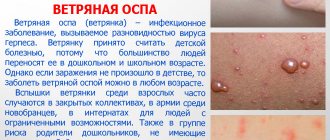
Reaching a respectable age and not having chickenpox is not a reason to rejoice. Chickenpox in adults is much more severe, and the chances of catching the virus are much greater. With age, the symptoms of chickenpox in adults can hide longer, which makes the disease much more dangerous. Moreover, many adults often do not pay much attention to the first symptoms that appear, and treatment for chickenpox begins late.
Sources of chickenpox infection
Chickenpox is caused by a herpes virus that can persist in the body for a long time. Infection occurs through contact with a sick person. The source of infection is the carrier of the virus 2-3 days before the appearance of the rash and for several days after the scabs disappear.
The household route of transmission of the disease is excluded, since the pathogen dies under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and high temperatures. If a person has had chickenpox, the recurrence of the pathology is unlikely.
Attention! In a state of immunodeficiency, chickenpox may re-develop in adults.
In a child, the disease is characterized by a mild course. The crusts leave no traces, and healing occurs in a short time. In adults, the disease causes numerous complications. Because of this, parents used to consciously try to infect their children with the virus. However, a connection has recently been identified between the causative agent of chickenpox and herpes zoster. After this, people began to avoid infection by all means.
Incubation period and duration of treatment
You can become infected from a sick person after he or she develops all the symptoms. The source of infection is not only a patient with chickenpox, but also a patient with herpes zoster. The incubation period ranges from 1.5 to 3 weeks, after which the characteristic symptoms of chickenpox appear. The pathogen spreads throughout the body, invades the circulatory and lymphatic systems.
In mild cases, all negative manifestations disappear after 2-3 days. When chickenpox is of average severity, the rash persists for 4-5 days. The severe variety is characterized by rashes for 9 days. The onset of recovery is indicated by the drying of papules, which turn into crusts and fall off.
Related article:
How does chickenpox begin in children - symptoms and treatment
Reasons for appearance
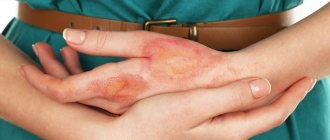
scars after chickenpox
In the typical course of chickenpox, light crusts form in place of the formed blisters, which gradually fall off. Underneath, unchanged skin remains, without any scar changes.
Chickenpox is accompanied by severe itching, as viral particles of the pathogen actively multiply in the skin. To eliminate itching and prevent scratching, antihistamines (Suprastin, Claritin) are used, however, not all patients use them.
When scratching the blisters, bacterial microorganisms may attach to the inflammatory focus.
In this case, purulent inflammation develops in the skin, leading to significant damage to the epidermis and underlying parts of the skin.
Purulent melting leads to the formation of defects in the form of dimples, which either persist in the form of scars after chickenpox throughout the patient’s life, or disappear within several years.
In order to get rid of such scars, it is necessary to begin their treatment in a timely manner. At the initial stages of scar formation, the use of medications that affect skin restoration is effective.
If the skin defects are severe, then doctors prescribe surgical interventions aimed at excision and plastic surgery of the skin.
It is important to note that any therapeutic methods are selected only by the attending physician.
Medicines have a number of indications and contraindications that must be taken into account when prescribing treatment, since otherwise scarring may progress or side effects from the drugs themselves may develop.
Chickenpox symptoms in adults
Once the virus enters the body, no changes occur.
Only after some time do those infected experience the following signs of the disease::
- Weakness.
- Discomfort in joints and muscles.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Problems with orientation in space.
- Convulsive contractions in the muscles.
