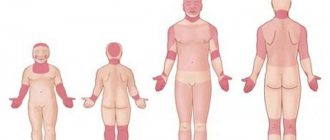
The appearance of various redness on the clean and delicate skin of newborns is always a cause for concern for their parents. Why do they appear? What do they mean for the child’s health? Only a specialist can answer all these questions. Don't worry ahead of time. After all, most often, redness is a simple contact dermatitis in a baby. This pathology is caused by irritants that come into direct contact with delicate skin. The rash can even be caused by your baby's clothes or toys. But, do not neglect consulting a dermatologist. After all, this disease can become chronic.
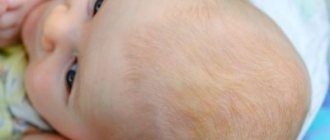
The skin of infants is very delicate and susceptible to dermatitis
What it is?
Contact dermatitis in children is a disease characterized by deformation of the skin. When interacting with an irritant, various symptoms appear that directly indicate the onset of the disease. It is worth noting that contact dermatitis is a seasonal disease. Most children become infected in winter, since it is at this time of year that the number of viruses increases.
This disease goes through several stages in its development:
- erythremal, when the child develops swelling and redness on the skin;
- vesicular-painful, characterized by the addition of pustules to the previous symptoms, from which ulcers form;
- necrotic, which is the most dangerous: with it, pustules transform into scabs, which over time leave scars on the skin.
Types, symptoms and photos of the disease
In infants, dermatitis can manifest itself in one of four types:
- atopic;
- seborrheic;
- contact;
- diaper
Each of these types differs not only in symptoms and causes of occurrence, but also in the approach to therapy.
Atopic dermatitis
- Statistically the most common type in children. Occurs in a chronic form.
- Most often, atopic dermatitis manifests itself several weeks after birth.
- An inflammatory process forms on the skin, the integrity of the dermis is disrupted. Infantile eczema is characterized by hyperemia and rash.
- The areas on the cheeks and buttocks of the baby become dry and begin to peel.
- Sometimes the disease is more severe, and the affected areas are wider.
- The cause of infant atopy is heredity, various allergens, dysbiosis, helminths.
- The peak of the disease is considered to be between 6 months and one year of age.
Seborrheic
- The causative agent of this type of disease is Mallasezia furfur. This fungus “lives” on the epidermis. Becoming pathogenic, it provokes the appearance of seborrheic dermatitis in infants 2–3 weeks after birth.
- It can go away within a year or last up to 3 years of age.
- A characteristic manifestation is gray scales on the skin in the hair growth area, behind the ears, and forehead.
- Occasionally, formations are observed on the face, chest, and neck.
- The disease does not cause concern and does not impair the child’s quality of life.
- Sometimes, if immunity is too low, general malaise and diarrhea may appear.
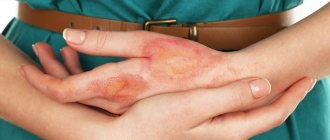
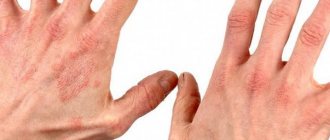
Contact
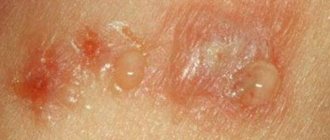
- A characteristic sign is its manifestation in the area of contact with the damaging factor. The inflamed area is limited and does not spread to healthy areas of the skin. The epidermis takes on a bright red color.
- Symptoms such as hyperemia are accompanied by itching and burning.
- As a result, ulcerative formations appear, followed by crusting.
- Contact dermatitis is successfully treated with timely detection of the irritant, as well as the elimination of its contact with the infant.
- Otherwise, the disease becomes chronic with possible complications.
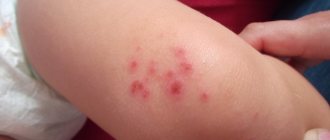
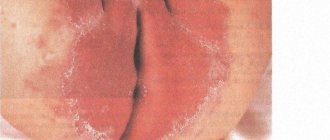
Diaper
- Diaper dermatitis in infants is a common occurrence. The reason is improper care when using diapers, irregular hygiene procedures.
- More often, this type of disease is observed in girls between 6 months and one year.
