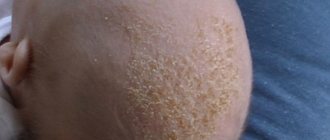
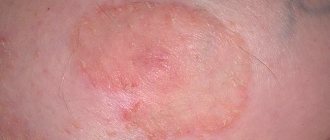
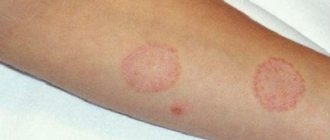
Folliculitis is a common form of staph infection. A sign of pathology is pimples or bumps around the hair on the arms or chest.
Folliculitis is a superficial or deep infection by bacteria that enter from the outside through the sebaceous glands or the hair follicle itself. Particularly prone to this type of inflammation are areas of the body where the skin rubs against clothing, such as the neck or back.
Reasons for the development of folliculitis
folliculitis in the photo
The disease is most common in countries with hot climates, as well as among people living in unfavorable unsanitary living conditions. Sometimes the disease is of an occupational nature and develops in people who have constant contact with chemicals.
Many people try to cope with the symptoms of folliculitis on their own and self-medicate. This is fundamentally wrong, since neglecting medical care is fraught with several health consequences.
There are several main factors that can provoke the development of the disease:
- constant living in conditions of heat and humidity, since it is precisely this environment that is favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic flora;
- wearing very tight clothing made from low-quality synthetic materials that prevent the normal flow of air to the skin;
- gross violations of basic rules of personal hygiene;
- insect bites;
- increased sweating;
- the presence of a serious illness in the body such as diabetes or anemia;
- frequent injuries and microdamages of the epidermis, through which bacteria and fungi can enter the body;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal medications.
Folliculosis very often occurs as a concomitant disease in the presence of other serious lesions of the body. For example, oily seborrhea can trigger the development of inflammation in the hair follicle. With a significant weakening of the immune system, pathogens become more active and accelerate the development of folliculitis.
Diagnostic methods used
An experienced dermatologist will easily make the correct diagnosis when examining a patient. The presence of a problem can be detected visually, but this is not enough to prescribe effective treatment.
The doctor must determine how deep the inflammation is and what pathogenic microorganism caused it. For this purpose, the following methods can be used:
- Questioning the patient, clarifying the time of identification of the first signs and suspected causes.
- Examination of the affected areas under a dermatoscope to determine at what depth the inflammatory process develops.
- Bacteriological analysis of the separated mass. This is necessary not only to identify the nature of the pathogen, but also to prescribe effective treatment.
- Using PCR diagnostics, diagnoses such as gonorrhea or syphilis can be excluded.
- Analysis for fungus is carried out by collecting scrapings from the affected area.
- General blood and urine tests are mandatory. Based on their results, you can understand whether there are other diseases in the body.
The deep form of the disease differs from the superficial one. Therefore, it is necessary to correctly differentiate the pathology. Only a qualified doctor will distinguish folliculitis from furunculosis, acne, toxicoderma and other diseases. If necessary, the patient is sent for a consultation with an allergist or immunologist.
Symptoms of the disease
ostiofolliculitis in the photo
Rashes with folliculitis are usually concentrated on the patient’s head, on the inner part of the epidermis of the elbow and knee joints, on the pubis, in the armpits, less often on the face and neck. The following signs should be taken into account:
- a small inflammatory formation on the skin of pink color;
- increase in the number and size of rash elements;
- the formation of small ulcers with characteristic contents and hair in the middle;
- the appearance of a crust at the site of the opened abscess;
- in some cases, fever and deterioration in health;
- pain and itching in the affected area.
Some patients with this disease experience hair loss in infected areas of the epidermis.
In medicine, there is such a thing as ostiofolliculitis, which differs from the disease in question in that the inflammation in it affects only the superficial part of the hair follicle. With deeper damage to the hair follicle (if timely treatment is not carried out), folliculitis occurs. If the inflammatory process occurs throughout the entire cavity of the hair follicle, then this is deep folliculitis, another name for which is sycosis. The deeper the infection penetrates, the more likely complications will occur.
The disease in question has no age restrictions, so its symptoms often occur in children for a number of reasons. Most often, children suffer from various dermatitis, as well as diseases that weaken the immune system.
Symptoms
- The initial stage is redness of the skin, moderate pain, and the formation of pustules.
- As it progresses, an infiltrate forms around the lesion.
