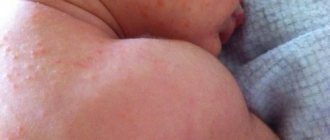
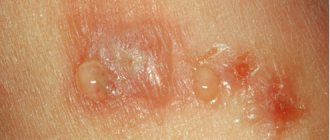
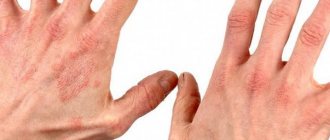
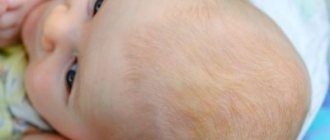
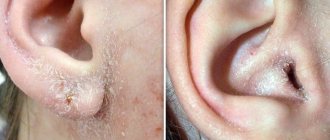
Fungal dermatitis is an infectious disease with a complex etiology and numerous provoking factors. Without treatment in the acute phase, it becomes a chronic process.
According to the degree of penetration into the layers of the epidermis, it is differentiated into several types. Diagnosis is complicated by its external resemblance to other skin diseases.
Types of dermatitis in humans
In medical practice, the term dermatitis refers to inflammatory changes in the skin of various locations caused by pathogenetic factors of endogenous and exogenous nature.
Skin dermatitis is combined into a group of allergic dermatoses, the manifestations of which are allergic reactions of immediate and delayed type.
There are several types of skin dermatitis with a clinical picture of local and generalized manifestations of the disease:
- allergic;
- toxicoderma;
- eczematous changes;
- atopic;
- nettle rash.
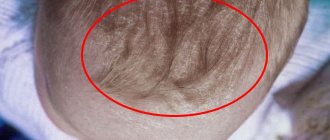
Characteristic rash
The development of pathology can be signaled not only by changes in the skin. Many patients experience various rashes.
Sometimes the following symptoms occur:
- Pustular elements. There is a tendency to form furunculosis and folliculitis. The source of such rashes is an immune imbalance. It occurs as a result of decreased liver function. The organ is not able to synthesize immunoglobulin in sufficient quantities.
- Allergic manifestations. This pathology in most cases characterizes liver disease. Skin symptoms: spots and papules, occur as a result of a violation of the detoxification function of the organ. That is why a person is faced with the occurrence of allergic reactions to familiar conditions.
- Hemorrhagic rash. Minor hemorrhages are observed on the surface of the skin. They are called petechial eruptions. They characterize a decrease in the synthetic function of the organ. Initially, the protein contained in the blood suffers. As a result, patients have an increased tendency, even with the slightest damage, to form hematomas.
Causes of dermatitis
Before you begin to actively combat inflammatory disorders of the skin, it is worth finding out the causes of dermatitis. Sometimes it is enough to eliminate the aggressive agent and the disease goes into a stage of long-term remission.
All etiological factors causing skin dermatitis are divided into 2 large groups: exogenous and endogenous. The difference lies in the characteristics of the immune reaction, the speed of response and the clinical picture.
It is important to know that a disease such as dermatitis can have combined pathogenetic factors, thereby reducing the likelihood of identifying trigger factors.
Exogenous etiological agents:
- Physical: hypothermia with frostbite of part of the body; sunburned surfaces with rash elements after exposure to ultraviolet rays; skin changes due to exposure to electric current; radiation; bites of hymenoptera and other parasitic insects; touching animal fur, pollen, juice, plant leaves; uncomfortable tight clothing, constant friction and compression;
- Chemical: neglect of safety precautions, interaction with salts, acids, alkalis without proper protection in production professions, factories, factories; household contact with aggressive detergents and cleaning agents; the use of low-quality cosmetics and body care products, incompatibility of the skin and ingredients of expensive cosmetic preparations; medications used for external application: ointment, cream, lotion, balm, solution and others; lack of vitamins B, A, E.
Endogenous etiological agents:
- Oral or parenteral use of drugs with the development of sensitization.
- Reduced immune response due to past infectious diseases, acquired immunodeficiency, malignant neoplasms.
- Eating foods that cause dermatitis on the skin.
- Infection with pathogenic bacteria, development of helminthic infestation, the appearance of mycosis of the mucous membranes and skin, lack of proper therapy for chronic internal diseases.
- Mental instability with obsession with scratching the skin.