- Affected areas are places of contact with diapers and diapers.
- Typical symptoms: redness, rash with signs of maceration on the buttocks, genital area, pubis. The inner side of the femoral surface of the dermis also suffers.
- It is important to start treatment immediately. Otherwise, you can observe a worsening of symptoms: blisters and nodules appear, and later ulcers form, followed by roughening and peeling of the skin.
- The acute form of diaper dermatitis is characterized by infant anxiety, lack of appetite, crying, and sleep disturbances.
Causes
Contact dermatitis in children appears at the moment when contact with an irritant occurs. Thus, the child’s body says that it no longer wants to interact with these substances. Among the irritants, antibiotics, cosmetics, metal objects, diapers, etc. are especially prominent.
Quite often the disease occurs as a result of temperature changes. For example, in severe frost or bright sun. It is worth noting that there can be many causes of contact dermatitis in a child. Here it is not the irritant itself that comes to the fore, but the body’s sensitivity to it. A factor such as heredity is of great importance. Scientists have found that if one of your immediate relatives suffers from skin diseases, then there is a chance that sensitivity will be passed on to the child.
Causes
The following factors can trigger the development of dermatitis:
- hereditary predisposition (if the baby’s parents and relatives had a tendency to skin diseases, the child will also suffer from dermatological diseases);
- severe pregnancy and childbirth;
- viral diseases in mother and baby during pregnancy;
- intestinal diseases;
- poor care, insufficient hygiene;
- early complementary feeding, improperly selected nutrition;
- immunodeficiency;
- fungal infections;
- immaturity of the skin in babies, caused by weakness of connective tissue, insufficient hydration and imperfect thermoregulation;
- contact with external irritants (physical, chemical, microbial).
The following may indirectly affect the worsening manifestations of dermatitis:
- temperature difference;
- nervous shocks;
- vaccinations;
- anemia;
- excess weight.
To prescribe treatment, the doctor must determine the type of dermatitis, which directly depends on the type of irritant and internal pathologies.
Allergic contact dermatitis
This disease is divided into several types. One of the most common is allergies. It is characterized by prolonged interaction of the irritant with the child’s skin. Most often, these are skin care products that contain dyes, various additives, etc.
There are cases where allergic contact dermatitis occurs as a result of prolonged use of one powder or soap. Here it is best to exchange these funds for others that are safer. For example, instead of baby soap, many people use refined oil to soften their skin. It sounds strange, but if you first boil it and then cool it, the oil will give its effect. As for the powder, it’s simpler - in this case you can hardly find better than potato starch.
It is best to limit your child from contact with all substances that contain dyes and harmful additives.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
In severe cases of atopic dermatitis in children, treatment requires the use of local corticosteroid drugs, together with emollients. This will serve to quickly eliminate symptoms. Moisturizers and emollients are used during any period of the disease. The goal of treatment is to:
- Change in the course of the disease
- Reducing the severity of exacerbation
- Long-term disease control
An indication for hospitalization of a child may be an exacerbation of the disease, as a result of which the general condition is disrupted, recurrent infections, or the ineffectiveness of the therapy.
Non-drug treatment consists of measures aimed at minimizing or eliminating the effects of factors that provoked an exacerbation of the disease: contact, food, inhalation, chemical irritants, increased sweating, stress, environmental factors, infections and microbial contamination, disruption of the epidermis (hydrolipid layer).
Drug treatment of atopic dermatitis in children is prescribed taking into account the period, stage and form of the disease. The age of the child, the area of affected skin and the involvement of other organs during the course of the disease are also important. There are means for external use and systemic action. Pharmacological drugs of systemic action, used in combination, or in the form of motor therapy, including the following groups of medications:
Antihistamines
There is currently insufficient evidence of the effectiveness of antihistamines for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children. Drugs with a sedative effect (suprastin, tavegil) are prescribed for significant sleep problems due to constant itching, as well as in combination with urticaria (see symptoms and treatment of urticaria) or concomitant allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
Among antihistamines for allergies today, the most preferred are 2nd and 3rd generation drugs, such as Cetrin (instructions for use), Eodak, Zyrtec, Erius - these drugs have a prolonged effect, do not cause drowsiness, addiction and are considered the most effective and safe, produced as in the form of tablets and in the form of syrups, solutions, drops (see list of all allergy tablets). The clinical effect of using these drugs is felt after a month, so the course of treatment should be at least 3-4 months.
