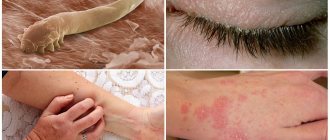
Peeling in the ears
Excessive peeling indicates dry skin or rapid division of epithelial cells, when the keratinized scales do not have time to slough off. This pathology can be caused by damage to the skin of the ear canal due to mechanical, chemical irritation, inflammatory processes or allergies.
If peeling develops for the first time, you will need to consult a doctor. Only based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis can one accurately determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe effective therapy. The appearance of unpleasant symptoms should not be ignored, because some ear diseases can lead to dangerous consequences.
Treatment for ear peeling
Correct diagnosis means effective treatment!
Treatment for ear peeling can begin only after the cause of the peeling has been established. Typically, treatment is aimed at eliminating both unpleasant symptoms and the root cause itself.
You cannot start treatment on your own before the examination and drip any drops available at home into your ear. The use of folk remedies such as herbal decoctions and natural juices is also dangerous. They can not only be ineffective, but also intensify the allergic reaction and lead to burns.
Symptom treatment method:
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial infections, purulent discharge from the ear, and otitis media. They can be local or general. In case of serious infection, oral antibacterial drugs are combined with the use of topical agents. The most famous antibiotic ear drops are Otipax, Anauran, Otofa, Otinum. They have a complex effect: they relieve itching, relieve pain and act on pathogenic bacteria. The drugs have contraindications and age restrictions, so it is advisable to consult a doctor before using them.
- Antihistamines. Antiallergic drugs are prescribed for allergies, dermatitis, and eczema. They are usually prescribed in tablets. These drugs block receptors that respond to the irritant and relieve all existing symptoms of an allergic reaction. Such drugs include Zodak, Cetirizine, Loratadine, Tavegil, Suprastin, etc. The drugs differ in composition and have contraindications. When treating eczema, you must also adhere to a diet.
- Antifungal topical agents. If a fungal infection occurs, topical medications are usually used. Medicines are prescribed depending on the type of fungus: mold, yeast, pathogenic. Typically, agents such as Terbinafil and Nitrofungin are recommended. For serious infections, oral medications such as Fluconazole are recommended.
- Surgery. Only boils usually require surgical treatment. If the drugs do not help, the boil increases in size, matures and does not break through, it is opened with a scalpel after local anesthesia, and then treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent complications.
Possible complications of the symptom
Ignoring a symptom increases the risk of developing serious complications!
Complications can arise not only in the absence of treatment, but also in the event of improper treatment. The severity of complications depends on the disease that caused the peeling process in the ear.
Even ordinary dermatitis can lead to undesirable consequences if it is started:
- Deep mycosis. Otomycosis (fungal infection of the ear) in severe cases can lead to deep mycosis. This is a dangerous disease when the fungus begins to penetrate inside the body, affecting organs and tissues. It is very difficult to cure this disease; it is often accompanied by relapses throughout life. The fungus can affect the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, upper respiratory tract, liver, and lymph nodes. Mycosis is usually self-limiting, but can be fatal in people with weakened immune systems, such as those infected with HIV.
- Sepsis. Otogenic sepsis leads to infection entering the blood and spreading throughout the body. Sepsis is severe, accompanied by high fever, profuse sweating, dehydration, and a drop in blood pressure. When the membranes of the brain are damaged, meningitis develops.
- Otoanthritis. This complication usually occurs in small infants, when inflammation from the middle ear during otitis spreads to the mastoid process. The disease can occur in a latent form or be accompanied by characteristic symptoms: fever, ear pain, active discharge of pus, and pus accumulates very quickly after its removal.
- Perforation of the eardrum. Inflammatory processes, ear rinsing procedures, and improper hygiene lead to damage to the eardrum. As a result of perforation of the membrane, hearing function is impaired, noise and buzzing in the ear, discomfort, and pain occur. If there is perforation, drops should not be instilled into the ear, as they can get on the auditory nerve, which leads to serious hearing impairment.
- Destruction of the auditory ossicles. The destruction of the auditory ossicles begins with long-term and severe inflammatory diseases of the ear. With this disease, hearing loss can be significant and quite long-lasting, as well as severe pain in the ear, a feeling of fullness, noise, and dizziness.
Causes
The following factors provoke the development of skin peeling are identified:
- Increased dryness of the skin in the ear, which is an individual characteristic of a person;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Development of furunculosis;
- Violation of hygiene rules;
- Diabetes;
- Frequent cleansing of the skin, which causes dryness;
- Insufficient intake of vitamins and nutrients;
- Fungal infection;
- Development of eczema;
- Allergy. In this case, the auricle and skin behind the ears peel off;
- Excessive sulfur formation;
- Old age of patients;
- Mechanical damage to the skin in the ear;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Frequent stressful situations.
