Formation and treatment of purulent formations on the tongue
An abscess on the tongue can appear in a person of any age. Children often suffer from this condition. If an abscess appears on the surface of the tongue or on the side, then treatment is necessary urgently, otherwise the infection will begin to spread further, and such formations will cover the entire oral cavity. Any injury can result in the appearance of a boil due to bacteria, fungi or viruses entering the area. You can cure such a disease yourself only if the boil on the tongue has appeared recently, and the inflammation has not had time to spread to neighboring tissues.
Causes of wounds
In principle, all the main factors that can lead to the appearance of sores on the tongue can be divided into several groups:
- Wounds resulting from the aggression of bacteria, viruses or fungi.
- Traumatic injuries.
- Tumor formations (benign or malignant).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Black spot on a child’s gum
Most often, sores occur due to injuries, and such a problem can be complicated by the addition of an infection. But we should not forget about other possible reasons, although they are more rare.
Development of pathology
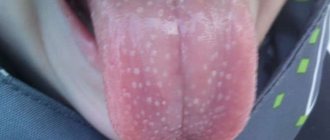
Due to the fact that the tongue does not have sebaceous glands, this organ is not capable of becoming covered with ordinary pimples. Typically, the presence of pimples under the tongue or on the surface of this area is called pustules. Lumpy formations of bright red color with a white coating appear due to damage to the damaged area of the oral cavity by bacteria of various types. Often this disease occurs after a person has bitten a place on the tongue or after eating rough food, such as candy.
Manifestations
After an injury, boils begin to form under the tongue or on its surface. This disease is called glossitis. Symptoms of the disease may be as follows:
Irritation of the damaged area that occurs after eating spicy, sour or hot food.- Further, a small tumor can be seen at this place.
- If you examine the area under the tongue or any other injured area of this organ, you may notice redness.
- Later a boil appears.
Typically, such a formation goes away on its own, without the use of medications, but if the state of immunity is weak at the moment, then there is a high probability of further spread of ulcers throughout the entire inner surface of the mouth. Therefore, it is better to start treatment immediately, at the first stage of the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
A consequence of glossitis can be the appearance of papillomas in damaged areas that have a rough structure.
Such complications occur only when the pathological process is advanced, when bacteria reach the deep layers of tongue tissue.
Why does it happen?
The causes of the disease are quite varied. Among the main ones are:
- tongue injuries, even microscopic;
- bad habits, such as regular drinking or smoking, are quite capable of causing pustular lesions of the mucous surface of the entire oral cavity;
- allergic reactions to any personal hygiene products, mouth rinses, toothpaste, lipstick or certain foods (rough, spicy, salty);
manifestations of thrush or tuberculosis. In this case, a person develops small ulcers on the tongue or on the side of the organ, and stay there for a long time, without growing and without causing significant discomfort;- anemia is a disease characterized by a lack of folic acid in the body, as well as vitamin B12. If a person has such a disease, then the surface of the tongue becomes smooth, and small red formations appear on the sides;
- diseases of the digestive and circulatory system. In this case, the tongue becomes covered with red spots;
- somatic illness - manifested by the appearance of a boil under the tongue. This condition indicates the development of a serious pathological process that affects the human immune system;
- stomatitis, which is more often found in children. Children often provoke this disease on their own when they constantly put dirty fingers in their mouth;
- manifestations of herpes.
Treatment for this condition depends entirely on the reasons for the abscesses. The dentist treats these formations, but often this doctor refers the patient to doctors of other specializations.
Drug treatment of fistula on the gum
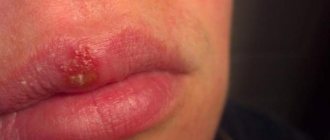
When a callus appears on the tongue, the patient may feel a burning and tingling sensation. If the callus is located at the tip of the organ, numbness may also be present. With a large callus, the patient may complain of pain while eating. In this case, the tongue often swells, increases in size and becomes bright red.
The callus itself looks like a skin pimple, inside of which there is serous exudate. In the absence of proper treatment, this exudate is replaced by pus, resulting in the formation of an abscess on the mucous membrane.