- The skin around the inflamed follicle becomes yellowish, which is explained by the presence of pus. After removing the crust of the pustule, pus is released and red skin is visible.
The number of inflammations can range from 1 to many, for example, when shaving under the armpit, most often a single inflammation is formed. Sometimes itching occurs. With extensive damage, the lymph nodes become enlarged.
Types of disease
There are several types of the disease, differing in the reason for its development and the type of pathogen:
- Staphylococcal folliculitis is caused by a pathogen called Staphylococcus aureus. Most often, the inflammatory process affects areas with stubble on the face in men who use razors. Sometimes the disease affects young children. Women suffer from this type of folliculitis in areas where hair removal is performed regularly. The reasons for the development of the disease include poor hygiene, weakened immunity, hormonal imbalances, poor diet, frequent stress, the presence of staphylococcal infection in the body, and vitamin deficiency. During normal activity of the body's defense system, contact with staphylococcus on the skin does not cause the development of an inflammatory process in the hair follicles.
- Eosinophilic folliculitis is characterized by the formation of specific rash elements on the scalp, torso, arms and legs. Rashes often bother AIDS patients and infants with pathologies. The exact cause of the development of this particular type of disease has not been established.
- Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is diagnosed on the scalp of men and teenage boys in most cases. This purulent disease is characterized by a long chronic course and the occurrence of abscesses containing pus and blood. The consequences of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis are partial alopecia, as well as the formation of deep scars. The exact factors responsible for the appearance of this disease have not been identified, but there is an assumption that the causes may be hereditary predisposition, poor hygiene, a decrease in the protective functions of the epidermis and the penetration of pathogenic flora.
- With prolonged use of occlusive dressings, candidal folliculitis, provoked by fungal microorganisms, may develop. The situation is aggravated if hormonal ointments are used under the bandage.
- Folliculosis can occur against the background of a dermatological disease called demodicosis. This disease is caused by the active activity of a subcutaneous tick.
How does the hair follicle work? Hair structure.
Published: 07/20/2014
Author: O.Shar
Categories: Hair care
Print this article
How does the hair follicle work? Structure. Diagram of a hair follicle. Human hair structure. Hair structure diagram. What parts does hair consist of? How hair grows. Why hair breaks and splits. Nutrition for improving hair.
Hair and skin are a single organ of the human body. Throughout life, hair is constantly renewed. We lose about 80 hairs every day. When a hair falls out, a new one begins to grow in the same place. The life cycle and growth of hair depends on age, hormonal changes, heredity, the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and the concentration of protein groups in the human body. For example, if your diet excludes a certain group of substances, then the quality of your hair deteriorates and hair growth stops. Each follicle contains seven different types of cells that interact with nerve and blood cells.
There are approximately 100,000 hairs on the human head. Blondes have thinner and thinner hair. Red-haired people have thicker hair. With a small amount of them, red hair is quite voluminous and thick in appearance.
To correctly assess your hair type and prescribe the right care, you need to understand what the hair structure is.
How hair works.
Hair consists of two parts: visible and invisible. The visible part located above the surface of the skin is called the core.
The invisible part
located
under the skin is
the root.
♦ Invisible part - Hair root:
The root is slightly thicker compared to the stem
and is located in the hair sac
- follicle.
The roots of the hair are located at a slight angle to the surface of the skin. Therefore, when hair grows, it does not stick out perpendicular to the surface of the skin, but grows at an angle. For example, if a person has an unruly part of his hair - a cowlick, then this is because in this place the hair has a different direction of growth.
In the lower part, the hair follicle expands and forms a hair follicle. At the end, the follicle forms a papilla, bifurcating and covering part of the skin. The papilla connects to blood vessels and nerve endings
1. follicle (hair sac)
2. hair follicle
3. hair papilla
4. sebaceous gland.
The papilla is responsible for hair growth. Above it is the sprout part. She divides and moves the hair upward. Therefore, when we stimulate the scalp with massage and nourish it with masks, we strengthen the hair follicle and our hair improves its growth. The germinal part also contains cells that produce the pigment melanin, which determines hair color. By using certain means we can regulate its production. For example, stopping gray hair. Hair loss is a natural process. Each hair has its own lifespan. The hair falls out along with the bulb.
♦The visible part is the rod.
Hair consists of a huge number of thread-like structures - keratin multifibrils.
They are covered with layers of transparent
keratin scales.
Multifibrils are composed of softer keratin
than the scaly layer.
