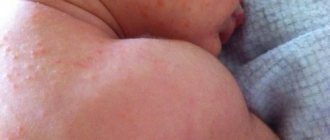
Dermatitis of any nature means a disease of the skin that is caused by various physical, chemical, and biological factors. Dermatitis can take a variety of forms, ranging from harmless flaking of the skin to serious dysfunction of the skin.
Ear dermatitis is an inflammatory process that occurs on the outer part of the ear canal. The whole danger of this type of pathology lies in the fact that if left untreated, it can develop in the inner part of the ear. This in turn will cause inner ear dermatitis.
Ear dermatitis ICD 10
According to ICD 10, dermatitis combines a whole group of skin diseases (seborrheic, atopic, dysmenorrheic, allergic, etc.). In the case of ear dermatitis, we are talking about a painful process that occurs strictly within the auditory canal.
This problem is not as harmless as it might seem. In some cases, dermatitis can go away on its own, but this does not always happen. Often, ear dermatitis seriously bothers both adults and children, annoying with constant itching, peeling of the skin, and irritation.
Ignoring symptoms leads to dermatitis progressing. Within a short period of time, it will be possible to observe a full-fledged inflammatory process, which will require more serious and high-quality treatment.
Main reasons
One possible cause cannot explain the disease. As with other dermatitis, here it is a combination of internal (genetic) and external factors (acquired).
The main reasons are as follows:
- This ear infection is a syntropic disease. – This means that it manifests itself together with other allergic inflammations of the skin and mucous membranes. – This disease is often observed in combination with atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis or conjunctivitis. – Syntropic diseases are caused by syntropic genes. – These large genetic complexes can be transmitted through both parental lines.
- A particular manifestation of psoriasis, which is currently classified as an autoimmune pathology.
- An infection in the outer ear or ear canal. – The lesion can be provoked, for example, by Staphylococcus aureus, meningococci, group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, etc. – An additional factor is the depressed state of the immune system.
- Hypothermia. It is often a concomitant symptom of cold otitis media.
With allergic sensitization of the body, dermatitis is provoked by:
- jewelry - earrings containing nickel;
- cosmetics - shampoos with a high concentration of lauryl sulfates.
The signs of a diseased ear affected by dermatitis are recognizable, the symptoms are characteristic and the treatment is determined.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
Because the symptoms of both types of seborrhea are identical, a veterinarian cannot make a diagnosis by relying solely on clinical signs. To make sure, for example, that the dog is suffering from a hereditary form of the disease, you need to check and exclude any possible causes of secondary seborrhea.
If, after a thorough analysis of the patient’s medical history, any possibility of secondary seborrhea is excluded, a biopsy is necessary to be completely sure of the diagnosis.
Treatment of this disease can be systemic and local.
To make a diagnosis of one or another type of skin inflammation, the veterinarian carries out:
- collecting anamnesis and detailed questioning of the animal owner;
- clinical examination;
- scrapings from the skin surface and bacteriological or mycological cultures from the affected areas;
- blood tests (biochemical, clinical, hormones), feces and urine.
Diagnosis requires physical and dermatological examination, knowledge of dermatological history and development of clinical signs. Otoscopic examination is the first diagnostic method of choice for assessing the external auditory canal and should be performed in every patient with signs of otitis externa.
It is important to note that a healthy ear canal may have small amounts of yellowish or brown wax. Through otoscopy, the clinician can evaluate the presence of inflammation, exudate, hyperplasia, stenosis, foreign body, neoplasm and evaluate the tympanic membrane.
Depending on the degree of pain, inflammation, and stenosis, it may be necessary to use modern systemic corticoids for two to three weeks before performing an adequate otoscopic examination.
Cytological analysis of the contents of the ear canal is necessary for diagnosis, and samples should be obtained from both the pinna and the external vertical and horizontal canal. Cytology can provide early information about the inflammatory response and the microorganisms or parasites involved in the pathological process.
Therapy for atopic dermatitis
With this disease, proper hygiene of the affected area is very important. Treatment of damage to the external auditory canal begins with treatment with a solution of soda or hydrogen peroxide. To dry wet areas and blisters, it is recommended to use solutions of boric or picric acid and apply a thin layer of Zinc ointment to the skin.
To eliminate itching, it is necessary to take antihistamines . Adult patients are prescribed Loratadine, Fenkarol, Suprastin in tablets, children - Cetirizine, Parlazine drops.
