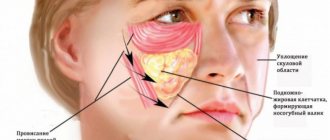
From our article you will learn about the causes and methods of treating a lump on the tongue.
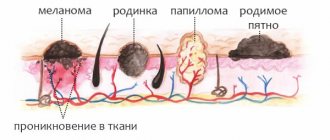
A lump on the tongue is a dense growth that most often appears on the back (deep) part of the tongue.
Here are some of the most common reasons for the appearance of a hated lump:
- sialadenitis;
- lipoma;
- papilloma;
- adenoma;
- botryomyxoma;
- fibroma;
- myoma;
- neurofibroma;
- hemangioma;
- lymphangioma;
- cystic formation;
- struma of the tongue;
- malignant or benign tumor;
In fact, it is very difficult to determine the cause of a lump on the tongue on your own. Under no circumstances should you treat this problem. As soon as you feel discomfort and deviations from the norm, you should seek help from a specialist as soon as possible. There is no point in delaying this, as this can only make the situation worse.
First, you should visit a therapist. It is very important to seek help from a doctor on time. The therapist will conduct an examination on the spot and then refer you to a specialist, this could be a dentist, otolaryngologist, oncologist and surgeon.
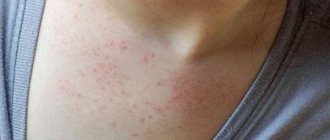
White bumps on tongue
A lump on the tongue is an unpleasant and unaesthetic neoplasm that can ruin the life of any person. In order to cope with this problem, it is necessary to understand why a seal forms on the tongue and how to deal with it.
Causes of seals
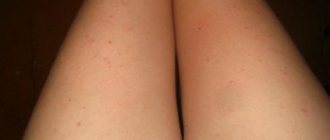
Lumps on the tongue vary in their external characteristics, as well as the reasons that cause them. They can be large, small, irregular in shape or, conversely, spherical. They can be soft or hard, and there may be serous filling, blood, pus, or fibrous tissue inside.
In addition, they can be of different colors: from bright red to white and transparent. All the diversity of these neoplasms suggests that no methods of self-diagnosis, let alone self-medication, will help cope with the problem; professional help from a specialist is needed to solve it.
Here are the main reasons for the appearance of bumps:
Cysts and hematomas
If a person accidentally bites his tongue while eating, a small hematoma—a red, swollen spot—will most likely appear at the site of the bite. At the initial stage, medical assistance is not required, since everything will disappear on its own in 3-4 days. However, if the hematoma is too severe and does not go away for more than 10 days, then most likely it has turned into a cyst.
In this case, surgical intervention is required. Cysts are usually white or gray in color; if left untreated, they continue to grow, preventing a person from eating and speaking normally. Treatment consists of excision of the cyst followed by cleaning of the wound channel.
A ranula under the tongue often appears due to injury. The cyst can develop into a dermoid form.
If any infection is attached to the cyst, it becomes more painful and, accordingly, more dangerous. In this case, the treatment is carried out comprehensively; simultaneously with the removal of the cyst, the patient undergoes a course of antibiotic treatment.
Sialadenitis
This is an infectious disease that affects the salivary glands located under the tongue. In this case, the tongue is covered with numerous bumps.
In addition, the disease manifests itself with other symptoms: the throat swells, pus may be released from bumps on the tongue, the person’s body temperature rises, weakness occurs, as well as pain in the joints and muscles. These are all signs of general intoxication.
Struma
Quite a rare disease. During the formation of the digestive system, thyroid tissue enters the root of the tongue, subsequently forming a dense knot. Since the disease is of genetic origin, it is treated as prescribed by a geneticist.
Stomatitis
With this disease, red or white growths appear on the tongue. They are quite painful pimples. The cause of their occurrence is the ingress of dirt from hands or food, usually fruit.
Since children are most often susceptible to the disease due to their habit of putting their hands in their mouths, it should be dealt with only preventively: teaching children to maintain hygiene, wash their hands before eating, as well as fruits and vegetables. Due to the fact that the disease is severe, the patient has difficulty eating and swallowing, children remember the lesson quite quickly.