The structure of the hair core is even softer and more porous. It is a conductor for moisture and nutrients. Cuticle -
This is the outer layer of the hair. It consists of dead keratin cells that form flat scales. They overlap each other like the scales of a fish.
The cortex is a significant fibrous layer. Cortez provides elasticity and strength to the hair. When we dye our hair and perm it, we affect exactly this part of the hair. Therefore, excessive use of chemicals leads to brittle hair.
Medulla
is a channel inside the hair shaft. It consists of a chaotic mass of fibers and air cavities.
Lipid layer. Between the cuticle scales and between the cuticle and cortex there is a lipid layer. Thanks to the lipid layer, the scales fit tightly to each other, which protects the hair from external influences. Accordingly, its destruction leads to the fact that the scales break off and expose the cortes. The hair becomes untidy in appearance, dry, and difficult to comb. By making oily hair masks, we restore lipid deficiency. The scales fit tightly to each other and become silky, shiny and smooth.
1. cuticle
2. cortex
3. medulla
4. lipid layer
Foods to improve hair structure and growth.
- Seafood:
Fish of the Salmon family (any fatty fish). This type of fish has a unique fatty acid composition, including Omega-3. A deficiency of this acid leads to dry scalp and deterioration of hair structure. Salmon is also rich in proteins, vitamin B12, and iron.
Oysters perfectly strengthen and nourish hair, thanks to the zinc content they contain.
- Meat, poultry.
Young lamb and beef are healthy. This type of meat contains a sufficient amount of zinc.
Chicken and turkey meat is a source of protein, which is, first of all, a building material for hair growth. Protein deficiency in the body leads to hair loss and structural damage. Lack of proteins leads to hair losing its beauty and elasticity. shine.
- Eggs.
Eggs, like poultry, are a unique source of protein. They contain substances such as biotin, vitamin B-12.
- Oil containing Omega 3.
Linseed oil. To maintain the beauty of your hair and strengthen it, include 1-2 tablespoons of unrefined flax oil in your diet. It is an excellent source of essential fatty acids.
Walnut oil is also rich in alpha-linoleic acid.
- Vegetables.
Green vegetables. Spinach, broccoli and chard are very rich in vitamins A and C. The body needs them to produce enough sebum, which acts as a natural conditioner for the hair. Dark green vegetables also help provide iron and calcium to your hair.
Carrots are very rich in vitamin A, which is very important for a healthy scalp and good vision. The better your scalp feels, the healthier, shinier and stronger your hair will be. Therefore, feel free to include carrots in your daily menu, both on their own and in salads.
- Legumes.
Beans, beans, lentils, mung beans and other legumes are a source of protein. They are rich in microelements: iron, zinc and biotin. Hair fragility and fragility are caused precisely by a lack of biotin.
- Nuts.
Nuts contain large amounts of zinc. Brazil nuts are very rich not only in zinc, but also in selenium. Walnut contains omega-3, which improves hair condition. Cashews, pecans and almonds are high in zinc. Lack of zinc in the body leads to hair loss.
- Whole grain.
Whole grain bread contains zinc, iron and B vitamins. These microelements help strengthen hair and make it vital.
- Dairy products.
Milk and dairy products are sources of calcium. It plays an important role in strengthening hair. Dairy products contain whey and casein, valuable sources of protein.
How to improve your hair with essential oil>>>
How to make shampoo>>>
Interesting on the topic:
Aromatherapy products for hair improvement.
How to determine your hair type. Table of essential and fatty oils for hair….
Essential oils for hair. Which oil is best for hair? List….
Fatty base oils for hair. Which vegetable oil is best for hair...
Localization of inflammation
Symptoms of folliculosis can occur on various parts of the human body, but they are most likely to appear where hair grows. These are areas such as:
- scalp;
- pubis;
- limbs;
- axillary area.
The scalp is susceptible to the disease in question due to the use of other people's personal belongings, for example, combs, towels, hats, etc. After the appearance of characteristic signs (rash, small ulcers), timely medical treatment is required.
Inflammation of the hair follicles in the pubis and groin affects both women and men. The symptoms of the disease are exactly the same as when other areas with hair are affected. But if the disease is advanced, then the lymph nodes may enlarge, and scars or cicatrices may form at the site of healing of the ulcers. Often there is complete loss of hair in this area of the body.