Therapy for atopic dermatitis consists of treating the affected areas in two stages:
- First, to relieve itching, inflammation and swelling of the ear canal, drops containing an antibiotic and a corticosteroid hormone are injected inside. You can use Sofradex drops, which have proven themselves well. The drug Polydexa is also suitable. This remedy is suitable for adult patients and contains a steroid component and an antibiotic.
- The second stage of treatment is the application of corticosteroid ointment, gel or cream (Lorinden, Fluorocort) to the inflamed areas of the epidermis. To treat children's skin, it is recommended to use Geocorton aerosol. It is easy to use and contains an antibiotic. The product relieves inflammation, soothes the skin, and prevents re-infection.
If dermatitis is caused by wearing an accessory, device or jewelry, then treatment will not work until the irritant that caused sensitization is eliminated.
Drops and their purpose
Basically, to relieve inflammation inside the auricle and in the external auditory canal, drops based on anti-inflammatory drugs are used. The composition includes both conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (salicylates) and corticosteroids in combination with antibiotics. They are indicated when a bacterial infection is attached. For example, Polydexa (dexamethasone + antibiotic), Otipax (phenazone + lidocaine). Drops are instilled 3-4 drops, 3-4 times a day. In addition to relieving inflammation, they promote analgesia.
Causes
Ear dermatitis is directly related to a person’s attitude towards himself. Often the cause of the disease is a careless attitude to hygiene, to the selection of jewelry, glasses and other personal items.
In second place are health problems. However, it must be remembered that sometimes completely unpredictable factors can cause an inflammatory process:
- irritation due to exposure to chemicals;
- incorrectly selected glasses frames;
- decorative cosmetics;
- wearing headphones, hearing aids;
- incorrectly selected ear jewelry;
- allergic reaction;
- reaction to purulent discharge that appears as a result of an illness in the inner ear canal;
- cosmetics for hair styling.
The onset of the disease can be triggered by a wide variety of medications (side effects), allergens, especially food ones. If you notice suspicious redness and peeling, you should consult a dermatologist for advice to avoid complications.
Also, mechanical damage to the skin can often cause the inflammatory process. This includes not only specific contact of the skin of the ear with any object, but also the bite of an animal, as well as an insect.
The following can become a catalyst for the occurrence of ear dermatitis:
- low protective abilities of the immune system;
- chronic diseases of various types;
- metabolic disorders;
- tendency to allergies;
- intoxication;
- work in hazardous production;
- unfavorable environment.
Special attention should be paid to the irritation that children have. In this case, you absolutely cannot hesitate, since the infection has an extremely negative effect on the condition of delicate, baby skin.
Until you go to the doctor, you should not treat the skin, comb it, or try to remove flaking skin. Some measures taken independently can have an extremely negative impact on the general condition of the epidermis.
Causes and symptoms
Ear dermatitis, by definition, is an inflammatory process involving the pinna and external auditory canal. Develops under the influence of internal and external stimuli.
The close connection of dermatitis with concomitant pathologies is manifested in similar symptoms, transition from one form to another, seasonal exacerbations, and stubborn resistance to treatment. Thus, detected dermatitis behind the ears does not cause serious inconvenience to the owner at first. Such a peaceful course of the disease leads to an imperceptible transition to an acute form and, in the absence of treatment, the capture of new areas, up to the inner ear. The expansion of the affected area is accompanied by an increase in the number of symptoms and the strength of their manifestation. At the initial stage, dermatitis in the area of the auricle is manifested by slight peeling of the skin and slight itching. Gradually the itching intensifies. Depending on the type of disease, the following appear:
- redness;
- swelling;
- swelling;
- hyperpigmentation;
- painful sensations when pressing on the auricle;
- characteristic rash;
- purulent discharge.
The causes of dermatitis are usually hidden in jewelry boxes, hearing aid containers, headphone packaging, and glasses cases. Each of the familiar objects can act as a provoking factor:
- Costume jewelry, hair ornaments, hairpins containing nickel and palladium. Both metals often cause an allergic reaction.
- Glasses. Low quality eyeglass frames made of metal or plastic.
- Devices for hearing correction, headphones with the inclusion of special stabilizers and urea in the body material.
- Enhanced skin and hair care products.
Skin lesions are also caused by medications, food products, mechanical damage, bites, and prolonged contact of the ear with foreign objects.