This also includes pip: the video below talks about this well:
Herpes
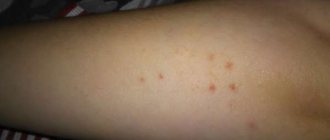
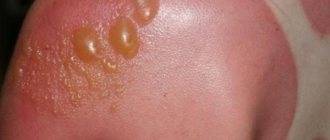
The herpes virus usually affects the skin around the lips. But it happens that it appears on the mucous membrane of the mouth, including the tongue. With this disease, the tongue becomes covered with painful pimples, with a whitish liquid inside.
Tongue herpes.
Herpes lasts for 12–15 days and disappears without a trace. However, treatment is necessary to facilitate its course by relieving pain.
Sarcoma
This formation is malignant. It grows rapidly, does not have a permanent shape, and can become covered with ulcers and bleed. Spreads metastases to nearby organs. Bottom formation can appear in people over 40 years of age.
In addition to the neoplasm itself on the tongue, there are some other symptoms: pain, putrid breath, increased salivation, disruption of the taste buds, pain when talking or eating.
Sarcoma is treated comprehensively, and the treatment is quite difficult, including radiation therapy and chemotherapy. And still there is no guarantee of 100% cure.
If you notice a lump on your tongue, under no circumstances should you squeeze it out or pick it with anything, you should immediately contact a specialist!
Papilloma
Formed from epithelial cells. Its shape resembles a small cylinder and can grow either as individual specimens or as conglomerates. The causative agent of the disease is the human papillomavirus. It can only be treated surgically, electrocoagulation or laser removal.
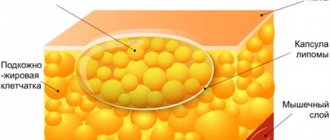
Lipoma
Despite the fact that this formation most often occurs on the scalp, it happens that it appears on the mucous membrane of the tongue. A lump of this origin is non-painful and mobile.
Lymphangioma
These bumps usually appear on the side or tip. They consist of lymphatic tissues. They are formed in the womb and can be so numerous that they cover the entire surface of the tongue.
Neoplasms are extremely traumatic, bleed heavily when damaged and cause pain. If neglected, they have extremely unpleasant consequences:
This 14-year-old child has lymphangioma of the tongue, floor of the mouth and chin.
Other reasons
- Fibroma. This bump has a stalk that is attached to the mucous membrane of the tongue. The formation consists of fibrous tissue, the color is natural, non-painful.
- Botriomycomoma.
occurs due to a chemical or thermal burn. It is a large spot of a smooth surface, up to 5 cm in diameter. Sometimes it is covered with some dividing lines. - Adenoma. The tumor occurs on the mucous membranes of the throat and esophagus, however, it can also appear both on the tip of the tongue and on its root.
- Myomas. These formations appear only on the upper part of the tongue and resemble small papillae.
- Hemangioma.
This benign formation is extremely traumatic and bleeds heavily after damage. In this regard, if left untreated, it can degenerate into a malignant tumor. - Neurofibromas.
Like a regular fibroma, this formation consists of fibrous tissue. What distinguishes it is that it is located on a nerve root. In this connection, it is extremely painful not only when touched, but also in a calm state.
What should be the treatment?
Neoplasms on the tongue are characterized by the fact that in the absence of proper treatment or constant injury, benign lumps can very quickly turn into malignant ones. And tongue cancer is just as difficult to cure as cancer in other organs.
Therefore, there is no need to be lazy; it is better to undergo a full diagnosis of the disease. It will include a visit to a therapist, dentist, infectious disease specialist, immunologist, surgeon, all of whom will prescribe tests.
In most cases, any neoplasm from the tongue is surgically removed. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and hospitalization is not required. And the removed content undergoes histological examination for cancer. In addition, this analysis will help to understand the cause of this pathology.
Source: https://glivec.su/2018/08/31/shishki-na-jazyke-belye/
What to do at home if a growth appears - folk methods
In addition to traditional treatment of growths under the tongue, many patients use traditional recipes. It is impossible to replace treatment with a completely unconventional method, but nothing prevents you from trying it.
Popular folk recipes for growths under the tongue:
Any infections and viruses developing in the body signal a decrease in immunity, so during the treatment period you should take care of taking fresh vegetables and fruits. A good vitamin complex is also suitable for these purposes.