However, for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, the effectiveness of antihistamines without sedation has not yet been proven and the need for their use is determined by the doctor in each clinical case. Also, the effectiveness of oral administration of cromoglycic acid and ketotifen for atopic dermatitis has not been proven.
Antibiotics
The use of systemic antibiotics is justified only if a bacterial infection of the skin is confirmed; long-term use of antibacterial drugs is not permissible. Antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed externally for skin infections with streptococci and staphylococci:
- Antiseptic solutions - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Fucaseptol, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green alcohol solution 1-2%, fucorcin
- Antibiotics - Bactroban ointment (mupirocin), Fucidin (fusidic acid), Levosin (levomycetin, sulfadimethoxin, methyluracil), neomycin, gentamicin, erythromycin, lincomycin ointments, Levomikol (levomycin + methyluracil)
- Xeroform, dermatol, furatsilin ointments
- Argosulfan, Sulfargin, Dermazin
- Dioxidine ointment
They need to be used 1-2 times a day. In case of severe pyoderma, additional systemic antibiotics are prescribed (see 11 rules on how to take antibiotics correctly). Before treatment with antibiotics, it is recommended to first determine the sensitivity of the microflora to most known drugs.
Systemic immunomodulatory therapy
Uncomplicated atopic dermatitis does not require the use of immunomodulators. Only after a thorough diagnosis can an allegrologist-immunologist prescribe immunomodulators in combination with standard therapy with local agents if the symptoms of dermatitis are combined with signs of immune deficiency.
The danger of using immunostimulants and immunomodulators in children is that if close relatives have any autoimmune diseases (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome, diffuse toxic goiter, multiple sclerosis, vitiligo, myasthenia gravis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.) ) even a one-time use of immunomodulators can cause the onset of an autoimmune disease in a child. Therefore, if a child has a hereditary predisposition to autoimmune diseases, you should not interfere with immune processes, as this may result in hyperactivation of the immune system, triggering immune aggression on healthy organs and tissues.
Vitamins and herbal medicines
Vitamins B15, B6 help to increase the effectiveness of treatment, thereby accelerating the process of restoration of functions of the liver cortex and adrenal glands and accelerating repair processes in the skin. The resistance of membranes to toxic substances increases, lipid oxidation is regulated, and the immune system is stimulated. However, in a child with a tendency to allergies, some vitamin complexes or certain vitamins, as well as herbal medicines (medicinal herbs, decoctions, infusions) can cause a violent allergic reaction, so the use of vitamins and herbal medicines should be treated with great caution.
Medicines that restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
Drugs that restore or improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are indicated in the subacute and acute periods of the disease, taking into account the identification of changes in the functioning of the digestive system. They are used to improve digestion, correct impaired functions, these are Panzinorm, Pancreatin, Creon, Digestal, Enzistal, Festal, as well as choleretic drugs and hepatoprotectors: Gepabene, rose hip extract, Allohol, corn silk extract, Hofitol, Leaf 52, Essentiale Forte. Duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
Antifungal and antiviral drugs
When the skin is affected by fungal infections, external antifungal agents are prescribed in the form of creams: clotrimazole (Candide), natamycin (Pimafucin, Pimafucort), ketoconazole (Mikozoral, Nizoral), isoconazole (Travocort, Travogen). When a herpes infection occurs, antiviral drugs are indicated (see list of antiviral and antifungal ointments for stomatitis).
Sanitation of foci of infection
You should remember about the treatment of concomitant diseases, the purpose of which is to sanitize foci of infection - in the genitourinary system, biliary tract, intestines, ENT organs, and oral cavity. Depending on the phase of the disease, antibacterial, keratoplasty, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic skin care preparations are used.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for external use are divided into 2 groups: those containing glucocorticoids and non-hormonal drugs.
Glucocorticoids are effective in chronic and acute forms of the disease in children. Such creams are not used as prophylaxis; moreover, glucocorticosteroid ointments and creams should be used strictly as prescribed by a doctor, in short courses, followed by gradual withdrawal of the drug (see the list of all hormonal ointments in the article ointments for psoriasis).