The influence that facilitates the development of pathological processes is exerted by:
- decreased ability of the immune system to perform protective functions;
- a history of chronic diseases;
- otitis;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased content of harmful substances in the body;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- stressful conditions;
- features of professional activity;
- place of residence (polluted environment).
It is important to correctly determine the provoking factor, since when choosing therapeutic therapy for ear dermatitis, the reasons for its development play a decisive role.
Detailed instructions for using ointment for neurodermatitis are discussed in our article. Find out more!
This material discusses in detail the instructions for use of Solipsor cream: indications and contraindications of the drug, features of administration.
How to treat psoriasis with warm and hot baths with celandine is presented in the material - ointment based on celandine.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis in the ears
There are several causes of dermatitis in the ears. Symptoms appear if some systems and organs of the body are not healthy. Among the main causes of pathology:
- improper metabolism; weakened protective functions of the body;
- diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys; avitaminosis;
- unstable psychological background;
- hormonal changes in orgasm or disruptions in its functioning in adulthood.
Contact dermatitis, which occurs as a result of the skin touching something, occurs for other reasons. Among them:
- the use of allergy-causing chemicals for cleaning and washing;
- wearing low-quality earrings;
- instillation of untested drops for ear otitis.
Dermatitis increases due to sebum secreted by the skin. If toxic substances enter the body (from GMO foods, smoking, alcohol), this intensifies symptoms and accelerates the growth process.
Symptoms
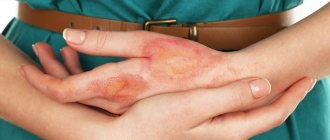
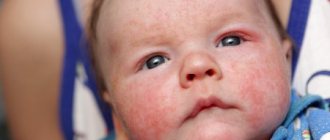
The first sign is slight redness of the skin, which may worsen after eating spicy or hot food. If treatment measures are not taken immediately, in the future the redness will be more pronounced and will be complemented by many small ulcers with a color palette from bluish-red to light brown tones.
Most often, the lower part is affected, sometimes involving the temporal lobes, and in extremely rare cases, the entire face. Subsequently, the skin thickens in places, becomes uneven, rough, and pigment spots may appear. The affected areas are painless, but there may be an unpleasant feeling of itching or burning during acute periods.
Symptoms
The main and most important symptom of ear dermatitis is a change in the color of the skin of the ears. On examination, there is obvious hyperpigmentation and the top layer of skin is noticeably thickened. The patient develops unbearable itching, which he strives to constantly eliminate, which is absolutely forbidden to do.
Signs of the disease include the following changes:
- swelling;
- swelling;
- redness;
- peeling;
- the presence of wet areas of the skin;
- release of exudate;
- the presence of warts (in the chronic form of the disease).
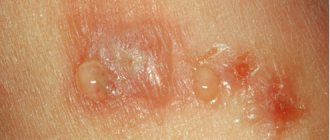
In some cases, with ear dermatitis, hard crusts and blisters can be found. Sometimes the common form of ear dermatitis can progress to a weeping stage, which contributes to the appearance of wounds, pus and an unpleasant odor.
Itching in the ears as a symptom of dermatitis:
Course of the disease in children
Symptoms of dermatitis in childhood can be observed due to the persistence of residual maternal hormones in the body of children. In addition, there is an opinion that seborrheic dermatitis, which often accompanies ear diseases, can be inherited by children.
The disease in children most often develops in the first months of life and, as a rule, goes away on its own. However, it should be understood that this does not mean that these symptoms in children can be ignored.
It is not difficult to identify the disease in childhood, since the ears are covered with greasy scales that constantly peel off onto clothing. Most often, the disease is accompanied by dandruff, which proves the relationship with the seborrheic form of dermatitis. Often, seborrheic and ear dermatitis leads to secondary infection, and if the child does not have preventive measures and appropriate care, antibiotic therapy may subsequently become necessary.
Treatment is carried out taking into account the general condition of the baby. In young children, treatment can be carried out externally, and in more severe cases, hydrocortisone ointment is recommended, which is considered the weakest hormonal agent and is quite suitable for children.
Treatment
Treatment of ear dermatitis should be comprehensive and only under the strict guidance of a doctor. The main basis is built on the use of various ointments and creams. In difficult cases, antibiotics and physiotherapy are prescribed.