- Regular stressful situations, nervous tension, severe shock.
- Family history, diagnosed and registered cases of dermatitis in the family.
The patient’s living conditions, standard of living and social status are of no small importance. Sometimes the causes of dermatitis are combined, which complicates diagnosis with accurate identification of the trigger and treatment.
Signs of pathologies
As a rule, liver disease is accompanied by skin symptoms. It is, first of all, a yellowish tint. In addition, the patient experiences heartburn and feels nauseated. There is a sharp, extremely unpleasant odor of sweat. Therefore, typical cases do not cause difficulties in diagnosis.
In most cases, a doctor can already visually suspect liver disease. Skin symptoms and the patient’s discomfort give the doctor an idea of the nature of the pathology.
The main signs of liver diseases are:
- pain, discomfort in the organ area;
- liver enlargement;
- general malaise, weakness;
- headache;
- impairment of thinking and mental abilities;
- swelling;
- increased sweating;
- jaundice;
- skin itching;
- rash;
- increased tendency to bleeding, fragility of blood vessels;
- symptoms of hypovitaminosis;
- changed color, character of feces, unstable stool;
- the presence of a venous pattern on the abdomen;
- weight loss;
- increased abdominal size;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- temperature reaction;
- cracks in the tongue, white or brown coating on it.
Symptoms of dermatitis
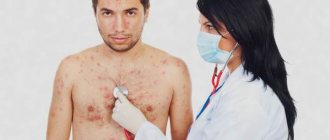
The clinical picture of dermatitis depends on the etiological factor of the lesion, the severity of the course and the stage of the disease. All types of dermatitis are characterized by the main symptoms of changes in the skin.
Acute dermatitis is characterized by 5 diagnostically significant signs of inflammation:
- hyperemia (erythema): redness of the epidermis is associated with activation of the immune response, synthesis and release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, prostaglandin and other kinins. A cascade of biochemical reactions is launched with the appearance of itching and burning;
- local hyperthermia: activation of the protective properties of the skin leads to an increase in local temperature, as the body tries to neutralize irritating antigens;
- tissue swelling: a violation of the acid-base balance towards acidosis provokes the destruction of proteins and the dissociation of vital salts, as a result of which oncotic and osmotic pressure is disrupted. Another mechanism of edema is excessive blood flow through the blood vessels to improve the trophism of affected cellular structures and neutralize decay products to avoid intoxication;
- pain: one of the protective functions of the skin, signaling the location and extent of damage in dermatitis. Many peripheral nerve endings (nociceptors) are irritated by a trigger, edematous tissues, substances due to cell lysis, inflammatory mediators;
- dysfunction: painful stimuli limit movement in a certain area of the body, the protective, resorption, metabolic, secretory functions of the affected area change.
The degree of manifestations of dermatitis depends on the duration of contact with the pathognomonic antigen, the age of the patient (in young people the clinical picture is brighter), as well as concomitant diseases and general health.
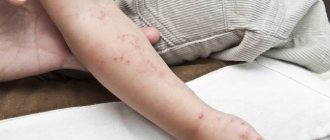
The inflammatory process of the skin is accompanied by the appearance of a rash, the nature and location of which depends on the type of dermatitis. With genetically predisposed (atopic) dermatitis, itching, burning, scratching and the formation of papules occur.
Raised nodules are localized in different parts of the body: cheeks, elbows, legs, buttocks, abdomen. Plaques and microcracks form, causing pain. Subsequently, with adequate therapy, crusts dry out and appear. The skin feels dense to the touch, lichenification is noted, and the pattern intensifies.
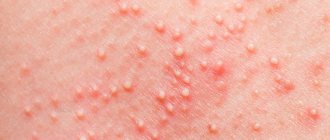
Eczematous rashes are usually polymorphic, so different elements of the rash are located on one area of the body. Eczema is characterized by vesicles that can open and turn into erosions. As it heals, crusts appear. In the zone of resolved lesions, pigment spots with characteristic peeling remain.
Allergic dermatitis due to contact with a chemical, physical or biological trigger is accompanied by a rash with the formation of papules, vesicles, spots, bullae.
It is worth noting that the rashes are localized, precisely at the site of contact with the allergen. After the cessation of exposure to the antigen, the clinical picture begins to decline.