In addition to poor hygiene, the causes of folliculosis in the groin are staphylococcal and fungal yeast infections, herpes virus infections on the skin, wearing low-quality synthetic underwear, and the presence of microdamages on the surface of the epidermis.
On the legs and armpits, folliculitis most often develops due to carelessly performed hair removal or depilation.
Other causes are allergic reactions of the body, insect bites, excessive sweating, and wearing tight clothing made of non-breathable artificial materials.
You should not open the resulting pustules yourself, since a purulent infection may spread, which can worsen the disease and cause serious complications.
Degree of follicle damage
Based on how the disease progresses, superficial and deep forms . The superficial form of folliculitis often occurs easily and without any negative consequences. It is expressed in the form of a small sore, which is quite difficult to see with the naked eye. With this form there is no pain. After a few days, the ulcer opens on its own, removing pus. A crust subsequently forms on the site and slight skin pigmentation is observed at the site of the abscess.
If folliculitis occurs in a deep form, large ulcers appear, the size of which reaches 10 centimeters . The center of the ulcer is the hair follicle, and at the top of the skin there is suppuration. The abscess is accompanied by noticeable pain. After some time, the abscess independently secretes pus, after which it becomes covered with a yellowish crust. Depending on the individual characteristics of each person’s body, the number of abscesses caused by folliculitis can be completely different.
Diagnostics
It is very important to consult a doctor on time and undergo the necessary diagnostic procedures. The following activities are carried out:
- identification of the causative agent of the disease;
- establishing the presence of other pathologies in the body that can provoke inflammation in the hair follicles;
- determining the depth of damage to the hair follicle, or dermatoscopy;
- immunogram, etc.
During diagnostic procedures, the doctor excludes the presence of other dermatological lesions, for example, furunculosis, phrynoderma, etc.
Preventive actions
After treatment, preventive procedures need to be carried out. The main rule is hygiene. You need to take special care of your scalp and hair.
If skin damage occurs, for example, when scratching, you should immediately treat the scratch with an antiseptic.
Men should use disinfectant cosmetics after shaving. You can use cologne for this.
For preventive treatment of the skin, you need to use antiseptic soap. Benzoyl peroxide is also a good remedy.
To prevent the disease from progressing to a complicated or chronic stage, you need to monitor the condition of your skin and general well-being. If folliculitis does not disappear, this is a reason to see a doctor.
Complications
In most cases, this disease does not cause serious consequences for human life and health. But if there is no proper treatment, the infection penetrates deeply and the disease becomes more complicated. The situation is aggravated if the patient neglects the rules of hygiene, and also if he has a significant weakening of the immune system.
Complications of the disease include the following:
- furunculosis and carbuncles;
- dermatophytosis;
- formation of scar tissue;
- rotting of tissues.
Scars and cicatrices are formed as a result of attempts to squeeze out pus from inflammatory elements.
BMP restores the ability of BC cells to control hair growth
Maintaining the activity of “profile” genes in a culture is, of course, a very interesting result. However, how much more interesting it would be to test whether BC cells treated with the differentiation factor BMP-6 can induce the formation of a hair follicle - and, ultimately, trigger hair growth!
This assumption was tested in a way that would make animal rights activists' hair stand out. A suspension prepared from a fragment of the skin of a transgenic mouse, whose keratinocytes produced green fluorescent protein, “flavored” with the BC cells of another mouse, was transferred to cut-out depressions on the back of a third mouse - completely “naked” (hairless) due to a genetic mutation. The naked mouse was chosen for several reasons. Firstly, she has no hair. And secondly, she is distinguished by weak immunity, which is why she practically does not reject the organs and tissues transplanted to her. (The “naked” mouse is a common laboratory strain (nude) used to study cancer, immune diseases, etc.) A fluorescent protein in keratinocytes, which stains them emerald under the lens of a fluorescent microscope, was needed in this case to monitor the effectiveness of the “transplantation” and the processes associated with the formation of hair follicles.