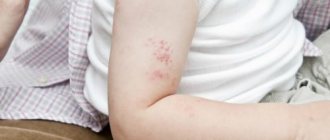
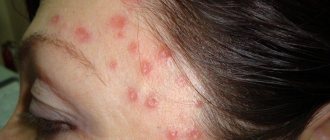
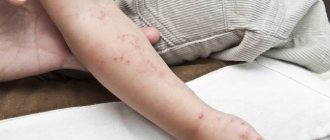
Before the rash appears, the patient's condition worsens, the body temperature rises, after which the patient poses a danger to others. The rash is red spots with small blisters that gradually open up. In an adult, such papules decorate the entire body, affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, genitals, trunk and limbs.
A purulent infection may develop, which can only be treated with an antibiotic. If left untreated, chickenpox can lead to an abscess, tissue necrosis, and problems with the functioning of internal organs.
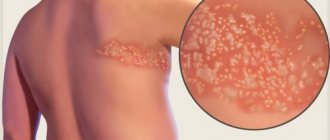
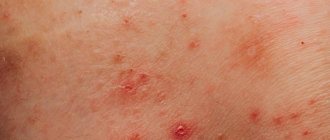
The nature of the rash with chickenpox
In adults, this virus causes massive rashes throughout the body, often accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. At first, the rash looks like small pinkish spots, about 2 mm in size. A few hours after their appearance, they enter the papules stage, then crusts appear on them, which disappear over time.
Rashes can also develop on the mucous membranes; they take the form of small ulcers and disappear together with the main symptoms of smallpox.
Types of chickenpox - photo
To select a high-quality treatment for chickenpox, you should take into account not only the examination results, but also the type of pathology.
The course of chickenpox may be:
- Typical . A mild form of pathology with a slight increase in temperature. There are no signs of intoxication, and new rashes appear over several days.
- Average _ Signs of intoxication, papules appear within 5-6 days, and temperatures reach 40 degrees.
- Heavy . Severe intoxication of the body with a prolonged increase in temperature. The rash densely covers the entire body and affects the internal organs. The meninges and peripheral nervous system are affected.
- Gangrenous . Accompanied by wound infection. Requires skin treatment with antiseptic agents.
- Hemorrhagic . It is characterized by bleeding from wounds, which is life-threatening.
- Generalized . Chickenpox affects internal organs and disrupts their functioning. Formed during chemotherapy or taking certain medications.
The specialist determines the type of disease, and then draws up a scheme of exposure. In some cases, an adult patient with chickenpox will have to stay in a hospital to avoid negative health consequences.
Related article:
Chickenpox in children: what to treat besides brilliant green?
Treatment
Chickenpox is treated at home under the supervision of a physician. He selects external medications and medications for internal use, which allows you to recover in a short time.
Therapy is based on three principles:
- Bed rest.
- Proper treatment of the skin.
- A gentle diet with a predominance of dairy and plant foods.
If an adult gets chickenpox, hospitalization may be required. The decision about it is made by the attending physician in the presence of damage to internal organs. How long treatment will last depends on the severity of the symptoms of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
Medicinal methods of influence
To recover without consequences, you must strictly follow the recommendations of a specialist. Do not scratch papules or abuse water treatments. It is also recommended to exclude self-administration of medications.
Medicine for adults is selected by the attending physician, but most often used:
- Antiviral drugs to eliminate complications and reduce the number of rashes - Valtrex, Famvir, Acyclovir.
- Antihistamines to relieve itching - Diazolin, Suprastin, Fenistil.
- Antiseptics.
- Furacilin, potassium permanganate and boric acid - for severe lesions of the oral cavity and genitals.
- Antipyretic tablets are necessary for severe fever. It is recommended to take ibuprofen or paracetamol, and aspirin is excluded.
- Antibiotics for chickenpox - when a purulent infection is attached.
- Painkillers for severe pain.
Attention! For prophylaxis, it is best to take acyclovir after a visit to a sick child or adult for several days.
A person will be cured sooner if he seeks medical help in a timely manner. Attempts to get rid of the rash and other manifestations of chickenpox on your own end in a huge number of complications.
Folk remedies
To alleviate the external manifestations of chickenpox in adults, folk remedies are actively used.