The patient also needs to remember that dietary adjustments are recommended for treatment. The therapeutic diet involves the exclusion of possible allergenic and heavy foods, as well as sweets and flavorings. Such nutrition additionally allows you to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Medication
Drug treatment is prescribed only by the treating dermatologist. Having familiarized himself with the existing diagnosis and its form, he makes the necessary appointments. In the standard version, the patient receives the following list:
- ointments and creams to combat ear dermatitis;
- antibiotics;
- drinking medicinal mineral water;
- physiotherapy, consisting of x-ray therapy, UHF and UV.
Treatment of dermatitis should be carried out according to a strictly prescribed scheme. Departure from the doctor’s recommendations can provoke an increase in painful symptoms, which will reduce all the effort expended to zero.
Folk remedies
Natural substances are excellent in helping to cope with ear dermatitis. They have excellent antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. The main problem is to choose exactly the tool that will be useful specifically in your case.
So, for help, you can turn to the same doctor with whom you are being treated or use special medical literature.
Folk remedies help perfectly in such cases:
- lack of quick results through drug treatment;
- chronic dermatitis;
- acute dermatitis or advanced disease.
Properly made product allows you to achieve good results within a short period of time. After the first use, the patient feels significant relief, itching goes away, redness and swelling go away.
Herbal medicine cannot be taken as a basis in the treatment of dermatitis. In more advanced cases, it will not bring results, but will only worsen the situation.
For simple forms of ear dermatitis, it is best to use:
- strawberry leaves;
- juniper;
- anise;
- elder;
- centaury;
- smoker;
- beans;
- celery;
- Tartar;
- chamomile;
- Oak bark;
- thuja;
- sorrel;
- bedstraw.
It is best to use medicinal herbs as tea. They will strengthen the immune system, improve metabolism and help speedy healing of dermatitis. In some cases, lotions are indicated for treatment. But it is better to discuss their use with your doctor.
Causes of appearance in people
There are several types of ear dermatitis. The most common of them is seborrheic. Contact, allergic and microbial forms of pathology are less common.
The causes of seborrheic dermatitis in the ears are:
- Weakened immunity. It is observed in persons with severe diseases of internal organs after antibiotic therapy. A decrease in immunity also occurs in patients with malignant neoplasms after courses of radiation and chemotherapy, while taking high doses of corticosteroids.
- Metabolic pathology. These include diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and other endocrine glands, disorders of protein and lipid metabolism.
- Hypovitaminosis. It is observed in the winter-spring period, subject to a strict unbalanced diet, fasting, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas.
- Hormonal imbalances. They can occur during puberty, pregnancy and menopause.
- Genetic predisposition. Patients whose immediate relatives suffer from these ailments are more prone to seborrhea, including seborrheic ear dermatitis.
- Frequent stress, excessive psychological and physical stress, lack of sleep and proper rest.
In addition to seborrhea, there is also contact dermatitis, which appears due to exposure to the following factors:
- Wearing hearing aids, earplugs, low-quality jewelry (earrings, piercing jewelry made of plastic or medical steel), frequent use of in-ear headphones.
- Using aggressive detergents (shampoos, hair conditioners, dyes, styling products) that can cause skin irritation and allergies.
- Wearing tight synthetic hats or swim caps that cause extreme pressure.
- Use of inappropriate ear drops in the treatment of otitis media.
Ear dermatitis can be complicated by the addition of bacterial or fungal flora, which most often occurs when:
- Scratching and damaging the skin of the ear canal.
- Using someone else's headphones or earplugs.
- Incorrect use of cotton swabs for cleaning ears.
A major role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis is played by microorganisms from the genus Malassezia, which are activated by improper ear hygiene and excess sebum.
Traditional therapy
A dermatologist prescribes drug treatment for ear seborrheic dermatitis on an individual basis after diagnosis. Therapeutic therapy involves the use of medications in the form of tablets, drops, cream, ointment, gel. Weeping areas of the affected skin are treated with ointments that have a drying effect. For the same purpose, a solution of boric or picric acid is used. Other forms of medications are used for:
- Relieving the intensity of itching (antihistamines in the form of drops, tablets or injections).
- Eliminate the inflammatory process with drops.
- Destruction of pathogenic microorganisms (hormonal and non-hormonal ointments, gels, shampoos).
- Restoring the function of the immune system (dragées, tablets).
- Stabilization of metabolic processes (tablets).