Before using an unconventional approach, you should consult your doctor to rule out contraindications.
A lump on the side of the tongue hurts: causes and methods of treatment
If a lump appears on the side of the tongue and it hurts, it causes not only discomfort, but also difficulties with eating and speaking. Why a lump may appear on the tongue, what diseases this may indicate, and what to do if a lump appears.
Why is there a problem?
When tumors appear in the tongue, you should not engage in independent treatment. Only a qualified specialist can make a correct diagnosis after carrying out preliminary diagnostic measures.
If even a small ball forms on the surface of a muscular organ, a histological examination of its contents will be required. To conduct this study, the lumps must be removed.
But first you need to find out the reason for their appearance.
The main reasons why bumps or pimples form on the tongue include:
- sialadenitis;
- lipoma;
- mechanical damage - injuries or burns;
- papillomas;
- adenomas;
- botryomyxoma;
- fibroids;
- fibroids;
- neurofibromas;
- hemangiomas;
- cysts;
- struma of the tongue.
- malignant neoplasms.
- consequences of an advanced form of glossitis.
Internal formations can be of different sizes and different densities. Both single bumps with serous contents and compactions without clear boundaries are formed. Color can vary from white to scarlet or burgundy. The formations can be mobile or located in the form of a growth. You cannot violate their integrity on your own.
Struma and sialadenitis
Another reason why a growth may form on the side of the tongue is sialadenitis. This disease is characterized by an inflammatory process in the salivary glands.
This disease often appears in children. With the development of inflammation, an increase in the size of the ducts of the salivary glands occurs, so a large tumor is formed.
Additionally, this is accompanied by swelling of the neck and hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
The bumps on the tongue are painted white, they are located under the organ or on the side, in the area where the salivary glands are located. After a while, purulent fluid begins to be released from the tumors. The formation is painful and causes discomfort during conversation and eating. The purulent process is accompanied by hyperthermia, weakness and other signs of intoxication of the body.
The struma of the tongue begins its development in the prenatal period. Thyroid tissue enters the tongue during the formation of the digestive organs. A nodule appears at the root of the muscular organ. This disease is very rare and dangerous. Treatment and examination are carried out by a geneticist.
Benign tumors
These include lipoma. This is a formation consisting of lipid tissues. Most often localized on the scalp and body, but sometimes found on the surface of the mucous membranes, in particular on the side of the tongue or at the tip of the organ. Outwardly it looks like a moving ball. Does not cause pain or discomfort.
Fibroids are pedunculated growths formed from connective tissue. These are benign tumors that do not differ in color from the color of the mucous tissue.
Botriomyxoma is a large formation. The circumference can reach five centimeters. Its surface is smooth, divided into small segments.
The cause of the appearance is trauma and mechanical damage to the organ, burns.
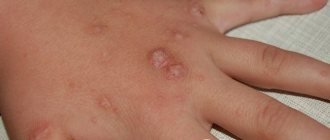
Papillomas are a consequence of the activity of the human papillomavirus. Such growths can be located either singly or in multiples. Formed from mucous epithelial tissues. They do not grow to large sizes, but over time they can transform into malignant tumors.
Fibroids are small lumps on the surface of a muscle organ. Most often located on top. Hemangiomas are tumors that are composed of blood vessels. Their color varies from light pink to blue-scarlet.
Usually such formations are benign, but over time they can turn into malignant.
Neurofibromas arise from the tissues of the nerve branches of the organ. Their appearance is accompanied by pain, severe discomfort during conversation and eating. Most often located on the back walls and side of the tongue.
Lymphangiomas are located at the tip and side of the organ. This is a congenital hard lump, formed from cells of lymphatic tissues.
With mechanical damage, an inflammatory process begins to develop, and lymphangioma grows.
In some cases, the growth spreads to the entire surface of the muscular organ.
Malignant formations
Malignant tumors and sarcomas are characterized by rapid growth and rapid progression. Outwardly they look like a scattering of lumpy cones. Their structure is heterogeneous, and so is their consistency. They may become covered with erosions and ulcers. They differ in metastasis deep into nearby tissues, into internal organs and into the lymphatic system.