Subsequently, a bleeding wound appears at the site of the callus. It brings the patient much more unpleasant sensations than a callus. In addition, it is more difficult to treat.
A fistula on the gum can appear for one single reason - an acute inflammatory process at the very top of the tooth root. As a result, soft and bone tissues are destroyed, which leads to the formation of a fistula canal that connects the source of inflammation and the oral cavity. Inflammation is always accompanied by the release of pus (blood and pus); it comes out through the fistulous tract.
- caries or pulpitis;
- poorly sealed canal;
- cyst;
- granulating periodontitis;
- complicated wisdom tooth eruption;
- dentist's mistake during treatment, removal or implantation.
Consequences of caries
Often a fistula forms if dental caries is not treated on time or is not completely treated.
An acute inflammatory process begins in this area and a large amount of pus is released. Purulent inflammation of the root apex is called a periodontal abscess. Gradually, the tissues are destroyed, a hole appears between the gum and the tooth, through which pus comes out.
This reason is one of those for which unscrupulous dentists are to blame. As a result of the fact that the doctor did not provide the filling material, did not reach the very root, left voids, inflammation begins in the canal. Gradually it grows, affects neighboring tissues and leads to the appearance of a hole in the gum.
Therapeutic measures
Due to the fact that the appearance of ulcers under the tongue, on its surface and on the sides is often caused by ordinary trauma to this organ, medications are selected mainly with an antiseptic effect. Folk remedies with similar properties can also be effective.
Medication methods
Boils on the tongue are treated mainly through drug therapy; surgical methods are used only in exceptional cases. Preparations for external use:
- Iodine solution.
- Hydrogen peroxide.
- Baking soda solution.
- Propolis (tincture and spray).
- Local antibiotics (Chlorhexidine).
If treatment of a more advanced pathological process is necessary, the doctor will prescribe other medications. Therapy is selected individually for each patient.
More powerful means include:
- Flucinocide.
- Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone).
- Pain relieving ointments (Lidocaine or Benzocaine).
- Antifungal drugs (Nystatin, Levorin).
- Antiviral topical medications (Acyclovir ointment).
There are cases when ordinary stomatitis in a child or adult causes a number of severe symptoms, an increase in body temperature to high thermometer readings or swollen lymph nodes with an inflammatory process, which means the need to undergo treatment in a hospital. Often, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents (Amoxiclav, Cefixime) are added to therapy.
Alternative methods
Traditional methods for treating pustules on the tongue are very diverse, but before using them you should definitely consult a doctor, especially when it comes to children.
What should you do when you feel pain in your gums after installing a denture?
Every patient sooner or later has a dental problem that leads to the loss of one, several or even all teeth.
In this case, in order to prevent loss of normal chewing function and problems with the gastrointestinal tract in the future, a person with partial and complete secondary edentia turns to a prosthodontist to install an artificial prosthesis. Orthopedists offer patients a large number of designs. These include single crowns, bridges, and removable dentures. Removable dentures can be partial or complete. It all depends on the specific clinical situation. After installing an orthopedic structure, especially if we are talking about a removable denture, an unpleasant consequence may occur when the prosthesis rubs the gum, which ends in the appearance of an ulcerative surface. In this clinical situation, you need to know how to treat gums rubbed with a prosthesis.
First of all, when pain occurs, you cannot correct the situation yourself. You need to see your dentist the next day for correction. Before going to the appointment, you need to put on the prosthesis approximately 1-2 days before and even try to eat in it. This will allow the doctor to immediately see the rubbed area and remove hangnails on the prosthesis that cause this defect.
Removable dentures can be made from the following materials:
- Acrylic plastic.
- Nylon plastic.
- Combined: plastic metal. Such a prosthesis is called a clasp prosthesis.
The least amount of chafing occurs during the manufacture of nylon prostheses, because this material is very light, soft and flexible. Such designs completely replicate the prosthetic bed, which eliminates the appearance of ulcers. Some patients, after installing a prosthesis, do not go to the dentist, believing that pain is normal.