It is worth taking a closer look at the main causes of ear peeling.
About the causes of itching and flaking in the ears in our video:
Inflammation
In most cases, the ears begin to peel off due to inflammatory processes. Inflammation can lead to damage to the outer and inner parts of the hearing aid. The following diseases are distinguished:
- Otitis externa;
- Dermatitis;
- Furuncle;
- Fungal infection;
- Eczema.
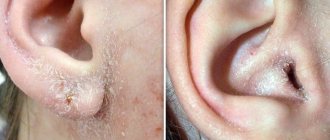
Peeling with otitis externa or dandruff in the ear canal
Otitis
Inflammation of the external auditory canal in children and adults can develop as a result of an infectious process caused by staphylococci. The disease often provokes the development of the following symptoms:
- Peeling of ears;
- Hearing loss;
- The appearance of a feeling of congestion;
- Development of pain syndrome. The pain usually appears suddenly, but can be constant and debilitating;
- The appearance of purulent discharge.
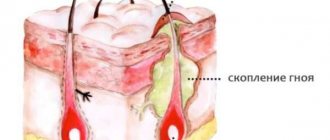
Furuncle
Often, peeling of the ear develops against the background of a boil. The main cause of the disease is infection of small wounds on the skin. The development of a boil may indicate inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and dermis.
The initial stages of the disease are characterized by the appearance of itching, swelling and slight redness of the skin in the affected area. Then acute pain syndrome occurs without impairment of hearing quality.
When a boil develops, the use of drug therapy is ineffective. Surgical removal of the formation is recommended, after which long-term antibiotic therapy is required.
Dermatitis
When the external auditory canal is irritated by chemical compounds or prolonged discharge of pus, dermatitis can develop. The disease leads to the development of unbearable itching, swelling of the skin, the appearance of weeping wounds, and peeling.
Hard crusts and blisters often form on the affected areas. Characterized by a gradual increase in symptoms in the absence of therapy.
Treatment of dermatitis should be comprehensive. It is recommended to use the following groups of drugs:
- Drugs with antihistamine effect;
- Corticosteroids for external use;
- Antibiotics for secondary infections;
- Hydrogen peroxide or soda solution. Allows disinfection and elimination of exudate
You should adhere to a hypoallergenic diet until the symptoms of the disease are completely eliminated.
About the causes of dermatitis in the ears and methods of its treatment in our video:
Eczema
Pathology refers to allergic diseases that can occur in acute and chronic forms. The duration of the acute stage does not exceed 21 days. It is characterized by damage to the upper layers of the epidermis.
The use of effective therapy can completely cure the disease. Otherwise, a secondary infection may occur, immunity may decrease, and the disease becomes chronic.
The following symptoms of eczema are distinguished:
- Redness of the skin;
- Development of itching;
- The skin becomes dense;
- The appearance of a small rash similar to dermatitis;
- The appearance of dry crusts and cracks that provoke peeling.
Therapy of the disease is based on the use of external agents. When weeping wounds develop, wipe with alcohol or Oxycort-based preparations. If dry crusts occur, then the application of anti-inflammatory ointments with antifungal and vasoconstrictor components is indicated. In rare cases, antibiotic therapy is indicated.
Fungus
Quite often, the cause of peeling ears is a fungal infection of the skin. The disease develops in patients with reduced immunity, when favorable conditions arise for the development of fungi. Fungal infection leads to the development of the following symptoms:
- The appearance of tinnitus;
- Development of severe itching;
- The skin is peeling;
- The occurrence of headache;
- The appearance of a sensation of a foreign body in the ear;
- The appearance of discharge with a specific odor.
As part of the treatment of the disease, local and systemic drugs that have an antifungal effect are used. Antihistamines can relieve severe itching.
Peeling in the ears due to eczema and dermatitis
Treatment
When a leak occurs from the ear, the first question that arises is what to treat, but self-medication is strictly forbidden. Therapy directly depends on the cause of the pathology and the intensity of the inflammatory process.
Otitis of the external and middle ear involves the following therapy:
- antibiotics – Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Rifamycin;
- combination drugs – Sorphadex, Candibiotic;
- antiseptics – Miramistin;
- antifungal drugs – Clotrimazole, Pimafucin.
The dosage and combination of drugs are determined only by the doctor based on the intensity of the pathological process and the individual characteristics of the body.