With the development of tongue cancer, growths of keratinized scales appear. They are localized on the side or in the middle of the mucous membrane of the muscular organ. As they develop, they become hard and additional symptoms appear. Various reasons contribute to the appearance of such tumors.
A simple fibroid, under favorable circumstances, can degenerate into cancer if there is no proper therapy. Males over the age of 40 are more often exposed to oncological processes. At the initial stage of development of the disease, a painless tubercle appears.
As the disease progresses, it begins to grow rapidly, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe pain;
- putrid odor from the mouth;
- increased formation of salivary fluid;
- changes in the quality of taste sensations;
- difficulty eating;
- difficulties during conversation.
Metastases spread to the lymph nodes, which become larger in diameter, this is accompanied by severe pain.
It must be remembered that if any ball has formed in the mouth, even if it is painless and does not cause discomfort, you need to seek advice from specialists.
This is necessary, since any formations under the influence of unfavorable factors can transform into malignant ones and become a threat to health and life.
You can't try to get rid of bumps on your own. It is unacceptable to warm them up, squeeze them out or try to eliminate them by other methods. Otherwise, this may cause malignancy and infection of the formations. The best thing to do is to seek help from a doctor.
What to do
What to do if a lump appears on your tongue? First you need to consult a therapist.
Additional diagnostics are prescribed, after which a visit to a dentist, infectious disease specialist, immunologist, surgeon or oncologist may be necessary. It is important not to delay visiting specialists so as not to waste time.
If the malignant nature of the formation is not confirmed, you can safely remove the growth surgically.
Removal is simple, the operation usually lasts no more than 20 minutes. The doctor excises the lump under local anesthesia. You may need to be hospitalized immediately after surgery. A day later, the patient goes home. After removal of the cyst, it is sent for histological examination. The result will be known in ten days.
Source: https://tvoyzubnoy.ru/bolezni-i-ih-lechenie/yazyk/shishka-na-yazyke-sboku-bolit.html
Types of processes
Most often, flat or pointed warts form in the oral cavity:
Another type of growth is condylomas lata, which are localized not only on the tongue, but also on other parts of the oral mucosa. The reason for their appearance is syphilis.
A lump appears on the tongue: causes and methods of treatment
The appearance of a lump on the tongue will lead to problems with eating, as well as to disruption of the aesthetic appearance of the organ. If it hurts, then the patient cannot fully speak, and will even refuse to eat.
Moreover, a lump on the tongue causes concern among people because it may turn out to be a tumor. It is important to contact a specialist so that he can carry out a professional diagnosis.
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe treatment that will help get rid of this pathology.
- 1. Reasons
- 2. Symptoms
- 3. Diagnostics
- 4. Therapy methods
Causes
A lump in the tongue area may appear suddenly, and it will be difficult to miss. It may have a white or reddish tint, and is usually accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The pathology not only disrupts the aesthetic appearance, but also complicates articulation, disrupts taste perception and generally brings a lot of discomfort.
Some people do not want to visit a doctor because they hope that the problem will go away on its own. Lack of treatment can lead to serious complications, some of which can even be life-threatening.
Let's look at the possible reasons.
- Benign tumors
These neoplasms come in different types, so it is difficult for a citizen to independently determine the specific type. For example, a lipoma may appear, which is formed from adipose tissue. It will look like a ball that is located on the side of the tongue and does not cause pain.
Papilloma may also appear; it is of viral origin. Its danger lies in the fact that a malignant course may begin.
It often happens that a person bites his tongue when communicating or eating. A hematoma appears at the site of the injury, which looks like a swollen red spot. It disappears on its own within 4-5 days, and no professional treatment is required. But if after 10 days the lump remains on the tongue, this indicates the formation of a cyst.
It has a white or grayish tint and will continue to grow without treatment. To eliminate the pathology, surgical intervention is required, otherwise there is a risk of infection at the site of the cyst.
This disease is of infectious origin, which affects the salivary glands under the tongue. When pathology appears, the organ becomes covered with bumps with pus, and the throat also swells. You can observe an increase in body temperature, weakness and soreness in the muscles, which indicates intoxication of the body.
The disease most often appears in children due to the fact that they do not have a strong enough immune system and have a habit of putting dirty objects into their mouths. It is because of poor hygiene that bumps appear on the tongue, which can be white or red. Pimples are painful, making eating much more difficult.
