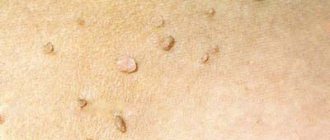
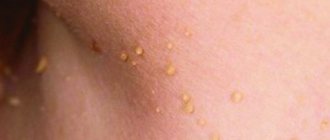
Flat papillomas, also known as flat, juvenile or juvenile warts, are benign skin growths. The cause of their occurrence is the human papillomavirus (HPV, papillomavirus), infection of which occurs as a result of direct and indirect contact with a sick person. The formations are localized mainly on the dorsum of the hands, forearms, and face in children, adolescents and young adults. Treatment of flat papillomas includes various methods of their removal and systemic therapy with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
Flat warts are called juvenile warts because they most often affect children and young people
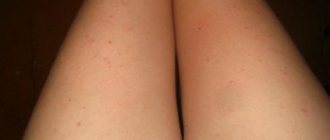
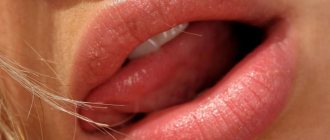
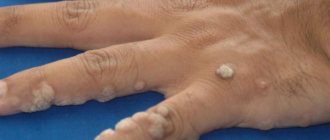
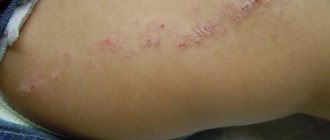
The photo gives an idea of the appearance of flat papillomas on the face and body.
Reasons for appearance
Juvenile warts are caused by the human papillomavirus. To date, more than a hundred types of virus have been identified that can infect the skin and mucous membranes. One of the most common pathologies resulting from infection with human papillomavirus is warts. All of them are divided into eight clinical varieties, each of which is associated with a specific type of HPV.
| Clinical type of wart | Genotype of papillomavirus |
| Vulgar (ordinary) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 27, 29, 57 |
| Palmoplantar deep | 1, 3, 27, 29, 57 |
| Plantar mosaic | 2, 4 |
| Cystic | 60 |
| Flat | 3, 10, 28 |
| Butchers wart | 7 |
| Focal epithelial hyperplasia | 13, 32 |
| Verruciform epidermodysplasia | 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 19, 36 |
Penetration of papillomavirus occurs through direct contact with a patient or through linen, towels, and care items. An indirect route of transmission of the virus is unlikely, but possible, since viral particles can remain viable for some short time in the exfoliating skin cells of the patient. For infection, the most minor damage to the surface of the skin and mucous membranes is sufficient.
Traditional medicine techniques
Some folk recipes allow you to get rid of flat growths, but they are not always effective. Alternative medicine has always been popular among Russians. However, it is better to go for a consultation with a professional, as this will guarantee that there will be no relapses. The most effective and safest methods are as follows:
- Preparation of tincture based on lemon balm, nettle and plantain. Plants must be dried. You should take a teaspoon of each herb and pour hot boiling water for 2 hours. After this, the liquid must be strained and put on the stove to boil. The affected areas are treated 5 to 6 times a day. Treatment takes several weeks, but gives excellent results. The finished mixture must be kept refrigerated.
- Castor oil. Take a piece of cotton wool and soak it in this product, then seal it with a band-aid. It must be kept for at least 5 hours. The course of treatment is a week. Processing is carried out daily.
- Celandine. The juice is squeezed out of the leaves and applied to new growths up to several times a day. The plant extract can be purchased ready-made at the pharmacy. To treat with this natural remedy, treatment must be carried out for 2 weeks.
If the first signs of HPV infection appear, you should consult a dermatologist. A qualified specialist will prescribe the necessary tests to clarify the strain of the pathogen, and then prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Forms of existence of papillomavirus
In an infected cell, HPV can exist in two different states.