In toxicoderma, the antigen enters the skin through the hematological route and has a lightning-fast clinical picture with the appearance of rashes in the form of papules, vesicles, spots, and bullae.
There is peeling and symmetry of the rash. Bullous elevations reach gigantic sizes, open with the formation of ulcers, and epidermal necrolysis can be observed.
With urticaria, pale pink areas of the skin appear, slightly raised above the surface, the urticarial rash is very itchy and prone to spreading and merging. Reminds me of nettle burns.
Nature of pain
Most organ pathologies are immediately reflected on the human body and face. This allows you to promptly suspect liver disease. Skin symptoms are often accompanied by painful discomfort. The nature of the sensations can be quite different. Therefore, you should pay attention to the following discomfort:
- The occurrence of minor pain in the right hypochondrium. It can be aching and bursting. Or give a feeling of heaviness. This pathology signals a sluggish process of inflammatory, toxic origin. Discomfort often occurs as a result of organ enlargement or stretching of the liver capsule. As a rule, the patient cannot clearly identify the pain point.
- Intense, widespread discomfort in the right hypochondrium. This kind of pain is rare. It signals a pronounced purulent, inflammatory or traumatic process. Sometimes it can be characterized by stone damage to the bile ducts.
- Local, severe point pain in the liver area. Discomfort is not typical for liver damage. It is associated with pathology in the gallbladder or extrahepatic ducts.
Sometimes the patient does not experience pain, but meanwhile develops liver disease. Skin symptoms are the only signs that indicate pathology. As a rule, the absence of pain is observed with indolent diseases that go undetected for a long time.
Dermatitis. How to treat?
The main principle in the treatment of skin inflammation of allergic etiology is to neutralize the trigger factor and try to avoid repeated contact.
Timely treatment of bacterial, fungal, viral and parasitic infections will reduce the risk of developing the disease.
During the acute period of dermatitis, adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, exclude from the diet:
- hot, salty, spicy dishes;
- refrain from sweet desserts: chocolate, honey, marshmallows, marmalade, cocoa;
- carbonated drinks, coffee, strong tea;
- home-made and factory-made canned products;
- all types of mushrooms;
- seafood: red fish, crabs, caviar;
- fat meat;
- whole milk;
- egg.
The diet should include vegetable soups, porridges (with the exception of legumes), stewed seasonal vegetables typical of the region of residence, meat of mature animals, fruit drinks, compote of dried apples, biscuits, and dried fruits.
Drug therapy:
- In case of acute generalized reaction: intravenous administration of glucocorticosteroids: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone; parenteral antiallergic drugs: Diphenhydramine, suprastin, diprazine; intravenous detoxification: Reosorbilact, Reamberin, Sorbilact, Xylate; intravenous restoration of ABS (acid-base balance): Trisol, Soda buffer; forced diuresis; plasmapheresis.
- For a local process: antihistamine gels and ointments: Fenistil, Skin-cap, Protopic; ointments based on corticosteroids: Advantan, Prednisolone, Celestoderm-B, Gistan-N; ointment with corticoid and antibiotic for secondary infection: Belogent; ointment with corticoid and antifungal agent: Lorinden; regenerating and hemovascular liniments: Desitin, Pantestin, Dexpanthenol; oral antihistamines: Ketotifen, Fenistil, Zyrtec, Telfast, Erius; sorbents: Polysorb, Phosphalugel, Enterosgel, Atoxil; if it gets wet: bandages with Burov's liquid; washing with a solution of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine; specialized hypoallergenic cosmetics; sedatives: Valerian, Motherwort, Glycine, Adaptol.
If a secondary infection occurs, antibacterial, antimycotic ointments or oral medications are prescribed.
Diet. Healthy foods
If you have liver disease, eat the following foods:
- slightly stale (rye, wheat) bread, biscuits, biscuits;
- lean meat (rabbit, turkey, chicken, beef);
- fish - pike, pike perch, cod and other low-fat species;
- dairy products - low-fat kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, yogurt;
- oil (sunflower, olive, butter);
- eggs (1 piece per day);
- vegetable dishes from pumpkin, potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, cauliflower;
- cereals – rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley;
- pasta - any variety;
- fruits, berries (strawberries, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries);
- dried fruits and uzvar;
- fruit jam, honey (a little), marmalade.
Products must be steamed. It is allowed to eat food stewed, baked or boiled. Smoked and fried foods are prohibited.