Treatment for eczema:
- daily hygiene of the wet surface of the ear - solutions based on hydrocortisone or oxytetracycline are used, as well as special aerosols with a similar composition;
- anti-inflammatory ointments with antiseptic and antimicrobial effects (zinc ointment);
- vegetable or petroleum jelly for heavy accumulation of crusts;
- drug therapy - includes specific drugs aimed at suppressing the source of the disease (calcium gluconate, calcium chloride, sodium thiosulfate, by injection), as well as antiallergic drugs - Suprastin, Tavegil.
Treatment of an allergic reaction when leaking from the ears requires mandatory exclusion of contact with the allergen. Subsequent therapy is symptomatic:
- antiallergic drugs;
- anti-inflammatory ointments;
- antiseptic drugs;
- restorative therapy.
The use of traditional medicine for ear leaks in adults is not prohibited, but is of a secondary nature. Considering the causes of the pathology (inflammatory process with purulent contents), the use of only herbal decoctions is ineffective. In most cases, folk recipes have a good antiseptic and regenerating effect, but must be combined with drug treatment.
Traditional medicine includes the following recipes:
- Burdock - dry leaves are crushed and filled with water in a ratio of 50 g of plant per 1 liter of liquid. The mixture is boiled for 5 minutes. Take 100 ml 2 times a day after meals. The decoction has an antiallergic effect.
- Chamomile - 3 tablespoons of dry plant, pour 1 liter of water. The mixture is boiled for 5-10 minutes. The decoction is taken orally, 150-200 ml 3-4 times a day. The plant is a powerful natural antioxidant and has no contraindications other than individual intolerance.
- Preparation of the ointment - lanolin (15 g), petroleum jelly (15 g) and an alcohol-based solution of string (30 ml). The ointment is applied to the affected area. The product has an antiseptic and antiallergic effect.
It is worth remembering that each traditional medicine recipe must be agreed upon with the attending physician, and should not be used as the main therapy.
The ear canal is normally dry and clean, except for the presence of a small amount of earwax. The formation of fluid, the leakage of pus, deterioration of hearing - all this symbolizes the inflammatory process. It is necessary to seek medical help at the first symptoms.
What is the treatment for allergic origin of the symptom?
If the cause of peeling skin in the external auditory canal is an allergic reaction, then doctors use the following treatment tactics:
- Taking antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin, Loratadine, Erius). It is recommended to use systemic medications and topical agents. This will eliminate itching and burning;
- Use of sedatives (tincture of valerian, motherwort, hawthorn).
- Following a hypoallergenic diet;
- Wiping the skin with antiseptic solutions. This is necessary to prevent the development of secondary infection;
- Corticosteroid drugs. Local hormonal agents are prescribed to stop the acute process.
If peeling of the earlobe develops, you should stop wearing earrings and headwear.
Treatment depending on the cause
Treatment for flaking in the ears depends on the cause of the process. To begin with, a thorough examination of the auricle and ear canal is carried out, tests and samples of tissue or fluid are taken from the ear. This is necessary to determine the pathogen and prescribe therapy.
Medication
Drugs and procedures directly depend on the disease:
- Allergy – if, after excluding contact with the allergen, the inflammatory reaction does not go away, you should consult a doctor. He will assess the extent of the process and prescribe appropriate treatment. Creams and ointments with local antiallergic action, for example, Fenistil, are widely used. In case of a strong reaction, Suprastin tablets and a hypoallergenic diet are prescribed.
- Seborrheic dermatitis - the disease is treated with ointments and creams that contain zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole. Specific drugs and their combination are prescribed by the doctor depending on the patient’s condition and individual indications. At the same time, a vitamin complex is prescribed to strengthen the immune system and medications aimed at treating chronic diseases.
- Fungal otitis - the effect on pathology involves washing the ear canal with antifungal drugs, followed by the use of similar ointments. The choice of agent is made based on the type of pathogen. The drugs often used are Clotrimazole, Burov's liquid, Nystatin.
- Eczema is a disease that requires a course of treatment. The drugs used are calcium chloride, sodium thiosulfate, Resorcinol, Ichthyol ointment.
The choice of treatment, course duration and combination of drugs is determined only by the doctor.
Folk
Traditional methods of treating flaking in the ears can only be used as an additional effect and only after consultation with a doctor.
- Sunflower or olive oil - the method is effective for dry skin, when peeling is caused not only by improper hygiene or allergies to cosmetics, but also by incorrect selection of them. You will need 15-20 ml of oil and a cotton swab. It is moistened and introduced into the ear canal superficially. You need to hold the tampon in your ear for 5-10 minutes. If the earlobe peels or the skin peels from the outside, the surface is also wiped with a swab, and excess oil is removed. Thus, the skin is moisturized, minimizing epithelial detachment, and at the same time preventing the spread of scales through hair and clothing.