| Intracellular form of papillomavirus | Characteristic |
| Episomal (benign) | The virus does not integrate into the chromosomal apparatus of the infected epithelial cell, being in an inactive or dormant state. There are no clinical manifestations of HPV infection. |
| Introsomal (malignant) | This form of viral parasitism is regarded as malignant not because it necessarily causes the growth of malignant tumors, but because of the aggressiveness of the viral particles. They wake up and penetrate the cell's genome. This process provokes the reproduction of HPV-encoded proteins. In this case, the virus can have a productive or transformative effect on the epithelium. The first leads to the appearance of benign warts, the second leads to the formation of dysplasia of varying degrees. Without treatment, progression of dysplasia leads to the development of cancerous tumors. |
The danger of red papilloma
Thanks to the appearance of red papillomas, it is possible to diagnose health problems such as disorders of the pancreas (pancreatitis) and inflammation of the meninges (meningitis). In the latter case, the formation of red dots is associated with the following clinical picture:
- frequent limb cramps;
- labored breathing;
- chest cough for no apparent reason;
- a sharp increase in temperature to critical levels.
It must be remembered that a benign tumor can quickly become malignant, so the growth and number of red papillomas must be controlled. The first signs of transformation of hemangioma into cancer are:
- compaction of the neoplasm, as well as its expansion over the area;
- pain on palpation;
- increase in skin temperature at the site of tumor growth;
- a burning sensation and itching, which intensifies with mechanical damage to the painful area;
- change in color of papilloma;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- an inflammatory process that occurs when an infection enters through damaged skin.
In this case, you will need to consult an oncologist and a dermatologist, who will be able to determine the prerequisites for the formation of cancer cells and also prescribe appropriate treatment.
Provoking factors
The form of existence of the virus in epithelial cells is largely determined by the state of the immune system. A decrease in the body’s overall resistance occurs in a number of conditions, which include:
- prolonged hypothermia;
- traumatic injuries;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- excessive physical labor;
- passion for strong alcoholic drinks;
- smoking;
- diseases of viral, bacterial, fungal origin;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- taking medications (antibiotics, cytostatics, hormones).
The action of provoking factors can be isolated or combined.
Methods of infection
The number of warts that appear does not indicate that an infection has occurred: the virus “sleeps” in the body for months or appears in the first year after infection. A lot of papillomas can only mean a strong decline in immunity.
You can become infected, for example:
- through shared bed linen, towels;
- through sexual contact;
- through a handshake, especially if there is an abrasion or wound;
- through a kiss, a hug, shared dishes;
- while visiting a solarium, beauty salon, manicure salon;
- at the household level, and so on.
It is impossible to make yourself invulnerable to HPV, therefore, the number of infected people is close to one hundred percent, and it is impossible to get rid of it and remove it from the body.
Symptoms of flat papillomas
The characteristics of warts, called flat, are presented in the table.
| Sign | Description |
| Localization | They occur most often on the hands (back of the hands, forearms), on the face (forehead, area around the mouth) and in areas where hair is regularly shaved: in men - the lower part of the face, in women - the lower legs. The linear distribution of papillomas on the face and limbs is characteristic: they are localized along the course of scratching and habitual razor movements. The mechanism for the formation of this arrangement is explained simply: the person himself spreads viral particles to nearby areas of the skin when combing or removing hair during shaving. This route of infection is called autoinoculation, or self-infection. |
| Patient age | They can be found in patients of different age groups, but most often in children and adolescence, for which they received one of their names - juvenile warts. |
| Appearance | They are usually represented by multiple small nodules, or growths, with a flat, slightly raised surface and clear outlines. Processes of keratinization of the skin in the area of papillomas do not occur, so they have a smooth and shiny surface without any outgrowths or skin patterns. The formations often do not differ in color from normal skin, although color variations are possible: from pink to yellow-brown. The dimensions usually do not exceed a few millimeters (1–5 mm). |
| Symptoms | In most cases, the presence of papillomas is not accompanied by complaints. Slight itching may occur. But flat papillomas, especially on the face, are a cosmetic defect and often cause psychological discomfort in the patient. |
Color change
The main concern of a person with the appearance of papilloma, especially on the face, is appearance. The most important thing is not what color the papilloma is when it appears, but a change in its color, or an increase in shape - these are clear signs that you should seriously examine the growths that have appeared.
A sudden change in the color of the papilloma is perhaps the main sign of its degeneration into a malignant tumor.