Additionally, physiotherapy is prescribed in the form of UHF procedures.
Treatment options
Treatment of the disease is complex. In the case of contact and allergic dermatitis, first get rid of the causes of the specific reaction of the immune system:
- If a rash appears after wearing glasses, you should change the frames and start using them by wiping the skin behind the ears with antiseptic compounds. They dry the surface and prevent the growth of dangerous bacteria.
- Headphones are wiped with alcohol 1-2 times a week. In-ear models accumulate a lot of wax and dead skin particles at the joints. This provokes the development of contact form of dermatitis. Therefore, it is necessary to clean them after each use.
In addition, a diet is prescribed. It helps cleanse the intestines and the entire body of dangerous substances that are formed due to the presence of toxins and infections in the body. The patient is advised to exclude allergic foods from the diet: chocolate, citrus fruits, chicken eggs, etc. Sorbents free the gastrointestinal tract from undigested food debris, which can trigger the development of dermatitis.
The seborrheic form requires nutritional adjustments. Be sure to exclude spicy and smoked, fried, fatty foods. You will also have to forget about sweets for a while. The basis of the diet is a vegetarian menu.
Pharmacy medicines
Treatment of human ear dermatitis begins with disinfection. Usually 3% hydrogen peroxide is used. This is a safe and effective remedy. Solutions of picric acid are effective for blisters and weeping formations. Active components help dry their surface. As an alternative, boric alcohol is used. The prescription of antihistamines such as Zodak, Suprastin, Loratadine is practiced in the treatment of atopic form. Broad spectrum ear drops (Otofa, Otipax) help relieve itching, reduce swelling and inflammation.
The affected areas are treated with corticosteroid ointments (Flucinar, Gioxizon). They promote the healing of wounds on the ears that have formed due to constant scratching. They have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Medicines in this class have many side effects if used for a long time. Therefore, the use of corticosteroids is regulated by a doctor.
If seborrheic dermatitis has developed on the ears, then the main task is to eliminate the fungus. Therapy begins with treatment with antiseptic solutions. If there are no weeping spots, creams and tablets are used. For example, Ketoconazole, which is available in both forms. The drug slows down the proliferation of microorganisms. Applications are made from the ointment for 10-15 minutes. Then the product is removed with warm water.
If bubbles filled with liquid form on the skin around the ear and on the surface, treatment is recommended to begin with wiping with boric acid, a solution of pyoctannin (methylene blue). Homemade ointment is also suitable. Mix two parts of zinc oxide, the same amount of starch, one part each of lanolin and petroleum jelly.
Folk remedies
Natural components are easily absorbed into the skin, reducing the inflammatory process. Medicinal herbs are used in the form of infusions, ointments and extracts. After consulting a doctor, you can try the following traditional methods:
- For ear dermatitis of any form, use celandine juice, which is obtained by squeezing the crushed plant. Before use, it is diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:2. Applications are made on gauze napkins and tampons. Their duration does not exceed 10-15 minutes due to the irritating effect that celandine has upon prolonged contact.
- Decoctions and infusions based on a series are effective. To prepare them, pour a tablespoon of crushed product into half a glass of hot water and leave to infuse. The finished solution takes on a dark brown color. They moisten a gauze cloth with it and leave it on the affected area until it dries completely.
- Treatment of the ear affected by dermatitis in folk medicine is carried out with Japanese Sophora. The fruits of the tree are crushed and poured with boiling water in the ratio: a glass of water per 1 tablespoon of plant material. The decoction is infused overnight and drunk throughout the day in small portions.
- The healing properties of birch tar have been known for a long time. It improves blood supply to areas of inflammation and stimulates the restoration of damaged skin. The antiseptic properties make tar indispensable in the treatment of ear dermatitis, which is not accompanied by weeping spots and blisters with liquid. Dry rashes are treated with homemade tar soap. You will need to mix 100 g of melted baby hygiene product with 2 tablespoons of oil, tar and 100 ml of water.
But before using folk remedies for the ears, it is better to consult a doctor. This will help avoid adverse reactions and prevent cross-reactions with medications.
Possible complications
Complications from ear dermatitis are quite rare, but they do occur. The thing is that if left untreated, dermatitis spreads extremely quickly, affecting healthy areas of the epidermis. This brings many unpleasant symptoms, ranging from itching to severe inflammation and swelling of the affected areas.