- Chamomile – 1 tablespoon of the plant is poured with 100 ml of boiling water. It is necessary to insist for at least 25 minutes. Then cool, add 5-10 ml of vegetable oil and use a swab to lubricate the peeling area. Chamomile has regenerating soothing properties, which is effective for scratching. The oil moisturizes the skin and prevents instant evaporation.
What to do in case of fungal otitis
When a fungal infection develops, it is necessary to determine the type of fungus. This will help in choosing an effective drug. If mold fungi are detected, the prescription of Terbinafine is indicated. If the fungal infection is caused by yeast, then the use of Pimafucin is recommended.
To treat external otitis, local medications (ointments and drops) are used. In severe cases, antibiotics are prescribed . Preventive measures include eliminating moisture from the ears, avoiding swimming in polluted bodies of water and using sharp objects during hygiene procedures.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you how to recognize a fungal infection in the ears:
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
If peeling in the ears is not pathological, then consulting a doctor may not be necessary. This can be determined in the following ways:
- Absence of additional symptoms - any ear pathology occurs with several signs simultaneously. If they are absent, except for peeling, then the likelihood of an infectious process is minimal.
- In case of allergies, eliminating the influencing factor that causes peeling and itching relieves all symptoms. One day is enough to understand this. For example, if the cause of peeling was cosmetic products, then after stopping their use for 12-24 hours, peeling, itching and redness completely disappear.
- In the absence of hygiene - if you carefully care for your ears, which has not been done before, the peeling disappears on its own.
A visit to the doctor can be postponed only if all symptoms have disappeared. And if the peeling disappears, but there is still itching or some discomfort in the ear, a consultation and examination with a doctor is required.
How to get rid of dandruff in the ear
Dandruff in the external auditory canal or on the eyebrows develops against the background of frequent stressful situations, unbalanced and poor nutrition. Therefore, it is necessary to normalize the diet and daily routine. If the cause of dandruff is a metabolic disorder, then consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary.
In some cases, peeling and itching in the ear develop due to the characteristics of the skin type. If you have an oily scalp that requires frequent washing, or the appearance of white scales on clothes, you may suspect a dysfunction of the sebaceous glands in the external auditory canal.
To prevent flaking, you can use anti-dandruff shampoo, for example, Sulsena, Nizoral. It is also recommended to use cosmetics that will remove excess sebum and improve the condition of the epidermis.
How to properly clean your ears
If you carry out proper hygiene measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of various pathological conditions. First of all, it is necessary to stop cleaning the ear canal with hard objects. Their use is the main cause of microtraumas, through which infection can occur. Regarding whether it is possible to clean your ears with cotton swabs. Contrary to popular belief, these products also violate the integrity of the skin. It is not recommended to use them.
How to clean your ears at home correctly (basic principles):
You need to wash your ear every day. At the same time, the ear canal does not need such frequent hygiene. It needs to be cleaned once a week
It is important to know that penetrating into the deep parts of the ear canal is prohibited. Do not allow water to penetrate into the deep parts of the ear canal. To remove excess sulfur, you need to take a sterile swab, twist it into a rope, then moisten it in vegetable oil. After this, it must be carefully inserted into the ear canal, but not deeply
Then use a twisting motion to remove the tampon.
Compliance with these rules significantly reduces the risk of itching, flaking and other unpleasant symptoms.
Associated symptoms
Associated symptoms may vary, depending on the cause that led to the appearance of scabs. The color of the crusts is red, white and yellowish. Typically, before the onset of peeling, the following signs of illness appear:
- The skin becomes sensitive and inflamed. Blisters and bruising may occur.
- There is a feeling of skin tightness. The area behind the ears becomes darker in color and becomes rougher.
- The crust tightly covers the skin behind the auricle. After the crust falls off, bleeding occurs.
If itching behind the ears is accompanied by fever or symptoms of intoxication, you should see a doctor. The cause of this malaise can be serious illnesses.
Prevention
To avoid peeling of the skin behind the ears, you need to follow these recommendations:
- When bathing, wash the skin around the ears well and wipe them dry.
- In the summer, the area behind the ear is wiped with a solution prepared from a teaspoon of calendula tincture and a tablespoon of boiled water.
- Hats should be washed frequently.
- Babies should not wear a hat all the time, as this will cause the skin behind the ears to become tight.
If signs of a fungal infection of the scalp appear, you should immediately contact a dermatologist. Otherwise, the infection will spread to healthy skin.
Peeling behind the ears is often observed due to poor hygiene. The second common cause is pathogenic fungi. Treatment boils down to the use of antifungal drugs and natural oils.