That after a certain period of time the prosthesis will wear in and the pain will go away, however, this is a misconception. While a person suffers while waiting for this moment, serious ulcers will appear on the gums, which are not only covered with plaque, but also bleed. In this case, be sure to contact a specialist, only he will tell you and show you how to treat the gums rubbed with a prosthesis.
In this clinical situation, the dentist first adjusts the prosthesis. After this, the doctor recommends not wearing a denture for 24 hours, but actively rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs calendula, oak bark, chamomile, sage and yarrow.
To make the ulcers heal faster, you can treat them with medicinal oils based on sea buckthorn or rose hips. Collagen plates for the gingival margin “Farmadont” also have rapid clinical effectiveness. These plates contain medicinal plants, enzymatic agents and collagen. They have regenerative and analgesic properties.
However, most often dentists answer the question: “The denture has rubbed the gum, how to treat it?” answer as follows. For treatment, you need to use topical agents: Solcoseryl, Kamestad and Holisad. These drugs allow you to quickly and effectively cure ulcerative surfaces under the prosthesis.
Tongue abscess: causes, symptoms, differential diagnosis, treatment
A tongue abscess is an inflammation that forms in the thickness of the tongue with the formation of an abscess. This is a rather serious pathology, accompanied by elevated body temperature, general malaise, and difficulty eating and speaking. How dangerous is this disease? What causes it? How to treat?
To get answers to these and other questions related to this pathology, you need to familiarize yourself with the clinical picture of the disease, its symptoms and signs.
Nutrition
The first step is to remove the load from the tongue so that the disease does not worsen. To do this, use a special diet that limits the consumption of salty, sweet, pepper and spicy foods, and excludes alcohol, carbonated drinks, juices, various sauces, ketchup and mayonnaise from the diet.
Food should be soft, easy to chew, without touching the inflamed areas. This could be mashed potatoes, soy pudding, chicken broth, fruit yoghurts.
If the cause of the callus is an infection, the consumption of fermented milk products is strictly prohibited. The bacteria it contains create a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic organisms, which can aggravate the situation and slow down the treatment process.
If a pip appears on the tongue, not everyone knows how to get rid of the cause of the callus. Firstly, high-quality cleansing of the oral cavity is necessary. After each meal, you should rinse your mouth with plain water to remove any remaining food. Secondly, you should brush your teeth at least twice a day.
We suggest you read: How to treat an ulcer on the tongue quickly - ProfiMed
Tongue abscess: clinical picture
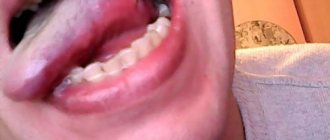
A purulent abscess located on the tongue is called an abscess.
This disease is characterized by severe inflammation, leading to the death of living tissue. In extremely difficult situations, in addition to high fever and inability to eat, difficulty breathing is noted.
That is why at the first signs of the disease you should immediately consult a doctor in order to avoid irreversible consequences.
Tongue traumatism: theory
Before you begin treatment of the tongue, you should carefully study the nature of the injury and its causes.
The first type of damage - mechanical - is the most common cause of tongue injuries. Due to mechanical damage, ulcers and superficial erosions form on the tongue.
Conditions under which mechanical injuries occur are of a domestic nature:
- damage to the integument by dental instruments - probe, bur, disc;
- the occurrence of a wound under the influence of a sharp object - a bone, a knife, a fork;
- biting the tongue while eating, epileptic seizure;
- the appearance of tongue injuries from blows to the face.
Healing of a wound caused by mechanical impact occurs depending on the depth and area of damage to the mucous membrane.
Chemical burn
Chemical injury to the tongue, as the second type of injury, occurs due to contact with the mucous membrane of a chemical substance of an acidic or alkaline nature.
Under the influence of an irritant, chemical burns occur on the tongue. The latter are characterized by the appearance of dark-colored areas, scars, blisters and blisters on the tongue (in severe cases).
Instant rinsing of the mouth with solutions with neutralizing properties is the key to rapid restoration of the integument.
For chemical burns, it is preferable to seek help from medical institutions.