The danger of prolonged and uncontrolled use of such drugs is the development of systemic side effects, inhibition of the function of the adrenal cortex, decreased local and general immunity, the development of skin atrophy, thinning, dry skin, the appearance of secondary infectious skin lesions, etc. If without such strong drugs you still cannot get by, you should know the rules for their use:
- These remedies are divided into: strong, moderate and weak activity. To treat atopic dermatitis in children, you should start with the weakest concentrated hormonal drugs. It is possible to increase the concentration only if the previous remedy is ineffective and only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Any hormonal ointments are used in short courses, then take a break and reduce the dose of the drug.
- Abrupt cessation of use worsens the condition and causes relapse of the disease.
- At first, pure cream is used, and when it is gradually withdrawn, the required volume of cream or ointment is mixed 1/1 with baby cream, after 2 days of such use the concentration is further reduced, already 2 parts of baby with 1 part of hormonal cream, after 2 days 3 parts of baby 1 part of the hormonal one.
- If you have to use local hormonal agents for a long time, you need to change the drug, which contains a different hormone.
- To eliminate puffiness, use the cream at night; to eliminate plaques, use it in the morning.
Non-hormonal - For minor manifestations of dermatitis, antihistamines are prescribed (Finistil gel 0.1%, Gistan, see review of allergy creams for children). Creams are also prescribed - Vitamin F 99, Elidel, Radevit (see creams and ointments for dermatitis in children).
- Burov's fluid - aluminum acetate
- Videstim, Radevit - fat-soluble vitamins
- ASD paste and ointment
- Zinc ointments and pastes - Tsindol, Desitin
- Birch tar
- Ichthyol ointment
- Naftaderm - liniment of Naftalan oil
- Fenistil gel
- Keratolan ointment - urea
- NSAIDs (see ointments for pain)
Treatment with creams and ointments with healing properties is also effective for atopic dermatitis; they enhance tissue regeneration and trophism:
- Dexpanthenol - creams and sprays Panthenol, Bepanten
- Gel Curiosin (Zinc hyaluronate)
- Solcoseryl, Actovegin - ointments and creams, gels with calf blood hemoderivat
- Methyluracil ointment (also an immunostimulant)
- Radevit, Videstim (retinol palmitate, that is, vitamin A)
- Cream “Forest Power” with Floralizin is a very effective cream for any skin diseases - eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, herpes, for dry and cracking skin. Floralizin contains a complex of natural biologically active substances - an extract from mushroom mycelium, containing enzymes with collagenase activity, vitamins, minerals, and phospholipids. Ingredients: floralisin, petroleum jelly, pentol, fragrance, sorbic acid.
Among the immunomodulators, we can highlight Thymogen ; its use is possible only as prescribed by a doctor.
Diet for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
Diet during treatment plays an important role, especially in infants. Based on the prognosis of the disease, it is necessary to exclude products containing the allergen. In the first year of life, children may be sensitive to cow's milk proteins, eggs, gluten, grains, nuts, and citrus fruits (see symptoms of citrus allergy). In case of allergy to cow's milk, you can use soy mixtures: Frisosoy, Nutrilak soya, Alsooy.
In case of allergic reactions to soy proteins and severe forms of food allergies, you need to use hypoallergenic mixtures: Pregestimil, Nutramigen, Alfare (Nestlé).
If you are allergic to gluten (25% of children), it is recommended to use hypoallergenic cereals based on buckwheat, corn, industrial rice - Remedia, Heinz, Istra-Nutrizia, Humana.
The introduction of each new product into food must be agreed with a doctor, no more than 1 product per day and in small portions. It is necessary to exclude foods that cause allergies in children if their intolerance is confirmed (you can take a blood test for a specific allergen).
Signs of the disease
Symptoms of contact dermatitis in a child include:
- redness at the site of interaction with the irritant;
- the appearance of ulcers on the skin;
- burning and itching;
- the appearance of small blisters.
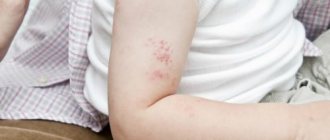
It is worth noting that most often symptoms appear on the faces of children and on the upper extremities. But if these parts of the body are not affected, it does not mean that the disease does not exist. Sometimes symptoms are characteristic of other areas of the skin.