There are many other reasons why the color of growths may change, these include:
- growth of papilloma under the hairline, in such a case repeated damage to the neoplasm becomes inevitable;
- the formation of a growth in the armpits and in the groin area, places where the papilloma can be damaged due to shaving, after which you can notice not only a change in color, but also the formation of a blood rim around it;
- infection;
- activation of the body’s protective functions, in the process of the body’s fight against the virus, the color of the papilloma may change due to the death of its cells;
- the use of medications, a natural growth reaction to its burning.
There is also a possibility that the color of the warts will not darken, but rather lighten.
The reason that the papilloma has turned white is mainly its death; this can be caused either by the use of medications or by the body’s own fight against the disease.
Diagnosis of flat warts
When juvenile warts appear, patients usually consult a dermatologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor performs:
- interviewing the patient;
- visual inspection;
- dermatoscopy (examination using an optical device - a dermatoscope);
- laboratory examination for the presence of HPV in the body and its typing (polymerase chain reaction - PCR method).
Differential diagnosis is carried out with other formations on the skin, the main differences of which are presented in the table.
| Type of skin formation | Distinctive features |
| Lichen planus | Flat nodules of lilac, red-violet hue, arranged in groups in the form of garlands, lines, rings. Localization: on the flexor surfaces of the limbs, in the groin, axillary areas, torso, oral mucosa. The nodules have a retracted middle and a surface with a waxy sheen. A characteristic feature is the presence of a network-like pattern on the surface of the largest formations. Severe itching is typical. |
| Seborrheic keratosis | Foci of seborrheic keratosis (thickening and keratinization of the skin) are characterized by darker pigmentation and have the appearance of “pasted” skin formations with a flaky surface. There may be a burning sensation when localized on the face. |
| Common wart | Dry nodules with an uneven surface covered with outgrowths of keratinizing epithelium. They can sometimes merge to form plaques up to 1.5 cm in diameter. Typical localization is the hands, especially the fingers. |
How to distinguish it from other skin formations
They are often confused with nevi and warts, but they have different origins. Red nevi are the result of heredity and exposure to external factors, such as solar radiation. Warts are a viral skin disease and can be infected. Papilloma has a stalk. The color is light, while warts are grayish to dark brown. Loose texture and blurry shape, rough edges. The boundaries of the wart are clear. Appears in the armpits, stomach, genitals, groin, head.
The body of the red tumor is connected to capillaries and nerve endings; when pressed, mild pain occurs.
They are benign tumors, do not have a toxic effect on humans and do not grow into tissues. Unlike warts, they recur – they grow back after removal. This happens because of the leg - if it is not removed, the tumor will grow again.
Treatment of flat papillomas
Quite often, spontaneous regression of formations is observed, especially against the background of antiviral and immunostimulating treatment. Patients often insist on priority destruction of flat warts, which are a cosmetic defect. The most effective treatment option for skin tumors caused by the human papillomavirus is a combination of local destructive effects on warts and systemic use of drugs that have immunomodulatory and antiviral effects. Treatment activities can be carried out simultaneously or in stages.
Flat warts can be removed using laser treatment
Removal of flat papillomas without systemic therapy leads to a high percentage of disease relapses within 6 months after destruction. In some cases, skin formations form in the same areas of the skin as before. This is explained both by the stages of the papillomavirus life cycle and by a decrease in the general and local immune response.
The variability and species diversity of HPV do not allow it to be completely eliminated from the body, therefore the main task of systemic treatment is to transfer the virus to an inactive, or latent, state.
The main therapeutic measures are presented in the table.
| Medical direction | Characteristic |
| Removal of flat papillomas | You can get rid of it in several ways: using salicylic acid preparations, freezing with liquid nitrogen, laser therapy, radio wave removal. Treatment should not be traumatic or accompanied by the formation of scars. For this reason, surgical excision and electrocoagulation are not usually used, especially when localizing papillomas on the face. The most widely used are salicylic acid preparations in the form of a liquid or patch, as well as cryotherapy through applications of liquid nitrogen. The freezing procedure does not require anesthesia and is therefore well tolerated even by small patients. |
| Increased systemic and local immune response | To increase the body's resistance, immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs are used: Interferon, Cycloferon, Allokin-alpha, Lykopid, Immunomax, Aldara. The availability of drugs in various dosage forms (injection solution, ointment, cream) facilitates their combination in order to achieve an effective result. |
Removal methods
Since HPV tends to grow, cause discomfort, and there is a danger of a malignant tumor, it is best to remove the papilloma.