The following methods are characterized by relative safety:
- Applying soda solution. Take 1 tsp for 1 glass. soda, after which the rash is treated with the composition.
- Baths with chamomile, calendula or celandine. Relieves local inflammation and reduces itching.
- A drink made from viburnum, raspberries, cranberries and lingonberry leaves helps fight intoxication and headaches.
- Celery juice. Removes signs of poisoning in the body and improves overall well-being.
Whether it is possible to use this other folk remedy when treating chickenpox in adults is determined by the therapist.
Related article:
Chickenpox: how many days does quarantine last?
Video:
Atypical course of the disease
How many people get atypical chickenpox? In this case, healing may take up to two months, and the disease may exhibit symptoms of herpes zoster. Atypical chickenpox causes structural changes not only on the skin, but on internal organs. The disease is manifested not only by an increase in temperature and the formation of blisters on the skin, but also by:
- pain in the lower back and abdomen;
- vomiting, nausea, lack of appetite;
- damage to the nervous system;
- decrease in pressure;
- arrhythmia, decreased heart rate;
- impaired renal function.
In this case, damage to internal organs occurs not so much due to intoxication, but due to the multiplication of the virus in the cells of the internal organs. Atypical chickenpox can be fatal. This disease most often affects people with chronic diseases that reduce the immune response: hepatitis, HIV and others.
Treatment of atypical chickenpox must be carried out by a doctor; it requires constant monitoring of the condition of internal systems.
Possible complications
If the patient does not pay enough attention to treatment, he will struggle with the complications of chickenpox for a long time.
Complications may be as follows:
- Herpetic rashes in segments of the respiratory system with respiratory failure. Herpetic stomatitis is one of the obvious complications of chickenpox
- Herpetic stomatitis.
- Pathologies of the liver and kidneys - hepatitis and nephritis.
- Damage to the central nervous system - encephalitis, brain cysts and paresis.
- Cardiovascular pathologies – myocarditis and thrombophlebitis.
- Inflammation of the genital organs - vaginitis in women and balanitis in men.
To prevent the development of severe disorders, preventive measures are required.
Prevention of chickenpox in adults and vaccination
The only way to avoid chickenpox is to limit contact with carriers of the virus. Strengthening the immune system and a healthy lifestyle is the best prevention for chickenpox and other pathologies.
Also reduces the chance of infection:
- Early identification of patients.
- Isolating them from healthy people.
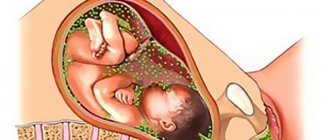
- Administration of immunoglobulin to children and pregnant women.
If you have frequent contact with infected people and work in medical institutions, vaccination is recommended. It ensures the development of lasting immunity against chickenpox. This measure is effective even in the first days after contact with the pathogen, and in case of late treatment the person is treated in the usual way.
Chickenpox in adults is fraught with a large number of complications, so it is advisable to avoid contact with infected people. It is also recommended to get vaccinated, which will protect against a dangerous disease for many years.
Prevention measures
People who did not have chickenpox in childhood are interested in the question: is it possible to avoid infection? Currently, there are several methods of prevention.
Emergency vaccination
There are two types of main vaccines used in Russia: Varilrix and Okavax. Emergency vaccination against chickenpox is carried out no later than 96 hours (preferably up to 72 hours or 3 days from contact with the patient).
Vaccination of an adult. The Okavax and Varilrix vaccinations are administered subcutaneously into the shoulder.
Administration of immunoglobulin intramuscularly
Immunization is carried out in case of contraindications to vaccination. Increases the body's resistance. Indicated for people with weakened immune systems who have not previously had chickenpox and have been in contact with a sick person. The risk zone includes: persons with severe chronic diseases, pregnant women, people receiving radiation therapy. Immunoglobulin is administered within 96 hours after contact (preferably up to 72 hours).