All these signs in children are accompanied by a deterioration in their general health. The baby loses sleep, his mood worsens, weakness and reluctance to do anything appear. Further treatment and prognosis depend on the form of the disease (acute or chronic). In the first case, when the symptoms are removed, the disease also goes away. In the second, the disease will recur from time to time, but with less force.
Nutrition
A diet for dermatitis involves avoiding potential food allergens (cocoa, citrus fruits, chocolate, honey, eggs), spicy, salty, fatty foods and simple carbohydrates (sweets, starchy foods). Include in your baby's diet:
- dairy products;
- vegetables and fruits that do not cause allergies;
- cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal);
- lean meat and fish.
If your child has a predisposition to food allergies, get a blood test, since the rash can sometimes be caused by the most “harmless” foods.
Contact dermatitis in infants
This disease is not uncommon for newborns. There are a huge number of reasons for this. A child may be allergic to various substances, and dermatitis may also occur as a result of failure to comply with normal hygiene rules. Sometimes infants experience unreasonably prolonged contact with urine or feces in a diaper, which for some reason has not been changed for a long time.
Dermatitis occurs due to friction with clothing or metal. In addition, the baby’s body may reject a certain ointment or oil. Many people experience diaper dermatitis, which is characterized by redness in the buttocks, perineum and inner thighs.
Treatment of contact dermatitis in children under one year of age comes down to the implementation of certain measures:
- control over diapers: they need to be changed frequently;
- You should constantly wash so that the child is always clean;
- Special creams with an anti-inflammatory effect should be applied to the skin.
What to remember
- The cause of dermatitis is most often an allergic reaction of the body to external allergens or the result of internal diseases.
- Atopic dermatitis is a hereditary pathology, which is completely impossible to get rid of. You can only reduce the number of relapses and prolong the period of remission with the help of medications and preventive measures.
- Do not bathe your child with soap more than 1-2 times a week. Hygiene products and chlorinated water dry out the skin and provoke the development of the disease.
- Therapy for dermatitis should be comprehensive and aimed at eliminating internal and external provoking factors.
- Treatment with folk remedies is effective only as part of complex therapy.
Diagnostics
As already noted, if parents realize in time and see that the child has skin problems, then serious consequences can be avoided. The main thing is to immediately consult a doctor in this situation. As soon as the first signs appear, you should immediately make an appointment.
The question arises: “Which specialist should I contact?” There are two options: an allergist or a dermatologist, and sometimes parents also take their children to a pediatrician. In fact, there is no fundamental difference; you need to make an appointment with an experienced doctor, he will immediately make a diagnosis.
To identify contact dermatitis in children, allergists use special tests. One of the main ones comes down to the fact that the doctor drips different substances onto the patient’s skin one by one. Thus, he determines what exactly is the irritant in a particular situation. Determination of the activator is considered a prerequisite for further treatment. After all, if the doctor knows what exactly needs to be treated, then the recovery process will be more conscious and correct.
Diagnostic methods
The pediatrician begins the diagnosis with a visual examination of the baby and interviewing the parents. The doctor evaluates the nature of the skin lesions, as well as the general condition of the child.
If breastfeeding is present, the baby's mother should describe her diet to identify a possible allergen product. Formula milk or complementary foods are also determined.
To clarify the diagnosis, the pediatrician prescribes the following additional procedures:
- blood analysis. Usually they do detailed (clinical) and biochemical;
- bacterial culture (if there is a suspicion of staphylococcal infection);
- stool analysis to detect dysbacteriosis, infection with worms;
- serum IgE testing;
- allergy tests (rare procedure for newborns);
- swab of the oral mucosa;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Atopy in infants is treated by an immunologist-allergist. Before an accurate diagnosis is made, parents are highly discouraged from self-medicating.
Therapy
Treatment of contact dermatitis comes down to a number of basic rules that need to be followed:
- initiation of treatment - identification of the causative agent of infection;
- the child’s recovery is carried out only under the supervision of an experienced specialist;
- if itching occurs, you need to prescribe the necessary medications, etc.
It is the identification of the irritant and the subsequent fight against it that is the basis for the treatment of dermatitis. After diagnosis, parents should listen to a specialist and monitor the baby’s recovery. Depending on the cause, different medications are prescribed. These can be antihistamines and sorbent medications. Damage to the skin is removed using various ointments.