Damage to the mucous membrane by steam, hot water, fire, electric current or ionizing radiation is called physical trauma to the tongue.
Characteristic of this type of injury is pain that gradually subsides from the moment of injury.
The main danger of physical injury is the development of acute catarrhal glossitis (inflammation). Consultation with a doctor in complex stages of injury is mandatory.
Deep damage to the tongue caused by various kinds of external irritants can be accompanied by complications: abscess or phlegmon of the tongue.
Painful swelling and accompanying difficulties with swallowing and speaking are symptoms of an abscess. In later stages, with increasing inflammation of the tongue, the abscess turns into phlegmon. The victim requires emergency hospitalization and surgical intervention.
Localization
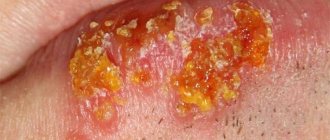
An abscess can be located both in the body and at the root of the tongue. The severity of the disease also depends on the depth at which the abscess is located. There are superficial and deep abscesses. Superficial is located directly under the mucosa. Upon examination, a swollen, hyperemic area of the mucous membrane is clearly visible.
Palpation reveals tightness and pain in the inflamed area. Quite often, superficial abscesses open on their own, resulting in significant relief for the patient.
With a deep abscess, a significant deterioration in the patient’s well-being is characteristic. During the examination, swelling and enlargement of the entire tongue are diagnosed, which makes it difficult for the patient to speak and makes it impossible to eat. The pain syndrome is accompanied by a high temperature, which can reach levels of more than 40 degrees. There is difficulty breathing.
What is an abscess, watch in our video:
Symptoms and signs
The disease develops quite quickly. Superficial and deep abscesses equally pose a threat to human health. Shallow inflammation is accompanied by acute pain when swallowing or chewing, which can radiate to the ear. This is why tongue abscess is often confused with otitis media. In addition to pain, the following symptoms appear:
- general fatigue;
- apathy;
- loss of appetite;
- salivation;
- heat;
- tachycardia;
- difficulty breathing.
The patient should be alerted to changes in the color of the mucous membrane of the tongue. The abscess and adjacent tissues turn blue and become covered with a whitish coating. An unpleasant odor appears. The earlier treatment is started, the easier it is to deal with the problem. Without adequate therapy, the size of the tongue can increase significantly, which will lead to difficulty breathing, and subsequently to suffocation.
Traumatic stomatitis of the oral cavity - the result of soft tissue injury
Any injury can sooner or later lead to serious delayed consequences. And although getting an injury to the oral cavity is more difficult than hitting a limb, damage to the teeth, gums, cheeks and tongue is not uncommon. The consequence of injury can be various diseases; in this article we will look at one of the options - traumatic stomatitis. From the article you will learn what the causes and symptoms of this disease are, as well as how it can be diagnosed and treated.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease consists of examining and clarifying the circumstances under which the tongue injury was sustained. The doctor will prescribe a general blood test. With an abscess, leukocytes and ESR will be significantly elevated. To identify the pathogen, bacterial culture is performed.
X-ray examination is also indicated. The doctor’s task is to differentiate an abscess from similar pathologies and prescribe adequate treatment. Similar symptoms may appear with Ludwig's angina, lymphadenitis, and lymph node abscess.
The photo shows a lateral abscess on the tongue
Treatment
The treatment method for superficial and deep abscess is significantly different. For superficial inflammation, you can often get by with drug therapy, including rinsing with antiseptics and taking antibacterial agents. A deep abscess is subject to surgical intervention, since its independent opening and healing is impossible.
Medication
With drug treatment, the main goals are to relieve pain, inflammation and swelling. The pain syndrome is relieved with drugs such as novocaine or lidocaine. Swelling and inflammation are relieved by a course of rinsing with antiseptic solutions in combination with taking antibiotics.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can also speed up the healing process of wounds on the tongue. Small pustules can be washed with saline solution. Dilute 2 teaspoons of salt in a glass of boiled water and rinse the mouth with this product 2-3 times a day.