When scratching, there is a high probability of infection entering the ear. This, in turn, is fraught with the appearance of an inflammatory process directly inside the ear canal. This greatly complicates the treatment process.
Inner ear dermatitis is incredibly difficult to tolerate, as it causes severe itching, redness and unpleasant pain.
How to recognize dermatitis in children, watch our video:
Kinds
It is not only the timely identification of characteristic symptoms that helps to successfully cure dermatitis in the outer and inner ear. It is also important for the specialist to determine the type of disease in order to take into account all possible nuances. The task is made easier by the presence of only three types of ear dermatitis:
- atopic;
- seborrheic;
- contact.
Each type has characteristic symptoms, which helps reduce diagnostic errors to zero.
Atopic
This type of ear dermatitis is unpredictable. On the one hand, it moves relatively quickly from one form to another. On the other hand, he patiently waits for the formation of favorable circumstances for his own development. Among the causes most often mentioned are the lack of treatment for allergic dermatitis, heredity, stress, and the wrong choice of cosmetics. The disease manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- severe itching;
- the appearance of red spots on the skin;
- formation of crusts at the site of spots;
- skin inflammation;
- nodules containing sulfur.
Both the symptoms of the pathology themselves and the consequences caused by attempts to alleviate unpleasant sensations pose a danger to humans. Atopic dermatitis located behind the ears in children leads to re-infection due to persistent scratching of the affected areas. Adults often become infected by trying to relieve discomfort with cotton swabs, matches, and pins.
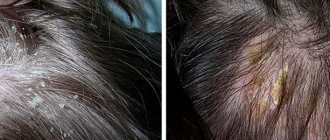
Seborrheic dermatitis
This type of skin disease prefers to be located in areas generously supplied with sebaceous glands: the scalp, the area of the nasolabial triangle, the area behind the ears. The culprit of the disease is considered to be a sharp increase in the population of yeast-like fungi Malassezia, caused by the transition of the sebaceous glands to an increased operating mode. Sebum is produced in excess. Opportunistic Malassezia, which lives in the epidermis layer of most people, receives sufficient amounts of essential fatty acids. The population of microorganisms grows, causing inflammation of the skin, itching and flaking.
However, it would be wrong to call the population of opportunistic microorganisms the main culprit of the disease. Fungi behave peacefully until the amount of resources necessary for life begins to increase. There are several reasons for increased sebum secretion, to which microorganisms have nothing to do:
- repeated stressful situations;
- allergic reactions, especially to the use of medications;
- avitaminosis.
If these factors are often repeated, and a person does not take any measures to eliminate them, seborrheic dermatitis in the ears may develop over time, the treatment of which will require much more effort. For people living in a state of constant stress, who do not care about their proper nutrition, or who suffer from allergies, it is important not to ignore the symptoms that appear on the skin of the ear and to begin treatment of the developing disease as quickly as possible.
Typical symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- appeared redness, swelling, swelling of the skin;
- formed bubbles filled with a clear, colorless liquid;
- nodules;
- replacing a burst bubble with a weeping lesion;
- itching and burning;
- small rashes;
- the appearance of films and crusts that have a yellowish and gray color;
- discharge of pus with an unpleasant odor;
- formation of greasy plaque;
- flaky skin;
- painful sensations starting from the side of the affected ear with further spread;
- accumulation of wax in the ear canal, cerumen plugs;
- elevated temperature;
- dizziness;
- bad feeling;
- irritability.
The disease quickly becomes generalized. The transition to a severe form is accompanied by the addition of a bacterial infection. In the future, the lack of treatment leads to the spread of lesions to the scalp behind the ear, face, neck, shoulders, back, chest, and the development of atopic dermatitis.
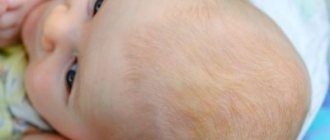
Seborrheic dermatitis in children
Young children who also have the seborrheic type of ear dermatitis get sick for other reasons. In addition, the symptoms of dermatitis in them may differ from those in adults. Poor hygiene is considered the most likely factor causing dermatitis in two-week-old infants or a newborn baby. Seborrhea in infants actually often develops if child care does not meet hygienic requirements. However, this reason is not the only one. The list of factors indicates the presence of:
- characteristic increased secretory activity of the sebaceous glands;
- overheating, accompanied by increased sweating;
- the presence of maternal hormones;
- weak immunity;
- pathological processes in the digestive system;
- excessive use of irritating hygiene products (soaps, gels, shampoos);
- hereditary predisposition.