It is worth noting that, in addition to traditional methods of treatment, parents often practice folk remedies. They can either help with conventional therapy or interfere with it. Therefore, the use of folk remedies is a purely personal matter. Treatment for contact dermatitis is prescribed by a doctor, and the parents’ task is to monitor the baby’s daily routine so that there are no deviations.
Folk remedies
Treat dermatitis with folk remedies only as part of complex therapy, since if used independently, it is unlikely to give long-term results.
Birch bud decoction
Ingredients:
- Dry birch buds - 1 tbsp.
- Cool boiling water – 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: Brew boiling water and pour it over birch buds. Keep the mixture on the fire for another 15 minutes. Cool and strain.
How to use: Rub the infusion into the affected areas of the skin daily 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Result: The rash gradually goes away, the inflammation disappears.
St. John's wort oil
Ingredients:
- Dry herb St. John's wort – 25 g.
- Butter (melted butter or vegetable) – 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: Place dry St. John's wort in a jar or bottle and fill with oil. Leave for 2 weeks, stirring occasionally. Strain and store the product in a dark place.
How to use: Rub into affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day.
Result: The skin softens, rashes disappear. Manifestations of dermatitis gradually disappear.
Decoction of linden and chamomile
Ingredients:
- A mixture of dried chamomile and linden flowers in equal parts - 4 tbsp. l.
- Boiling water – 1 l.
How to prepare: Pour boiling water over the dry mixture and leave on the fire for another 20 minutes. Leave for 3-4 hours. Strain and pour into a prepared bath with a water temperature of 36-37 degrees. How to use: Take a bath with the decoction at night. After the procedure, lightly pat the damp body with a terry towel.
Result: The rash gradually fades and goes away. The skin dries out, becomes smoother and cleaner.
Possible complications
Contact dermatitis in itself is not life-threatening. However, it can develop into a more serious disease, and then health problems cannot be avoided. Medical experts have come to the conclusion that the greatest danger in this case is the addition of an infection. In most cases, a fungal or bacterial infection occurs. If this happens to a patient, he needs careful care and a good course of therapy.
Contact dermatitis on the hands of children is different in that these places constantly want to be scratched. It is because of this that complications arise. Therefore, it is necessary to remind the child every day that such places should not be scratched. It should be explained clearly and clearly, and it is better not to bring the situation to the point of itching at all. If you deal with the symptoms at the root, then the baby will not even suspect what itching, burning, etc. are.
Concept
Contact dermatitis - photo:
The concept of “contact dermatitis” combines a number of skin diseases that develop due to contact with any irritating element . Contact dermatitis causes blistering, itching, swelling and redness in the affected area.
How can you apply diathesis on a child’s cheeks? Find out the answer right now.
Prevention
Contact dermatitis occurs very often in children. Even if you already had the disease, but you dealt with it, this does not cancel preventive measures.
To avoid relapses, you should do the following:
- You cannot save on children; you need to make sure that they dress decently and wear only high-quality things. The fact is that fabric can be an irritant, and you need to protect your baby from such situations.
- Children should not be completely covered as this may cause irritation.
- Change diapers regularly and maintain personal hygiene.
- Select hypoallergenic household chemicals so that as few harmful substances as possible get on the baby’s skin.
- Soap, shampoo, ointment, gel should be chosen carefully.
- Fresh air has never harmed anyone, so you need to take regular walks with your child.
- Do not allow the child to be exposed to the irritant. And if this is not possible, at least minimize this contact.
According to statistics, these measures help avoid relapse and protect your baby from this unpleasant disease.
Hygiene and regime
Of great importance in the treatment of any type of dermatitis is limiting contact with a potential allergen, maintaining hygiene and proper nutrition.
If you have diaper dermatitis, be sure to wash your baby when changing a diaper or diaper. Do not use soap every time you perform hygiene procedures, as it dries the skin and leads to increased manifestations of the disease. Wash your baby with soap once at night: this is enough.
If you completely bathe a child with dermatitis, use soap with herbal extracts of chamomile, string and neutral pH, or add infusions of medicinal herbs to the water. They dry the skin and prevent the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Dress your child in clothes made from natural fabrics such as cotton. Night pajamas should be loose and have as little contact as possible with inflamed areas of the skin.