If a wound on the back of a “naked” mouse was filled with keratinocytes alone, it healed, but no hair growth was observed. If hair papilla cells from culture were added to keratinocytes, sparse hair began to grow on the overgrown wound. Finally, the maximum effect with the growth of thick hair was achieved if the BC cell culture was treated with the growth factor BMP-6, which fully preserved the ability of the cells to induce the formation of a hair follicle (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Treatment of cultured hair papilla cells with bone morphogenetic protein enhances their ability to induce hair growth. Keratinocytes (Kcs), obtained from the skin of transgenic mice and synthesizing green fluorescent protein (GFP), were “transplanted” onto the back of “nude” mice. Keratinocytes by themselves only led to wound healing (left), but when papilla cells were added to them, hair growth was observed. BC cells taken from the culture gradually lose their ability to induce the formation of hair follicles (in the center), however, when the culture is treated with the morphogen BMP-6, this property is not only preserved, but also noticeably enhanced (right). The top two lines are a regular photograph; 3rd line - photo of the fluorescent glow caused by the GFP protein contained in the transplanted keratinocytes.
But even this is not the end of the scientists’ imagination. To establish the role of bone morphogenetic protein in hair growth even more reliably, they created a mutant line of mice in which the gene for the Bmpr1 receptor, responsible for the ability to respond to BMP-6, was deleted. Due to the loss of the receptor, BC cells stopped “sensing” BMP-6 and lost the ability to induce hair growth - which was also confirmed in a clever transplantation experiment (Fig. 3). The loss of the receptor, of course, changed the biochemical “portrait” of the cells - the synthesis of almost all characteristic proteins stopped - with the exception of... BMP-6 itself, the gene of which began to be expressed much more strongly. This fact most likely indicates the presence of negative feedback in the biochemistry of this cytokine. In addition, this confirms that the role of BMP-6 is not to directly initiate hair growth, but to “push” BC cells to start “construction” - the differentiation of epithelial stem cells in order to form a new hair follicle.
Figure 3. Targeted deactivation of bone morphogenetic protein receptors in hair papilla cells disrupts their ability to induce hair growth. Thin transverse sections of mouse skin in the area where keratinocytes and BC cells were “grafted” illustrate the histological details of hair growth. On the “control” sections (on the left), hair follicles are clearly visible, characteristic of skin with normal hair growth. In the case with “turned off” Bmpr1 receptors in BC cells (right), it is clear that follicle formation either does not occur at all, or they develop very weakly (marked by arrows). “Knockout” BC cells were obtained from a special transgenic line of mice in which the Bmpr1 gene was “switched off” under the influence of hydroxytamoxifen, and within a few days after treatment of the culture with this substance, the receptor completely disappeared from BC cells (and, consequently, sensitivity to KMB-6). A - hematoxylin/eosin staining. B - photographs under a fluorescent microscope.
By combining the findings obtained in various experiments, scientists were able to accurately establish that the “sensitivity” of BC cells to the morphogen BMP-6 is necessary for the ability to “conduct” the process of hair follicle formation and, therefore, determine hair growth.
“What we discovered is really exciting,” says Michael Rendl, first author of the Genes & Development paper [1] and a scientist in Elaine Fuchs' lab where the work was carried out. “It seems that different metabolic pathways, combining with each other, regulate the work of different sets of genes, giving each cell in the hair follicle unique qualities that are unique to it!”
Fuchs adds to his collaborator's words: “The complex circuitry involving BMP-6, used by cells to exchange information and commands with each other, may be part of the molecular mechanism that controls the development cycle of the hair follicle. If this is true, then we are one step closer to understanding the secret of hair growth" [3].
Treatment options
Folliculosis and ostiofolliculitis can be treated at home, but only after consultation with a competent specialist. Drugs are usually prescribed according to what exactly causes the disease:
- If the inflammatory process is provoked by staphylococci, then Miramistin, Bactroban, Levomycetin, Erythromycin can be used.
- In the presence of a fungal infection, antimycotic drugs are prescribed: Clotrimazole, Nizoral, Miconazole, Terbinafine, Itraconazole.
- Eosinophilic folliculosis is treated with Diphenhydramine, Isotretionine, Diprazine.
- Antibiotic medications, vitamin complexes, and drugs to strengthen the immune system may also be prescribed.
- For local treatment of dermatological lesions, you can use ordinary brilliant green, fucarcin, camphor alcohol to treat diseased areas of the epidermis. Ichthyol ointment is most effective against inflammation of the skin.
If necessary, the ulcers are opened and thoroughly treated on an outpatient basis. It is unacceptable to carry out these actions independently in order to prevent the formation of deep scars and secondary infections.
Some patients are indicated for physiotherapeutic procedures.
Methods from alternative medicine for the treatment of folliculitis are very effective. Decoctions and infusions prepared from the leaves, roots, fruits and flowers of the following medicinal plants are used:
- chamomile;
- rose hip;
- calendula;
- viburnum;
- nettle;
- dandelion;
- woodruff;
- burdock;
- yarrow;
- thistle;
- bloodroot.