However, doing this at home is extremely unsafe; the best solution in this situation is to contact a specialist.
- surgical
It is used quite rarely if there is a suspicion of a tumor and if the size of the growth is large. When surgically removing papilloma, local anesthesia is used, the operation lasts relatively short.
But the disadvantage is that when a tumor is removed, a healthy area of skin is also removed, and subsequently scars and cicatrices may remain.
- cryodestructive
Involves the use of liquid nitrogen to remove papillomas. Removal of warts using the cryodestructive method can occur both in a medical facility and at home.
The method is absolutely painless and leaves no scars. The use of this method if a malignant tumor is suspected is strictly prohibited.
- laser removal
It involves removing growths by burning it with laser beams for 60 seconds; redness may form around the growth, which will disappear in a few days; the wart itself will disappear within a week.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a tumor.
- electrocoagulation
Cauterization of growths using electrical discharges does not provide for age restrictions. Removal of papillomas occurs quite quickly, and damaged skin is restored within a week.
However, there are also disadvantages: depending on the sensitivity of the person, the procedure can be quite painful, and if the method is chosen incorrectly, there is a risk of scarring.
- radio wave
getting rid of growths through removal using high-frequency radio wave radiation. The radio wave removal method is absolutely non-contact, so it can be used to remove one or several papillomas.
The advantage of non-contact removal is that it can be used to remove tumors in all areas of the body. Currently, the most effective and painless way to remove papillomas.
Features of the development of strains 18 and 16 types in men
There are types of HPV that initially have an increased ability to cause the development of oncological processes. You should be wary and worried if papilloma type 16 or 18 is diagnosed. Moreover, the second strain causes the growth of formations that affect the body much faster than the first.
When treating growths caused by HPV types 18 and 16 in men, their removal is mandatory. After this, the patient undergoes a course of drug therapy. It is aimed at suppressing the virus living in the body and maximizing the immune system.
In a man in good health, HPV can remain harmless throughout his life. In order to maintain your body in this state, it is necessary to strengthen and stimulate the immune system. However, it is possible to avoid infection altogether. To do this, you need to have a regular sexual partner and observe the rules of personal hygiene in public places.
Disease prevention
Prevention of HPV recurrence is quite simple, which is why many do not pay due attention to the rules.
- Personal hygiene is personal because it does not imply using another person’s brush, sponge, or towel. It is better to avoid shared baths, showers, and saunas with questionable cleaning quality.
- Washing your hands is the most important thing to do after coming home.
- Clothing must be individual. Women love to exchange dresses with their friends.
- Vitamins, sports, daily walks, air quality in the apartment - all this helps strengthen the immune system. It is also important to control your diet.
- Adequate rest is very important for a modern person.
The main rule of health is to try to avoid stress and take care of your nerves. It’s not for nothing that they say that all diseases are caused by nerves. This is absolutely true, although it is far from the only factor accompanying the violation.
Diagnosis of the disease
If your body suddenly becomes covered with papillomas, the only way to ensure your own safety and peace of mind is to visit a specialist. Typing and treatment assignment occur after:
- external examination;
- taking a smear, scraping, and sometimes a biopsy may be required;
- carrying out tests.
Only after the doctor is convinced that the growth is not cancerous can we talk about treatment and choose a method for removing the growth.
Preventive measures for the occurrence of white papillomas on the human body
Preventive measures are divided into specific and nonspecific. The first include those that act directly on the virus itself, and not on external manifestations. The specific ones include:
- Use of the Gardasil vaccine. Prevents cervical cancer, protects against the occurrence of genital warts and cervical diseases.
- Vaccine Cervarix. It also helps prevent cervical cancer. Protects against HPV infection.
Non-specific:
- Avoiding sexual contact without a condom. The exception is intimate relationships with a verified and non-infected partner.
- Compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene.
- When carrying out hygiene procedures, you must use only personal shaving equipment.
- If white papillomas occur in a wife or husband, it is necessary to allocate a personal towel and wash it separately from the others.
- Take a course of therapeutic measures.
Following the correct preventive approach will protect you from developing the disease and infecting other people.
The article has been verified by the editors