Traditional medicine also advises rinsing with a decoction of calendula flowers. One tablespoon of raw material per glass of boiling water is enough. Rinse every 2 hours. Chamomile or linden flowers can be used as a medicinal herb. The juice of carrots, calamus and linden bark also promote wound healing.
Surgical methods
A deep abscess or abscess of the root of the tongue almost always requires surgical intervention.
The abscess is opened by making a dissection along the tongue. If the pathology is localized deep under the root, the autopsy is performed externally (under the chin).
After this procedure, the pus is poured out, the patient feels much better. The resulting cavity is washed with antiseptic and antibacterial solutions and drainage is installed to separate the newly formed pus.
After the intervention, drug treatment is also prescribed. It includes taking antibiotics, regularly rinsing or spraying the mucous membrane with antiseptics. After healing has begun, UHF may be prescribed to the affected area.
In what cases is it better to consult a doctor?
Even if the blister disappears after a few hours, which happens with allergies, you must tell your dentist, dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, or allergist about its appearance if the person is seen by this specialist. Rapidly increasing blisters, fever, or breathing problems require immediate attention. the victim, as well as purulent contents inside the bladder, which can leak into the oral cavity when opened independently and infect the nasopharynx if it flows inside.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, the prognosis of the disease is positive. However, the appearance of these pathologies can be avoided by performing simple preventive procedures. Necessary:
- maintain oral hygiene;
- promptly treat problems of teeth and gums;
- If small wounds or ulcers appear, rinse your mouth with an antiseptic and monitor their healing;
- strengthen immunity;
- consult a doctor if an unusual color of the mucous membrane appears.
If pain, wounds, or any changes in the mucous membrane appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will determine the cause of the problem, prescribe the necessary examination and appropriate medications.
Should I treat or remove my wisdom tooth?
Wisdom teeth almost always cause a lot of trouble and doctors often advise removing them immediately, since they can have an atypical location and cause significant discomfort during eruption. But what to do when a wisdom tooth breaks off: treat it or remove it? In this situation you need to think carefully. If the tooth is of normal shape and has grown correctly, then it is completely unnecessary to remove it. Like all other teeth, the wise tooth can be treated, restored and even prosthetically fitted, because, as you know, there are no superfluous teeth.
Any of the situations described above is quite unpleasant. Therefore, the main task is to prevent chipping of teeth and enamel. Proper oral hygiene and timely visits to the dentist can significantly reduce the risk of chipping the tooth wall. Also, life situations in which mechanical damage to the jaws and teeth in particular can occur should be minimized.
In addition, it is worth paying attention to the foods you eat and, if possible, excluding those that may be too hard or potentially dangerous because, as you know, the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and the entire body as a whole depends on the health of your teeth.
Abscess of the root of the tongue
When examining the oral cavity, dental surgeons are faced with a serious disease - a tongue abscess. This disease occurs when pathogenic flora (infection) enters the tissue of the tongue. The tongue consists of a body and a root.
The body of the tongue is separated by a fibrous septum. The lingual artery, which supplies the tongue with blood, is located longitudinally under the tongue. The branches extending from the artery form a network of vessels in the tongue. The lingual vein and nerves (lingual and sublingual) are located longitudinally. The root, with the help of muscles (genioglossus and hyoid), fixes the tongue to the jaw and hyoid bone. Infiltration of an abscess into the root of the tongue is especially dangerous.
Causes of tongue root abscess
An abscess occurs if inflammation along the body of the tongue spreads to the root or the infection gets from the lingual tonsil.
The disease can be a consequence of the inflammatory process in the lower teeth, a complication of purulent periodontitis. Stomatitis is accompanied by ulcers and erosions on the oral mucosa; pathogenic bacteria and viruses spread precisely through damaged tissues.
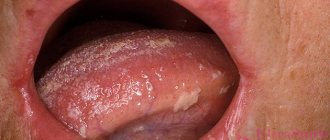
Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue. The mucous membrane of the tongue can become inflamed for many reasons, so it is necessary to examine the tongue. Plaque, change in color, size are alarming symptoms.