The symptoms observed in adults also have some differences. For example, a baby’s characteristic severe itching may be weak or absent altogether. Such features require immediate consultation with a doctor if only some of the characteristic symptoms of dermatitis were detected. Timely diagnosis will allow appropriate treatment and, in the future, avoid complications such as bacterial infection or atopic dermatitis.
Prognosis and prevention
With a correctly selected treatment regimen and timely consultation with a doctor, ear dermatitis can be quickly eliminated. It may take some time for the tissue to completely heal and restore the natural color of the skin.
In case of chronic dermatitis, it is necessary to take a more careful approach to treatment, following all the instructions and recommendations of the dermatologist. You should choose the optimal diet for yourself and avoid inappropriate jewelry made from gold, plastic, or low-quality metal.
Preventive measures for the usual form of dermatitis include being more careful with your body. So, it is necessary to protect yourself from low-quality jewelry, cosmetics, and accessories. The diet should not include excessive amounts of potentially allergenic foods.
To avoid any skin disease, including dermatitis, you should protect yourself from stress. Contact with chemicals that can cause burns and irritate the skin is unacceptable.
Types of dermatitis
Doctors distinguish several types of dermatitis, caused by certain etiological factors, for example, such
:
- an allergic type is characteristic of contact with a specific substance that causes pathological manifestations on the skin;
- Doctors diagnose contact dermatitis in the case of an inflammatory process in a specific area of the body after contact with an allergen;
- seborrheic dermatitis is treated by a dermatologist and endocrinologist, since in most cases the problem is caused by metabolic disorders, that is, the cause of skin episodes is excessive formation of sebaceous gland secretions;
- Doctors consider atopic dermatitis to be the most complex type, since the etiology is determined by the individual characteristics of the body, that is, genetic predisposition;
- damage to the skin due to exposure of the body to toxins or allergens that penetrate through the hematogenous route, which doctors call toxicoderma.
People with atopic dermatitis consult a dermatologist especially often, since the disease is common among the population and has certain stages of clinical course, that is, remissions in the summer and periods of exacerbations in the autumn-winter period, which requires constant assistance from a qualified specialist.
Self-medication, especially with this form of dermatitis, is not acceptable, therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor and carefully follow his recommendations to quickly eliminate unpleasant manifestations on the skin
Prevention
To avoid relapse, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- wash your hair with a special shampoo, which will be selected by a dermatologist;
- include a maximum of vitamin-rich vegetables and fruits in your diet;
- exclude hypothermia of the head;
- add pharmacy vitamin complexes containing magnesium, zinc and silene;
- monitor the quality of worn jewelry.
Ear dermatitis can be quickly treated with a combination of medications. People who constantly face the disease must eat a balanced diet, follow hygiene rules and diet.
What is this
Seborrheic dermatitis on the ears is an inflammation of the skin in these areas, which occurs as a result of reactions to irritants (can be external or internal). Depending on the source, the disease is divided into several types:
- atopic;
- seborrheic;
- contact.
Atopic and contact diseases do not spread to nearby areas of the skin, but seborrheic without treatment may well spread to the neck and head.
Dermatitis that occurs on the ears is divided according to external signs. The type is determined depending on the type of dermis (a person with oily skin will have different symptoms of the disease than a person with dry skin). There are several forms of the disease:
- Dry. This type of dermatitis resembles dandruff on the epidermis. Sebum does not come to the surface well, resulting in clogged pores. When mechanically cleansed, for example, with a hard brush or body scrubs, the area acquires a bright red tint.
- Fat. Sebum is produced, but too much of it accumulates on the surface, and this prevents the penetration of oxygen. This type of dermatitis has a slight yellow tint and an unpleasant odor. It often occurs in adolescents during puberty or in people with hormonal imbalances.
- Mixed. As a result of the fact that the skin has varying degrees of dryness and oiliness in areas of the ear, areas of dermatitis look different. A common form is when white scales appear at the tip of the ear, and yellowish ones closer to the auricle.
The severity of the disease depends on a number of factors. Peeling may spread to other areas of the face and neck. This threatens not only that the disease will be more severe and take longer to treat, but also that the skin will lose its attractiveness (in advanced cases, scars appear that are difficult to remove even with modern laser techniques).