Introduction
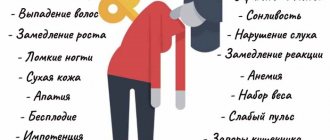
Children are not as prone to fungal diseases as adults.
According to statistics, a disease such as foot fungus can affect about 17 percent of patients under 14 years of age. The stimulus for this disease is, as a rule, pathological diseases, as well as injuries, which lead to a significant weakening of the immune system. Next, in the article we will look at fungal diseases in children and their immediate characteristics.
Causes of infection in a child
Among the so-called fungal diseases, dermatomycosis dominates . This is due to the fact that the skin of the legs is constantly in contact with the external environment. In children, these fungal diseases may represent a so-called sporadic case. But outbreaks of dermatophytosis are more common on the scalp.
In general, the distributor and source of certain dermatomycosis can be both humans and animals, but in rare cases the source can be soil. Infection with this disease occurs through direct contact of the skin of the child’s feet and the source .
In addition to contact with a person or animal, a hat, shoes or other personal item will be sufficient for infection. According to statistics, the most common place where a child’s feet become infected with a fungal disease is a swimming pool or shower room. This place can also be an ordinary beach or a hairdresser.
Due to the fact that children's skin is special, that is, immature, as well as the immune system, they contribute to the simple penetration of the disease into the epidermis, as well as the rapid development of infection.
Also, during the period of exposure to this disease, the child’s body may not have great strength.
The reason for this factor, as a rule, is poor ecology in the area, exposure to a stressful situation, lack of vitamins in the body, or some kind of chronic infection.
If the child’s immunity does not work fully during the period of infection, the fungus can develop into a pathogenic effect. This process inherently develops into a fungal disease.
Forms of fungus in children
There are four of them.
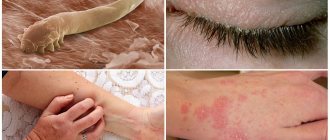
- Interdigital (intertriginous). Signs: a crack or rotting funnel between the toes (usually 3, 4, 5), surrounded by greenish or whitish peeling, making its way further to the toes. The most common fungus in children.
- Athlete's foot or moccasin foot (squamous, hyperkeratic). Less common. It’s as if a “footprint” of flaking skin is being pulled onto the child’s leg. Peeling forms on the soles - lamellar or circular. In very young children, the plantar lines of the foot and the folds between the toes seem to be sprinkled with flour - the so-called. "powdery peeling"
The nails are also affected - they become thicker, lose their transparency and change color to white, dirty gray, yellow and any other color except pinkish. The nail lags behind the bed on one side and, when cut, resembles a “bird’s beak.” The child is often plagued by itchy feet.
- Dyshidrotic or vesicular form. "Hydro" - water, liquid, "vesicle" - bubble. Blisters and blisters form along the arches of the feet, internal and external, under the bases of the toes, and sometimes on the soles. They mature, become cloudy and open, forming wet ulcers with clear boundaries. The danger lies in the addition of viral and bacteriological infections. The vesicular form can become chronic, and then allergic rashes will appear not only between the fingers, but even on the shins, almost up to the knee.
- The erased form gives an inexpressive picture: powdery peeling, “powdering” of the foot with whitish scales of the affected skin, microcracks between the toes. He himself doesn’t notice, parents are often confused and also don’t identify the fungus hidden in the folds between their fingers.
Forms of mycosis
In total, there are about one thousand species of fungi in the world. And moreover, each of them is completely different from one another. Medical experts were able to find out which of all types of fungi are dangerous for children and affect the skin of their feet. Next, let's look at the three types that are most dangerous for a child :
- The first type is called keratomycosis . This fungus is characterized by the fact that it harms only the surface of the skin of the child’s feet. It is a type of so-called tinea versicolor. The sign of this species is presented in the form of peeling of the human skin. It is worth noting that this type is less dangerous for a child’s feet;
- The second type is called candidiasis . The development of this type is caused by damage to the skin by a certain fungus of the same name. Often this type also affects the top layer of skin on the child's foot;
- And the third type is the so-called mold . This fungus can appear in places with high humidity. In the case of a child, these are sweaty feet in boots. In this case, it is not the mold that poses a certain danger, but its spores, which can spread into the external environment. Based on this, the child needs to avoid wet areas and moisture in the feet, especially if the child is prone to allergic reactions.
Important!
The most dangerous fungus for a child is candidiasis. This is justified by the fact that it is capable of infecting the child’s body directly during childbirth. Or before childbirth if his mother suffers from thrush. This fungus is also transmitted through breast milk.
Diagnosis of the disease
The only method for diagnosing foot fungus is microscopy, in which fungal mycelium is detected in the skin flakes of the disease. During cultural examination, the pathogen is identified.
Rice. 19. Microscopic view of the fungi Trichphyton rubrum (photo on the left) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale (photo on the right).
Differential diagnosis
The interdigital form of fungus on the feet should be distinguished from erythrasma, impetigo, punctate keratolysis, interdigital candidiasis, and interdigital infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Athlete's foot should be distinguished from psoriasis, dyshidrotic eczema, diffuse neurodermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, punctate keratolysis, and keratoderma.