The culprits of inflammatory processes are bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, anaerobic). Danger arises when the mucous membrane of the mouth or muscle tissue of the tongue is injured. This could be a puncture with a fish bone, biting the tongue, chewing on the cheeks, sharp edges of the teeth, or traumatic dentures.
Folk remedies for relief
If the inflammation is minor, many recommend treating tongue tip at home using both traditional medicine and pharmacy analogues.
The best way to relieve inflammation and disinfect the oral cavity is chamomile infusion. An infusion of oak bark will help heal ulcers and cuts, if any.
In pharmacies you can also buy ready-made concentrates of celandine, calendula, nettle or St. John's wort for rinsing the mouth. It is recommended to lubricate small pustules with sea buckthorn oil or rosehip oil.
Traditional medicine recipes are designed to alleviate the condition, but cannot replace drug treatment. Most of the tips help to numb the lesions, stop the spread of bacteria and viruses, and speed up regeneration.
The following recipes will help alleviate the condition:
- Chamomile, sage, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum berries are considered good antiseptics. To prepare the decoction, add a tablespoon of dry herb to 250 ml of water, which is brought to a boil and infused in a warm place for 2-3 hours.
- The wound-healing effect is inherent in aloe and Kalanchoe juice, calendula, sea buckthorn and rosehip oils. Concentrated juices and oils are applied directly to the sores.
- A universal remedy for treating ulcers is a solution based on salt, soda and iodine. The product has antiviral, wound healing and analgesic properties. You can prepare it from a spoonful of salt, a spoonful of soda and three drops of iodine per glass of boiled water. Rinse the mouth with this solution or make lotions with it. Less effective, but quite popular, is hydrogen peroxide. It is used to directly treat the affected areas with ulcers.
Symptoms of tongue root abscess
- profuse drooling;
- speech disorder;
- pain when talking, swallowing;
- increase in tongue size;
- swelling of the mouth;
- grayish coating on the mucous membrane;
- bad breath;
- pain when pressing;
- palpation of the seal in the tongue;
- difficulty breathing.
If the infiltrate has collected at the root of the tongue, the intervention of a doctor - a dental surgeon - is necessary. Infectious agents can spread to the mandibular, sublingual, and chin areas.
Treatment of tongue root abscess
Start conservatively. Frequent rinsing is carried out with antiseptic solutions, and antibacterial medications are prescribed. If conservative treatment does not help, surgery is necessary.
A deep abscess requires surgery. The surgeon opens the abscess, making a cut along the tongue. If the abscess is located deep under the root, the opening is done from the outside, under the chin. After the cut, pus flows out and the patient feels relief. The abscess cavity is washed with an antibiotic solution, and a drain is placed to drain the pus.
Sometimes a trachetomy (cutting the tracheal wall and inserting a breathing tube) is necessary if breathing is difficult. After the operation, antibiotics, vitamins, regular spraying of the oral mucosa with antiseptics, rinsing with soda solution and manganese are prescribed. It is recommended to rinse with decoctions of sage and chamomile. In the future, the UHF course is used.
Prognosis of inflammation of the root of the tongue
Abscesses of the body and root of the tongue in the mouth should not be neglected; the success of treatment directly depends on a timely visit to the doctor. Cure occurs within 14 days if the disease is not advanced and adequate treatment is provided. Otherwise, serious complications may occur.
A very dangerous complication is phlegmon. This purulent inflammation of fatty tissue quickly spreads into the surrounding tissues, muscles, and tendons. Difficult to treat. Mediastinitis is inflammation of the mediastinum. Sepsis (“blood poisoning”) – infection of the body, infection entering the blood. In such cases, there is a serious threat to life.
Preventive measures
You can prevent abscesses of the body and root of the tongue by following simple recommendations:
- Maintain oral hygiene, choose the right toothbrush and toothpaste;
- refuse food that irritates the mucous membrane (spicy, too hot);
- do not injure the oral mucosa (condition of teeth, crowns, dentures);
- if you accidentally bite your tongue, rinse your cheek with an antiseptic solution and watch the wound heal;
- strengthen the immune system (balanced diet, sports, walks);
- visit the dentist regularly;
- If you find wounds, ulcers in the mouth, plaque on the mucous membrane, or an unusual color, you should consult a doctor.