The disease is rare, but it can still appear in people. With the development of the digestive system, thyroid tissue enters the root of the tongue, causing a knot to form. It will look like a bump. The disease is of genetic origin, so treatment is carried out after consultation with a geneticist.
In most cases, it is found only in the lip area, but in rare cases it forms in the mouth. With it, the tongue becomes covered with small balls that contain white liquid inside. The disease lasts up to two weeks, after which it completely disappears. If a person wants to relieve symptoms and shorten the duration of the pathology, proper treatment must be carried out.
It is a malignant formation that grows quickly, changes in shape and can bleed. Metastases spread to nearby organs.
The disease is diagnosed in people over 30 years of age. Pain, bad breath, excessive salivation and problems with taste buds are sure to be present.
Therapy should only be comprehensive - it includes radiation treatment and chemotherapy.
If a person notices a lump on his tongue, he should not squeeze it or pick it. Such events can only aggravate the situation, so you should immediately contact a specialist.
This is not a complete list of ailments that cause a lump on the tongue.
There are many more diseases that lead to this pathology. In any case, a person himself will not be able to determine his diagnosis, because symptoms and an external examination are not enough for this. If there are suspicions of serious pathologies, then tests will be needed.
Until then, you should not treat yourself so as not to harm your health.
Symptoms
Bumps on the tongue can have different symptoms, because much depends on the cause of their occurrence. Quite often, when pathology appears, the ball is small in size, so it may not be noticed. However , it often does not hurt when it has just formed, which complicates diagnosis .
When the tumor grows, then a person can already notice it. Perhaps it can be seen during a visual examination of the tongue.
It may also hurt, which is especially noticeable when talking or swallowing food. At first, pain is not always observed; there may only be a feeling of a foreign body in the mouth.
Naturally, this symptom should not be ignored if you do not want to encounter complications.
If inflammation begins, then the tongue swells, there is swelling, and the color may also change. The lump itself is red and painful, and pus may form in it. In rare cases, necrosis of the affected area appears, which is a bad sign.
Symptoms will depend directly on what ailment has bothered the person and how far it has developed. All diseases are easier to treat in the initial stages, but in advanced cases, therapy may no longer help. That is why it is important for a person to visit a doctor and, if necessary, start taking medications.
In many cases, the prognosis is favorable, and the existing problem can be eliminated fairly quickly.
Diagnostics
When a lump appears on the tongue, you should not let the situation take its course and hope for a better outcome.
Because such pathologies may be invisible at first, or mildly disturbing, but over time they bring severe discomfort. Due to the small size of the tumor at the time of its appearance, it is difficult to detect immediately.
As a rule, people are lucky enough to see it when examining the throat or teeth, when there is not even a suspicion of problems with the tongue.
You can understand that you have to deal with a lump visually, as well as by palpation . Let us remind you once again that you should not squeeze a pimple, or try to get rid of it in any other way. This can only harm yourself, so the right decision would be to immediately visit a doctor.
In most cases, after examination, the doctor will prescribe a histological examination. It is necessary so that after removing the lump, you can understand the reason for its formation.
It is likely that you will have to visit various doctors, such as a surgeon, infectious disease specialist, dentist, immunologist or oncologist.
It all depends on what suspicions there are about the lump that has formed on or under the tongue.
Don't waste time and delay going to the therapist . If there is a serious pathology, then you will definitely need to start treatment.
The sooner a person is prescribed therapy, the greater the chance of a full recovery and not encountering any complications. Of course, sometimes a lump can even go away on its own, for example, if it is a hematoma.
But, if within 4-5 days the situation has not changed or has become worse, then it’s definitely worth visiting the hospital.
Therapy methods
Treatment will depend on what exactly is bothering the person. It may be noted that it is almost always necessary to remove a lump from the tongue surgically.
If a cyst has been diagnosed, then it is removed entirely, and then the tissue is treated to prevent infection. If there is a lipoma, it is removed only when it grows and causes discomfort to the person.
In other situations, it will be enough that the person controls the development of this pathology.
In more serious situations, when a person has been diagnosed with a malignant tumor, radiation or chemotherapy will be needed. The doctor will prescribe specific measures, and it will be important for the person to fully comply with them. With early treatment there is a chance of recovery.