Dyshidrotic dermatophytosis should be distinguished from bullous impetigo, allergic contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and blistering dermatoses.
How does infection occur?
The so-called mycotic type of infections in childhood is severe.
Often children affected by this disease complain to their parents of itching in the heels, as well as burning and pain in the feet.
Also, the lesion of this infection becomes red. Such symptoms mean that it is necessary to show the child to a specialized doctor. But how does this infection occur?
The main cause of fungal disease of a child's feet is onychomycosis . The risk of this disease is quite high due to the fact that children most often stay in a place where they are surrounded by peers - this is a school, kindergarten, and so on.
If a child walks barefoot on the floor, has close contact with other children, or has a sick person at home with a similar disease, then this all leads directly to the rapid and rapid spread of mycosis.
But having caught this infection? for a child this is not all. This is just the beginning of the contagious process. Further, everything happens due to certain factors that contribute to this process, namely:
- a weak immune system that is affected by one or another disease or has not yet had time to get stronger from the previous one;
- malnutrition;
- hypovitaminosis or avitaminosis;
- wearing shoes of another person or your own, but not comfortable ones;
- presence of flat feet.
Clinical manifestations of cracked heels
- cracking on the skin of the foot of varying depths
- itching, burning, pain and discomfort when walking and at rest
- sometimes – unpleasant smell from feet
The multiple causes of cracked heels often complicate diagnosis, and patients receive only symptomatic treatment. As a result, manifestations that have subsided for a while make themselves known with renewed vigor, the patient’s quality of life sharply decreases, and the risk of infectious complications increases. For effective treatment, it is important to eliminate all the causes of cracked heels, of which one patient may have several.
How to recognize a virus?
An infection of a fungal nature, like other infectious diseases, occurs in certain stages. In this case, there are three stages of the pathological process :
- The skin on the child's foot loses its normal appearance . Changes of this nature are associated with a problem in the structural relationship of the skin. The skin begins to exfoliate, and the top layer becomes thinner and somewhat rougher.
- At this stage, the skin on the child’s feet is often moist . The relief of the foot is no longer smooth, but more rough.
- This is the last stage and here the deformation of the skin composition on the foot reaches, so to speak, its peak. The structure of the skin is very much destroyed .
Causes
Mycosis of the foot (also known as foot fungus) is an infectious disease caused by a fungal pathogen.
Important: “The main problem in achieving long-term remission is the high infectivity of the parasite and constant re-infections”
There are more than 50 varieties of pathogenic fungal pathogens.
The root causes of the disease are:
- using other people's towels and linen, wearing shoes and socks;
- insufficient foot care;
- weakened immunity and impaired skin integrity and injuries on the heels of the feet;
- wearing wet shoes, visiting public wet places (swimming pool, sauna);
- consequences of incorrect surgical intervention.
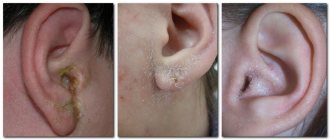
Photo of symptoms of illness in a child
How to treat (remove) mycosis?
It is very important to remember that self-treatment of fungal foot disease in children is strictly prohibited . When a parent discovers certain symptoms of so-called mycosis in a child, he should definitely go to a dermatologist for help.
Next, the doctor examines the feet and the child, takes a complete history and prescribes treatment that will most effectively help your child.
Medication (ointments, drugs)
The method of treatment with medication is quite wide. To a greater extent, everything will depend on the type of fungus, the method of its development and the main cause of this pathogen.
Treatment of fungus must be comprehensive . Moreover, in this case, an independent type of treatment is excluded, since any actions not coordinated with the doctor can lead to negative consequences. Often, a dermatologist may prescribe the following for your child:
- Various ointments and creams that are applied externally. They, as a rule, contain special components that are designed to have an antifungal effect. These components include bifonazole and clotrimazole.
- Internal use of medications is also mandatory. This includes special tablets as well as capsules.
- Various injections can also be prescribed by your doctor.
- Special antifungal patches or varnishes. Their composition is designed to have a detrimental effect on all spores of a certain type of fungus.
Previously, surgical interventions were undertaken to eliminate skin fungus, but today this method of treatment is strictly not used.
It is very important to correctly use medications prescribed by a doctor for external use.
The main rule for applying ointments is that the feet must be thoroughly washed. This type of product should not be applied roughly or in large quantities; everything should be moderate and correct.
Only in this case will the treatment be positive and rapid. If you skip procedures or treat treatment incorrectly, then self-medication will not bring the desired effect.
The drug of first and main choice is terbinafine (aka terbizil). It can be prescribed to children starting from 2 years old, the dosage depends on the child’s weight. Children under 3 years of age are prescribed treatment according to the so-called pulse-shaped scheme: the child takes the medicine for 10 days, followed by a 10-day break. The duration of the course is from one month to two.
