interacting with a diaper. In this regard, the barrier functions of the skin are disrupted. This form of dermatitis usually occurs between 9 and 12 months of age. Specific treatment is required to neutralize these symptoms. Diaper dermatitis is accompanied by diffuse erythema, as well as itching.
Often, allergies develop together with candida skin manifestations, which can complicate dermatitis. Most often, the genital type of the disease occurs in infant girls. Severe diaper dermatitis may present with acute epidermal necrolysis, called Lyell's syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by the presence of a rapidly opening blistering rash and detachment of the upper layers of the skin.
Acute allergic contact urethritis
This form of allergy is not much different from other genital diseases in women. The only difference is the neutralization of symptoms a short time after stopping interaction with allergens. As a rule, such an allergy is observed as a result of intraurethral installation of medicinal substances prescribed to prevent infection.
Acute (contact) vulvovaginitis
This type of disease is one of the most common on the female genitals. Most often, vulvovaginitis is provoked by the use of vaginal contraceptives prescribed during therapeutic treatment.
Fixed erythema
This form is a classic example of the development of diseases of the intimate organs as a result of the use of medications taken orally or parenterally. Erythema manifests itself as hyperemic spots that have clear boundaries. Erythema is not accompanied by pain.
Chronic allergies
Hypersensitivity to certain substances may occur due to prolonged interaction with them. This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of lichenification (thickening), itching, and dry skin at the site of localization.
Prevention
Measures to prevent genital herpes:
- In a pregnant woman, the manifestation of herpes is dangerous for the fetus. In the antenatal clinic, prevention begins, carrying out constant monitoring in order to promptly identify the primary symptoms of the disease in the mother.
- After the birth of a child, the most effective prevention is long-term breastfeeding.
- If a woman develops herpes on her lips, she should not kiss the baby. Be sure to wash your hands well and often.
- If you have had the infection in the past, the best prevention is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. It is important to avoid overheating and hypothermia. The child should spend enough time in the fresh air, eat properly, and take vitamin therapy in the spring and fall.
Causes of allergies in women
Genital allergies in women can occur for a number of reasons. The most common ones include:
- negative reaction to male sperm;
- for some types of contraceptives;
- on the latex from which condoms are made;
- for some groups of drugs. These include antibiotics;
- for underwear made of synthetic materials;
- if a woman has been diagnosed with candidiasis or mycosis;
- for some personal hygiene items, which include intimate area care products, tampons or pads;
- when using tampons for more than 3 hours;
- if personal hygiene is not observed;
- when using soap while washing;
- overheating;
- for injuries during sexual intercourse;
- with regular stress and nervous fatigue;
- with hypothermia;
- irritation may occur after epilation or using someone else's razor;
- with inflammation of the genital organs;
- for sexually transmitted diseases;
- if a woman has pubic lice;
- with vaginal dysbiosis;
- if diseases of the endocrine system are diagnosed;
- for diseases of the genitourinary system;
- for oncological diseases.
Any allergic rash should be a reason to consult a doctor.
Causes of allergies in children
Allergy to the labia of a child is often diagnosed. The reasons for its appearance are as follows:
- the presence of fungal infections;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene;
- infection with candidiasis from the mother;
- frequent use of certain groups of medications;
- presence of infections in the body
- worms;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- tendency to allergies at the genetic level;
- Allergies in infants can develop due to improper introduction of complementary foods;
- due to prolonged use of diapers.
Allergies to the genitals in a child weaken or completely disappear after effective drug therapy. Relapses may recur if personal hygiene rules are not followed.
Parents who have sick children are not recommended to self-medicate.
When should you take your child to the doctor?
Treatment of genital herpes cannot be carried out independently. At the first symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will prescribe therapy depending on the course of the disease and its location.
To make a diagnosis, clinical manifestations are most often sufficient, but in apathetic and asymptomatic forms it is difficult to identify the cause of the disease, so laboratory diagnostics will be needed. The exact criterion for diagnosing an infection is the direct detection of signs of the virus in the blood or other biological fluids.
The danger of genital herpes in children
The herpes virus, penetrating the blood and lymph, begins to spread throughout the body.
A complex form of herpes can have neurological complications such as hydrocephalus, meningoencephalitis and others. Diseases of this type affect the child’s brain. They can lead to disruption of the development of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, and even to death. Pneumonia and hepatitis may also develop, and vision and hearing may deteriorate. In addition, herpes infection can lead to mental disorders.