You should not remove the lump at home, especially without consulting a specialist. This can lead to infection, causing pus and inflammation. As a result, the situation will worsen significantly, and you will still have to visit a doctor.
Only a specialist with surgical training should remove a lump from the tongue. Moreover, he will do this in a sterile room, where there is no threat of infection. Rehabilitation takes place quite quickly, and at first it is important for a person to follow a gentle diet. You should not eat spicy foods, as well as fatty and salty foods. If necessary, you will need to use special medications. If you strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, then there should be no complications.
Source: https://tvoidantist.ru/lechenie/polosti-rta/shishka-na-yazyke.html
Prevention
Not all conditions and diseases can be prevented. But to prevent traumatic and scar changes, there are simple and effective methods:
- Timely treatment of structural disorders of the dental system and oral cavity (reconstruction of broken or caries-damaged teeth with sharp edges, frenuloplasty, etc.).
- Organizing proper nutrition (the child’s food should not be hot or cold, and until he learns to chew food thoroughly, it should be crushed).
- Choosing the right feeding accessories and their regular antiseptic treatment.
If you notice such symptoms in a child, be sure to contact your pediatric dentist or any other doctor.
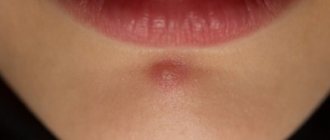
A lump has appeared on the tongue and it hurts - on the side or at the root
A lump on the tongue is not only unsightly, but also dangerous. A small formation can suddenly begin to grow, interfere with eating, talking, hurts and affect the quality of taste buds.
It can signal both minor changes in the body and the presence of a dangerous disease.
In order to notice this trouble in time, it is worth understanding the provoking factors for the formation of a lump and the main symptoms.
Factors that provoke the appearance of bumps on the tongue
In addition to damage to the tongue during chewing, several more common factors can be identified:
- Exposure to hot food, liquids, chemicals on the tongue.
- If a lump appears on the tongue, it can be caused by rupture or damage to blood vessels. Often this is the appearance of hematomas.
- Smoking or drinking alcohol.
- Lack or excess of vitamins in the body.
- Diabetes.
- Some diseases: tuberculosis, HIV, syphilis, immunodeficiency.
- Presence of herpetic infection. As a result, a white bump appears on the tongue (usually there is more than one), filled with clear liquid. There is no need to pick them out so as not to spread the infection throughout the body.
Bumps on the tongue: types
Depending on what caused the bumps to appear, they are divided into several types.
- Adenoma. The basis for formation is the gland of the mucous membrane. Cystoadenomas form at the tip of the tongue, but at the root there are polyps.
- Papilloma. Formed from squamous epithelium. In most cases, it is found on the tip or back of the tongue. They have an elongated or round shape, a light pink tint. Either one papilloma or several at once may appear. Papillomas do not grow to very large sizes, but if they begin to thicken the stratum corneum, there is a high probability of degeneration into cancer.
- Botriomyxoma. The tumor may have several lobules and be flat or spherical in shape. Initially, these are red bumps on the tongue, which later acquire a brown tint. The surface may vary. If left to its own devices, the disease will grow to the size of a walnut. The reason for its appearance is trauma to the tongue and cracks on it.
- Retention cyst. Usually located at the tip or bottom of the tongue. Often several appear at once. The material from which the cyst is formed is the nunnia gland.
- Fibroma. Formed from connective tissue cells. Consistency – elastic. Often the fibroma itself has a small stalk. Has a tint to the mucous membrane of the tongue, although sometimes it is yellowish or whitish.
- Lipoma. Its consistency is soft and elastic. Often tumor growth is painless and slow.
- Neurofibroma. Appears on the back. The material for the formation of neurofibroma is nerve branches. It develops very slowly. During growth, there may be severe pain in the area of the lump or no pain at all.
- Myoma. It originates as a result of the proliferation of tongue muscle cells. The average size is 1 cm. Myoma is very dense. More often it is found on the back of the tongue. Papillary growths may form on it.