Infusions are used for lotions and rinses, and some of them are taken orally. You can treat pustules and ulcers with essential oils and alcohol tinctures.
How to treat
Therapeutic measures depend on the nature of the pathogen, the location of the rash and the severity of folliculitis. As a rule, external agents, tablets and physiotherapeutic procedures are used. Comprehensive treatment increases the patient’s chances of a speedy recovery.
Antibiotic ointments
To diagnose the nature of the pathogen, laboratory culture of secretions from skin lesions is performed. If bacterial flora is detected, the patient is prescribed external agents and antibacterial agents.
They have a wide spectrum of action and are aimed at destroying the cell wall of bacteria and suppressing their further development. Erythromycin, Methicillin, etc. are considered popular ointments. The medicine is applied precisely to the affected area and rubbed in gently. The frequency of application depends on the degree of damage (from 2 to 4 times a day). During the treatment period, be sure to follow the rules of personal hygiene, avoid wearing things made of synthetic materials, etc.
Before applying the ointment, the abscess is treated with an antiseptic, opened, the contents are removed and a bandage with antibacterial ointment is applied. The course of treatment and frequency of application is determined individually for each patient. On average, therapy lasts 7-10 days (depending on the severity of folliculitis).
Treatment of children is carried out extremely carefully. Drugs are selected based on age and form of folliculitis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often used to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Antibiotics are mainly prescribed from the group of cephalosprorins, penicillins and macrolides. The duration and dosage are selected individually. To treat ulcers, use salicylic ointment, boric alcohol or brilliant green. For multiple formations, treatment is prescribed by a pediatric dermatologist.
In case of frequent relapses, the patient is prescribed antibiotics for oral use, and in parallel, immunostimulants are taken to strengthen the immune system. For deep lesions, compresses with ichthyol ointment are used, which “pull out” the purulent accumulation; severe forms of pseudomonas vasculitis are treated with antibiotics from the ciprofloxacin group.
Delaying the treatment of ulcers increases the chances of developing boils, carbuncles and other complications. In rare cases, the patient develops meningitis, nephritis, etc.
Antifungal drugs
If specialists identify fungal pathogens during culture, the patient is prescribed antifungal drugs.
They are taken orally or applied to the affected area (ointments, creams, gels, etc.). Popular and effective drugs include Terbinafine, Intraconazole, etc. They are applied to the affected areas 2 times a day, the course of treatment is determined individually.
If the pathology is diagnosed at an early stage, then they are limited to treating the affected areas with solutions of brilliant green or fucorcin. It is strictly forbidden to open the ulcers on your own or tear off the crust that has formed on the surface.
Ural Federal District
Ultraviolet irradiation is used as part of complex therapy. Patients are exposed to special lamps that emit rays of a certain wavelength. The number of courses is determined by doctors individually, based on the form and stage of hair folliculitis.
Ulcers in the area of hair follicles are very common. Folliculitis develops with the active action of a fungal, bacterial, viral or parasitic form. The disease is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms and requires mandatory drug treatment. Delaying therapy increases the chances of associated complications and repeated relapses in the future. For prevention, it is recommended to follow the rules of personal hygiene, strengthen the immune system and promptly treat existing diseases.
Folliculitis in HIV-infected people
There are some characteristics of folliculitis in the groin of HIV-infected people, which leads to the so-called eosinophilic folliculitis. This is a serious disease called eosinophilia. Manifests itself in the form of pustular folliculitis and severe itching throughout the body.
Unlike ordinary folliculitis, the rash that occurs on the inflammatory area is painful. In addition, the rash is similar to ordinary acne, as a result of which the doctor may make an incorrect diagnosis.
The nature of the disease can only be determined by a biopsy, in which a section of tissue or the contents of a pustule/pimple is taken and examined under a microscope. Thanks to this method, it is possible to make an almost 99.9% correct diagnosis.
Folliculitis in the groin in children
More often, children who often suffer from dermatitis are susceptible to folliculitis. Also children who have weak immunity.
The causes of folliculitis in children are:
- parents’ failure to comply with basic hygiene rules (when a child is bathed in dirty water)
- rarely examine the skin for microtraumas
- poor nutrition
- dressing a child in tight synthetic clothing
There are also ordinary reasons that do not depend on the parents. For example, climatic factors and profuse sweating of the child, resulting in skin irritation.