For very young children, therapy is prescribed only by a doctor . Most medications are used from the age of two. But there are also those that can be taken at 4 years old or even from 7 years old. The doctor will be careful and use only local therapy in the form of low-concentration antimycotic powders or varnishes.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies also have a place in the treatment of such a disease. But it is prohibited to abuse such methods, and even more so to do it at will. All measures for the treatment of this disease must be agreed with a doctor .
You can prepare an ointment with your own hands, but only on the advice and recommendation of a doctor. To prepare it, you will need one chicken egg, which will need to be mixed with one tablespoon of vegetable oil.
This oil can be replaced with vinegar under certain circumstances. This mixture must be applied to the child’s feet before bedtime and put on warm socks. The shelf life of the ointment is no more than three days, and the storage place is in the refrigerator.
Treatment
The disease is characterized by optimal contagiousness and significantly spoils the patient’s life, therefore treatment must be started as soon as the first signs appear, that is, immediately.
When everything is neglected, complex therapy is inevitable, it involves disinfection of home space, shoes, household items, recognized folk remedies in this matter are 25% formaldehyde, steam treatment and hot washing, but disinfectants from the field of classical medicine are also sold on the market.
Foot bath recipes
An excellent way to treat foot fungus in children are baths. The best option in this case is a bath based on milkweed . The recipe is simple enough to make it yourself. You will need about 300 grams of milkweed herb and boiling water. The grass is poured with boiling water and the bath is ready.
If you insist this milkweed in a steam bath, it should last about 30 minutes. The child himself should soak his feet in this broth for about 15 minutes. Next, you need to wash your feet in clean water and dry them as best as possible. Next, your feet are treated with a certain ointment that the doctors prescribed for you and the procedure is considered complete.
What is a fungal infection
A fungal infection is a highly contagious disease that is characterized by damage to any tissue of the human body and is accompanied by disruption of the function and properties of the affected area of the body due to the activity of the pathogen in it.
The fungus most often affects the skin of the upper and lower extremities. It is very rare to encounter a fungal infection of the trunk, although this depends on timely initiation of adequate treatment and the person’s lifestyle.
You can become infected with a fungus:
- When visiting a sauna, swimming pool and other places where visitors are in conditions of high humidity and a certain air temperature, at which fungi survive and reproduce very well. At the same time, regular cleaning of the premises using disinfectants does not always guarantee the absence of any infection. This is due to the developing resistance of any microorganisms to agents that adversely affect them.
- When using general personal hygiene products. When using shared towels, socks, slippers and even shoes, you can very quickly become infected with a fungal infection from a person. Moreover, there are cases when a person is simply a carrier of a small amount of fungus on his skin, his skin copes with the infection and the disease does not manifest itself clinically. But such a flora is not suitable for his “roommate”, and if even a small amount of the “neighbor’s” fungus gets on the skin, a violent clinical picture of foot or hand fungus immediately develops.
- Visiting beauty salons, using a common manicure set at home. Beauty salons have special methods for disinfecting and sterilizing any instruments they use. Considering that the master may simply forget or not have time to process the instrument or simply be negligent in his duties, the visitor, when performing a massage, manicure or other procedures, may become infected not only with a fungal infection, but also with other more serious diseases (hepatitis C and B). At home, a person who suffers from fungus also needs to purchase a personal manicure set so as not to infect his household. Even the best disinfection methods and thorough sterilization of instruments do not provide a 100% guarantee that all bacteria will be removed from the surface.
Prevention
In any case, treating foot fungus is a rather complex process. But in any case, this process can be avoided if preventive measures are taken. The rules of prevention are as follows:
- If a child visits a swimming pool or other similar places, it is necessary to use only his own things.
- Parents should take care of this.
- Children should not walk barefoot on the street.
- The child’s general health must be maintained. After a certain disease has passed, it is necessary to increase immunity.
- It is very important to avoid various leg injuries.
- Shoes for children should have a natural look and, most importantly, they should be comfortable.
- From time to time, preventative baths will not harm your child.
- If there are any signs of fungus, you should consult a doctor.
Types of fungus and their symptoms
Considering what fungus on the heels looks like, there are three types, each characterized by different symptoms.
Symptoms of dyshidrotic fungus on the heels:
- as a result of rupture of capillaries, redness of the upper layers of the epidermis is observed;
- if left untreated or done incorrectly, the infection spreads rapidly, which leads to an increase in body temperature;
- the formation of numerous small watery blisters, which after a certain time burst, forming wounds;
- affected areas emit unpleasant odors;
- severe peeling of the skin, the skin on the heels can be removed in pieces;
- swelling and itching.
Intertriginous heel fungus is accompanied by redness and slight peeling of the skin, the area itches and burns. The squamous type of fungus is considered the mildest, since its course does not cause severe discomfort to the patient.
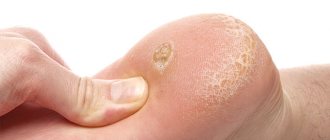
Symptoms of hyperkeratotic heel fungus are as follows:
- coarsening and thickening of the upper layer of the epidermis;
- dryness and tightness of the skin;
- floury peeling.
Mycosis of the foot is the most common form of fungal infections. People with excess body weight, patients with diabetes mellitus and varicose veins are susceptible to infection.