- Lymphangioma. Formed from lymphatic vessels. Characteristic only for children under 12 months of age. It can provoke a diffuse change in the tongue, which will lead to its enlargement. Usually such a bump is located on the tongue closer to the larynx or at the tip. The structure is warty, the presence of vesicular elements is possible. Trauma to the lump can cause inflammation.
- Hemangioma. Appears from the blood vessels of the tongue. More often appears in newborn girls or in the first years of life. The most common reason for the appearance of these types of cones is a violation of intrauterine development. If injured, they may bleed.
- Struma of the tongue. A rare type of tumor that develops from thyroid tissue. A healthy person should not have such tissues on the tongue. They appear only after embryonic differentiation is disrupted. Most often, the bumps are located on the root of the tongue and can measure up to 3 cm in diameter.
Neoplasms on the tongue: symptoms
A lump on the side of the tongue or anywhere else is often diagnosed very late, since the disease begins from a small pimple. Only when they increase in size can unpleasant symptoms appear:
- Bad feeling.
- Temperature increase.
- Bad breath, ulcers appear.
- The swelling hurts when swallowing or chewing.
- Speech is impaired.
- Feeling of a foreign body in the mouth.
Any of the symptoms may indicate the presence of one of the types of tumors, which can develop into a malignant tumor.
How to diagnose?
Basically, diagnosis is made only after the lump on the tongue hurts and has already increased significantly in size. First, it is better to consult a general practitioner, who will determine the type of lump and refer you for further examination to an oncologist, surgeon, infectious disease specialist, immunologist or dentist.
The specialist will palpate the tongue and the tumor that hurts. If necessary, material will be taken from the cone and sent for histology. After determining the cause, the specialist will prescribe treatment.
A lump is detected: what not to do
These tips will help not to aggravate the situation and not provoke the degeneration of the growth (especially if it hurts):
- It is forbidden to remove or injure the lump yourself: pick it out or burn it.
- Create a panic.
- Do not leave such formations and their increase to chance. After all, this may not be an ordinary injury, but the initial stage of cancer.
Treatment
How the lump is removed depends on the type of tumor. If the lump is benign, then it can be removed by excision, radio wave method, laser, using cryodestruction, electrocoagulation. During removal, local anesthesia is used. Hospitalization is generally not necessary.
Removal is as economical as possible; healthy tissue should not be damaged. Removal of benign lumps is often beneficial, but there is a chance that the disease will recur.
If the lump is malignant, then to eliminate it it is advisable to use an integrated approach: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, radical elimination. Irradiation is carried out both on the formation itself and on the area to which the metastases have spread. In severe cases, part of the affected tongue and the area with metastases are removed. In the future, it is realistic to carry out its reconstruction.
External manifestations (+photo)
Growths under the tongue in humans form in the form of warts, papillomas, and condylomas. All varieties are signs of the presence of VPI in the body. Their differences lie in the type of epithelium and external manifestation. Papillomas can be either protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane or flat with rough tissue. And condylomas always rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane with the help of a fairly high stalk.
Types of growths under the tongue:
Depending on the type and causes of formation, condylomas come in different colors:
Growths in the oral cavity are most often localized in the following areas:
Additional factors for the formation of processes
There are indirect circumstances, the presence of which can provoke the appearance of papilloma under the tongue and on the surface of its mucous membrane. Such risk factors include:
Depending on the individual characteristics of a person, his lifestyle, nutrition, there may be other circumstances that will become a connecting link in the process of penetration of the human papillomavirus and its further spread in the oral cavity in the form of foreign shoots.
Features of child treatment
The treatment strategy for growths under the tongue in children includes two main stages: improving the immune system and eliminating formations in the mouth.
There are difficulties in selecting agents for local action on papillomas due to the constant contact of the drug with saliva. Therefore, the first recommendation for children is to change their usual toothpaste to a professional product that has a bactericidal effect.
When choosing antiviral drugs, the priority is not effectiveness, but safety. The ideal option is a drug that contains a combination of ascorbic and rutic acids (for example, Ascorutin). Recommended immunomodulators include: Amiksin, Viferon.
When determining the most suitable method for removing papillomas, the accuracy and speed of the procedure, as well as the low level of risks, are taken into account.