Antibacterial therapy for folliculitis in the groin
If you have been diagnosed with folliculitis in the groin, then you should know which antibiotics to take. This, as we already know, is done by a dermatovenerologist, and you should contact him. He will prescribe appropriate treatment, including antibiotics if necessary.
The most common treatments for folliculitis are:
- If the causative agent is staphylococcus and pseudomonas, then erythromycin, methicillin or minocycline are prescribed. Antibiotics can also be used topically, applying them directly to the site of inflammation itself, and such a drug is mupirocin. For more severe forms of folliculitis, ciprofloxacin will be prescribed
- If the causative agent is bacteria, your doctor will most likely prescribe you medications that contain benzoyl peroxide. Also, for bacterial folliculitis, ampicillin isotretinoin should be prescribed. There are cases when a drug such as sulfamethoxazole is prescribed
It is impossible not to describe such a well-known drug as Zinerit. It has proven itself very well in the fight against folliculitis.
It contains the chemical element zinc. As you know, zinc has astringent properties. Thanks to this, it binds the cells of the sebaceous glands, preventing their secretion.
In addition to zinc, the drug contains erythromycin, which is aimed at antibacterial fight against microorganisms. In addition to the fact that Zinerit is used in the treatment of folliculitis in the groin, it has proven itself in the treatment of acne, especially in adolescence.
Radical hair growth lotion?
Of course, it is still very early to talk about a new remedy against baldness - after all, until the results obtained in research laboratories reach the stage of implementation in medications, and until these drugs reach the market, it will take more than one year. However, most likely, the moment will come when baldness will be combated not by transplanting one’s own hair follicles from places where they are in abundance to the bald area of the head, but with the help of some artificially created growth factor. The main thing is that after this the horny plates do not grow along with the hair - so it’s better not to rush yet!
The article was originally published in the journal “Cosmetics and Medicine” No. 2, 2008 [4].
Folliculitis in the groin due to scabies
Folliculitis, which occurs in the form of scabies, is called ostiofolliculitis.
Manifests itself in the form of a purulent-inflammatory process of the skin. The main causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus.
After some time, a pustule appears at the site of inflammation, which has a cone shape with a diameter of 5 mm. It is painful when pressed.
On the top of the head, such a pustule has a yellow “cap” from which hair emerges. The rash with ostiofolliculitis occurs in the form of a scattered, ungrouped focus. Pustules are located in all parts of the body and are chaotic in nature, affecting unprotected areas of the body.
Folliculitis in the groin in women
The main decisive reason why folliculitis occurs in women in the groin is a technique such as depilation. When microtraumas of the skin layer itself occur, microcracks occur.
There are often cases when hair grows into the skin itself, causing tears in its walls. Due to this, inflammation of the hair root itself occurs and folliculitis occurs.
Also, the causes of folliculitis in the groin in women can be wearing synthetic tight-fitting underwear, when it is very hot outside, with heavy sweating. Especially in people who are overweight.
Treatment of folliculitis in the groin occurs with a properly selected set of measures, including both systemic and local. In general, antibiotics are prescribed that suppress the activity of microorganisms and prevent their reproduction in the future.
Antibiotics should be prescribed only if the purulent process worsens. As part of the overall complex, immunostimulants should also be prescribed, leading to increased protective properties of the body. Also adaptogenic drugs and biogenic stimulants.
Local treatment includes measures such as treating inflammation with local antiseptic drugs. Such as antibacterial powders, disinfectant solutions, various creams and ointments.
Local therapy for folliculitis in the groin
In addition to general measures to combat folliculitis, local treatment is used.
Various creams and ointments are applied to the inflammatory area of the skin. The most commonplace, but very common method in the fight against folliculitis is the application of tetracycline ointment. In addition to the ability to destroy folliculitis pathogens, tetracycline ointment has a good soothing effect on the skin.
In addition to tetracycline ointment, various disinfectant antimicrobial and antiseptic drugs are prescribed locally for folliculitis, for example:
- Zelenka or iodine
- Ichthyol ointment
- Erythromycin ointment
In addition to local measures, there are techniques for applying tea tree oil, calendula or chamomile decoction to inflammatory areas. Various compresses are also applied: from thistle, from various berries (viburnum, rose hips, green nut shells). Also a bread compress with regular homemade salt.