The doctor will sanitize the oral cavity, detect and eliminate the cause of injury to the mucous membrane, recommend personal hygiene products and methods for disinfecting wounds at home. And if necessary, he will prescribe examination and treatment. The painful symptoms listed above should seriously alert you and should not be ignored!
Home remedies
To speed up the healing of wounds in the mouth, you can use:
- Rinsing wounds with saline solution - 2 teaspoons per glass of warm boiled water.
- Treat the wounds with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine. To prevent the infection from spreading, apply a separate cotton swab to each wound.
- Apply ice to relieve inflammation.
Traditional medicine recommends:
- Wipe the wounds with a mixture of milk (100 ml), yolk and honey (1 dessert spoon) using a finger wrapped in a bandage.
- Rinse your mouth with a decoction of calendula flowers (1 tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water) every 2 hours.
- Rinse with a decoction of calendula, linden, chamomile, linden bark and calamus, pour 500 ml of boiling water over the mixture.
Carrot juice, horseradish, and horse sorrel help heal wounds.
Why are abscesses of the body and root of the tongue dangerous? The disease is accompanied by high fever, pain and other very unpleasant symptoms. The patient can only sit almost motionless, since the slightest movement causes sharp pain.
A strong increase in the volume of the tongue impairs the patient’s speech and can block breathing! Advanced stages are fraught with serious complications!
Rules for caring for calluses
Calluses on the lips of a baby, formed during sucking, do not require special care. If you reduce the load and apply it correctly to the chest, it will disappear without intervention.
It is forbidden to pierce the growth or tear off the exfoliated area of skin. Such actions will lead to infection.
We suggest you read: What does the yellow color of the tongue mean?
If the blister bursts on its own, the following care must be taken:
- Take a cotton swab.
- Dip in 3% hydrogen peroxide solution.
- Gently wipe the affected area.
If the formation occurs due to thrush, you can carry out the following manipulations:
- Soak a sterile cloth in a mixture of baking soda and warm water.
- Disinfect nipples and objects with which there is contact (toys, bottles, nozzles, breasts).
- Lightly wipe away plaque from the mouth. Perhaps the mucous membrane will bleed.
- Repeat the manipulation 4-7 times a day.
If formations appear due to herpes or stomatitis, an examination by a specialist is necessary. Some doctors advise cauterizing the callus with iodine, brilliant green, or furatsilin solution. This treatment should be used under the supervision of a therapist so as not to cause a burn on the baby’s delicate skin.
A wet callus on the upper lip of a baby has several differences:
- placed clearly in the middle of the upper lip along the edge of the mucous membrane;
- the defect itself is round in shape;
- white bubble with liquid, diameter 5-6 mm.
If the callus is dry, the crust will be dense. A thick top layer appears. In this situation, its color is close to pale pink with a subtle yellowness. When touching a wet or dry callus, the child will not feel discomfort, there is no pain. Other pathologies that do not correspond to the description pose a danger to the baby.
With thrush and stomatitis, the callus may have a yellow, gray, or white background. The edges of the formation may turn red and the tissues may swell. The baby develops increased salivation.
With herpes, the callus is accompanied by swelling; there may be several blisters at the edges of the mouth. There is a burning sensation and redness around the lesion.
If parents notice that the baby has a callus on the sponge, they should not touch or treat it. However, care should be taken to ensure that such formation does not arise again.
First, you should find out whether the baby is attached to the breast correctly, and also check the width of the hole in the nipple.
The position in which the baby eats food also matters. When breastfeeding, it is convenient to place the baby on his side, but you should make sure that his mouth is at the level of the nipple. If a child has to strain and reach for a food source, he may rub the mucous membrane. In some cases, it makes sense to place a rolled up diaper under the neck and head.
When bottle-feeding, you need to make sure that the baby lies on his side when feeding. If you feed the baby while lying on his back, the upper body should be slightly elevated.