How to diagnose such a disease
Diagnosis in most cases is made when the lump has already reached medium size. Why does this happen? A small tumor is quite difficult to detect (only if it is seen by chance). The detected tumor must be examined and palpated, after which the doctor prescribes treatment. Sometimes biomaterial is sent for histology. This is usually done after surgery (if one has been performed).
Tongue cancer in the second stage
What not to do if a tumor is detected
- Pierce the tumor yourself or use other methods of influence (cauterization, picking).
- Leave it to chance. This can be either a simple injury or a serious illness leading to irreversible consequences, including death.
- Panic.
Cysts and hematomas
If a painful tubercle appears on the right or left side of the tongue due to mechanical damage - biting or burns, medical intervention is often not required. After a short period of time, the pip on the tongue dissolves on its own, leaving no scar. If the lump does not go away on its own after a week, this may indicate that a hematoma has formed as a result of the injury. And old hematomas tend to develop into cysts, and here surgical intervention is already necessary to get rid of them. This is fraught with the formation of scars.
Externally, cysts resemble small pimples. They are prone to overgrowth. Usually not accompanied by additional symptoms. Treatment involves excision of the tubercle. They are white or gray in color. Cysts are of the following types:
Often, bumps on the root of the tongue or on the side appear as a result of glossitis. This complication occurs as a result of infectious processes in the mucous membrane, as well as due to the proliferation of connective tissues. When an inflammatory process occurs, it is important to visit a specialist in a timely manner to prevent further unpleasant consequences.
What happens if the growth under the tongue is not treated?
The appearance of growths under the tongue indicates a malfunction of the immune system. Weakening of protective functions makes the body vulnerable to infections and viruses. Therefore, alarming symptoms cannot be ignored .
When neglected, papillomas quickly spread throughout the body, appearing in the most inconvenient places. Often, neoplasms change their benign nature to malignant, and dealing with an oncological problem is much more difficult.
Source
Why does inflammation occur?
Inflammation, which manifests itself in the form of a ball or blister on or under the tongue, can appear due to various life circumstances. They can be associated with external or internal manifestations of the body.
- Thermal. Tongue damage occurs due to a sharp change in the temperature of food or liquid consumed. A product that is too hot or cold can cause significant irritation. As a result, a lump or small bubble appears on the lingual area. As a rule, it goes away on its own after some time.
- Mechanical impact. It involves causing damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue. Typically, fish or meat bones, seed shells, and toothpicks act as traumatic factors. A person may sometimes not even notice minor damage, but after a few days or the next day a specific ball will appear on the muscle organ. Injuries also often occur due to a banal bite, which is difficult to miss.
- Chemical exposure. The mucous membrane of the tongue is extremely vulnerable, so excessive consumption of salty foods or spicy seasonings can lead to inflammation. Burns can be caused by using vinegar or chemical household cleaning products.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How a dental bridge is removed
When the tongue is damaged, a ball appears, which can vary in consistency. It depends on the degree of injury. As a rule, a small bump appears on the first day; it is either light in color or deep red. The first color option indicates that the vessels are not damaged, the second indicates that they are injured.
When examining, specialists always pay special attention to pain, the shade of inflammation, its location and shape. If, for example, there are many small bubbles, we are most likely talking about the body’s response to internal changes in the functioning of the endocrine system or gastrointestinal tract.
Traditional medicine recipes
There are non-traditional approaches to the treatment of papilloma on the tongue. Traditional healers recommend using effective methods for getting rid of growths and processes on the surface of the tongue, which consist of performing the following actions:
Traditional medicine recipes do not have a laboratory conclusion about their effectiveness, so the therapeutic benefits of this type of treatment by specialized specialists are often questioned. Dermatologists, immunologists and surgeons recommend the use of herbal decoctions as aids in treatment with medications.
Source
Diagnostics
Verification of the disease is based on the following:
- anamnesis;
- inspection;
- lab tests;
- histological examination.
From the medical history, the doctor finds out whether the patient has had contact with an infected person and assumes a risk of infection. Based on information about how long ago it was, the specialist compares the timing of the latent course and clinical manifestations.
Of the laboratory tests, the most informative is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It makes it possible to isolate viral material from biological fluids and determine the type of pathogen, which is important for treatment.
Taking a section of tissue for histological examination allows us to exclude malignant neoplasms. This is especially important because the growths can eventually develop into tumors with invasive growth.