With proper nutrition, many patients feel their liver disease receding. Symptoms and treatment (diet and drug therapy) should be monitored by a doctor throughout the entire period of combating the pathology.
Dermatitis: traditional methods of treatment
Herbal components have wound-healing, soothing, anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects. Properly selected herbal medicine helps speed up the process of restoring the integrity of the skin, eliminating rashes and peeling. Medicinal herbs include:
- Celandine. The juice of the plant is mixed with chilled boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 2, respectively. A sterile gauze pad is soaked in the solution and applied to the site of inflammation for 15-20 minutes.
- Periwinkle. An infusion is made from the leaves by brewing in boiling water (10-15 minutes). The resulting mass is filtered and cooled. Add to bathing water.
- A series. Pour 2 teaspoons of chopped dried string into 150 ml of boiling water and leave. Use the resulting infusion and a sterile gauze pad to apply to the affected areas of the skin.
For dermatitis at home, you can use tar soap, tea tree oil, geranium oil, potatoes and aloe.
From Roaccutane
The drug for the treatment of acne, Roaccutane, based on isotretinoin, is available in the form of capsules. Each capsule, depending on the dosage, can contain from 10 to 20 mg of isotretinoin.
It is difficult to describe all the side effects from this medicine - there are too many of them. but as for the skin, the following can be distinguished:
- Rash.
- Itching.
- Facial erythema/dermatitis.
- Sweating.
- Pyogenic granuloma.
- Paronychia.
- Onychodystrophy.
- Increased proliferation of granulation tissue.
- Persistent hair thinning.
- Reversible hair loss.
- Fulminant forms of acne.
- Hirsutism.
- Hyperpigmentation.
- Photosensitivity.
- Photoallergy.
- Easy skin trauma.
At the beginning of treatment, acne may worsen and persist for several weeks.
Prevention
The cause of inflammation can be many chemicals used in everyday life, so it is almost impossible to completely protect yourself from this disease. However, there are several simple recommendations that will help reduce the likelihood of allergic dermatitis:
- When using jewelry or any other metal accessories, avoid alloys containing nickel and chromium .
- Contact of household chemicals with skin should . When working with them, it is recommended to use protective equipment, for example, household rubber gloves and masks.
- For people with problem skin, it is recommended to use special hygiene products. Specialized gels, ointments and shampoos will help strengthen the skin, maintain its water balance and reduce the likelihood of inflammation.
- General rules of a healthy lifestyle - properly organized nutrition and sleep patterns, moderate physical activity, absence of bad habits, and so on.
- At the first symptoms of the disease, you should consult a doctor . Timely diagnosis and treatment will help quickly and effectively cure allergic dermatitis.
An important factor that cannot be excluded from view is the characteristics of professional activity. Some professions and types of work involve frequent contact with potential irritants.
The risk group includes doctors, nurses and other medical workers, hairdressers and cosmetologists, food and industrial workers. If the dermatitis is chronic, you should consider changing jobs or otherwise limiting contact with allergens.
Diagnosis of the disease
Due to its pronounced symptoms, the disease is recognized quite easily in a clinical setting. To make a diagnosis, you need to be examined by an allergist and dermatologist. As a rule, skin tests are prescribed. This is a simple test during which the source of the allergy is identified - strips with substances applied to them are glued to a certain area of the skin and the reaction is detected.
In addition, they may prescribe a blood test for biochemical composition and sugar levels, urine and stool tests, and conduct an examination of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. Additional tests may be needed to determine the type of dermatitis and to rule out other skin diseases with similar symptoms.
After diagnosis, the dermatologist prescribes treatment, which includes local and general therapy aimed at reducing allergic sensitivity. Treatment is carried out at home, but in some cases hospitalization may be necessary.
Undesirable combinations
It is not advisable to prescribe retinoids simultaneously internally and externally.
Retinoids cannot be combined with keratolytic and exfoliating agents (salicylic alcohol and any other alcohols, scrubs, peeling).
The effect of external retinoids is weakened when combined with glucocorticosteroid ointments. The effect of systemic retinoids is reduced by taking alcohol and tetracycline antibiotics.
How long does retinoic dermatitis last? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally. but often unpleasant symptoms last throughout treatment with drugs from this group. And this causes a lot of trouble for a patient with acne.